Method for manufacturing shake-proof strip of steam generator of nuclear power unit
A technology for steam generators and nuclear power units, which is applied to the primary side of steam generators, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the danger of radioactive irradiation of maintenance personnel, waste of manpower, financial resources and incidents, so as to improve the performance of processing technology and realize automation. , the effect of reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
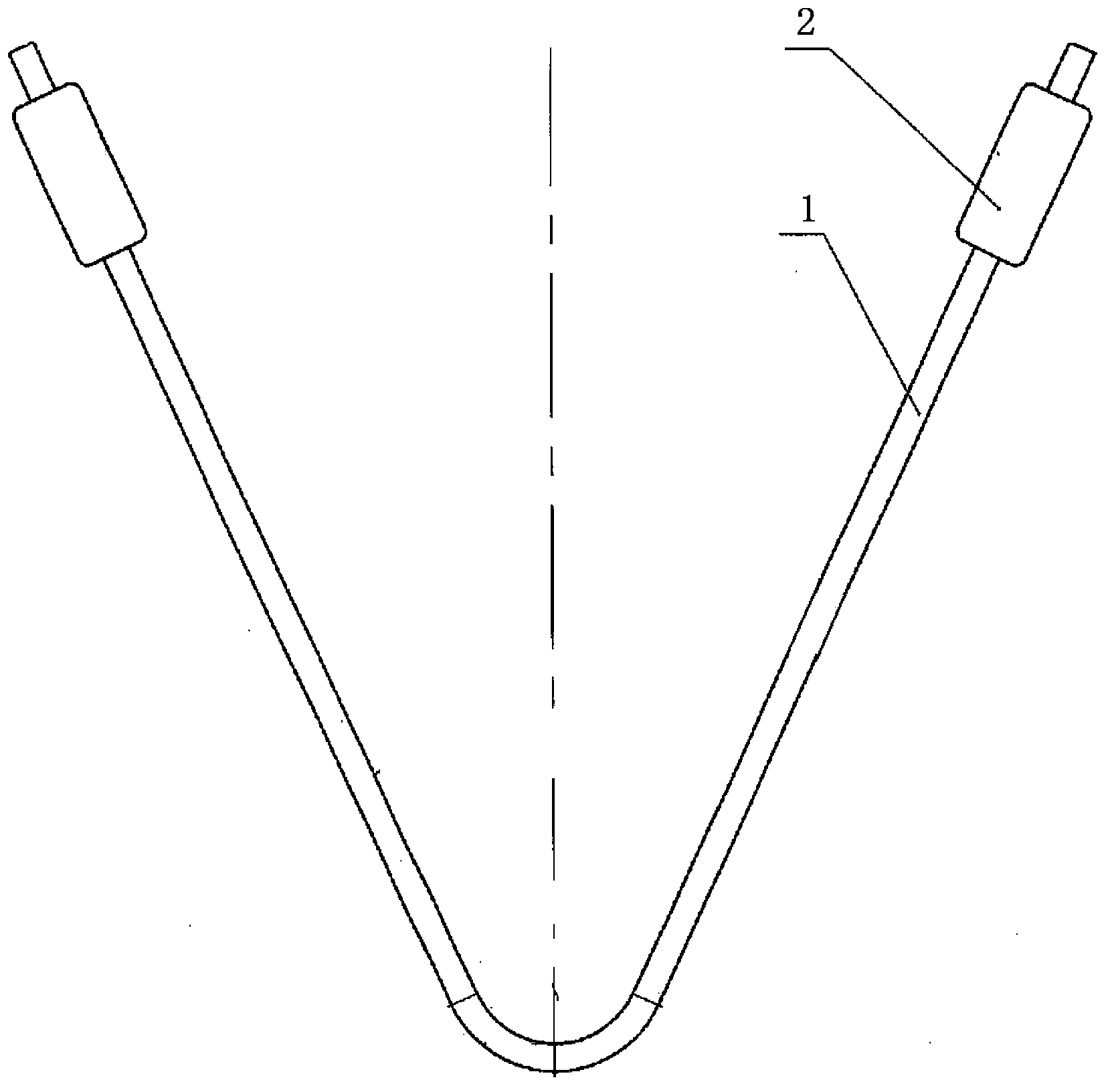
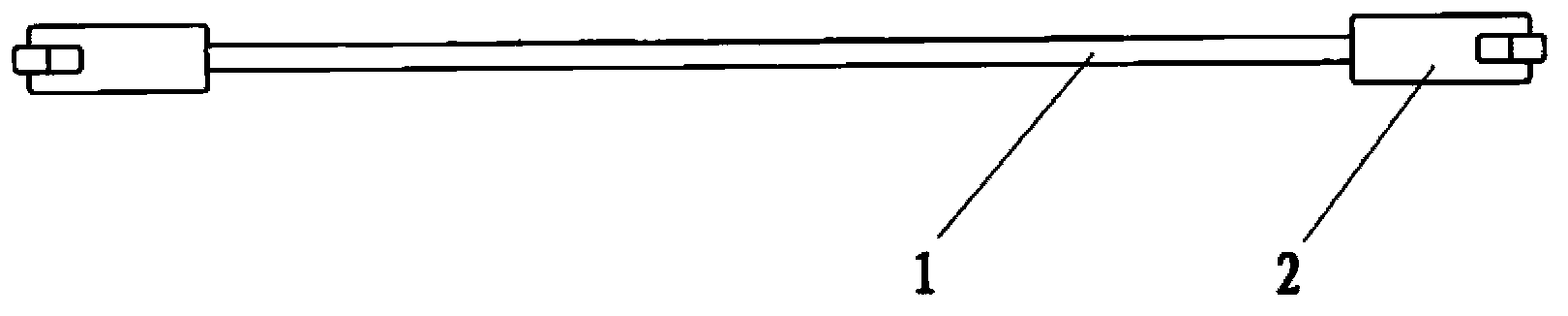
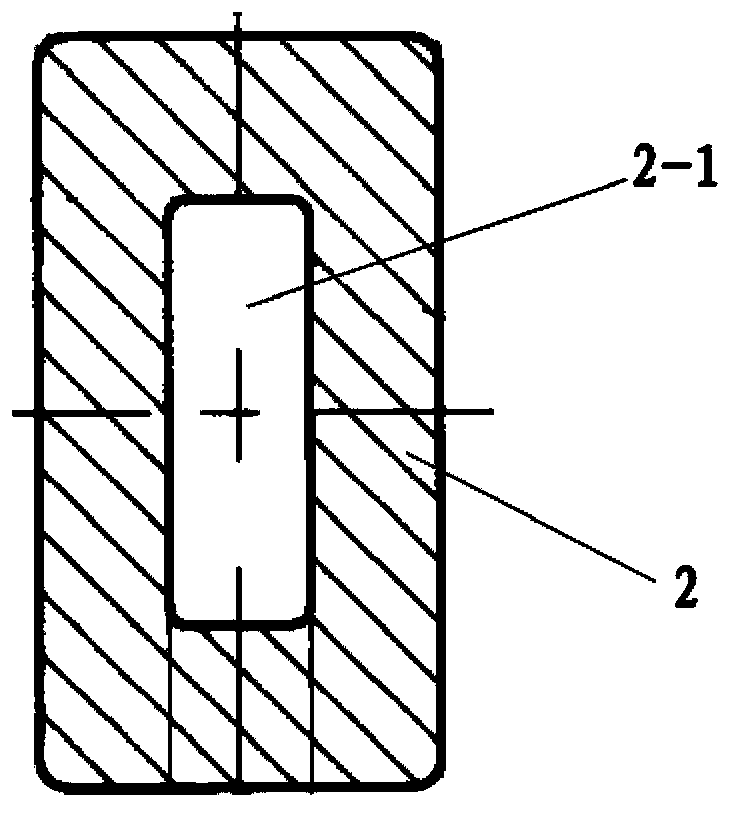
[0062] Such as figure 1 , the anti-vibration strip assembly of the steam generator of the CAP1400 unit of the present embodiment, which includes: the anti-vibration strip 1 of the V-shaped structure and two end caps 2 fixedly sleeved at the two ends of the anti-vibration strip; the section of the anti-vibration strip It is rectangular, and the cross-section of the end cap is back-shaped, so as to facilitate the fixing of the anti-vibration bar and the end cap through upsetting.
[0063] The anti-vibration bar 1 is made of 405 stainless steel (SA-479 TYPE405); the end cap 2 is made of 690 nickel-based alloy (SB-166 UNS N06690).
[0064] The center of the end cap 2 and four places on the anti-vibration bar 1 adjacent to the two ends of the end cap are crushed. The two flattened places at the ends of the end caps on the anti-vibration strip 1 are distributed symmetrically.
[0065] The preparation method of the above-mentioned anti-vibration bar assembly includes: preparation o...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The preparation method of the anti-vibration bar in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 includes the following steps in sequence: induction furnace smelting, smelting analysis, forging, hot rolling, first heat treatment, performance test (tensile, hardness) and metallographic inspection, product Analysis, cold drawing, second heat treatment, finished product processing, performance testing (tensile, hardness) and grain size inspection, dimensional inspection, marking, cleaning.
[0073] The induction furnace smelting: when the alloy material is smelted, a nickel plate, pure iron, and metal chromium are placed at the bottom of the induction furnace, and they are mixed and packed densely. After melting 70%, 2% of the total weight of the slag is added to carry out steelmaking. After the molten steel temperature reaches the tapping temperature, pour the molten steel into the ladle, calm down for 1-2 minutes, and pour it into steel ingots and bars. The weight of each ingot is 4...
Embodiment 3
[0114] The preparation method of the end cap in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 includes the following steps in sequence: induction furnace smelting, electroslag refining, smelting analysis, forging, ultrasonic inspection, hot rolling, heat treatment, performance test, product analysis, end cap car processing, size Inspect, mark, clean.
[0115] The induction furnace smelting: when the alloy material is smelted, a nickel plate, pure iron, and metal chromium are placed at the bottom of the induction furnace, and they are mixed and compacted. After melting 70%, 2% of the total slag is added for steelmaking, and the measured After the temperature of the molten steel reaches the tapping temperature, pour the molten steel into the ladle, calm down for 1-2 minutes, and pour it into steel ingots and bars. The weight of each ingot is 40-50kg.
[0116] The electroslag refining: After the alloy material is smelted, electroslag refining is required to effectively improve the purity and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com