Method for detecting content of soluble salt in slag aggregate of waste incinerator
A technology of waste incineration slag and detection method, which is applied in the field of detection of soluble salt content in waste incineration slag aggregates, can solve problems such as no test method for soluble salt content in aggregates, and achieve simple test equipment and sample The effect of small quantity and easy purchase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1: Sampling method for slag aggregates: multiple groups of slags uniformly distributed and roughly equal in quality are selected from the top, middle and bottom of the slag aggregate pile, and mixed uniformly to form a group of samples. Preparation of leachate from slag aggregates: Dry in an oven at 105°C for 8 hours, grind in a mortar, mix slag aggregates with different particle sizes and distilled water at a mass ratio of 1:5 and shake for 5 minutes to prepare multiple sets of suspensions, filter The obtained slag leachate was stored in a glass bottle with a stopper at room temperature and away from light.
[0017] Cl- content detection: take 100mL slag leaching solution respectively, and add 0.15mL 0.02mol / L sodium bicarbonate dropwise to it until the solution just turns yellow, add 0.25mL 50g / L potassium chromate indicator; add 0.04 mol / L silver nitrate, shake with the drops until the brick red precipitate no longer disappears; calculate the chloride content...
Embodiment 2
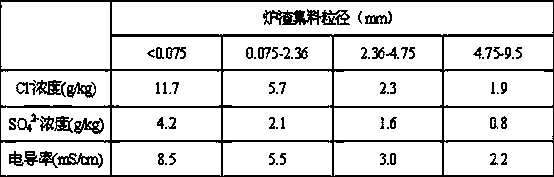
[0024] In order to further verify the effectiveness of the present invention, this embodiment tests slag leachate with different particle sizes, and the results are shown in Table 2. The smaller the particle size of the slag, the higher the concentration of chloride salt and sulfate, and the higher the electrical conductivity, indicating that the content of soluble salt in the fine particle size is higher. It can be seen that the detection method of the present invention can effectively distinguish the soluble salt content in slag with different particle sizes.
[0025] Table 2 Test results of various indicators of slag leachate with different particle sizes
[0026]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com