Technology for constructing deepwater bridge underwater pier large-diameter bored piles in bead-stringed type karst areas
A construction technology, technology of bored piles, applied in sheet pile walls, foundation structure engineering, filling, etc., can solve the problems of lack of systematicness, comprehensiveness and operability, difficulty, high rock strength, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
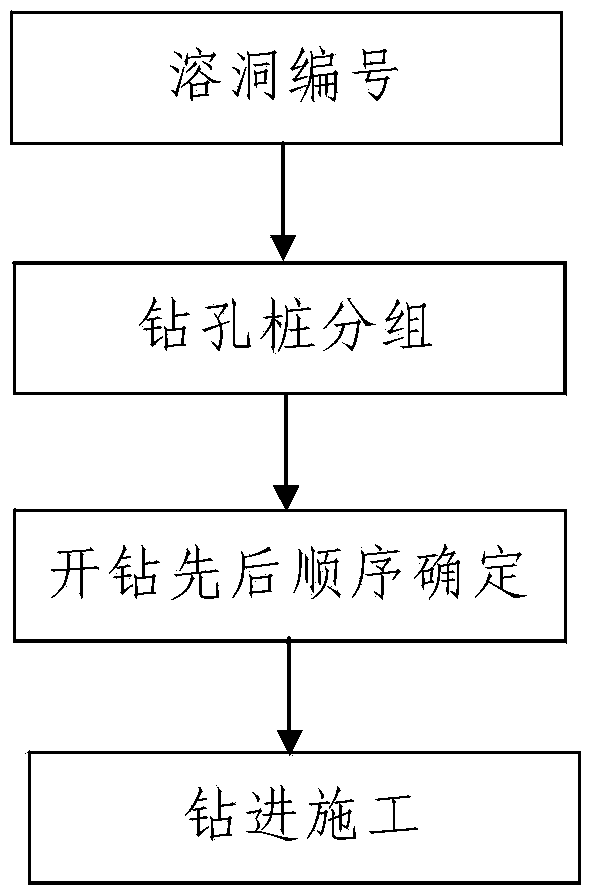
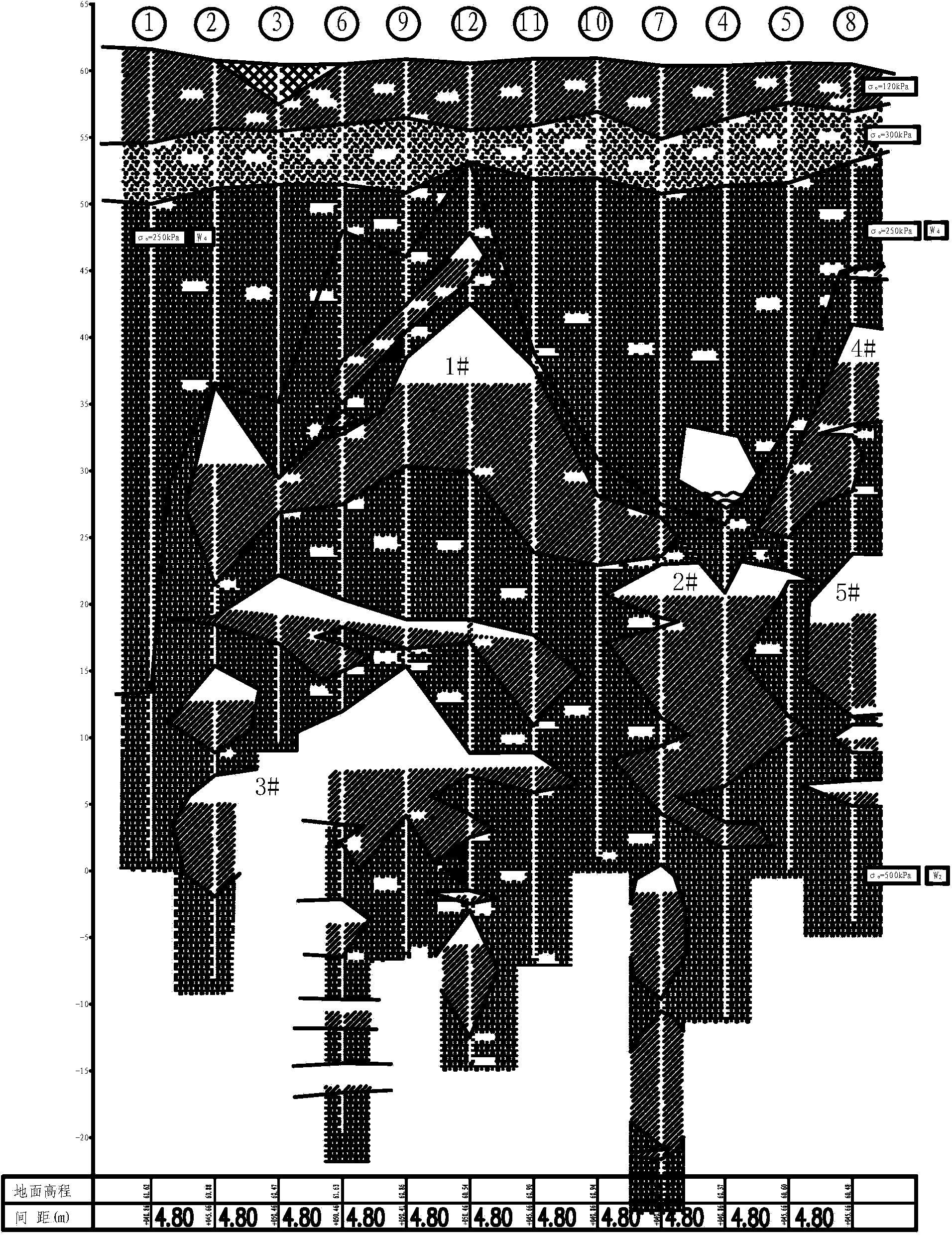
[0062] Such as figure 1Shown is a construction technique of large-caliber bored piles for deep-water bridges in deep-water bridges in karst areas. The pile foundations of the constructed piers in water include a plurality of first bored piles. Through multiple caves, the construction process includes the following steps:
[0063] Step 1. Numbering of karst caves: respectively numbering each karst cave in the construction area where the pile foundation is located.
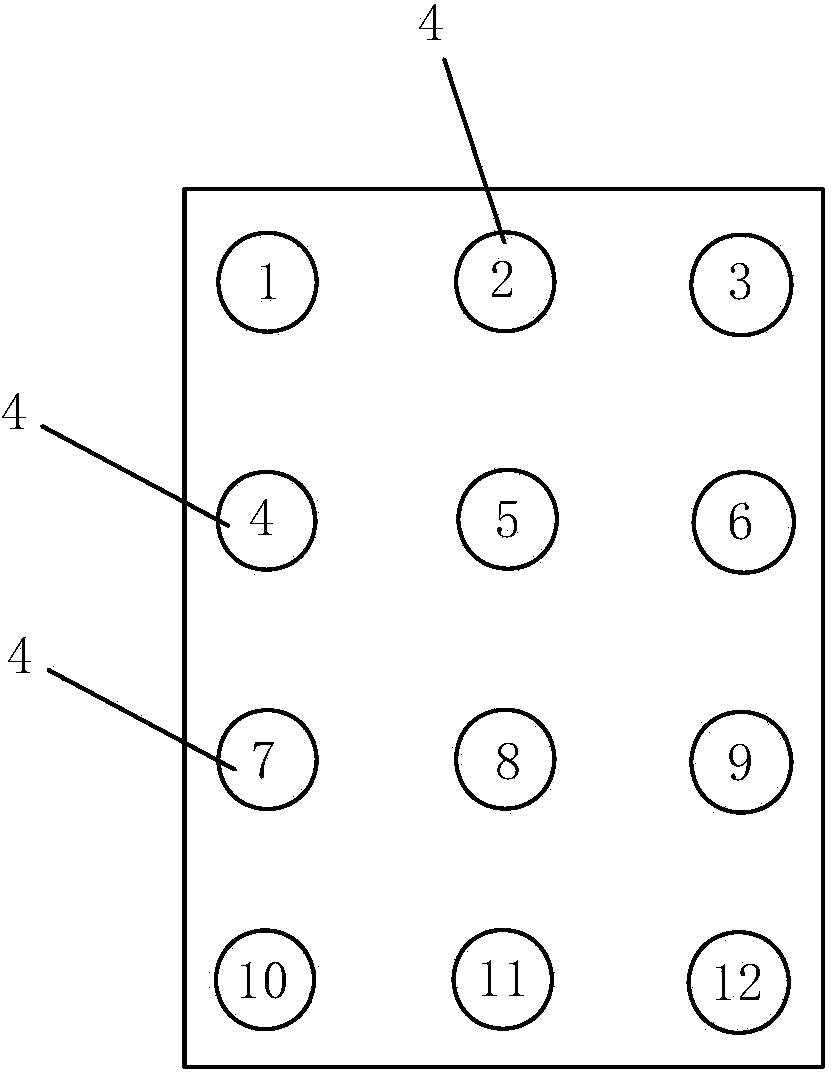
[0064] Step 2, grouping of bored piles: Divide multiple first bored piles into multiple groups according to the numbers of the karst caves traversed from top to bottom, and divide all first bored piles in the same group of bored piles from top to bottom The caves traversed for the first time are all the same.
[0065] Step 3. Determination of the sequence of drilling: according to the layout position of each first bored pile in the first crossing of the karst cave, the sequence of drilling of all the first bored p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com