Arsenic removal method used in pyrometallurgucal process for antimony
A technology for pyrometallurgical smelting and crude antimony, applied in the field of pyrometallurgical smelting of antimony, can solve the problems of easy formation of slag bubbles, reduced antimony recovery rate, inability to effectively remove arsenic, etc., and achieves the effect of ensuring the effect of removing impurities and shortening the smelting time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
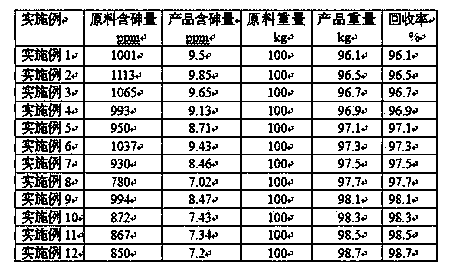
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) Take the following raw material proportions by weight to form a composite melting agent, 70 parts of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 10 parts of sodium nitrate, 0.5 parts of quartz sand, and 1 part of borax, mix well and set aside.
[0018] (2) Take Industry 2 # 100kg of antimony, broken into small pieces, put 2kg of compound melting agent into the crucible boiler together, heat until completely melted; then smelt, the melting temperature is 700°C, and the melting time is 3 hours; in the later stage of smelting, blow compressed air; the smelting is over After cooling, slag removal and separation are carried out to obtain antimony material;
[0019] (3) The antimony material obtained in step (2) is repeated 3 times according to step (2), and the smelting time is 2 hours;
[0020] After the last smelting and slag removal, the molten antimony can be directly cast into antimony ingots or water-quenched antimony.
Embodiment 2
[0022] (1) Take the following raw material proportions by weight to form a composite melting agent, 80 parts of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 15 parts of sodium nitrate, 5 parts of quartz sand, and 3 parts of borax, mix well and set aside.
[0023] (2) Take Industry 2 # 100kg of antimony, broken into small pieces, put 3kg of compound melting agent into the crucible boiler together, heat until completely melted; then smelt, the melting temperature is 1000°C, and the smelting time is 4 hours; in the later stage of smelting, blow compressed air; the smelting is over After cooling, slag removal and separation are carried out to obtain antimony material;
[0024] (3) The antimony material obtained in step (2) is repeated 3 times according to step (2), and the smelting time is 3 hours;
[0025] After the last smelting and slag removal, the molten antimony can be directly cast into antimony ingots or water-quenched antimony.
Embodiment 3
[0027] (1) Take the following raw material proportions by weight to form a composite melting agent, 75 parts of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 12 parts of sodium nitrate, 3 parts of quartz sand, and 2 parts of borax, mix well and set aside.
[0028] (2) Take Industry 2 # 100kg of antimony, after being broken into small pieces, put 4kg of compound melting agent into the crucible boiler together, heat until it is completely melted; then smelt, the melting temperature is 850°C, and the smelting time is 4 hours; in the later stage of smelting, blow compressed air; the smelting is over After cooling, slag removal and separation are carried out to obtain antimony material;
[0029] (3) The antimony material obtained in step (2) is repeated three times according to step (2), and the smelting time is 3 hours;
[0030] After the last smelting and slag removal, the molten antimony can be directly cast into antimony ingots or water-quenched antimony.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com