Tungsten trioxide-titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst for degrading formaldehyde
A photocatalyst and photocatalytic technology, applied in the field of photocatalysis, can solve the problems of low efficiency of photogenerated carriers, complex reaction conditions, and difficulty in realizing industrial production, and achieve the goal of promoting photocatalytic reaction, high photocatalytic degradation rate, and inhibiting recombination. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
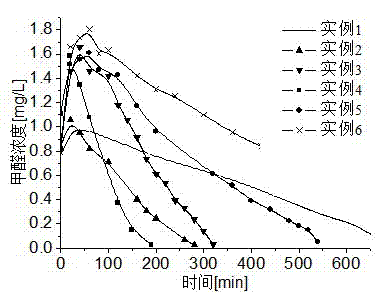
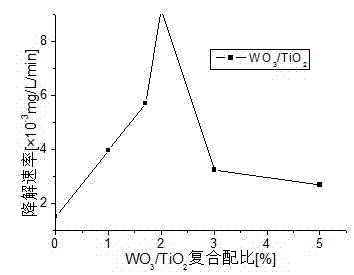
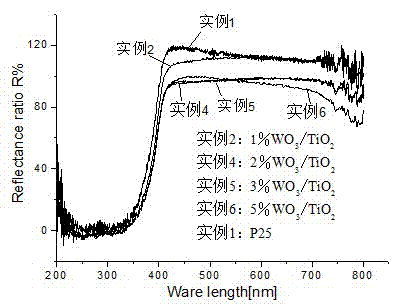
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The photocatalytic material of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with examples, rather than limiting the present invention.
[0018] The tungsten source of the present invention is ammonium tungstate, which is dissolved in a certain amount of hot ammonia water, and then wet-milled with a certain amount of P25 for 20 minutes, continuously stirred to make it fully mixed, and then the cleaned foam Nickel is completely immersed in it, pulled out at a certain speed after 10 seconds, placed in an electric blast drying oven at 100°C to dry, repeated several times, so that the single-sided loading density of each piece of nickel foam reaches 0.02g / cm 2 ~0.03g / cm 2 , to obtain a dry loaded nickel foam precursor. Finally, the dried loaded nickel foam precursor was calcined at a high temperature in a 500°C tube furnace (the tube furnace was raised to 500°C at a rate of 2°C / min), and after constant temperature for 1 hour, the sample was cooled ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com