Method for producing D-lactic acid through repeated batch fermentation by utilizing surface immobilization technology
A secondary fermentation, lactic acid technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve the problems of limited laboratory-scale operation, single immobilization carrier, affecting the fermentation rate, etc., to reduce substrate inhibition, high economic utilization value, and improve cell The effect of density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
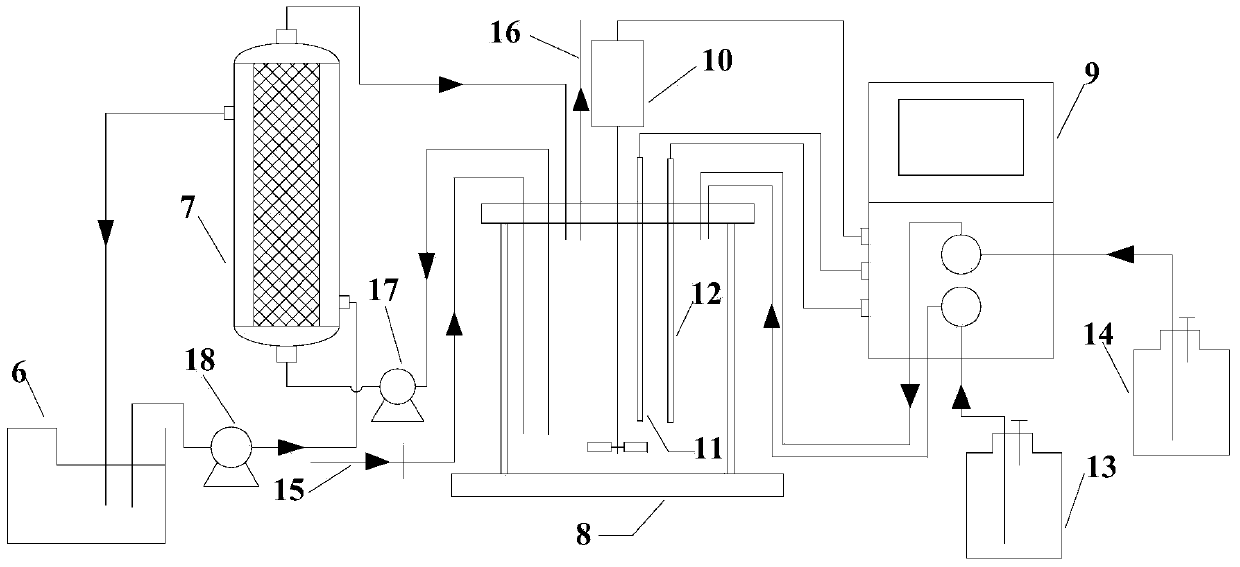
[0048] In this example, cornstarch is used as raw material, and the feed form of synchronous saccharification and fermentation is used for immobilization and repeated batch fermentation. The method steps are as follows:
[0049] Plate medium (g / L): glucose 80g / L, yeast extract 8g / L, anhydrous sodium acetate 2g / L, anhydrous magnesium sulfate 0.8g / L, KH 2 PO 4 2g / L, ferrous sulfate 0.1g / L, manganese sulfate 0.1g / L; seed medium (g / L): glucose 30g / L, peptone 10g / L, anhydrous magnesium sulfate 0.4g / L, ferrous sulfate 0.1g / L, manganese sulfate 0.1g / L, CaCO 3 20g / L;
[0050] Fermentation medium (g / L): corn starch 150g / L, yeast extract 6.5g / L, anhydrous magnesium sulfate 0.8g / L, anhydrous sodium acetate 4g / L, ferrous sulfate 0.1g / L, manganese sulfate 0.1 g / L.
[0051] 1) Plate culture: inoculate the frozen-preserved bacterial strains on the plate medium, and culture them statically at 35°C for 60 hours in an anaerobic box to activate them.
[0052] 2) Seed culture: Pick bacteria ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In this embodiment, immobilization and repeated batch fermentation are carried out in the form of single batch feeding, and the specific method steps are as follows:
[0062] Plate culture medium and seed culture medium are the same as embodiment 1.
[0063] Fermentation medium (g / L): glucose 150g / L, yeast extract 4g / L, corn steep liquor 15ml / L, anhydrous magnesium sulfate 1g / L, anhydrous potassium acetate 4g / L, ferrous sulfate 0.01g / L, Manganese sulfate 0.01g / L.
[0064] 1) plate culture and 2) seed culture are the same as step 1) and step 2) of Example 1.
[0065] 3) Immobilized repeated batch fermentation:
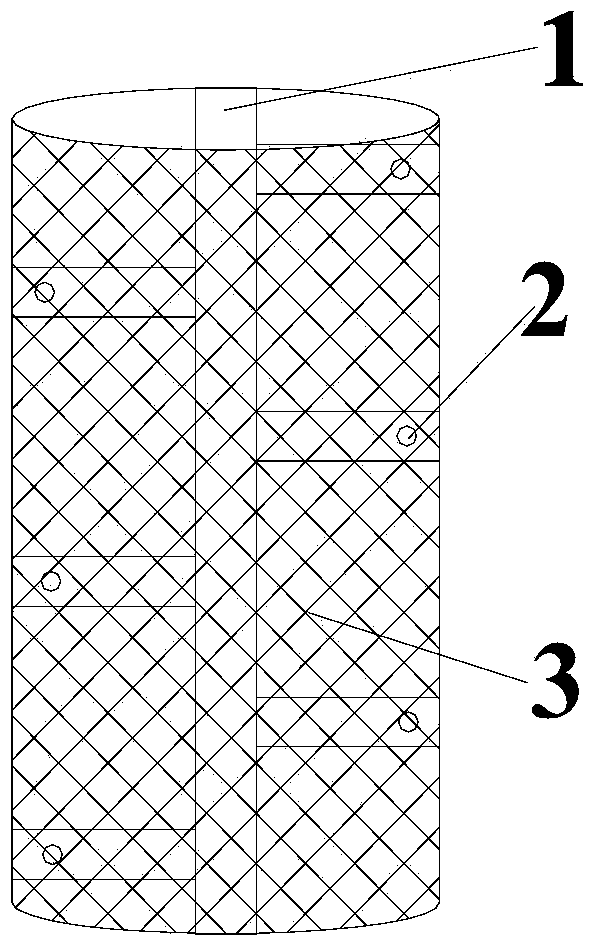
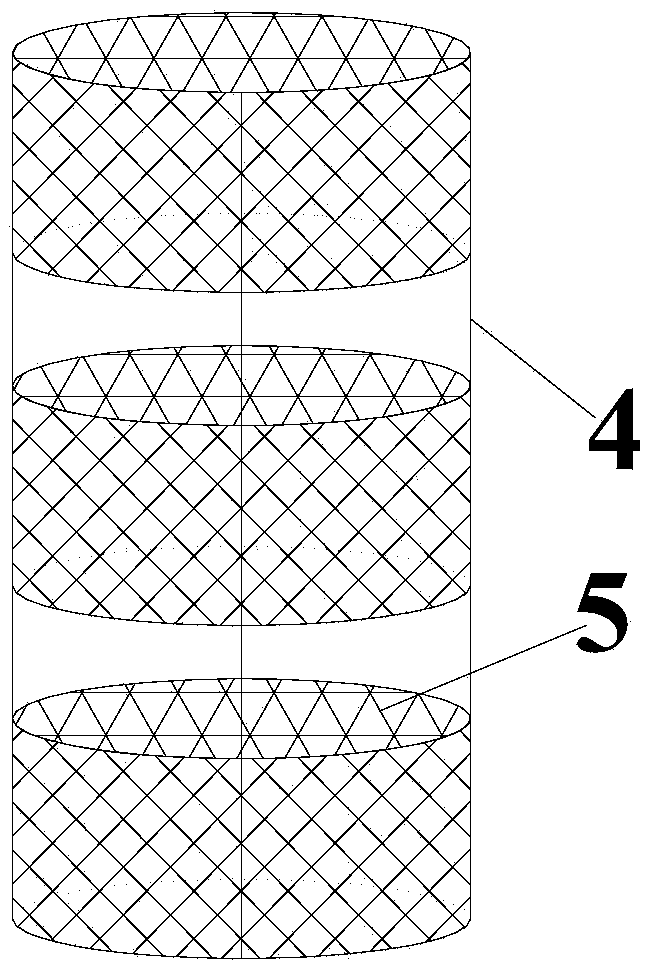
[0066] ①Construction of the immobilization reaction system: Fill the corncobs in the stainless steel bracket 4 with mesh grooves and put them into the jacketed stainless steel column to construct the immobilization reactor, and other steps are the same as the step ① of Example 1.
[0067] ② The immobilization process is the same as the step ③ in Example 1.
...
Embodiment 3
[0073] In this embodiment, cornstarch hydrolyzed sugar solution is used as raw material, and immobilization and repeated batch fermentation are carried out in the form of fed batches. The specific method steps are as follows:
[0074] Plate culture medium and seed culture medium are the same as embodiment 1.
[0075] Fermentation medium (g / L): 60g / L cornstarch hydrolysis sugar solution, 20g / L yeast extract, 1g / L anhydrous magnesium sulfate, 2.5g / L anhydrous potassium acetate, 0.04g / L ferrous sulfate, sulfuric acid Manganese 0.04g / L.
[0076] 1) plate culture and 2) seed culture are the same as step 1) and step 2) of Example 1.
[0077] 3) Immobilized repeated batch fermentation:
[0078] ①Construction of the immobilization reaction system: fix the activated carbon fiber on the periphery of the stainless steel support and put it into a stainless steel column with a jacket to construct the immobilization reactor. The other steps are the same as the step ① of Example 1.
[007...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com