A chip-based method for high-throughput and high-sensitivity detection of 5-hydroxymethylated cytosine
A sensitive detection technology for hydroxymethylated cytosine, which is applied in the field of high-throughput and high-sensitivity detection of 5-hydroxymethylated cytosine, can solve the problems of high detection cost, false positive test results, inaccurate test results, etc. Achieve high sensitivity detection, high specificity, high sensitivity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
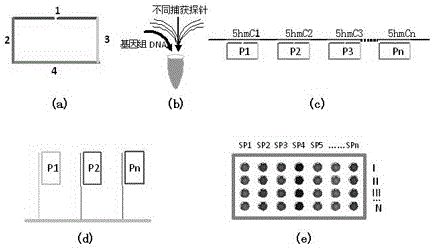
[0034]Realize the detection of the hydroxymethylated cytosine (hmC) status of the first C site (194-59366) of the 68 CCGG sequences of the BDNF gene (NT_039207.8) in the spinal cord of mice with chronic inflammatory pain.
[0035] (1) Design specific amplification primers with acrylamide modification at the 5' end for the first C sites of the above 68 CCGG sequences, dilute to 20uM and fix on acrylamide-treated glass slides to form a microarray chip. Two open-loop detection probes were designed for each C site of the above-mentioned 68 CCGG sequences, which are open-loop detection probe I and open-loop detection probe II (among them, open-loop detection probe I is used to detect non-hmC states, The open-loop probe II is used to detect the state of hmC. The main sequence of the open-loop detection probe is shown in List 1.
[0036] (2) Treat 1ug of mouse spinal cord DNA with T4-BGT, that is, treat the mouse genomic DNA to be detected with β-glucosyltransferase, and glycosylate ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Realize the detection of the first C-site hydroxymethylated cytosine (hmC) status of the 33 CGCG sequences of the BDNF gene (AC_000143.1) in the plasma DNA of patients with chronic rheumatoid pain.
[0042] (1) Specific amplification primers with acrylamide modification at the 5' end were designed for the first C sites of the above 33 CGCG sequences, diluted to 20uM and fixed on acrylamide-treated glass slides to form a microarray chip. Then, two open-loop detection probes were designed for each C site of the above-mentioned 33 CGCG sequences, respectively, open-loop detection probe I and open-loop detection probe II (among them, open-loop detection probe I is used to detect non-hmC state , the open-loop probe II is used to detect hmC status. The main sequence of the open-loop detection probe is shown in List 1.
[0043] (2) Treat 1ug of the patient's plasma DNA with T4-BGT, that is, treat the genomic DNA of the mouse to be detected with β-glucosyltransferase, and glyco...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Combined detection of hmC status of the first C of 19 CCGG sequences (40945-59475) of the BDNF gene (NT_187012.1) and the first C of 10 CCGG sequences (771-15422) of the COMT gene (NT_187012.1) in spinal cord DNA of mice with chronic neuropathic pain .
[0048] (1) For the first C of the 19 CCGG sequences (40945-59475) of the above-mentioned BDNF gene and the first C of the 10 CCGG sequences (771-15422) of the COMT gene (NT_187012.1), respectively design the 5' end with acrylamide The modified specific amplification primers were diluted to 20uM and fixed on the acrylamide-treated glass slide to become a microarray chip. Two open-loop detection probes were designed for each C site, respectively, open-loop detection probe I and open-loop detection probe II (among them, open-loop detection probe I was used to detect non-hmC states, and open-loop detection probe II Used to detect the state of hmC. The main sequence of the open-loop detection probe is shown in List 1.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com