High-temperature hyper-salinity water-base fracturing fluid
A high-salinity, water-based fracturing technology, applied in the field of high-temperature fracturing fluid, can solve the problems of complex preparation process and high cost, and achieve the effect of convenient fluid preparation process and delayed cross-linking time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Add 9939kg of seawater to the liquid mixing tank, slowly add 40kg of sulfonic acid hydroxypropyl guar gum, add 10kg of sodium thiosulfate and 1kg of glutaraldehyde after circulating for 10 minutes, and finally add 10kg of dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide , and recirculate for 10 minutes to obtain a uniform and transparent viscosified liquid. The viscosity measured by a six-speed rotational viscometer was 57 mPa·s, and the pH was 8.2.
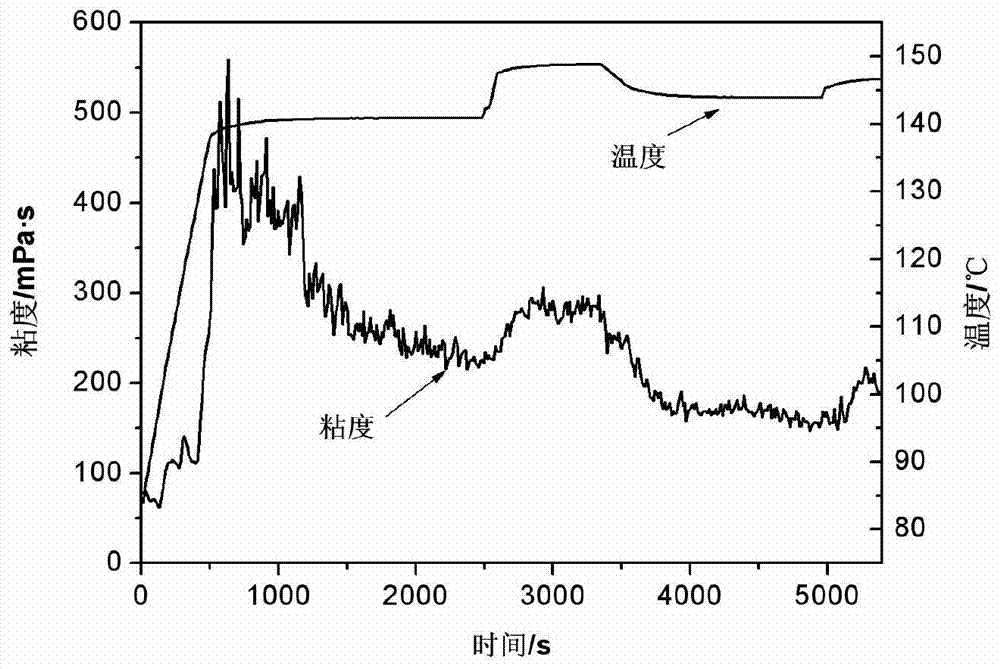
[0023] Take 1000g of the prepared thickened liquid, add 2g of cross-linking agent under rapid stirring, and continue stirring for 8 minutes to obtain a pickable jelly. The rheological properties of the jelly were tested at 140°C using a RS6000 rheometer (see figure 1 ).
[0024] Add 1 g of ammonium persulfate to 1000 g of the jelly prepared in the previous step, and place it in a water bath at 80°C for 2 hours to fully hydrate the jelly.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add 9902kg of formation produced water into the liquid mixing tank, slowly add 50kg of sulfobetaine amphoteric guar gum, add 15kg of sodium thiosulfate and 3kg of formaldehyde after circulating for 10 minutes, and finally add 30kg of hexadecyl trimethyl bromide ammonium, and recirculate for 10 minutes to obtain a uniform and transparent thickened liquid. The viscosity measured by a six-speed rotational viscometer was 66 mPa·s, and the pH was 8.5.
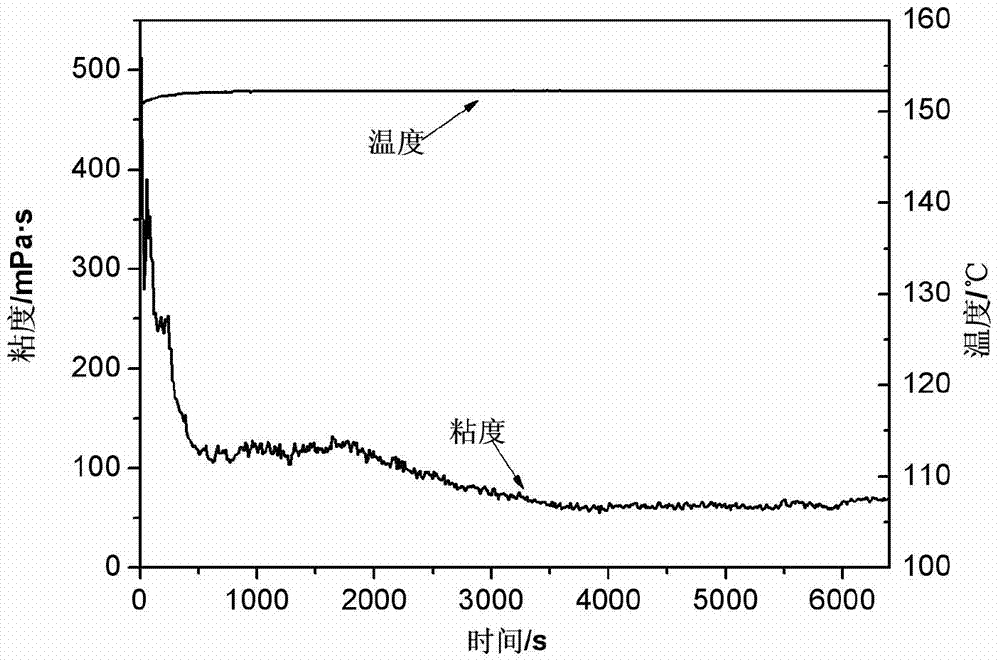
[0027] Take 1000g of the prepared thickened solution, add 4g of cross-linking agent under rapid stirring, and continue stirring for 7 minutes to obtain a pickable jelly. The rheological properties of the jelly were tested at 150°C using a RS6000 rheometer (see figure 2 ).
[0028] Add 1,000 g of the jelly prepared in the previous step, add 5 g of ammonium persulfate under stirring, and place it in a water bath at 80°C for 3 hours. The jelly is completely hydrated. After hydration, the viscosity of the liquid measured by a ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Add 9864kg seawater in the liquid mixing tank, slowly add 60kg carboxymethyl guar gum sulfonate, add 20kg sodium thiosulfate and 6kg glutaraldehyde after circulating for 10 minutes, and finally add 50kg cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, Recirculate for 10 minutes to obtain a uniform and transparent thickened liquid. The viscosity measured by a six-speed rotational viscometer was 78 mPa·s, and the pH was 8.7.
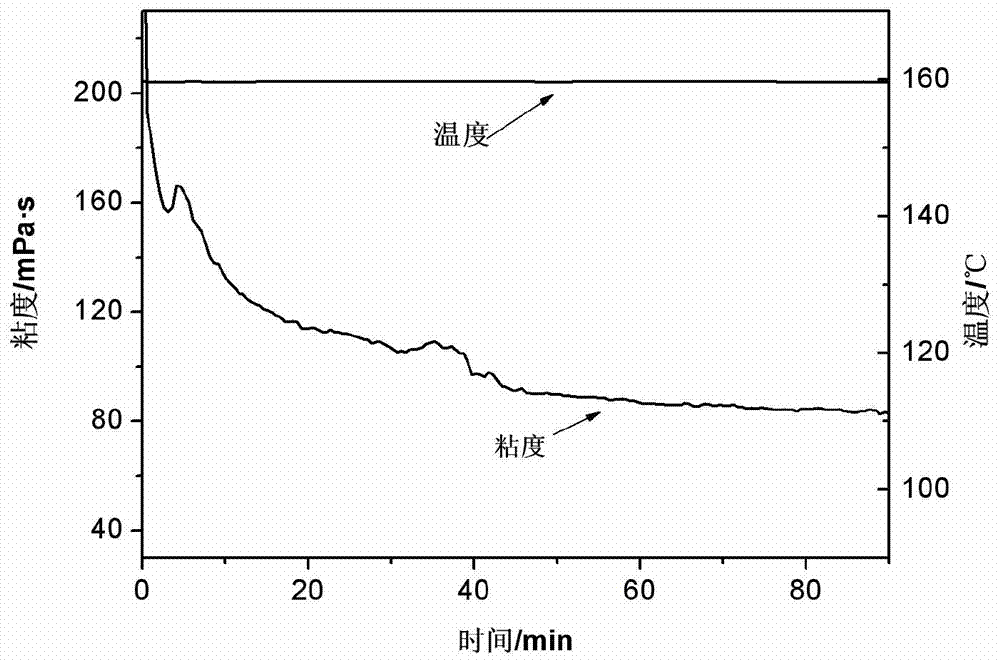
[0031] Take 1000g of the prepared thickened solution, add 6g of cross-linking agent under rapid stirring, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain a pickable jelly. The rheological properties of the jelly were tested at 160°C using a RS6000 rheometer (see image 3 ).
[0032] Add 10 g of ammonium persulfate to 1000 g of the jelly prepared in the previous step, and place it in a water bath at 80°C for 3 hours to fully hydrate the jelly.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com