Single-module DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and connecting method for TALENs (transcription activator-like effector nucleases) identification modules
A technology for identifying modules and connecting methods, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of difficulty in DNA preservation, material cost, time cost, high sequencing cost, cumbersome operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Connection between TALENs recognition modules and construction of recombinant vector
[0064]1. 4 identification modules (modular)
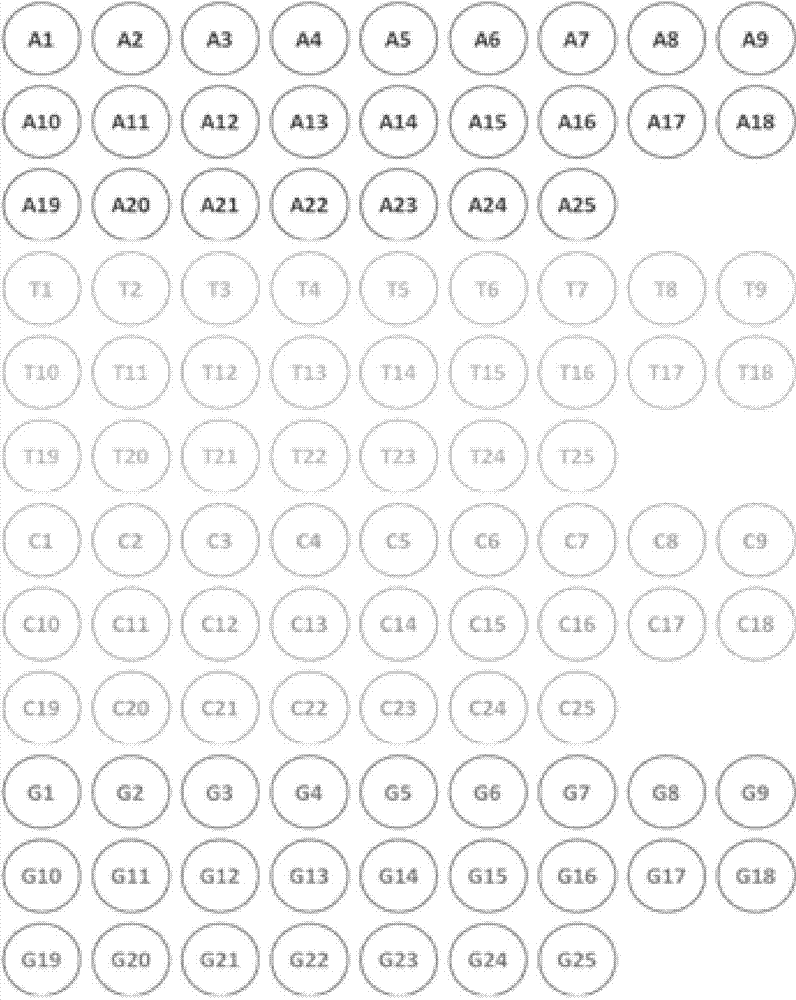
[0065] (1) Synthesis of recognition modules NI, NG, HD, and NN that recognize four single bases A, T, C, and G respectively. The sequences are shown in Table 1, as shown in SEQ ID No.1-4, respectively.
[0066] Table 1 Sequences of four single-base recognition modules
[0067]
[0068] 2. Make 100 plasmid libraries by adding restriction sites and linkers to the recognition module
[0069] (1) PCR amplification to add enzyme-cut recognition sequences and connection adapters
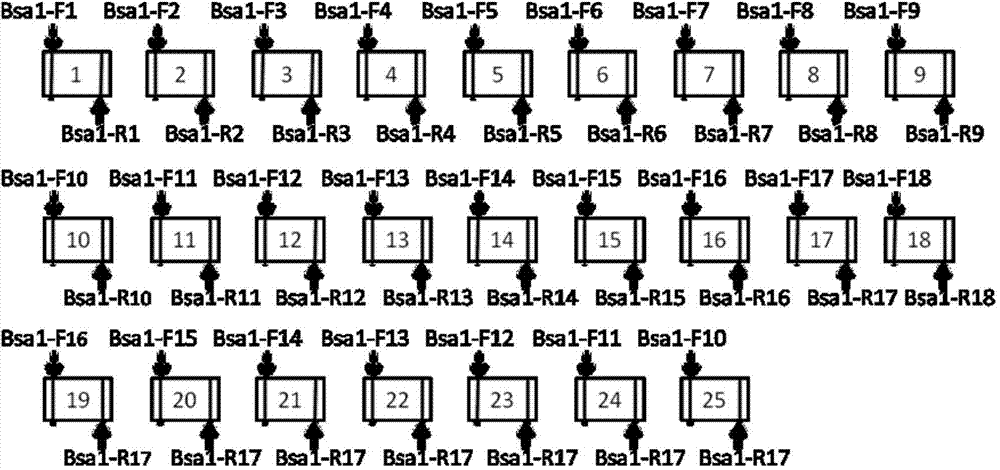
[0070] F1 / R1; F2 / R2; F3 / R3; F4 / R4; F5 / R5; F6 / R6; F7 / R7; F8 / R8; F9 / R9; F10 / R10; F11 / R11; F12 / R12; F13 / R13; F14 / R14; F15 / R15; F16 / R16; F17 / R17; F18 / R18 were used as primers, and the T vector containing 4 single-base recognition modules was used as a template for PCR, a total of 4×18=72 ( The first part connects the unit, taking n=18 as an example);
[...
Embodiment 2
[0131] TALENs (SEQ ID NO: 47 and 48) that recognize the following DNA sequences were ligated:
[0132] Fragment 1: CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGT;
[0133] Fragment two: CCCACTCCCCATCCAGT.
[0134] (1) Select the desired recognition module from the PCR library
[0135] For Fragment 1 (CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGT), 18 linking units need to be connected (the carrier already contains the 19th T recognition module); select figure 1 Single-base recognition modules C1, G2, C3, G4, C5, G6, C7, G8, C9, G10, C11, G12, C13, G14, C15, G16, C17, G18; the connection vector is pEF1a-NLS -TALE backbone-Fok1(R)-pA;
[0136] For Fragment 2 (CCCACTCCCCATCCAGT), 16 linking units need to be connected (the recognition module of the 17th position T was already contained on the carrier); select figure 1 Single-base recognition modules C1, C2, C3, A4, C5, T6, C7, C8, C9, C10, A11, T12, C13, C14, A20, G18 in the single-base recognition module; the first cohesive end of A20 is connected with the first section 14 The...
Embodiment 3
[0151] The steps and methods of Example 1 were used to construct the recognition module and recombinant vector.
[0152] 1. The synthesis of four single-base recognition modules is the same as in Example 1.
[0153] 2. Make 100 plasmid libraries by adding restriction sites and adapters to the recognition module.
[0154] (1) PCR amplification to add enzyme-cut recognition sequences and connection adapters
[0155] Taking n=18 as an example, the construction method for the first part of the connection unit is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0156] In the second part of connecting units, the primer pairs used for connecting units 19-25 are: F8 / R15, F9 / R15, F10 / R15, F11 / R15, F12 / R15, F13 / R15, F14 / R15. That is, m=7, q=14, p=7~13.
[0157] Restriction sites, cohesive end sequences and primer sequences are the same as in Example 1. All the other are with embodiment 1.
[0158] (2) Gel recovery and purification of 100 PCR products, and connection into the PMD18-T system
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com