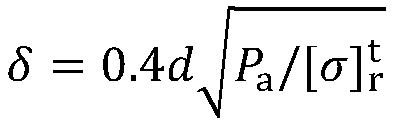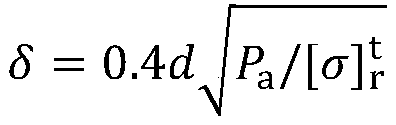Patents
Literature
220results about "Steam generator primary side" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
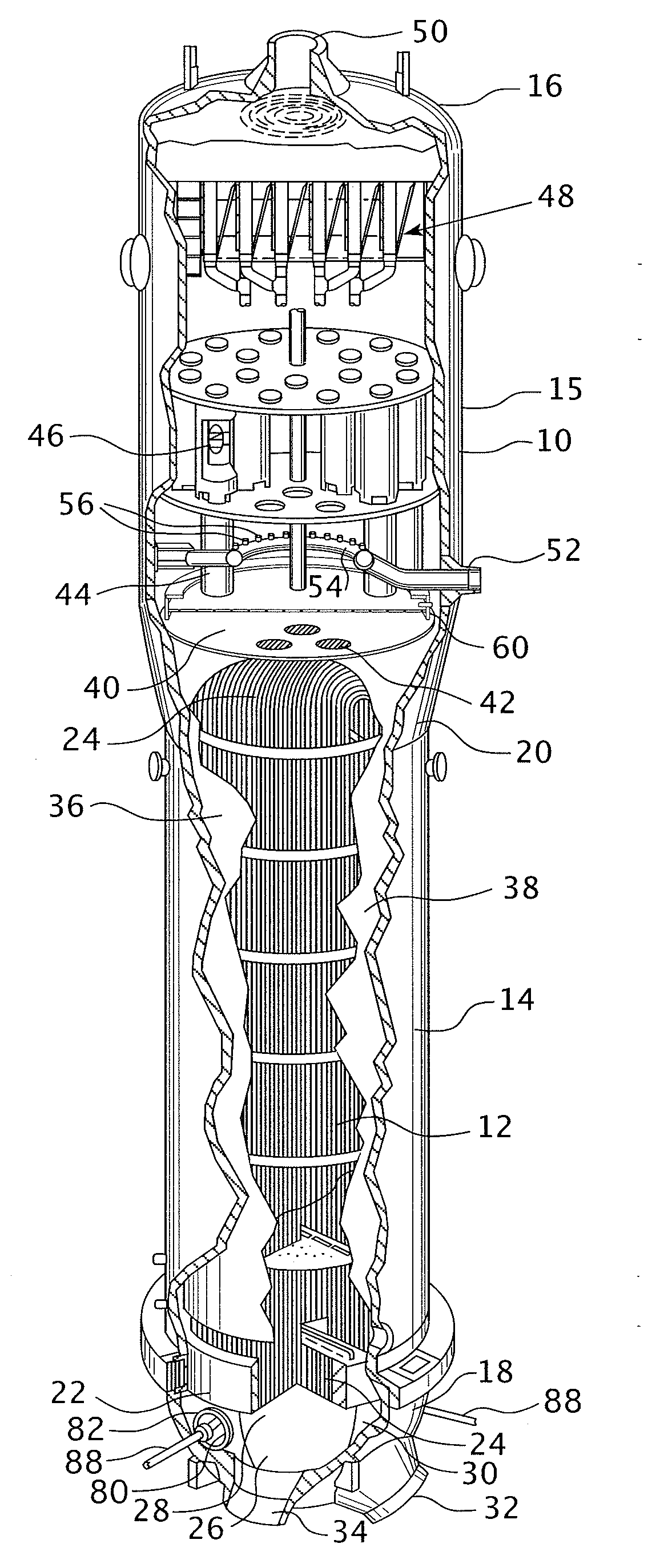
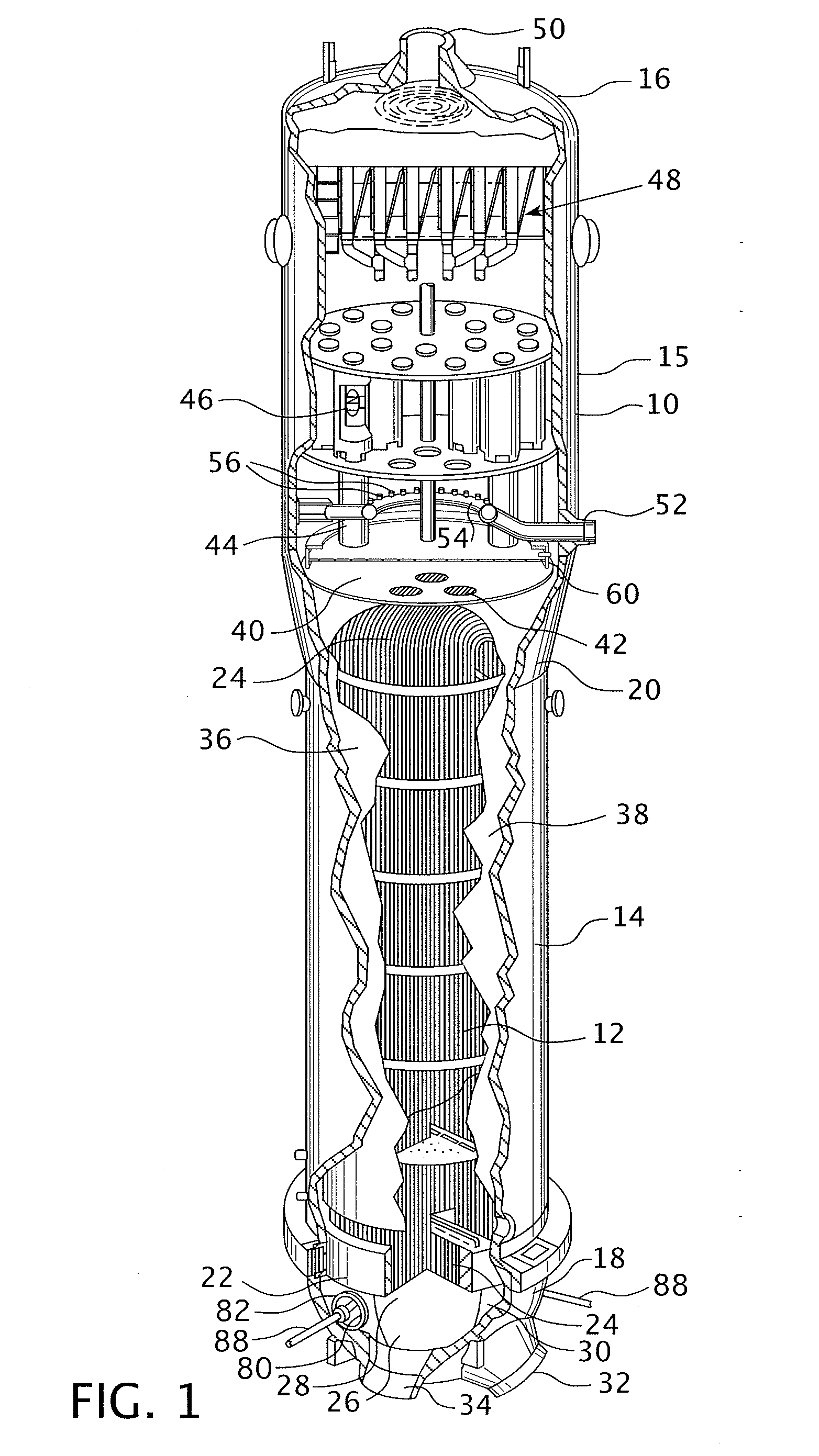
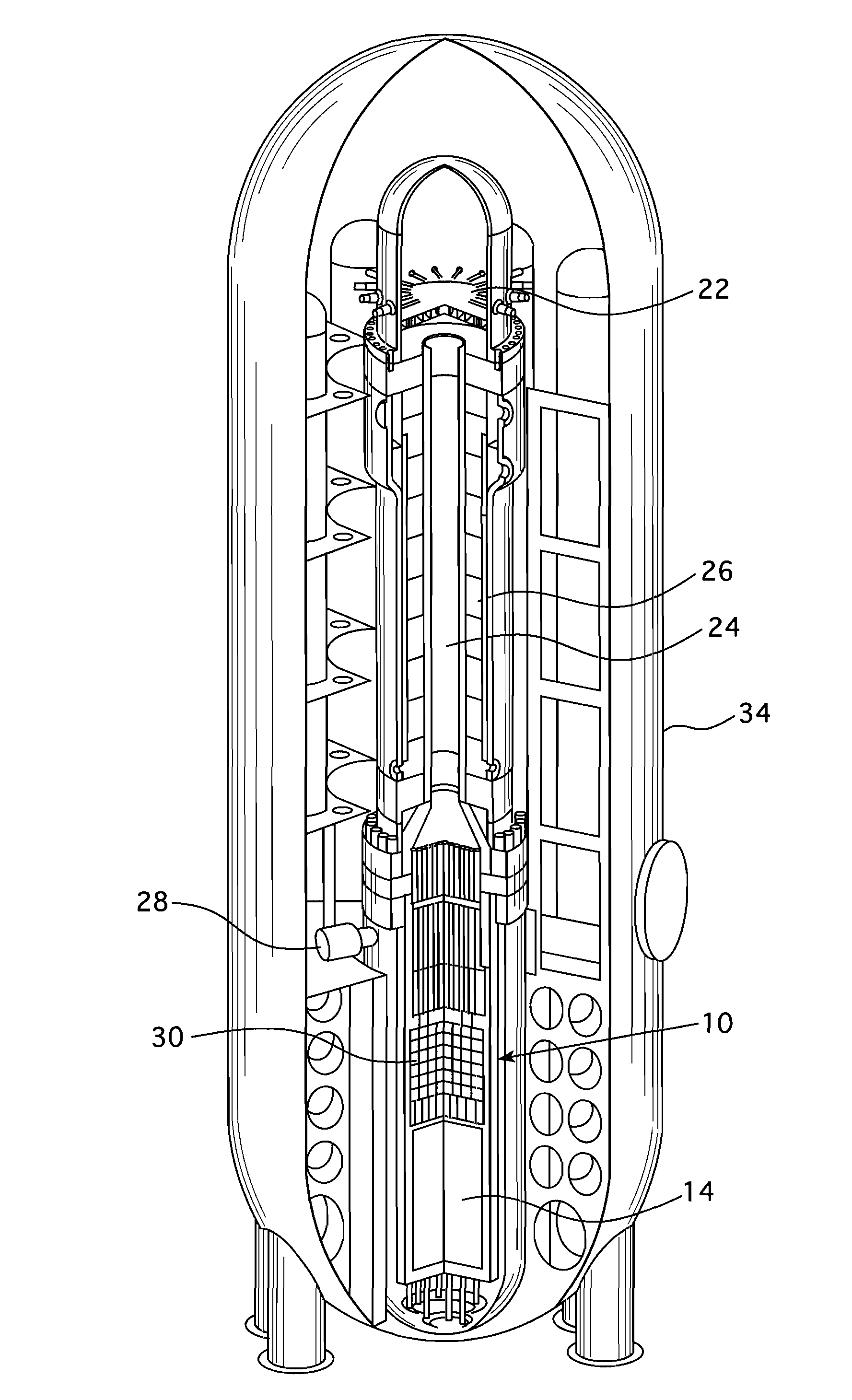
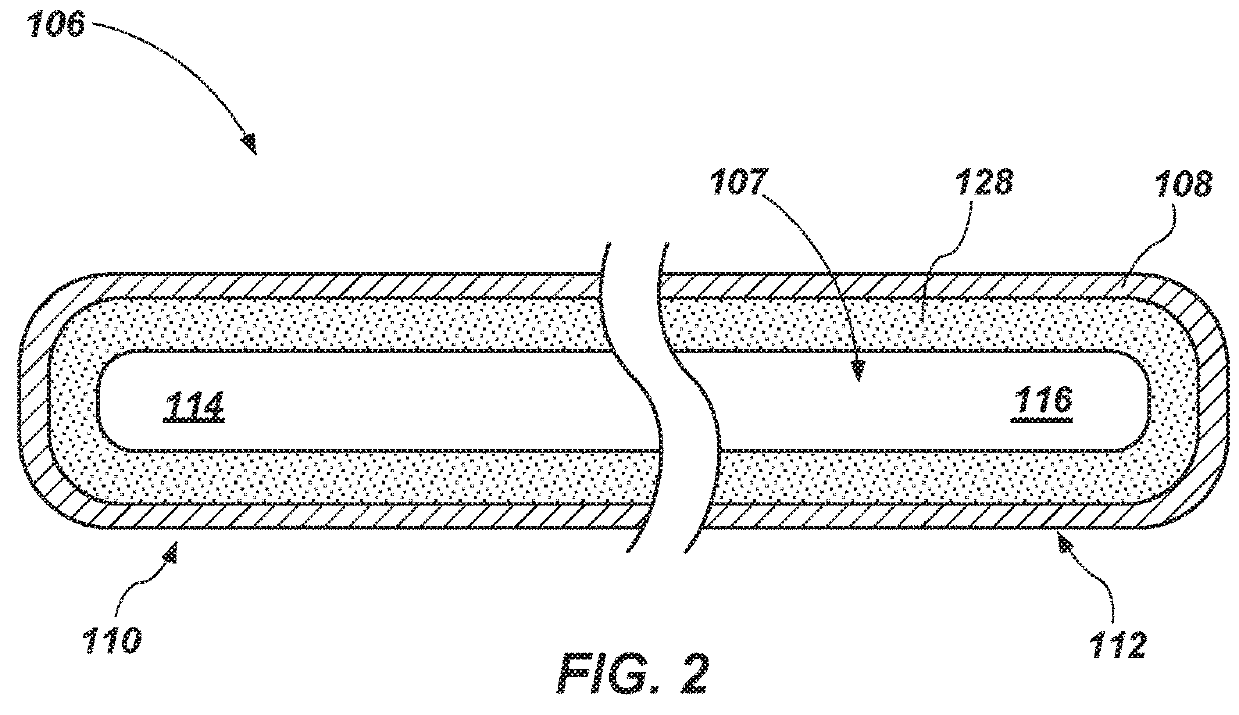
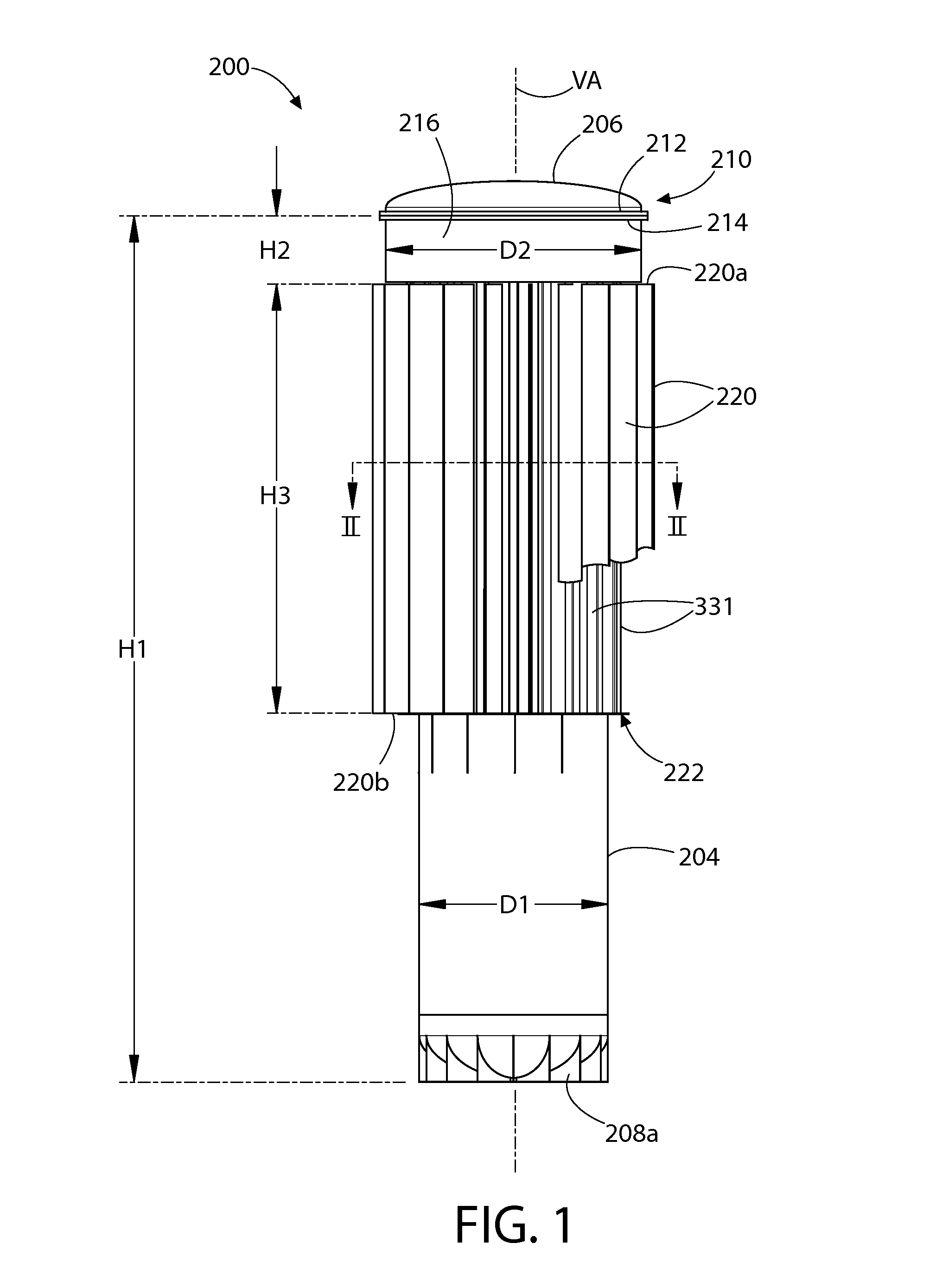
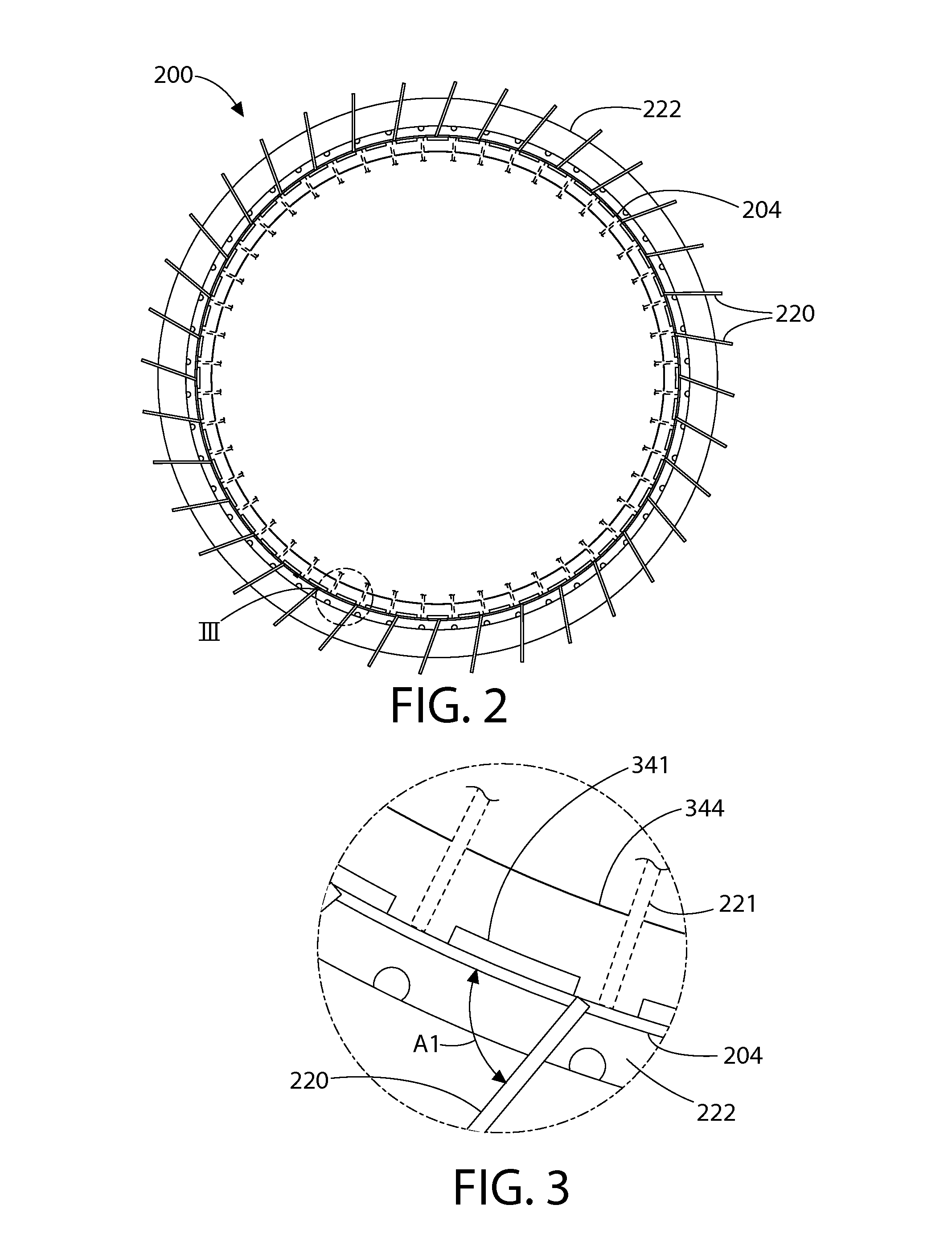
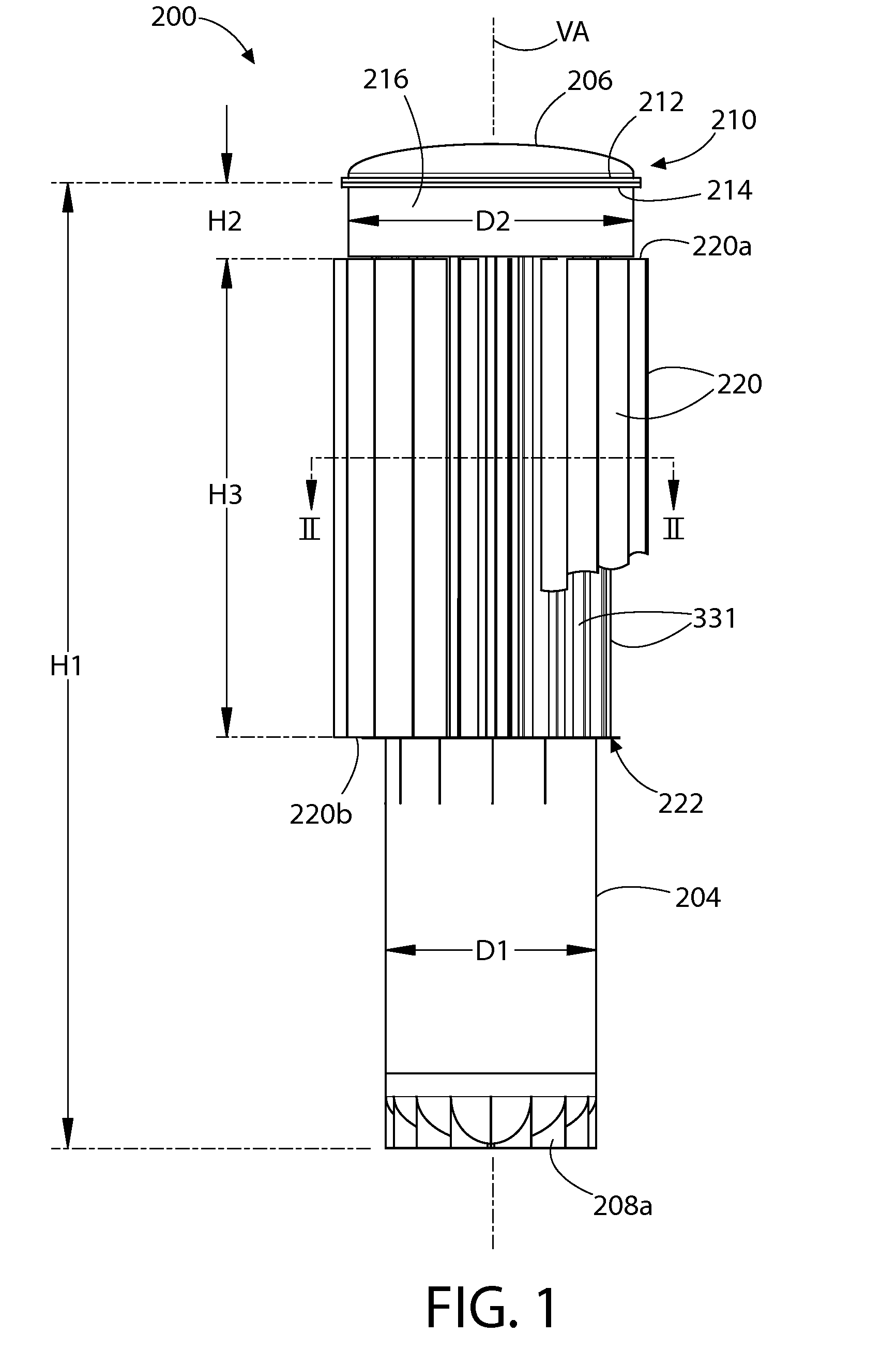
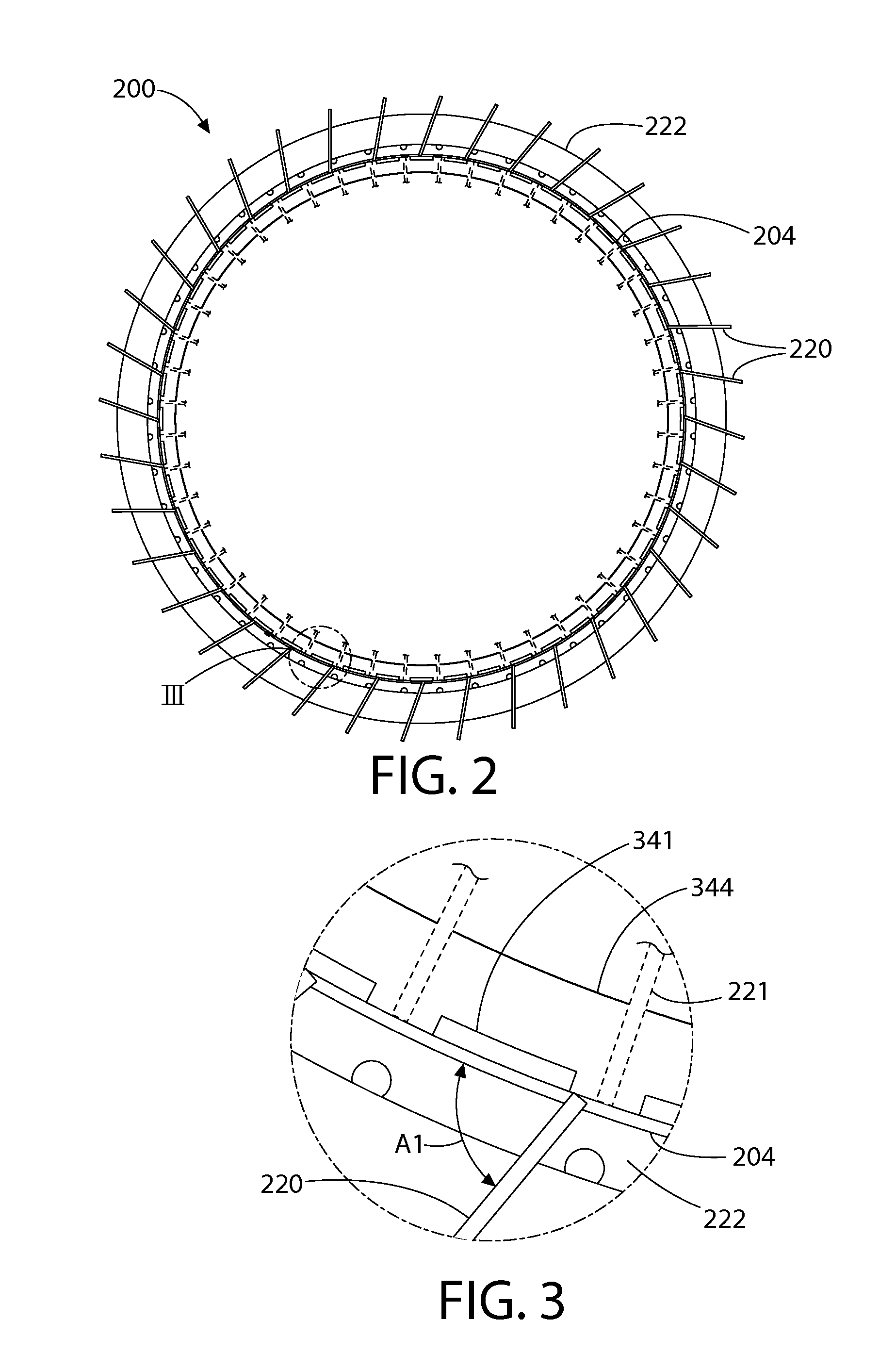
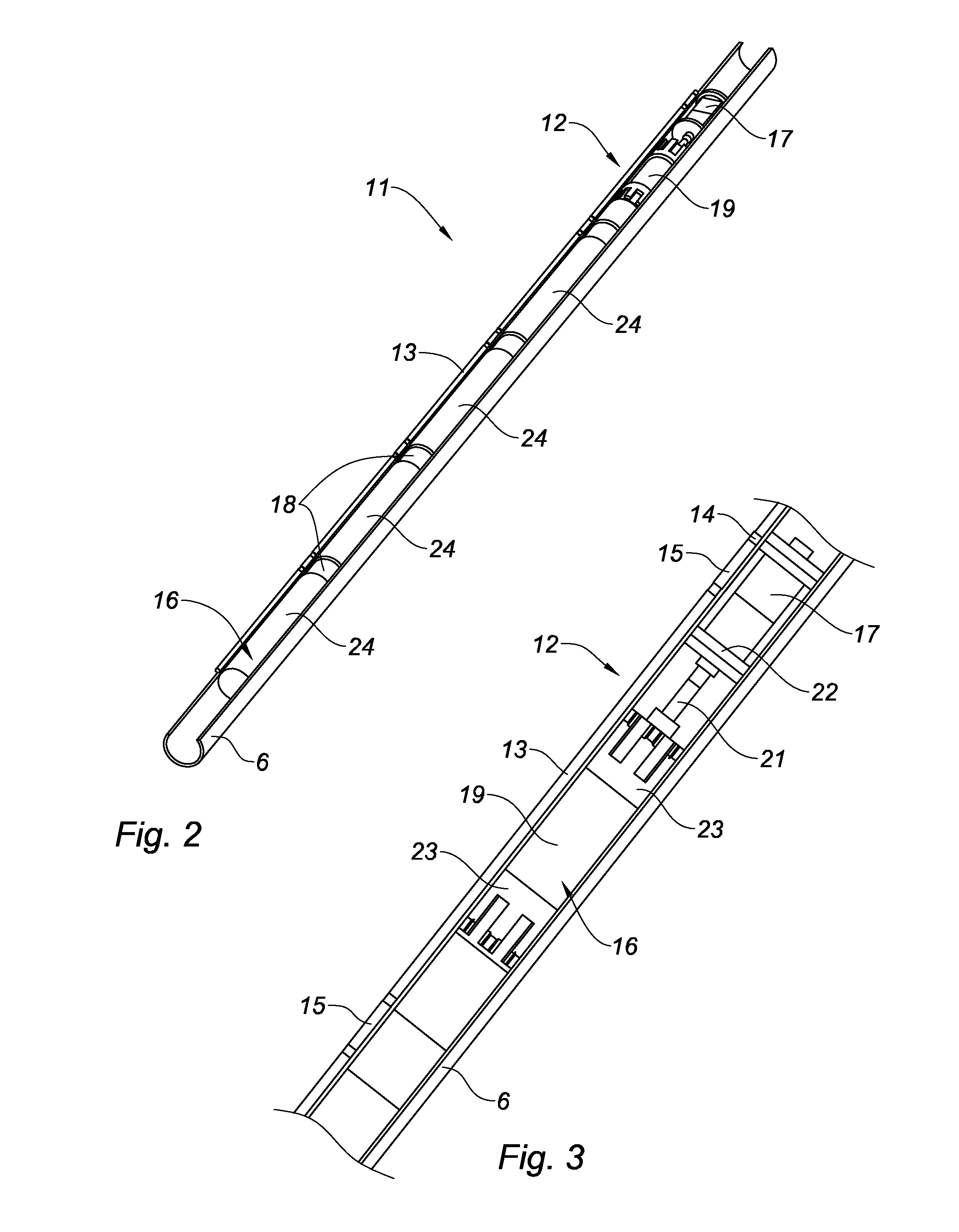
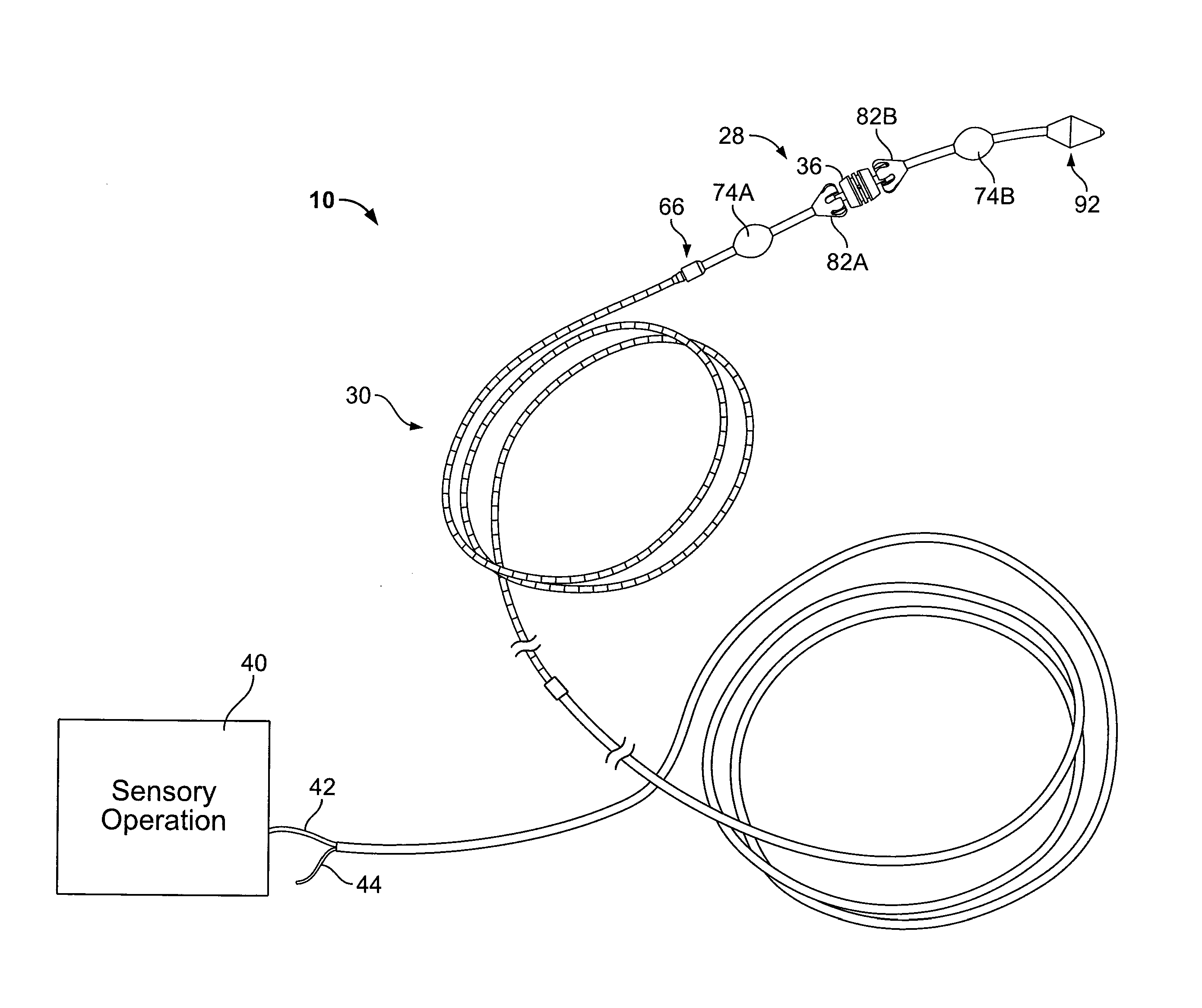
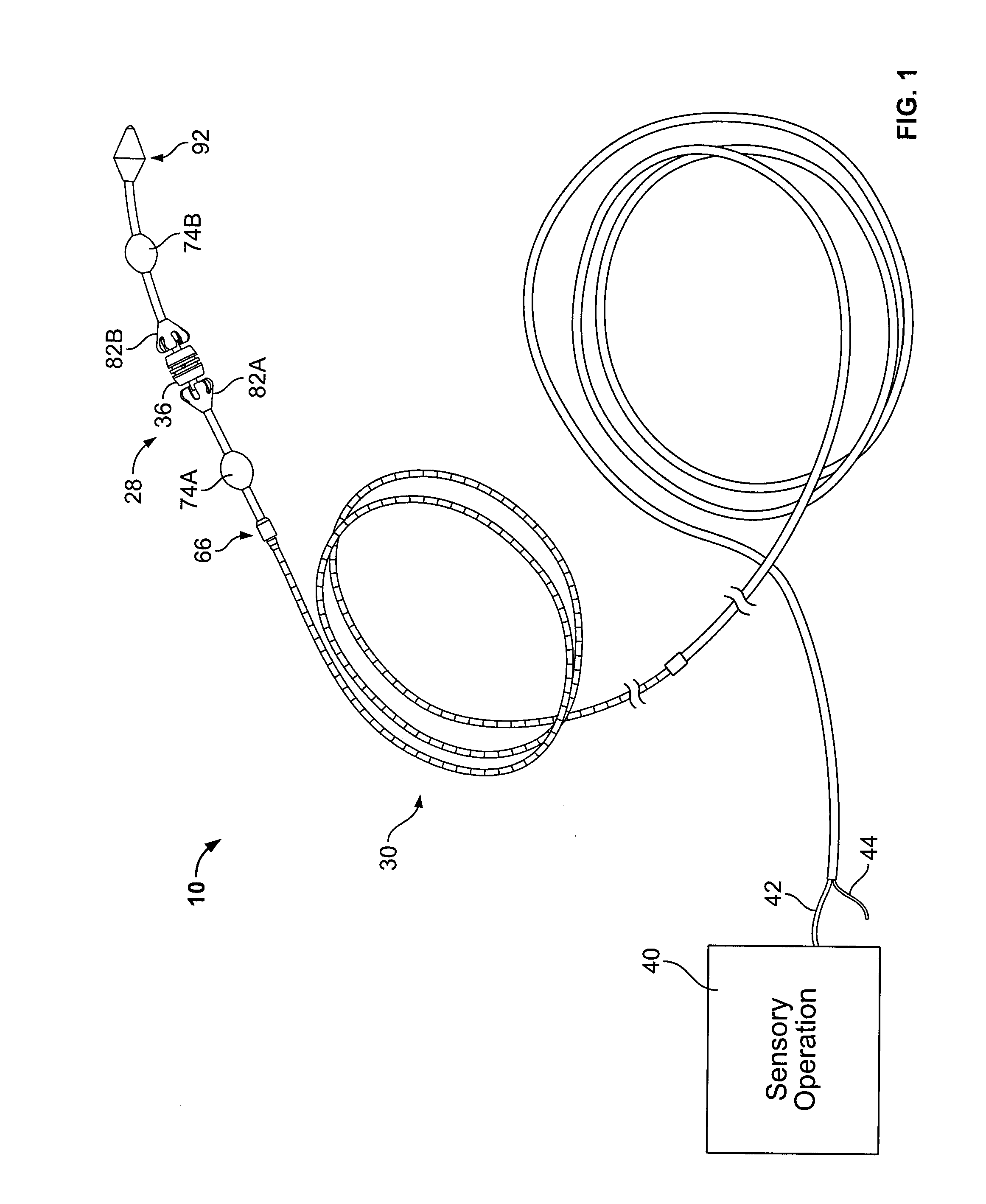
Tetherless tube inspection system
InactiveUS20110125462A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNuclear energy generationData acquisitionEmbedded system
Apparatus and a method to inspect tubing by means of a free flying, autonomous inspection head that is not attached by wires to external control and data acquisition equipment. The inspection head travels through the tube with an attached module that integrates all the necessary support for the electronic and mechanical control of a nondestructive sensor within the inspection head.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
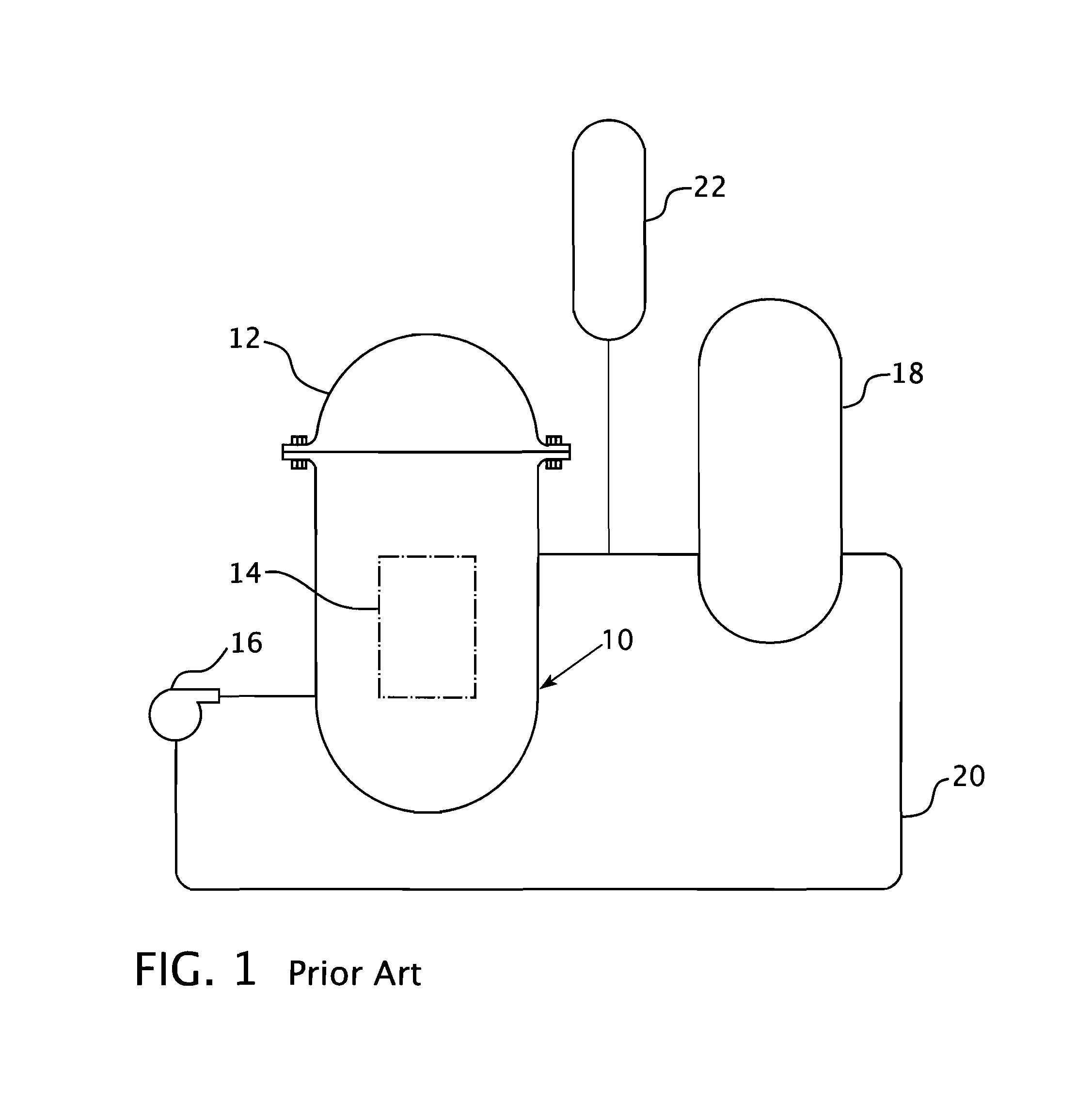
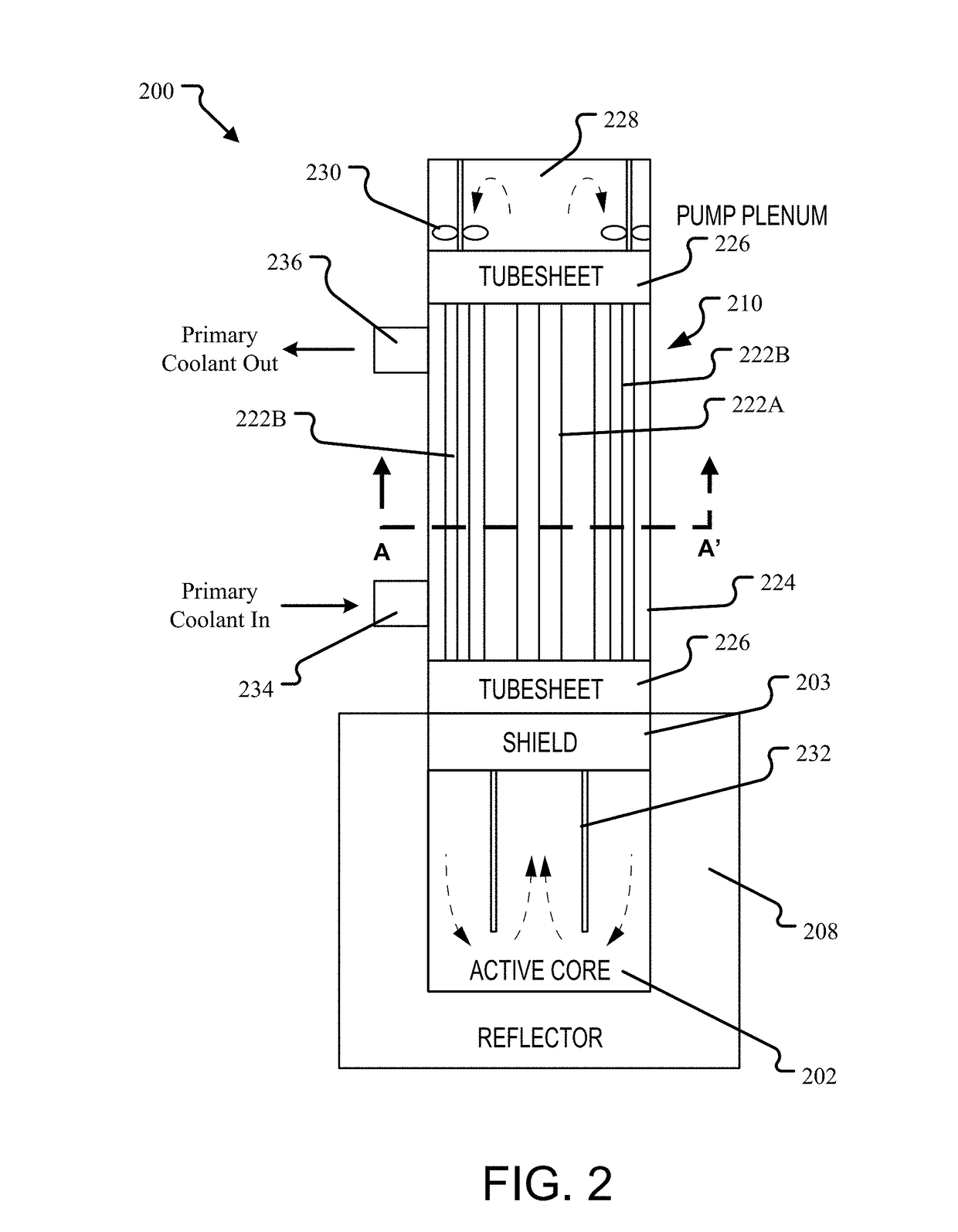
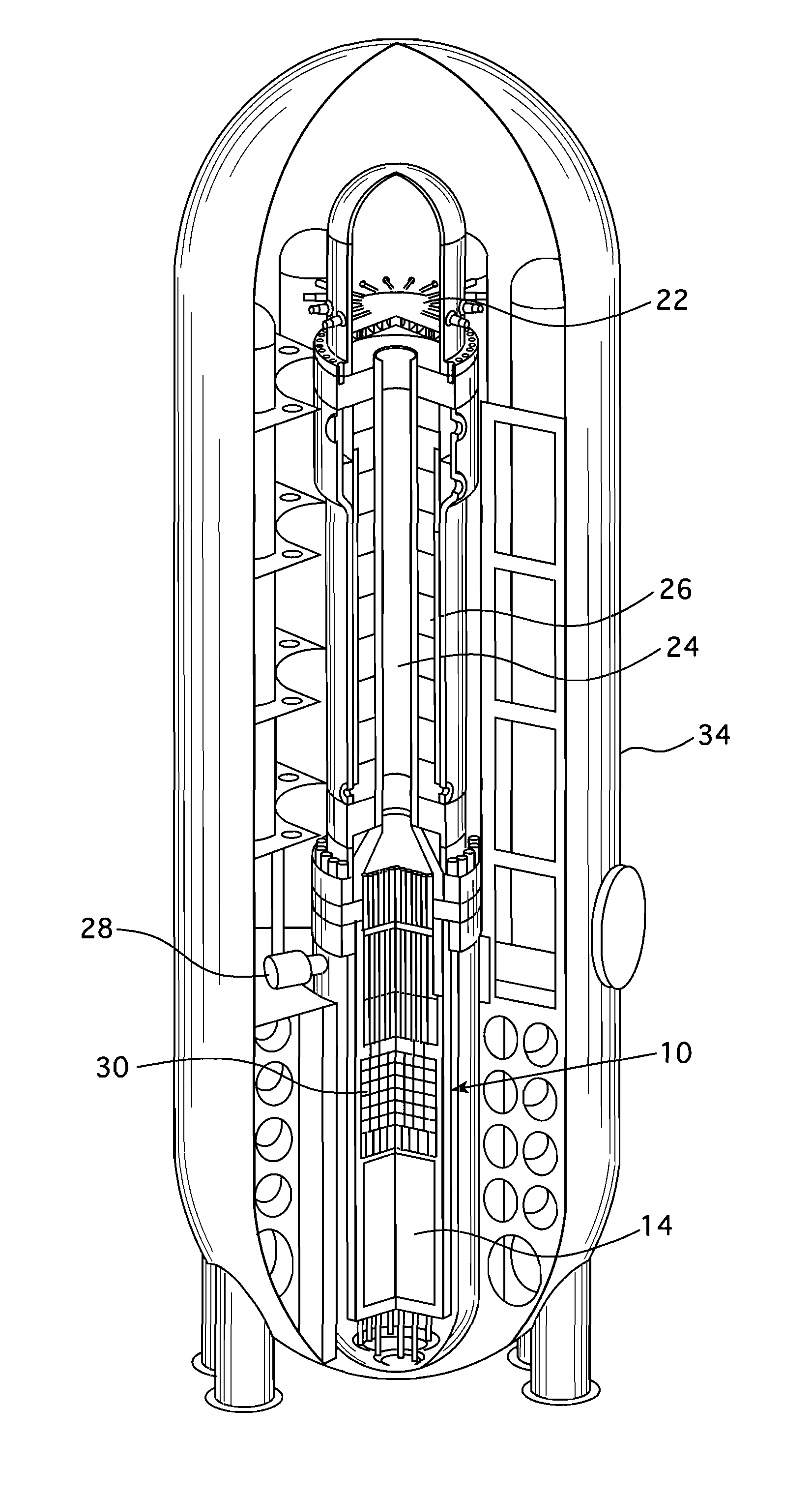
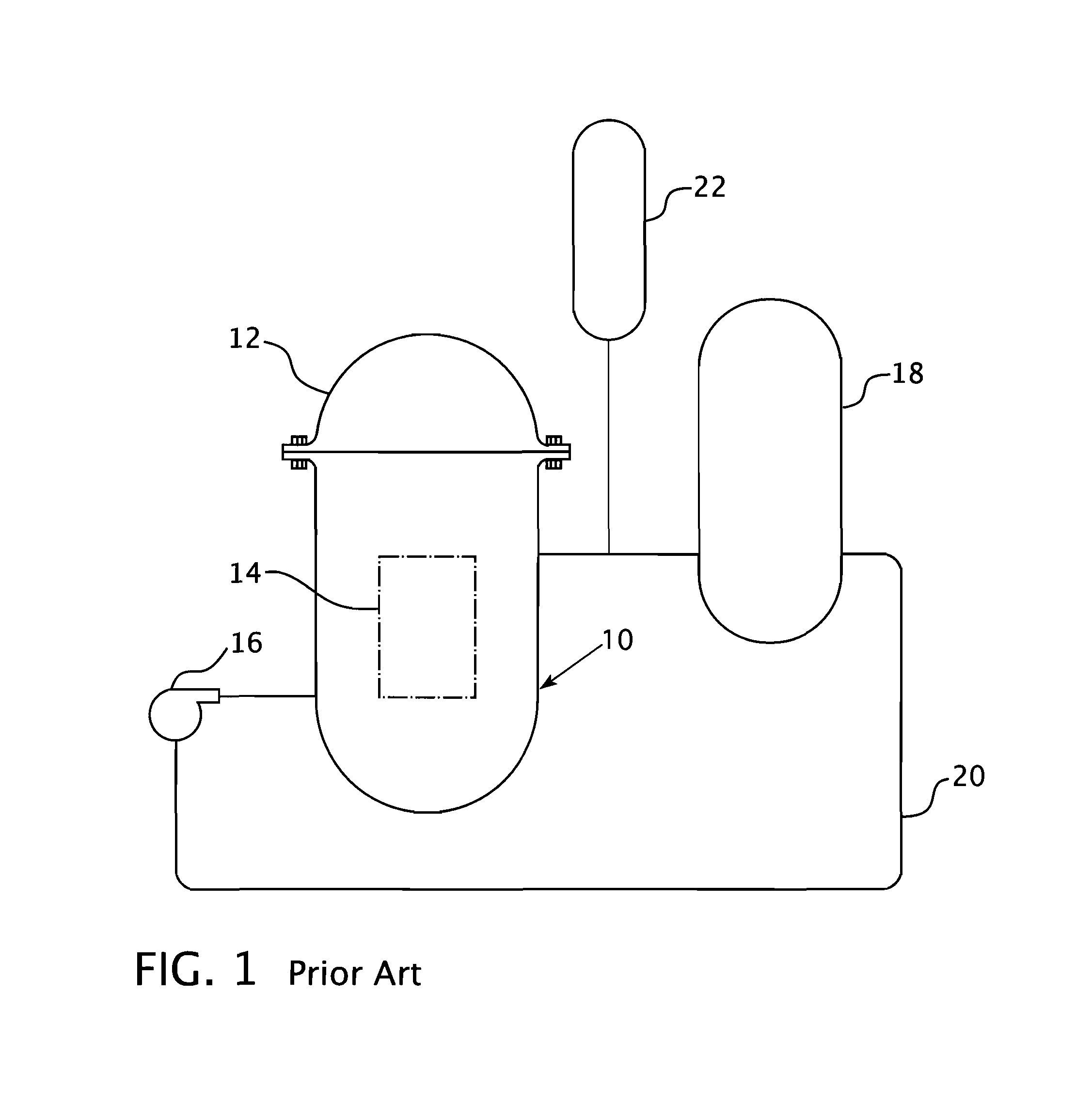
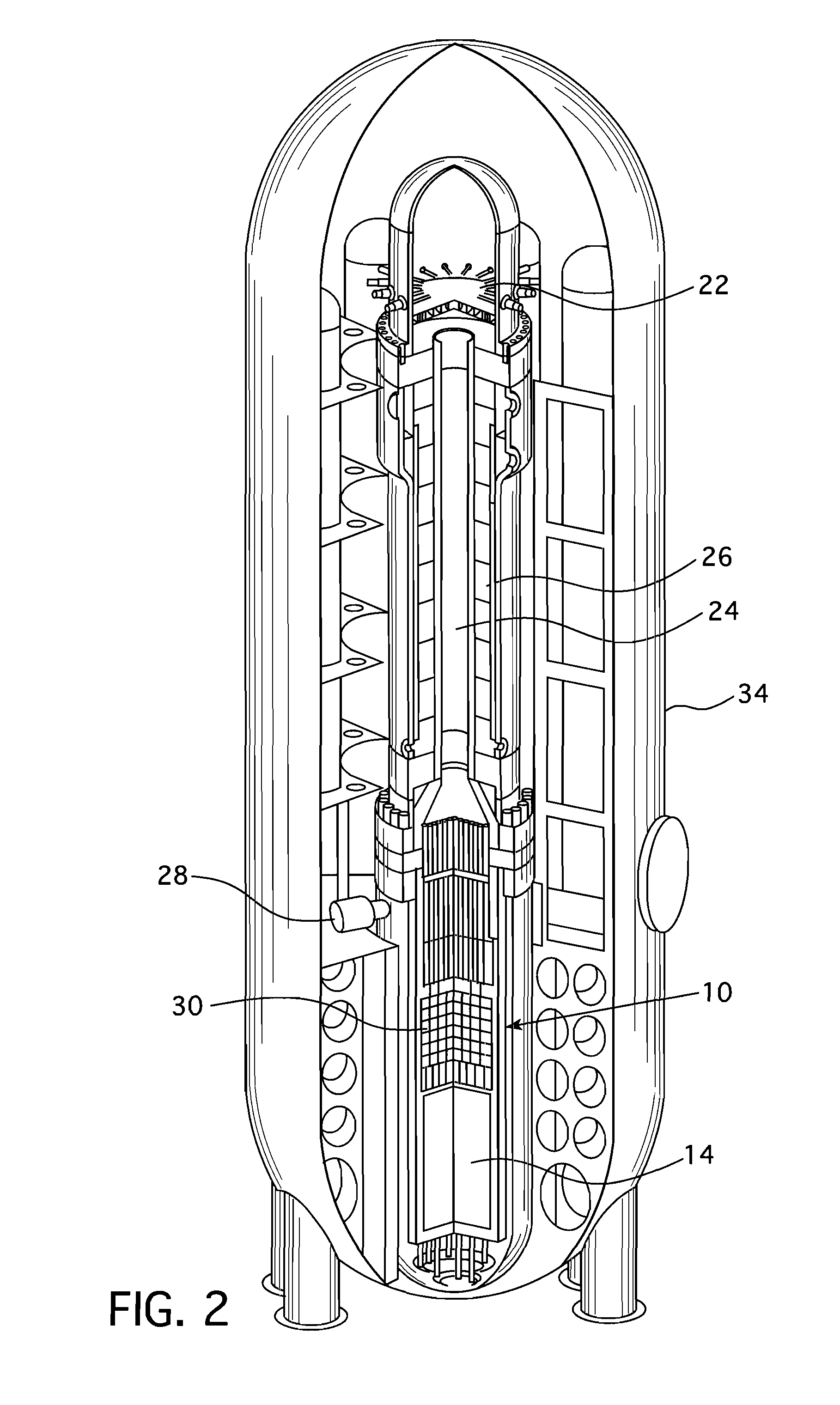
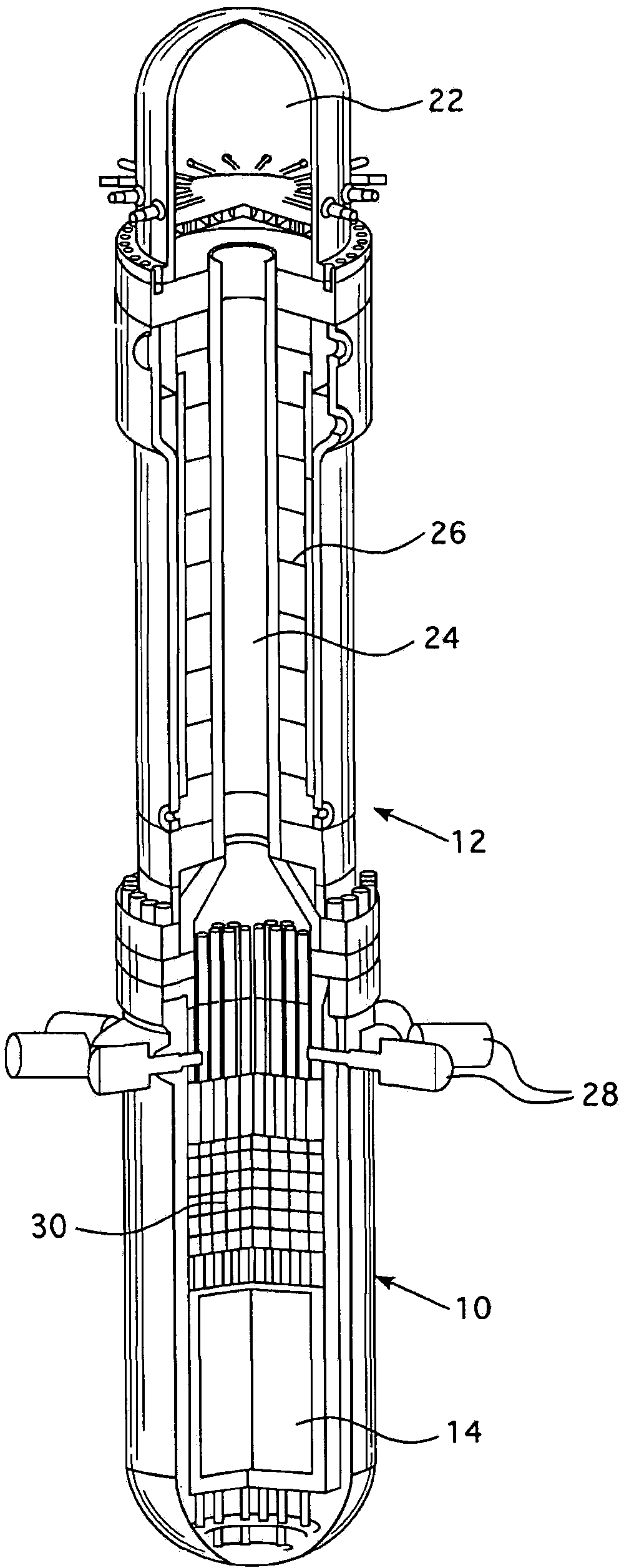
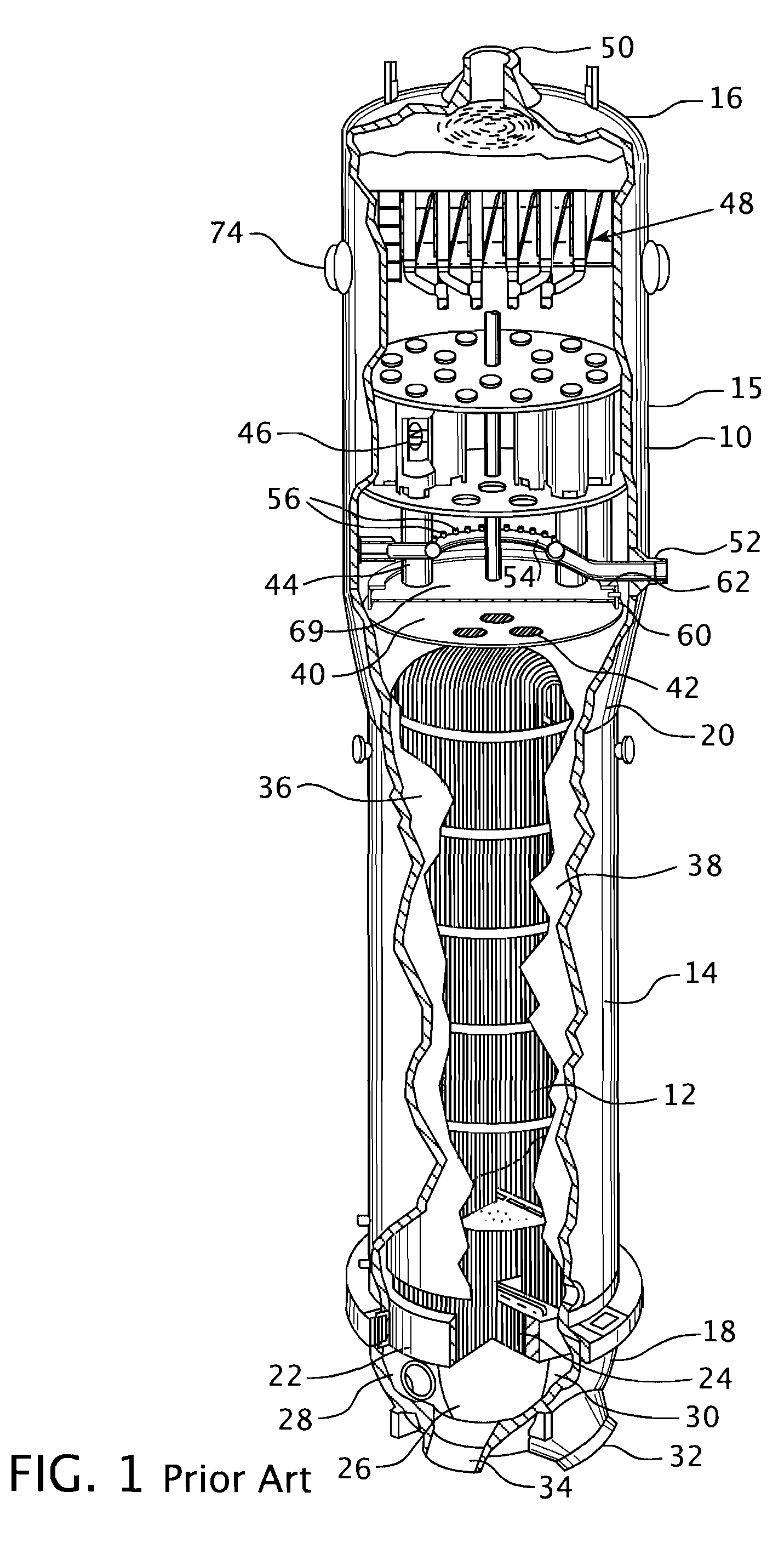
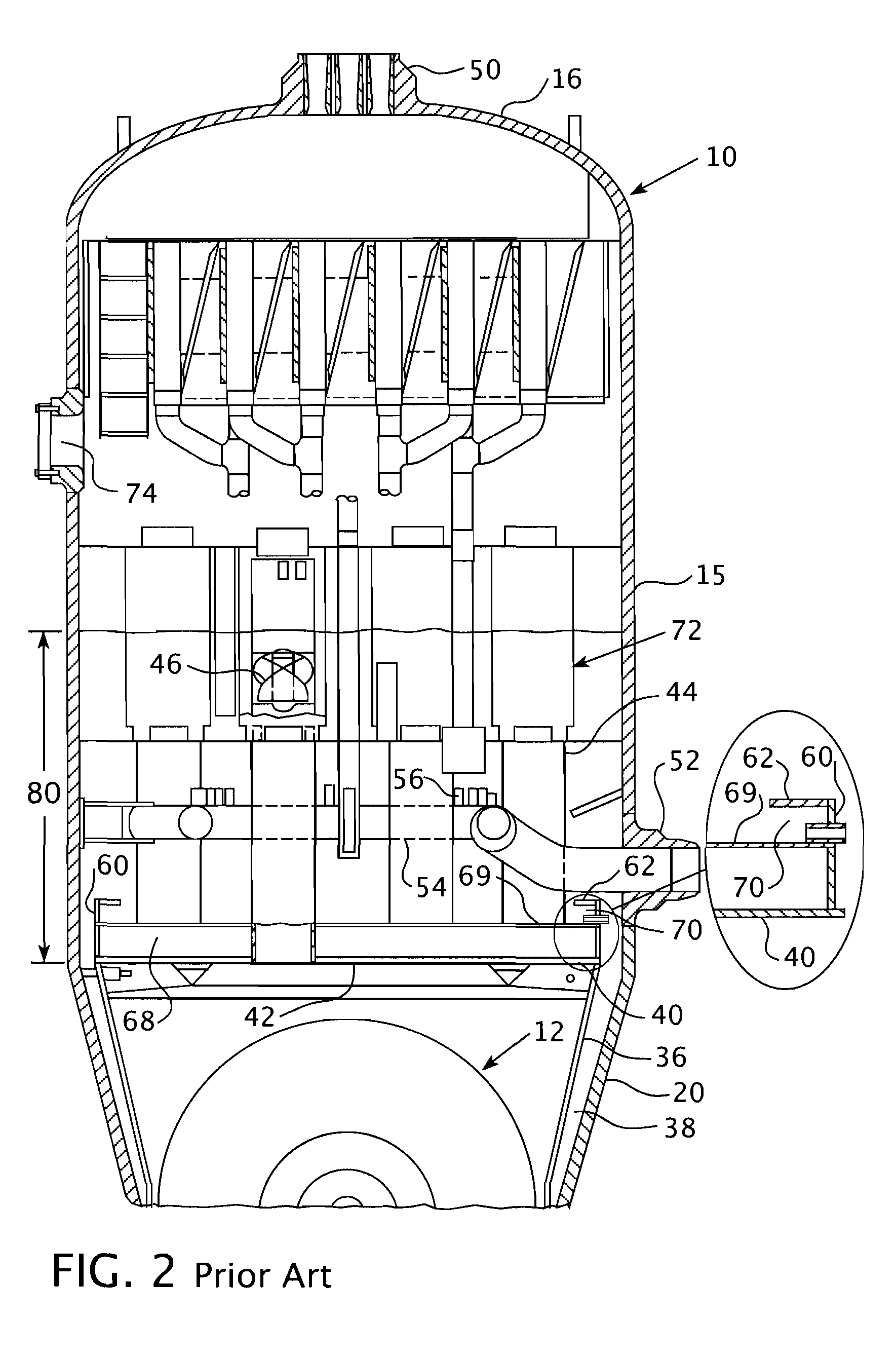
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
ActiveUS20130336442A1Facilitate natural recirculation of recirculatingBoiler drums/headersIntegral reactorsPressurized water reactorSteam drum
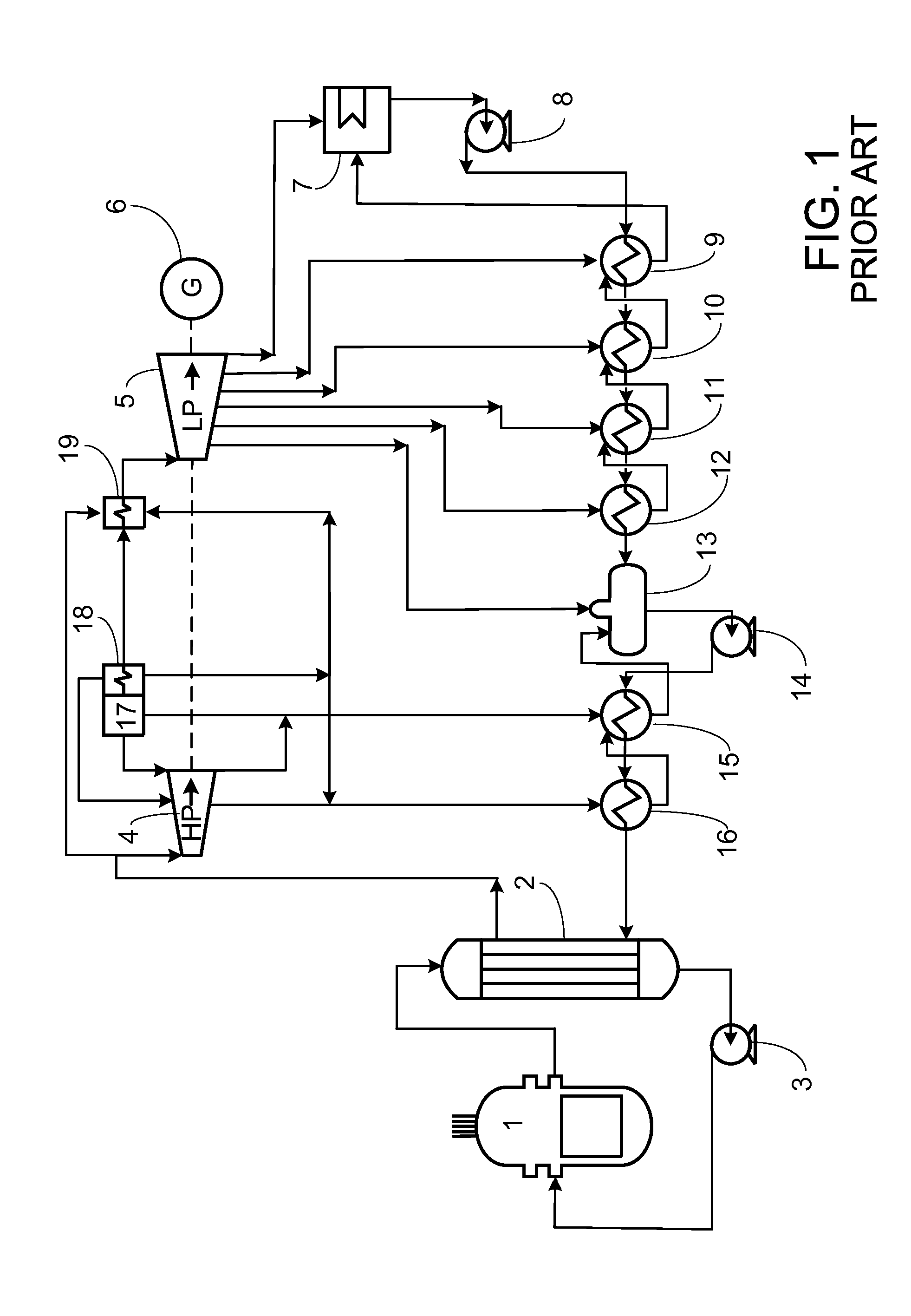
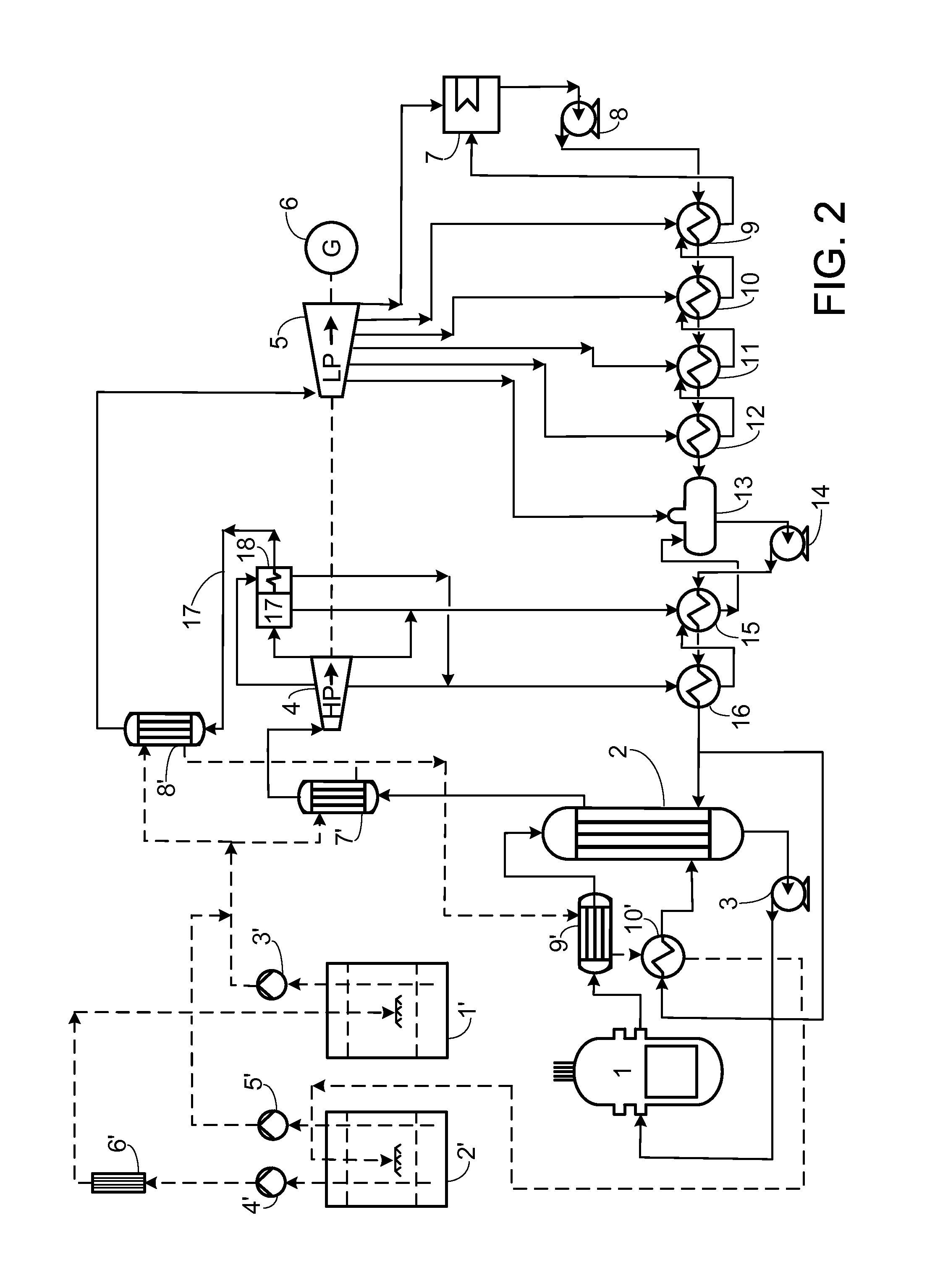
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Vertically-segmented nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20180019025A1Improve power densitySave on fuel costsIntegral reactorsFuel elementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
This disclosure describes various configurations and components of a molten fuel fast or thermal nuclear reactor in which one or more primary heat exchangers are located above the reactor core of the nuclear reactor.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Tetherless tube inspection system
InactiveCN102422155ADetection of fluid at leakage pointAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComputer moduleData acquisition
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
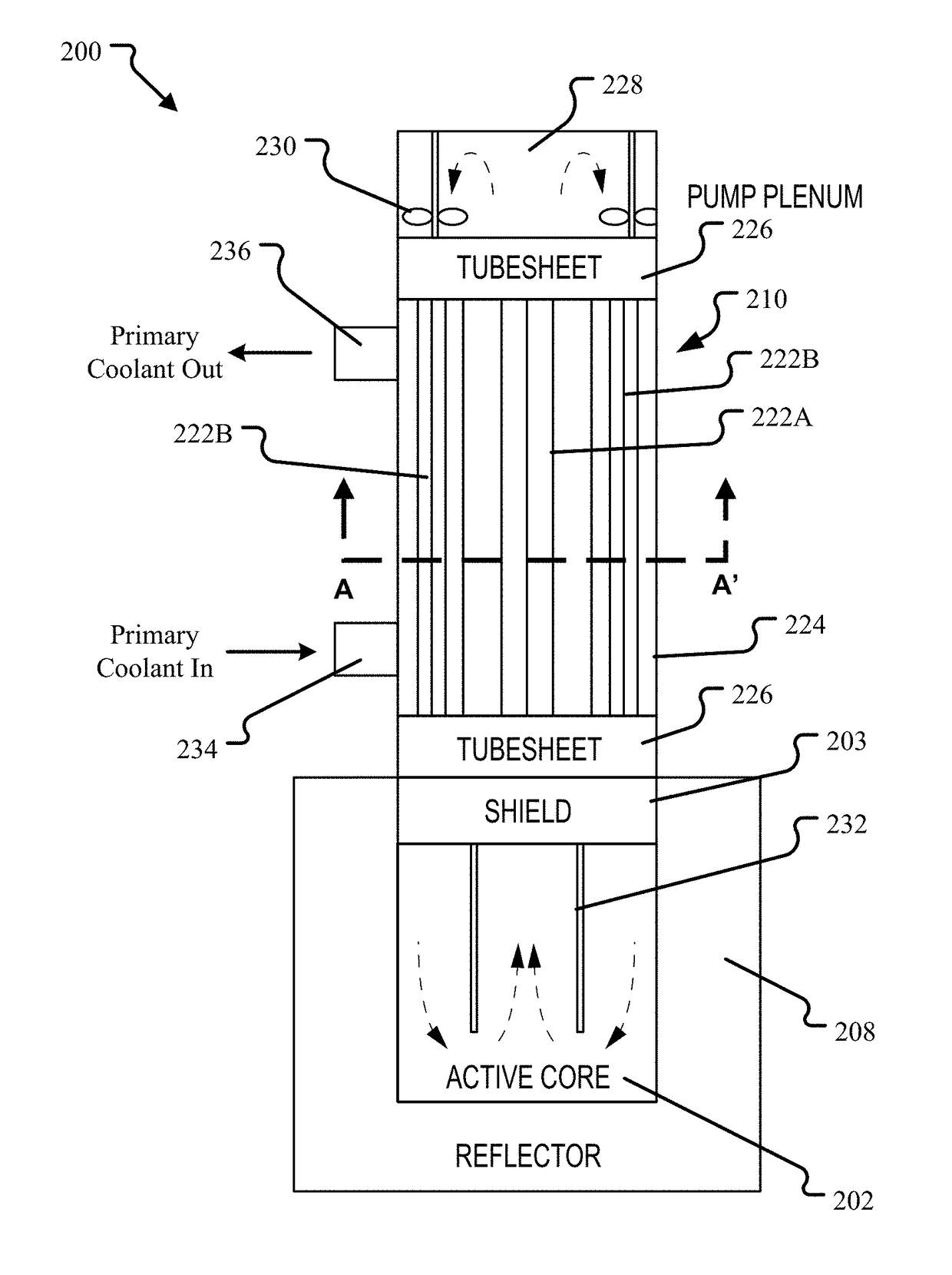
Steam generator for nuclear steam supply system
ActiveUS20160196885A1Reduced fretting damage rateAvoid failureBoiler supporting/setting arrangementsSteam generation heating methodsWorking fluidCoolant flow
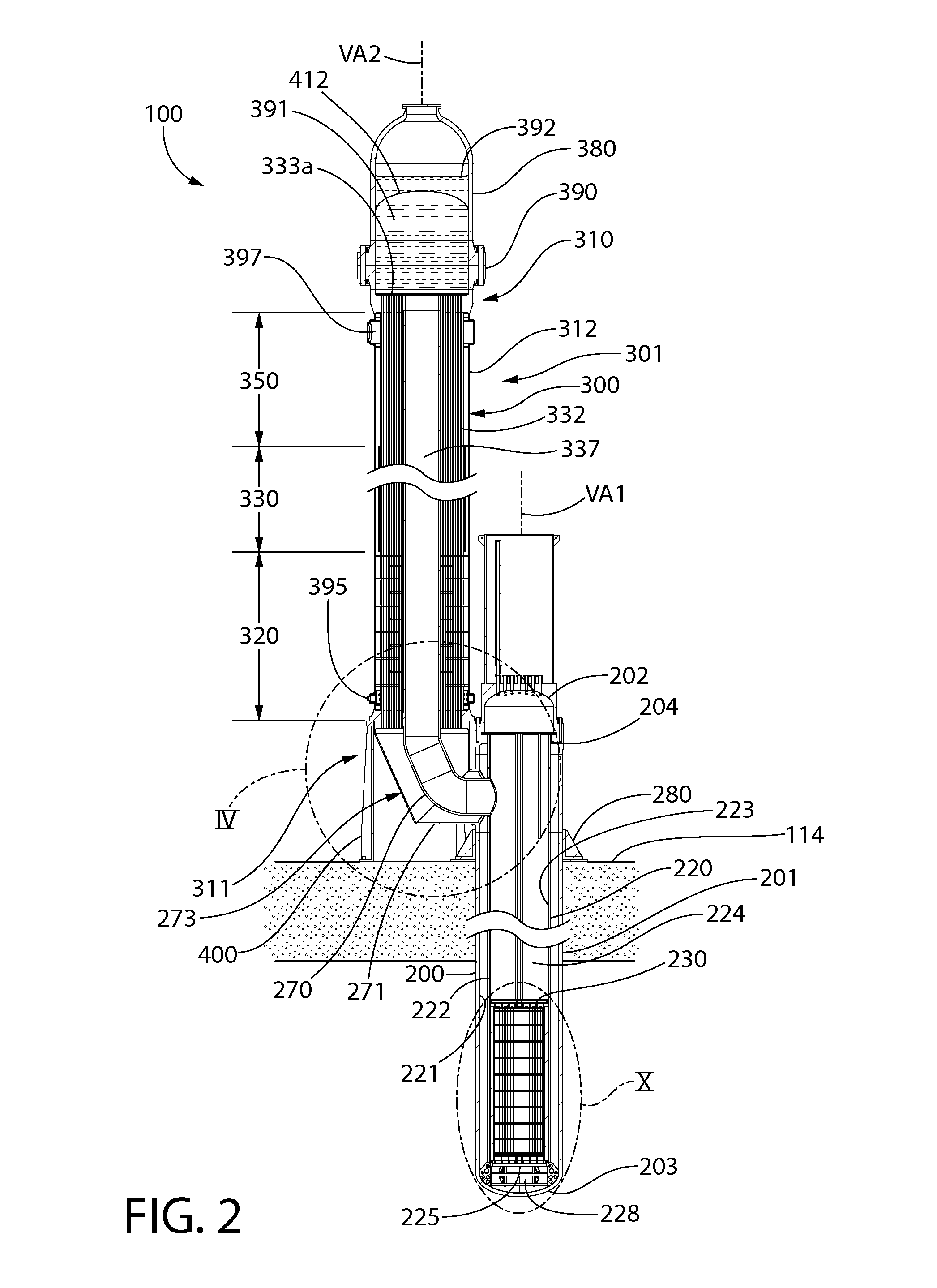
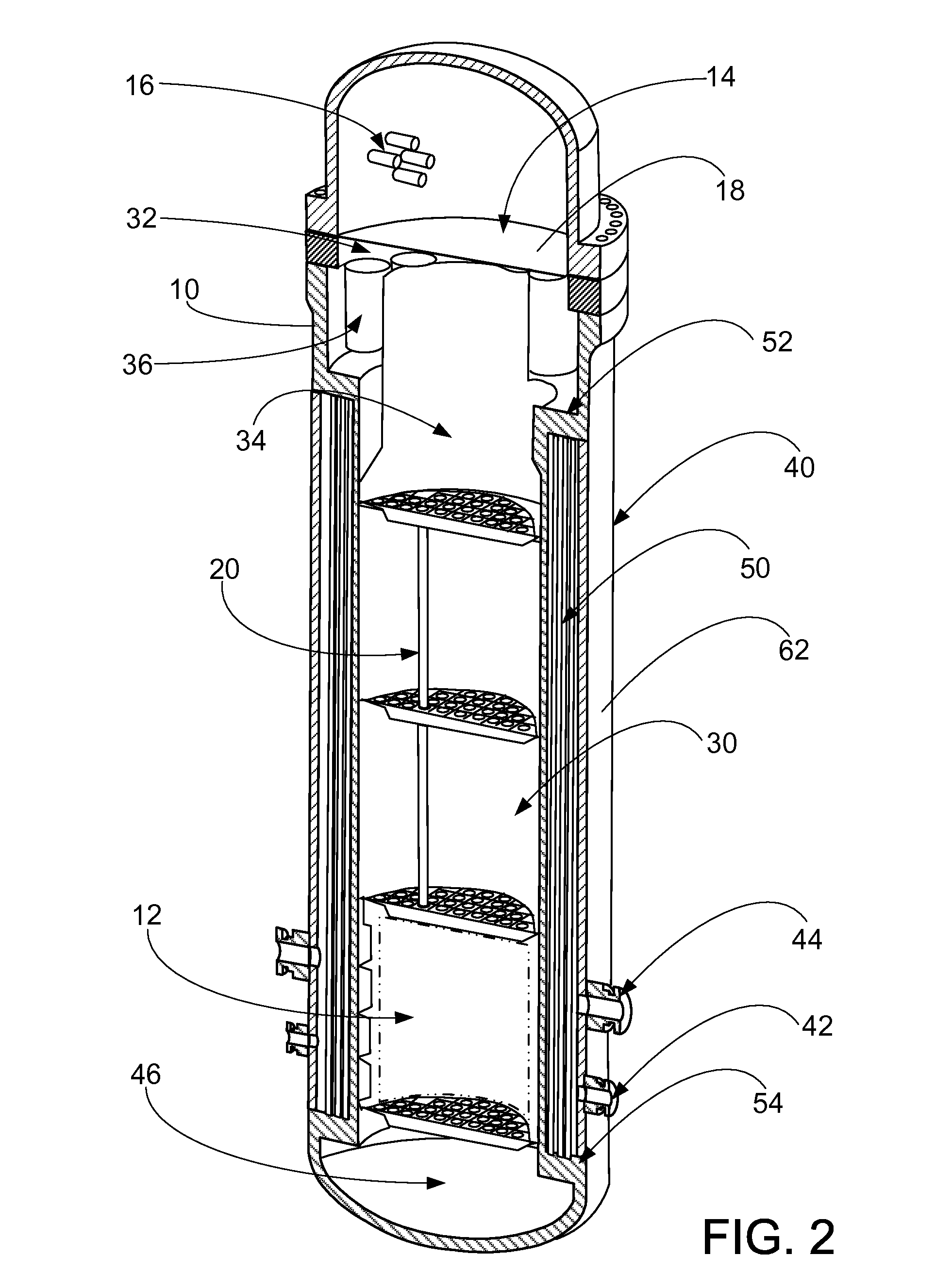
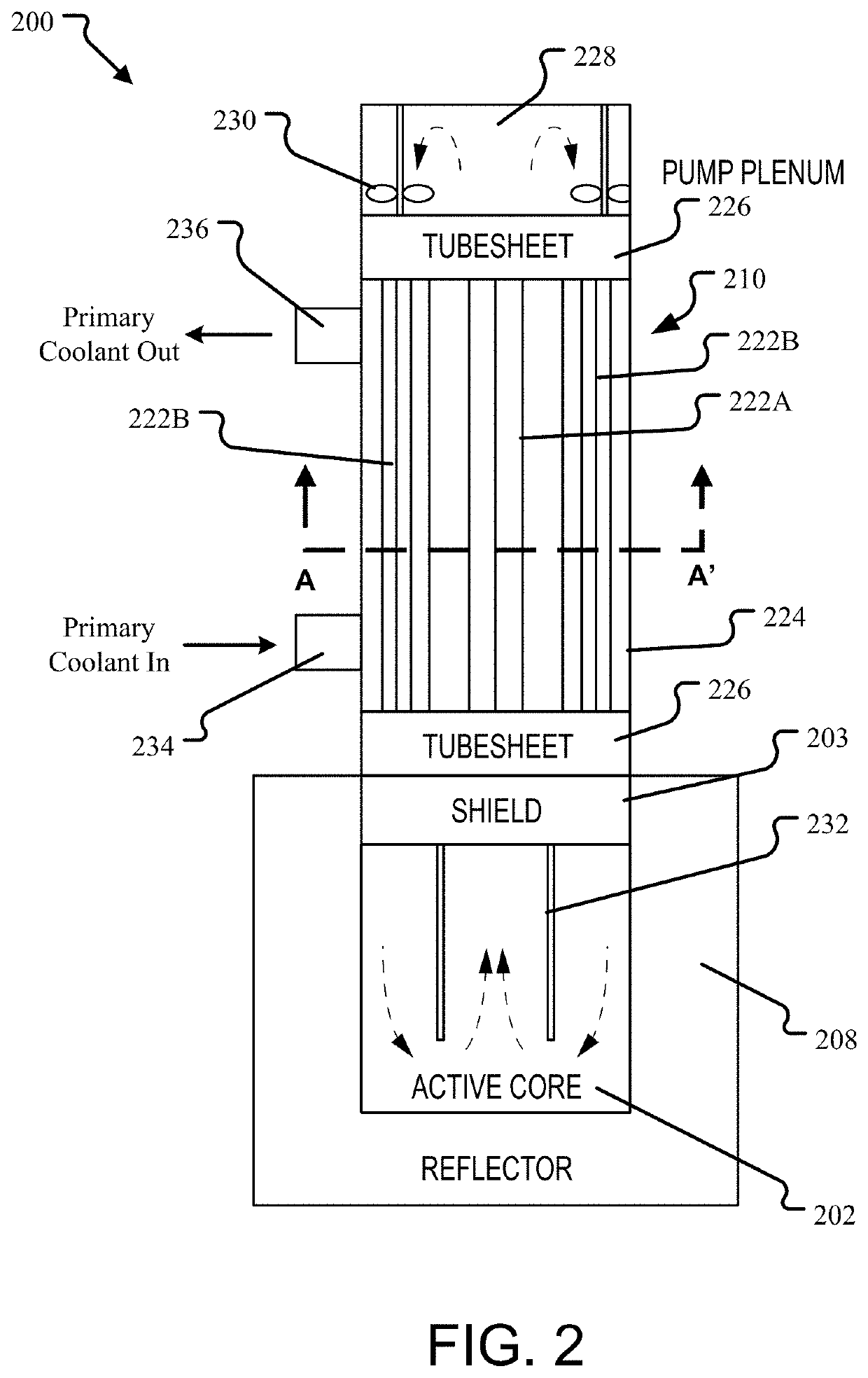
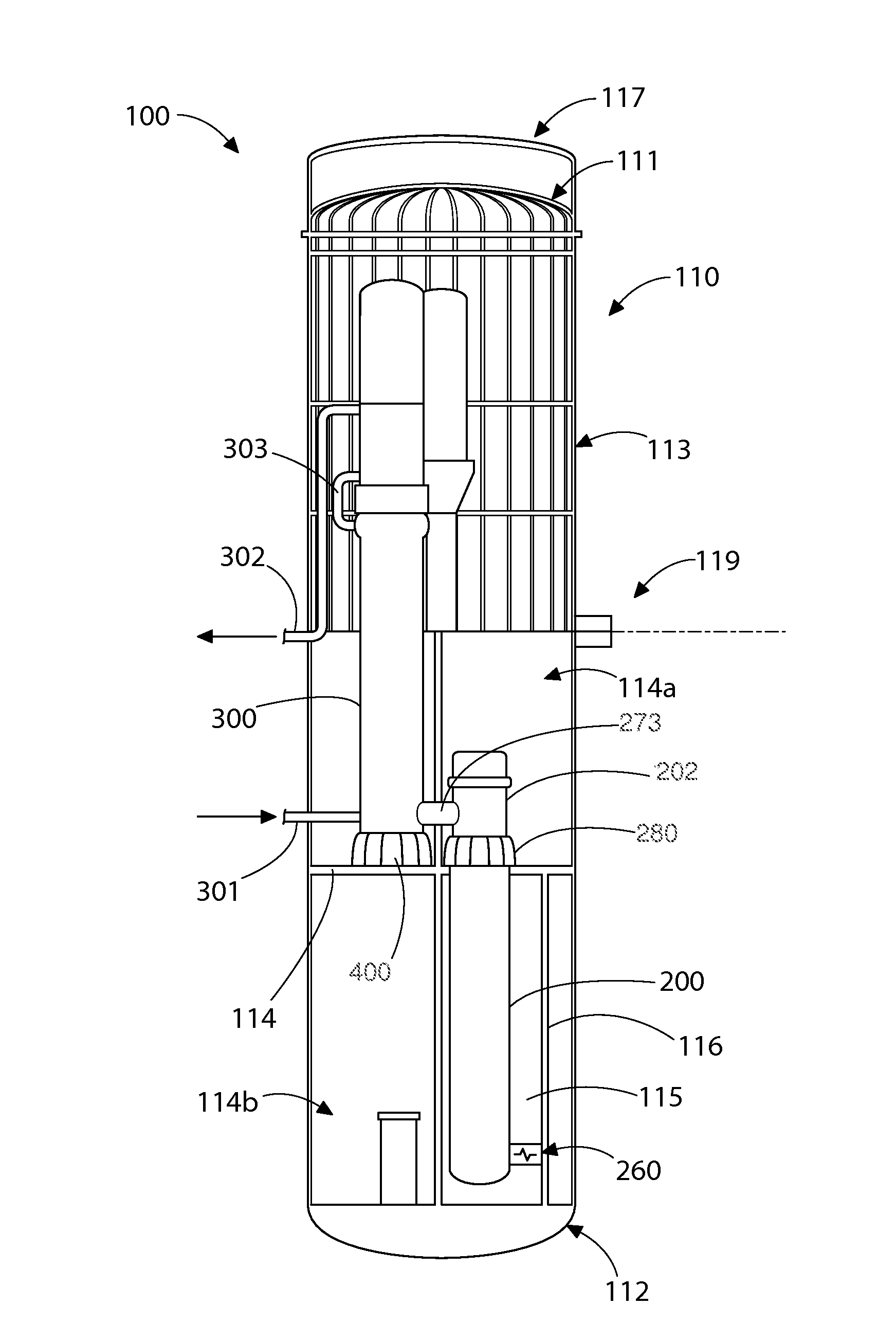
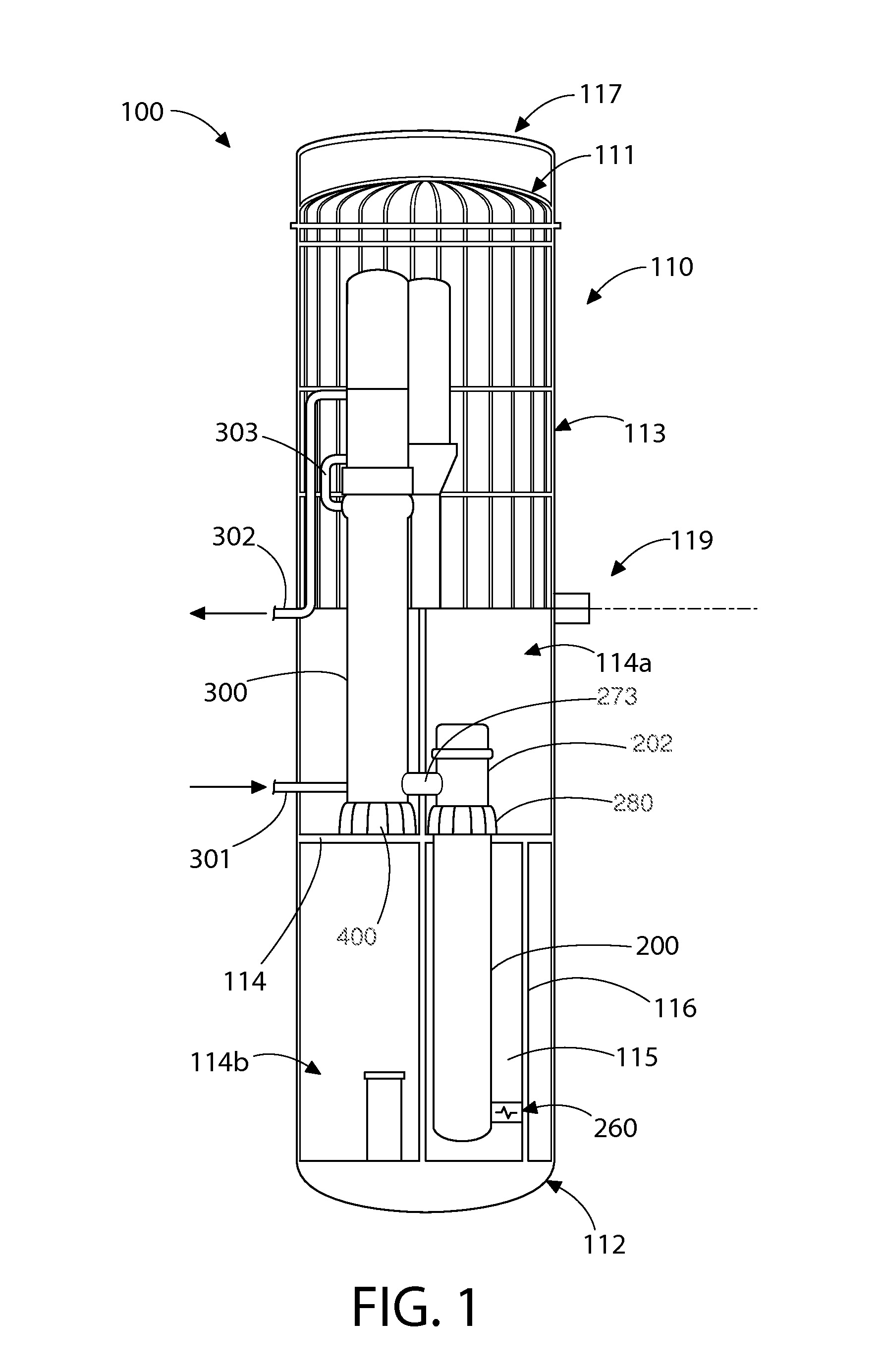
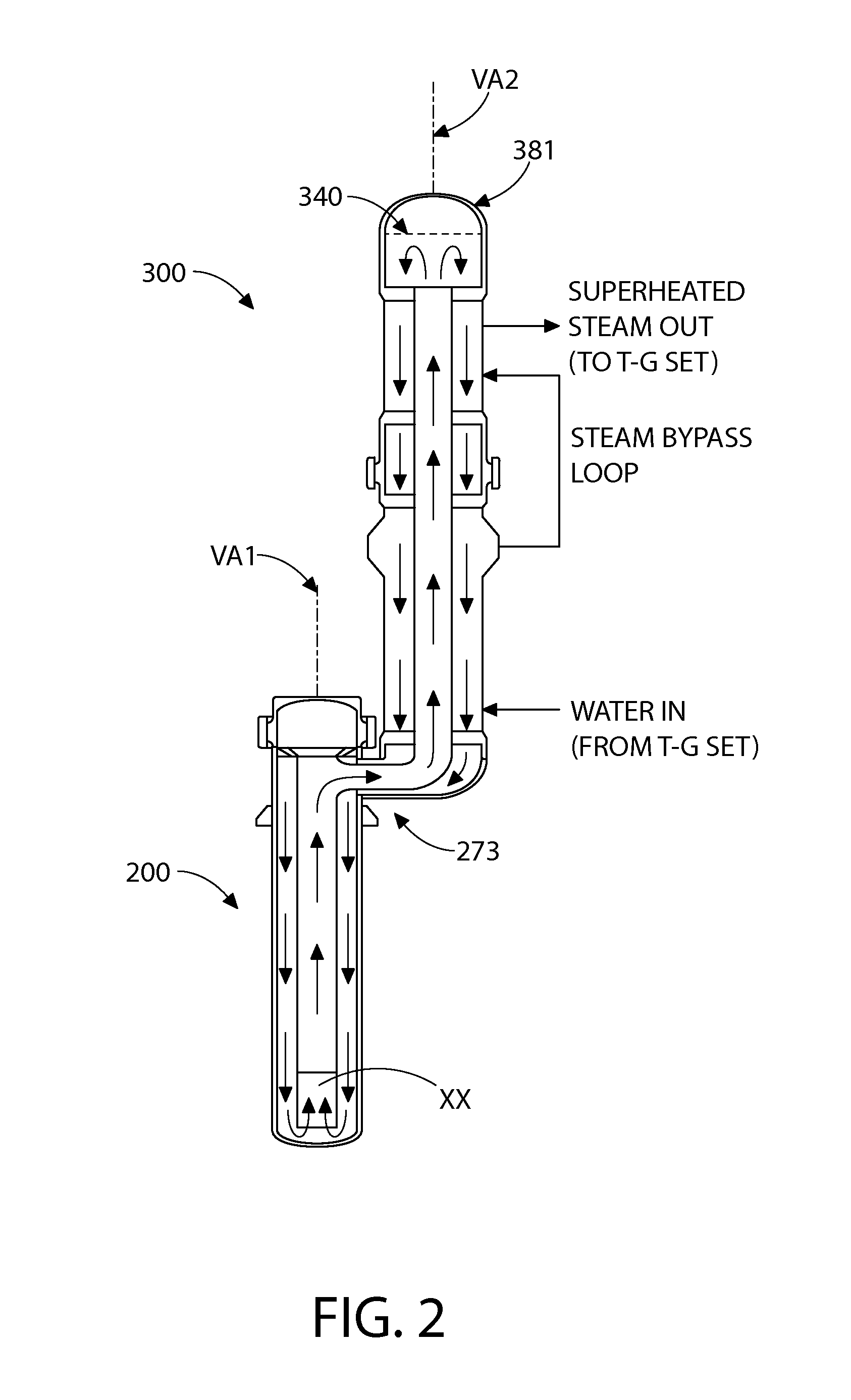
A nuclear steam supply system utilizing gravity-driven natural circulation for primary coolant flow through a fluidly interconnected reactor vessel and a steam generating vessel. In one embodiment, the steam generating vessel includes a plurality of vertically stacked heat exchangers operable to convert a secondary coolant from a saturated liquid to superheated steam by utilizing heat gained by the primary coolant from a nuclear fuel core in the reactor vessel. The secondary coolant, may be working fluid associated with a Rankine power cycle turbine-generator set in some embodiments. The steam generating vessel and reactor vessel may each be comprised of vertically elongated shells, which in one embodiment are arranged in lateral adjacent relationship. In one embodiment, the reactor vessel and steam generating vessel are physically discrete self-supporting structures which may be physically located in the same containment vessel.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC
Nuclear reactors including heat exchangers and related methods
A nuclear reactor including a reactor core comprising a plurality of fuel materials and a plurality of heat pipes. The nuclear reactor further includes a heat exchanger coupled to the reactor core defining a flow path in an open volume including at least two heat pipes of the plurality of heat pipes. Methods of operating a nuclear reactor include passing fluid through an open volume in a heat exchanger including at least two heat pipes extending from a reactor core.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
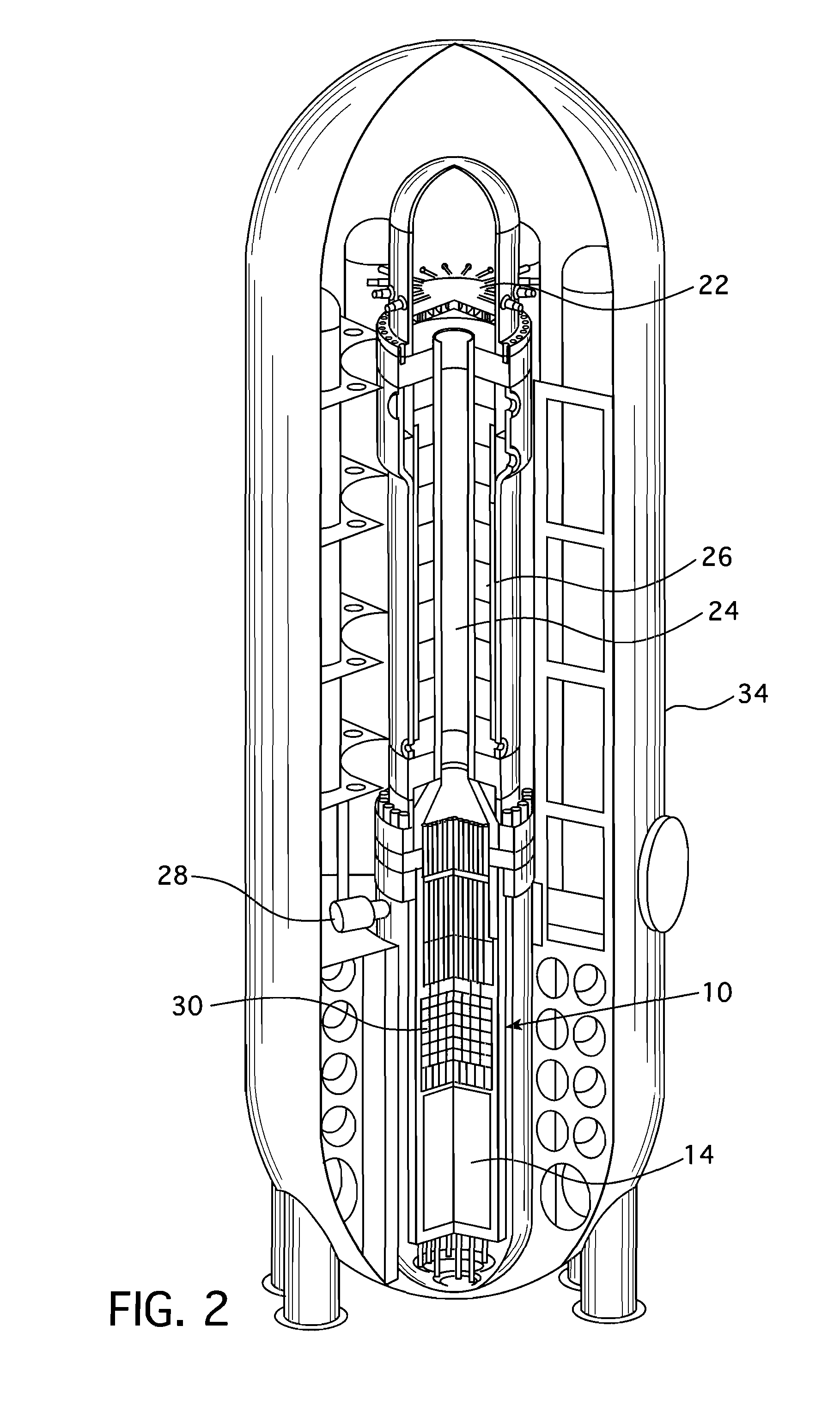
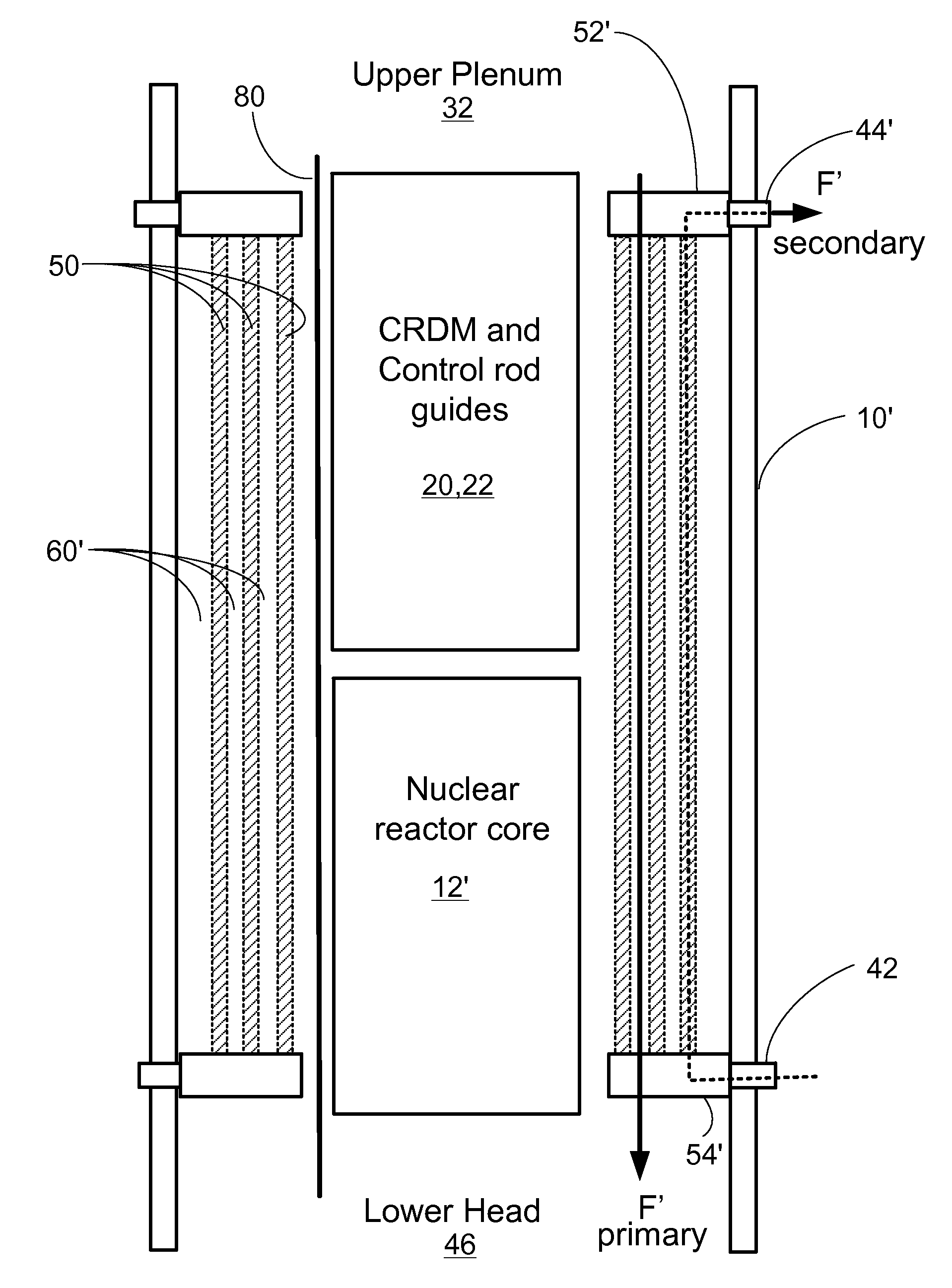
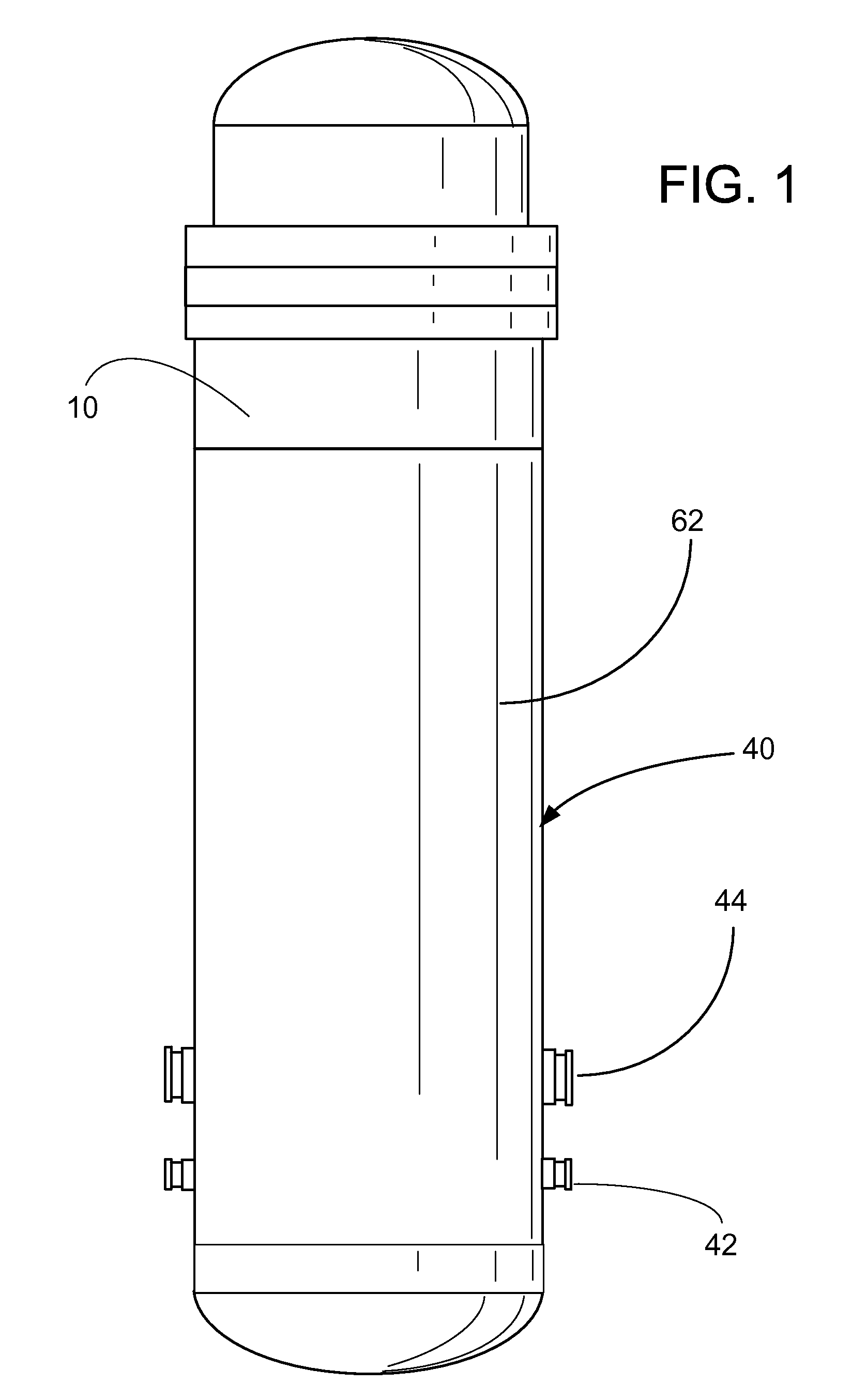
Compact integral pressurized water nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20120263270A1Integral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor corePressurized water reactor
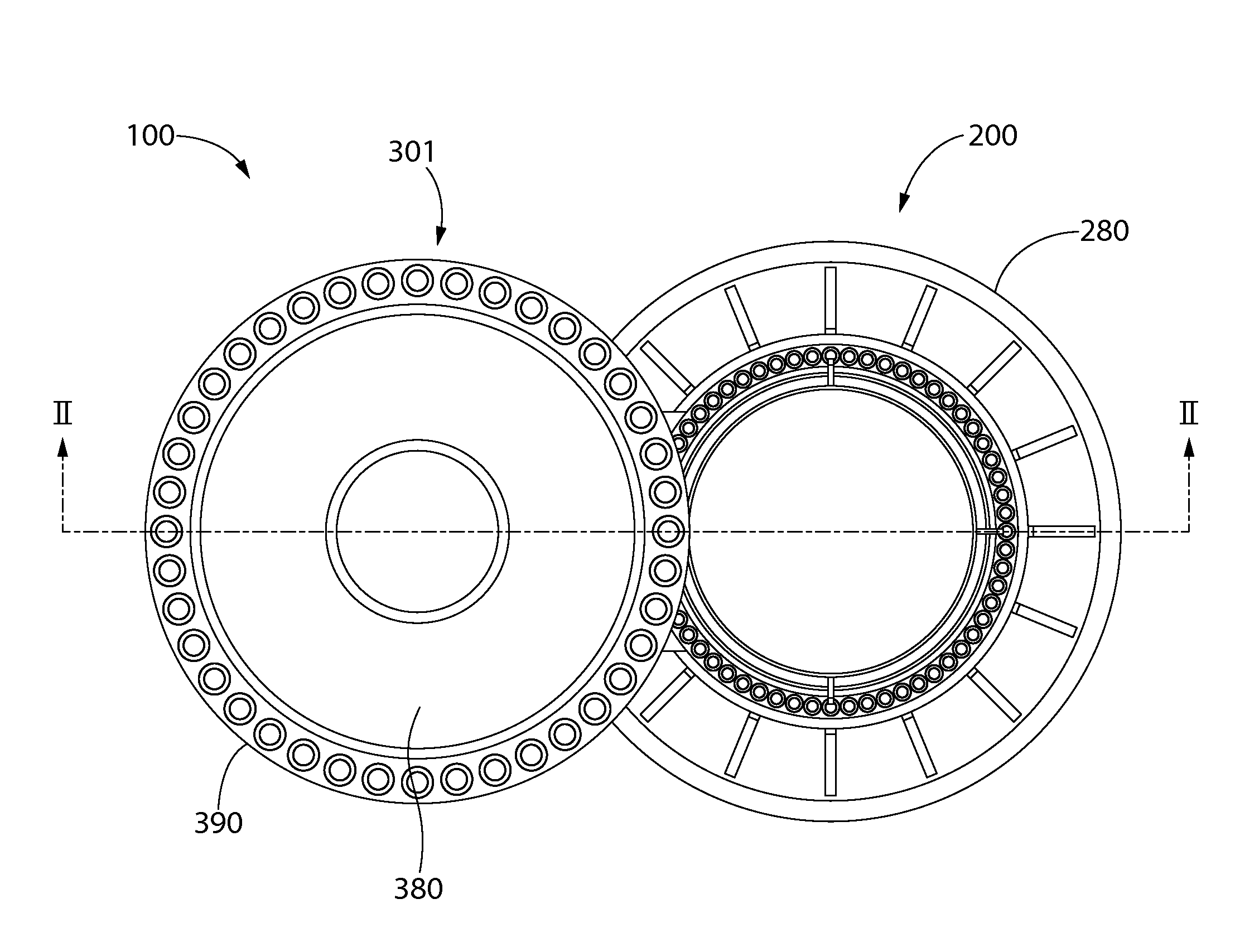
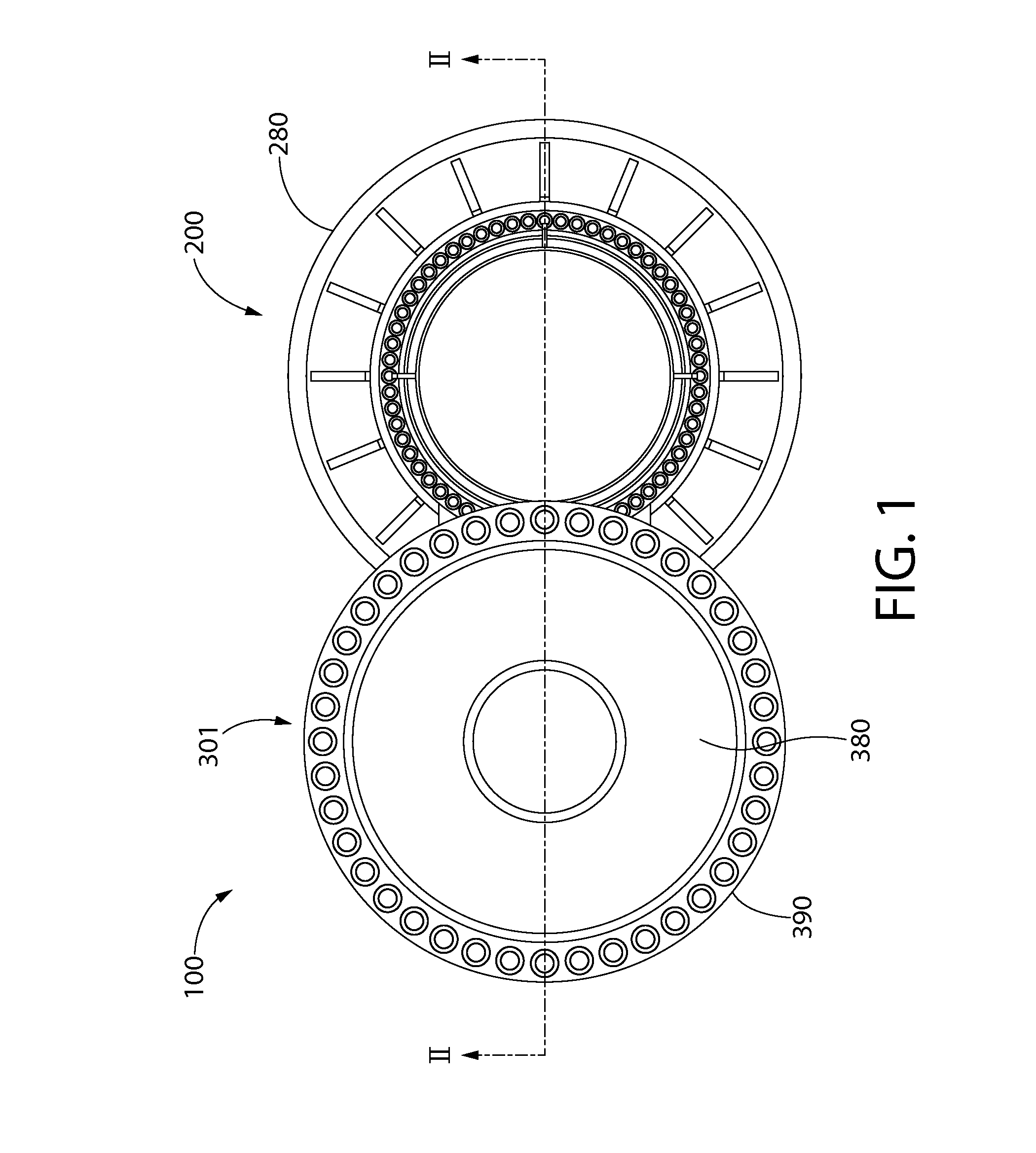
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) includes a cylindrical pressure vessel defining a sealed volume, a nuclear reactor core disposed in a lower portion of the cylindrical pressure vessel, one or more control rod drive mechanisms (CRDMs) disposed in the cylindrical pressure vessel above the nuclear reactor core, and an annular steam generator surrounding the nuclear reactor core and the CRDM. In some such PWR, a cylindrical riser is disposed coaxially inside the pressure vessel and inside the annular steam generator and surrounds the nuclear reactor core and the CRDM, and the steam generator is disposed coaxially inside the cylindrical pressure vessel in an annular volume defined by the cylindrical pressure vessel and the cylindrical riser. In other such PWR, the steam generator is disposed coaxially outside of and secured with the cylindrical pressure vessel.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Vertically-segmented nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20200185114A1Improve power densitySave on fuel costsIntegral reactorsFuel elementsNuclear reactorAtomic physics
This disclosure describes various configurations and components of a molten fuel fast or thermal nuclear reactor in which one or more primary heat exchangers are located above the reactor core of the nuclear reactor.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Nuclear reactor configured to have molten fuel pass through plural heat exchangers before returning to core
ActiveUS10497479B2Improve power densitySave on fuel costsIntegral reactorsFuel elementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
This disclosure describes various configurations and components of a molten fuel fast or thermal nuclear reactor in which one or more primary heat exchangers are located above the reactor core of the nuclear reactor.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
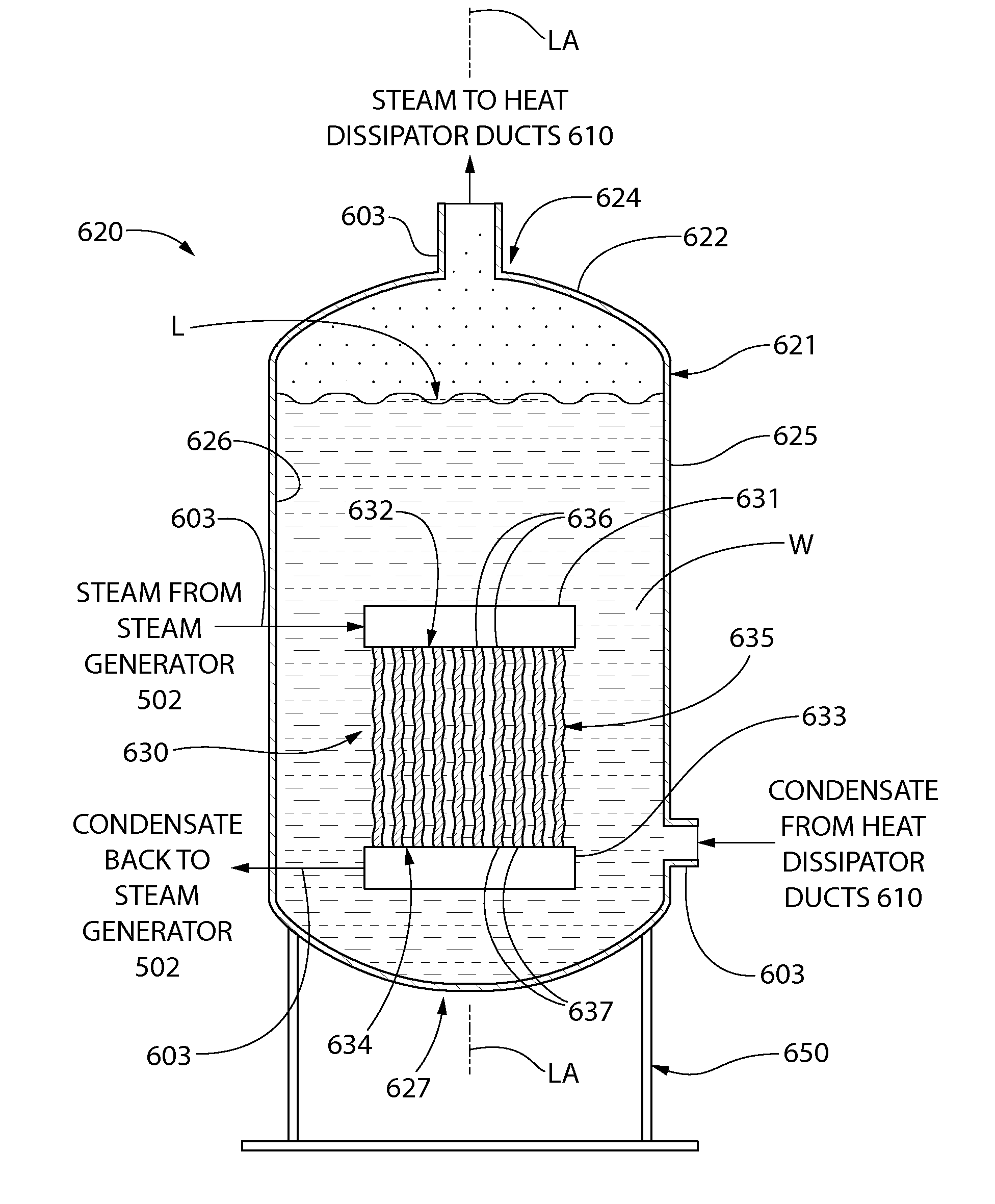
Loss-of-coolant accident reactor cooling system
ActiveUS20140321597A1Avoid warpingNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactorWater storage tank
A nuclear reactor cooling system with passive cooling capabilities operable during a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) without available electric power. The system includes a reactor vessel with nuclear fuel core located in a reactor well. An in-containment water storage tank is fluidly coupled to the reactor well and holds an inventory of cooling water. During a LOCA event, the tank floods the reactor well with water. Eventually, the water heated by decay heat from the reactor vaporizes producing steam. The steam flows to an in-containment heat exchanger and condenses. The condensate is returned to the reactor well in a closed flow loop system in which flow may circulate solely via gravity from changes in phase and density of the water. In one embodiment, the heat exchanger may be an array of heat dissipater ducts mounted on the wall of the inner containment vessel surrounded by a heat sink.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC +1
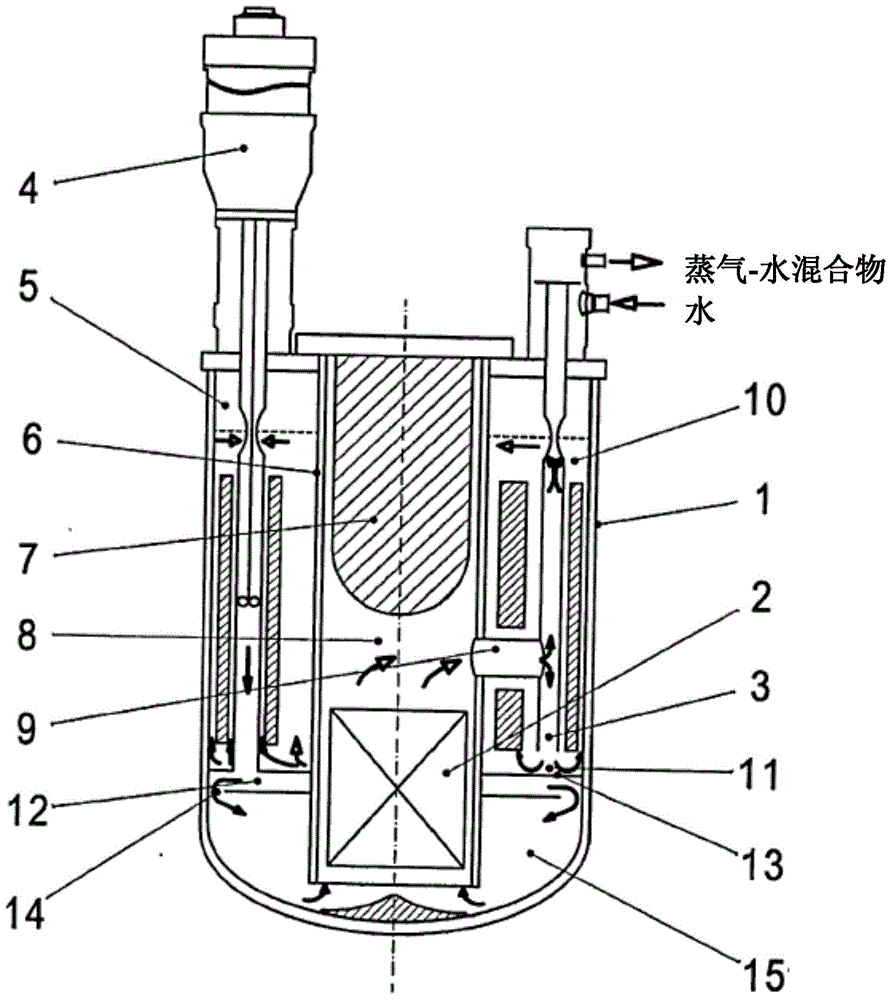
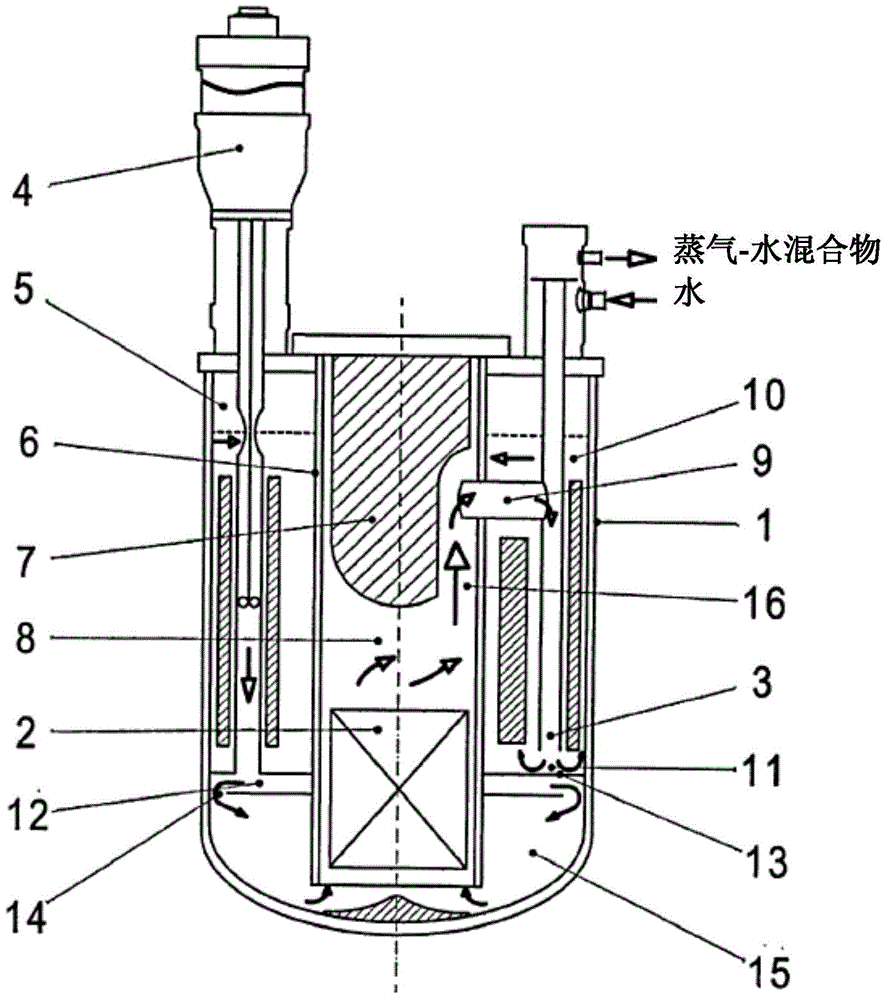
Nuclear reactor with liquid metal coolant
ActiveCN104885160AImprove reliabilityImprove performanceNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The present nuclear reactor with a liquid metal coolant comprises a housing (1) having a separating shell (6) disposed therein. In the annular space (5) between the housing and the separating shell are disposed at least one steam generator (3) and at least one pump (4). Inside the separating shell (6) there is an active region (2), above which a heat collector (8) is disposed which is in communication with the vertically central portion of the steam generator (3) in order to separate a stream of liquid metal coolant into ascending and descending flows, or the heat collector (8) is in communication with the upper portion of the steam generator in order to create a counter-flow heat exchange regime. Below the reactor head is an upper horizontal cold collector (10) with an unfilled level of coolant, and below the steam generator (3) is a lower accumulating collector (11) in communication with the upper cold collector (10). The inlet of the pump (4) is connected to the upper cold collector (10), and the outlet of the pump (4) is connected to a lower annular pressure collector (12), wherein collectors (11) and (12) are separated by a horizontal partition (13), and collector (12) is in communication with a distributing collector (15) of the active region.
Owner:ISHENG ENG JOINT CO LTD
High-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator small-flow cooling system and control method
ActiveCN112435765AImprove economyReal-time monitoring operationNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringIsolation valveProcess engineering
The invention relates to a high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator small-flow cooling system and a control method thereof, the cooling system comprises a main water feeding pump, a main water feeding isolation valve, and an auxiliary boiler room arranged in an auxiliary electric boiler between the main water feeding pump and the main water feeding isolation valve to generate auxiliarysteam, a steam generator heat exchange pipe is cooled through a main water feeding pipeline, a bypass small pipe is arranged on a main steam pipeline, after capacity expansion and temperature reduction, the steam is discharged into a pool for collection; temperature measuring points are arranged at an inlet and an outlet of a heat exchange tube of the steam generator, a high-precision regulating valve and a flow meter are arranged on a small bypass tube, opening and closing of the inlet and outlet temperature measuring points, the flow meter and the regulating valve are controlled in an interlocking mode, system operation is monitored in real time, auxiliary steam flow is regulated, the cooling rate is smaller than 5 DEG C / h while the cooling speed is increased, efficiency and safety factors are considered, and the economy of a power plant is improved.
Owner:HUANENG SHANDONG SHIDAOBAY NUCLEAR POWER CO LTD
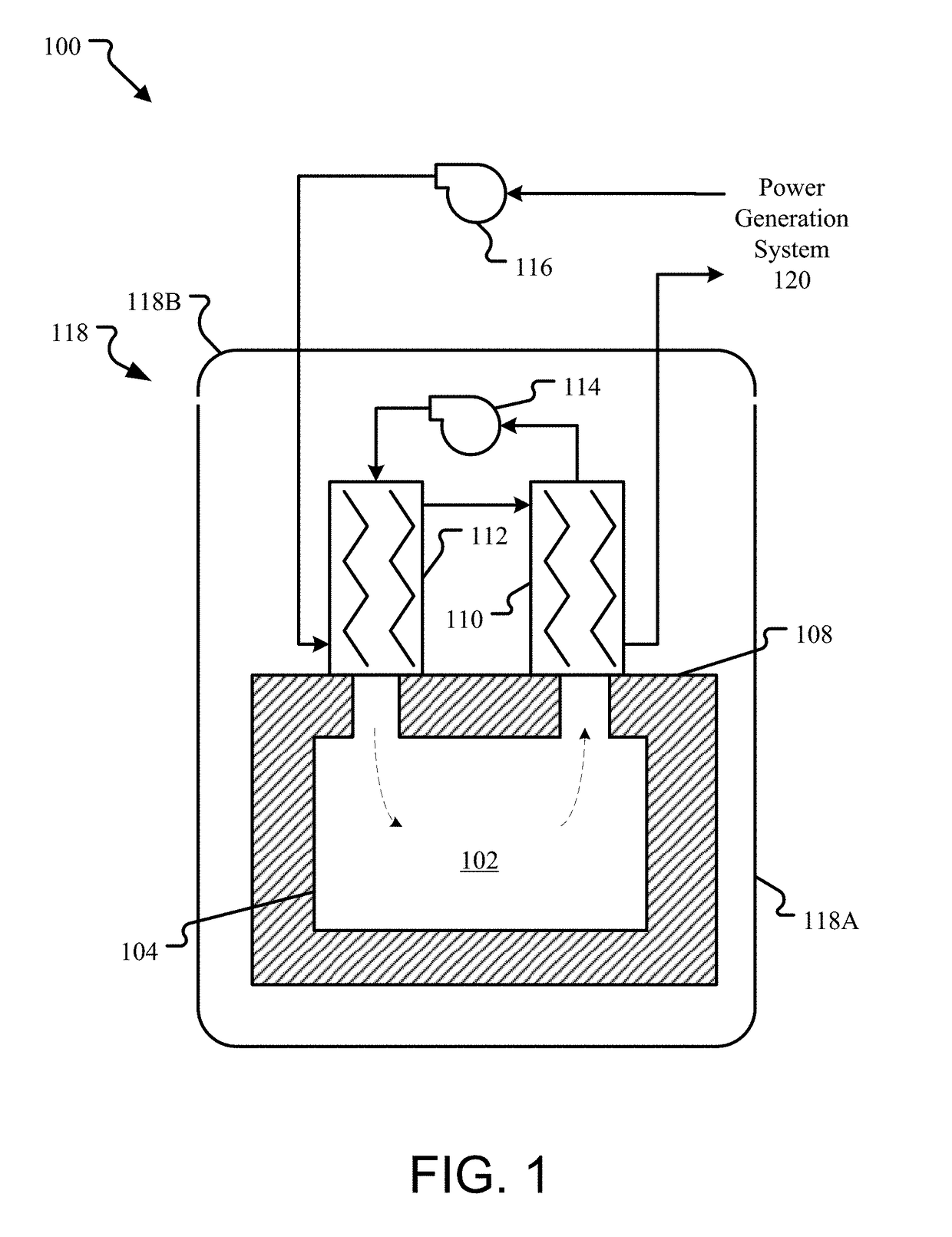
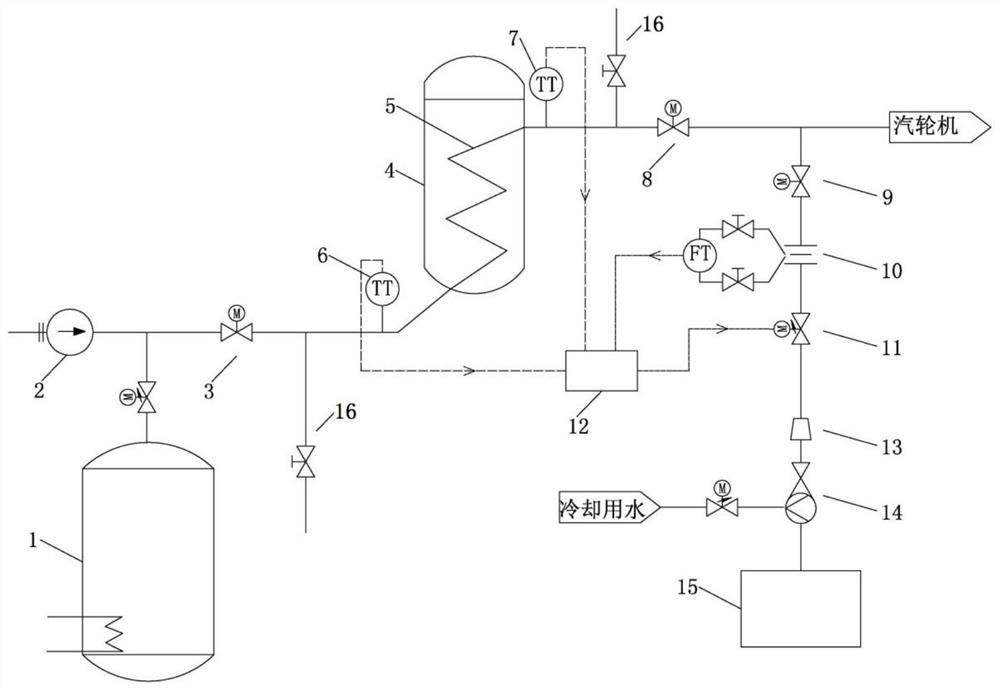
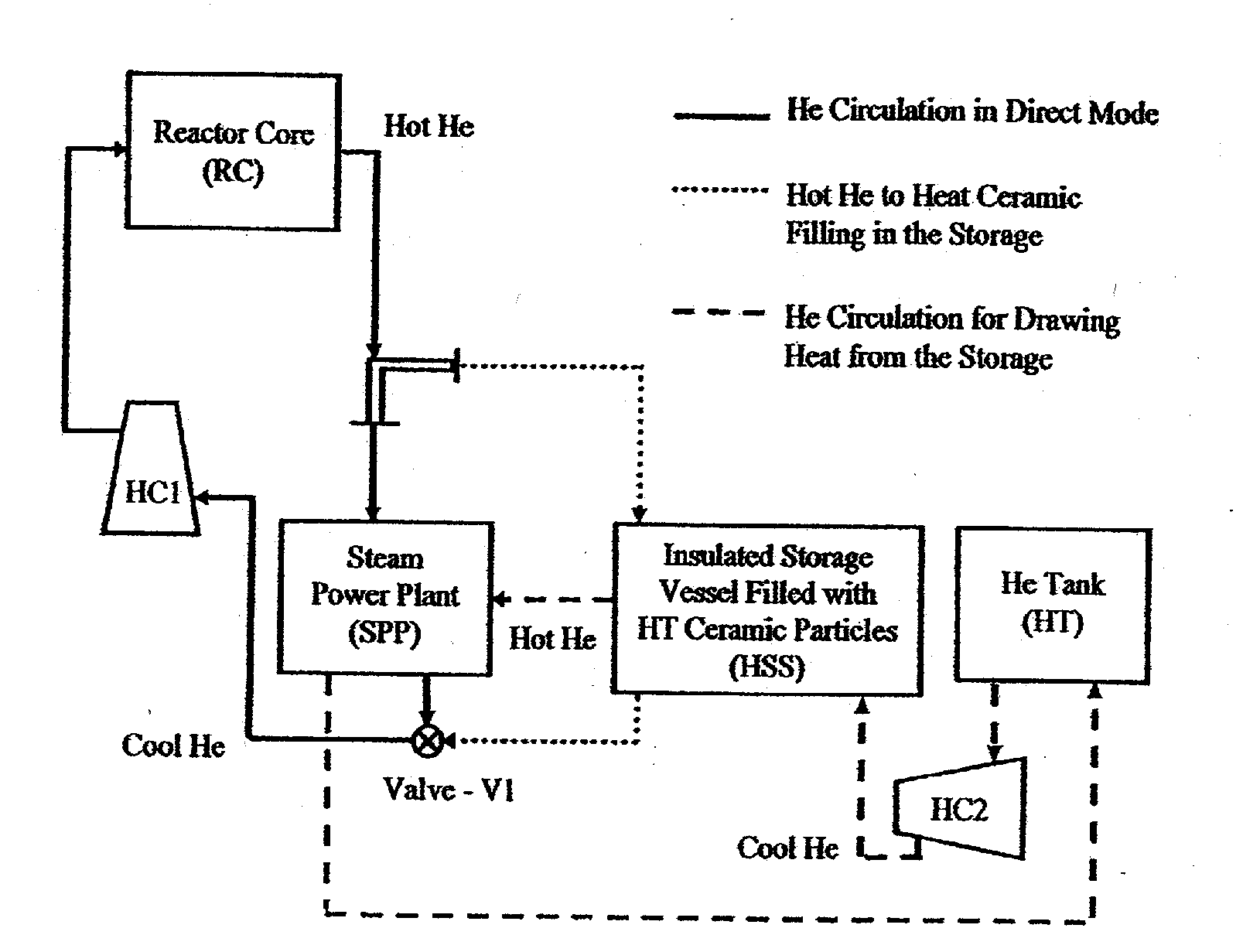
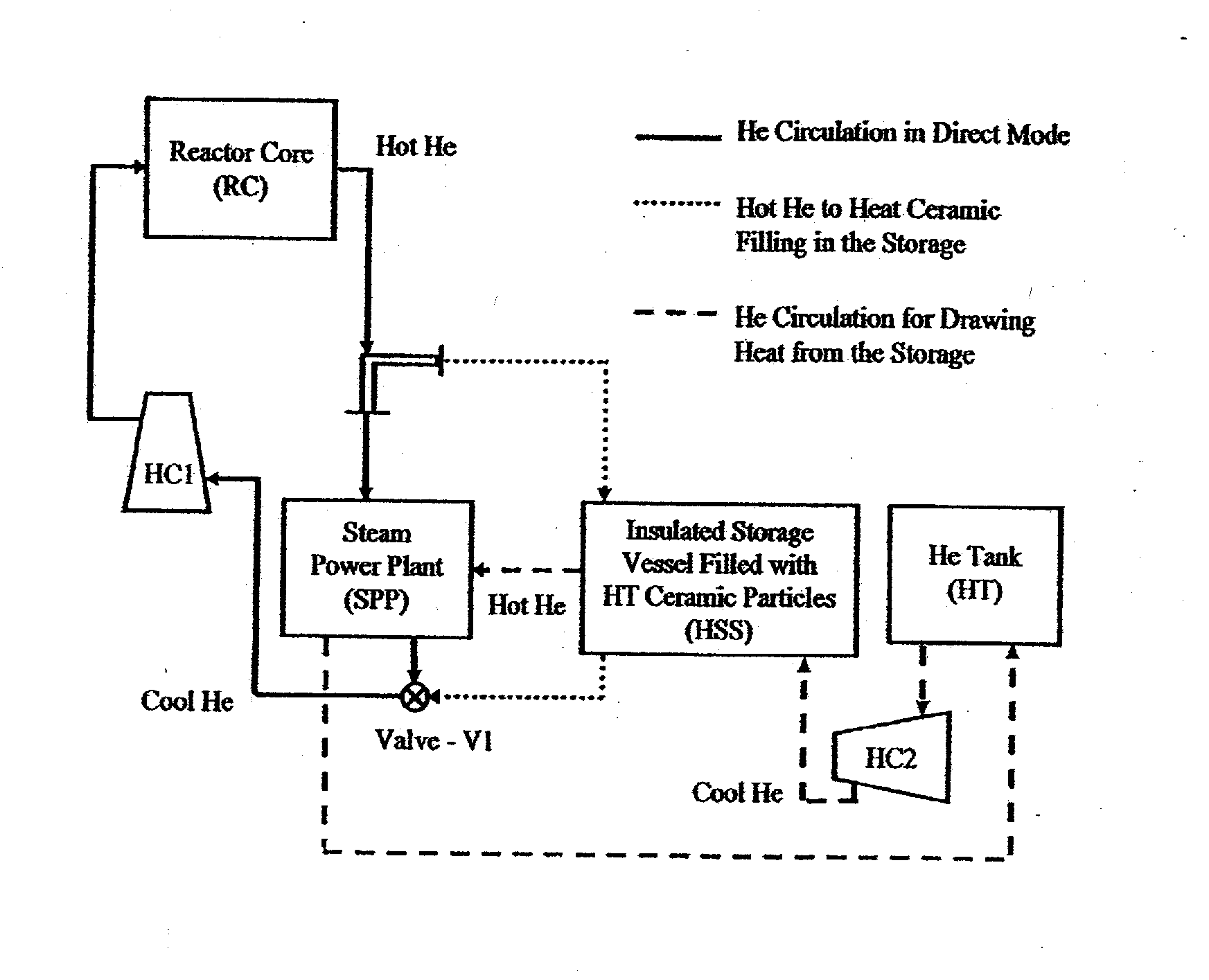
System and method for storing energy in a nuclear power plant
ActiveUS20100202582A1Increase the turndown ratioRapid responseSteam generation heating methodsNuclear energy generationNuclear plantPower station
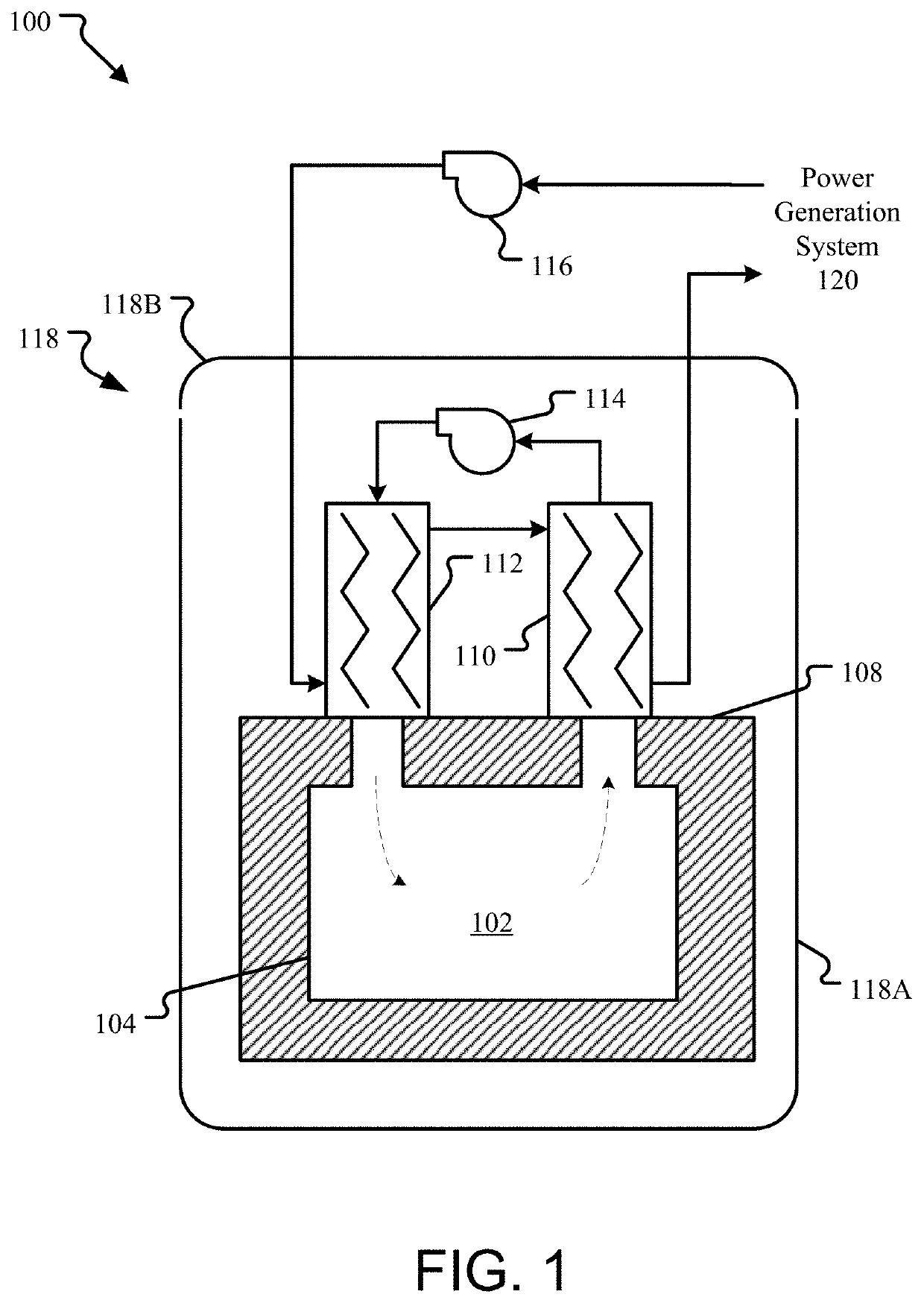
A method of storing heat includes moving a portion of a heated fluid from at least one reactor core to at least one tank having solid media, storing heat from the portion of the heated fluid in the solid media, and transferring the stored heat from the solid media to a fluid that can be used by a power plant to generate electrical energy. A system for storing heat in a nuclear power plant includes at least one tank comprising solid media structured and arranged to store heat and an arrangement structured and arranged to pass a first fluid through the at least one tank, transfer heat from the first fluid to the solid media, store the heat in the solid media, and transfer the heat from the solid media to a second fluid. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Solar-nuclear hybrid power plant
A solar-nuclear hybrid plant includes a nuclear energy loop, a solar energy loop, and an electrical generation loop. The three loops are closed loops. The nuclear energy loop transfers energy to the electrical generation loop through a steam generator. The solar energy loop transfers energy to either the nuclear energy loop and / or the electrical generation loop through one or more heat exchangers in the appropriate loop. This cogeneration plant has higher efficiency compared to a nuclear power plant alone.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
Sealed stopper for an opening in a tubing for joining a chamber and a piping, particularly in the steam generator of a nuclear pressurised water reactor
InactiveUS20120279965A1Shorten service timeEasy to implementNuclear energy generationPipe elementsEngineeringPressurised water reactor
A sealed stopper for an opening in a tubing for joining a chamber and a piping including a fastening ring is provided. The stopper includes a rigid bearing plate and a sealing member carried by the bearing plate, and includes a seal having a planar and flexible central portion with a reduced thickness extending below the bearing plate and a peripheral portion radially deformable by a central expander of the peripheral portion against the inner surface of the fastening ring.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
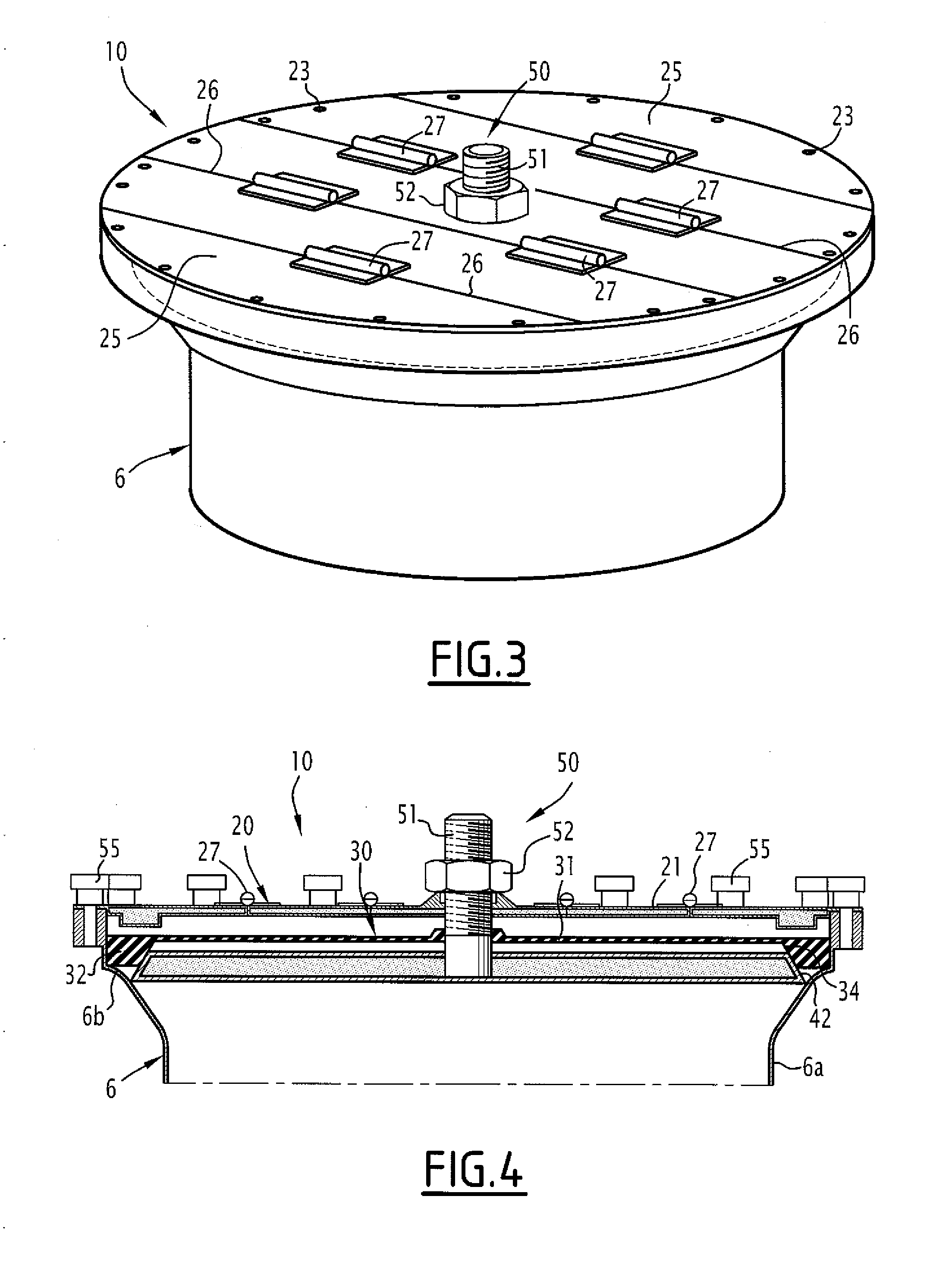
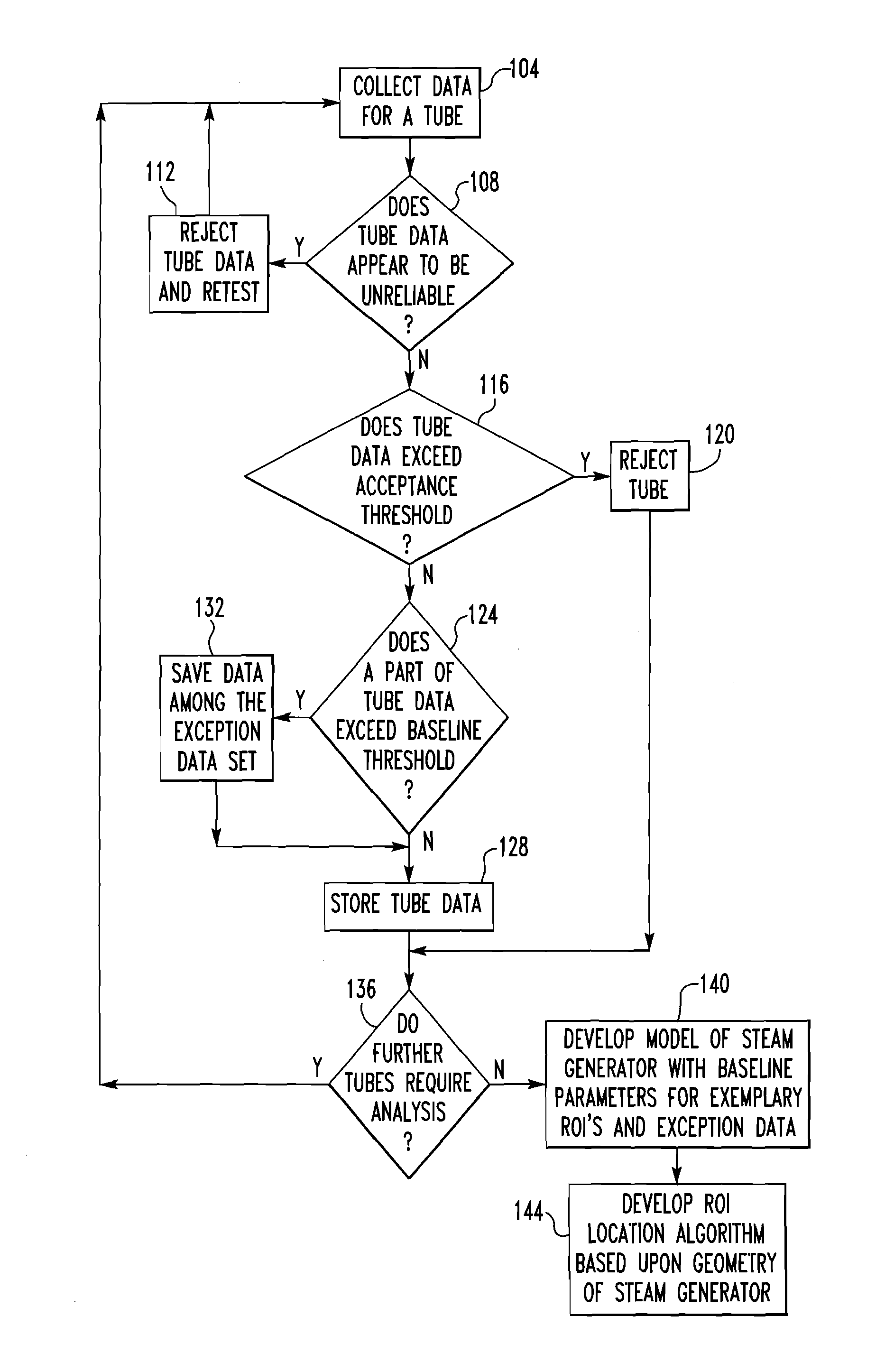
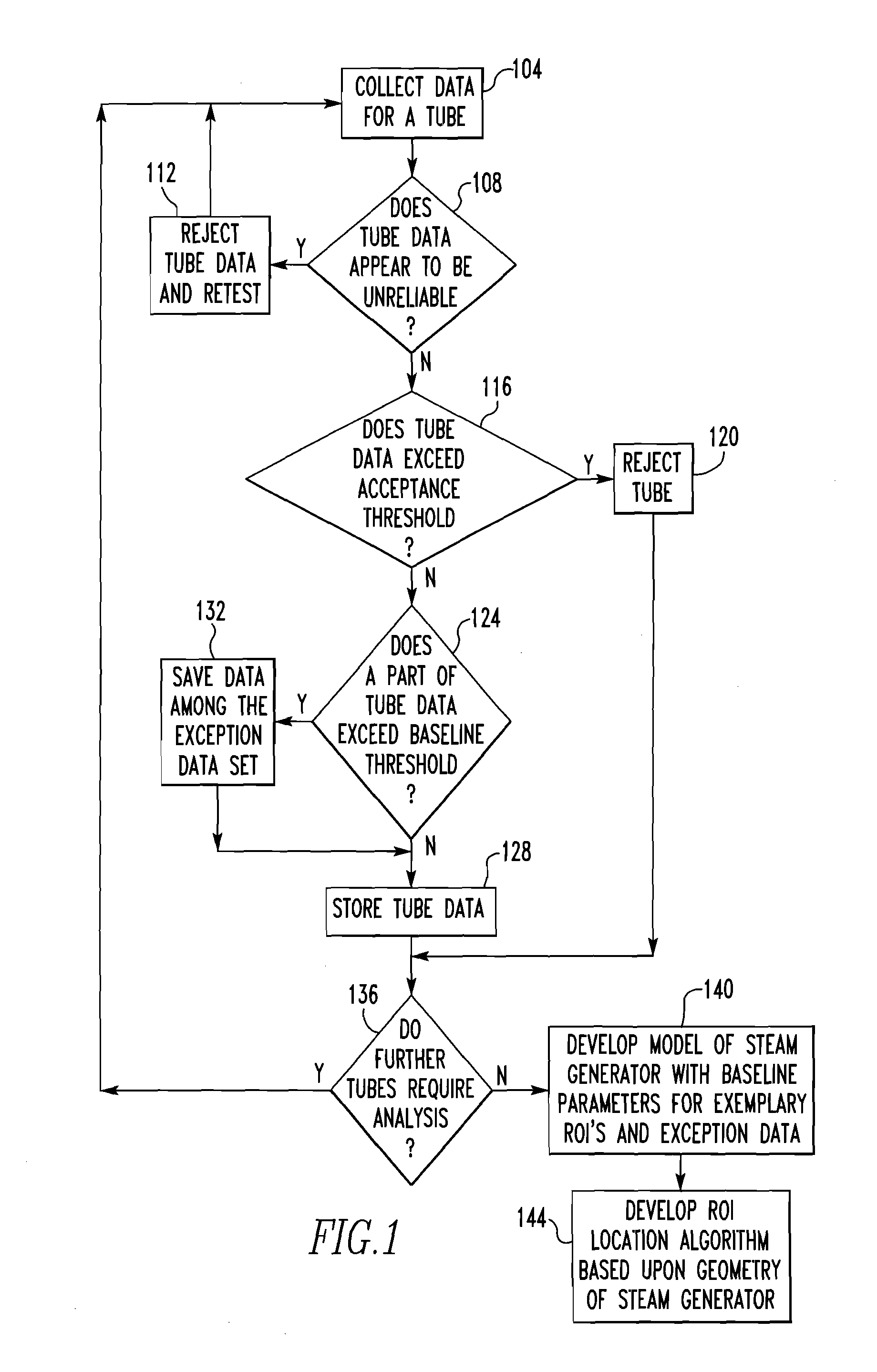
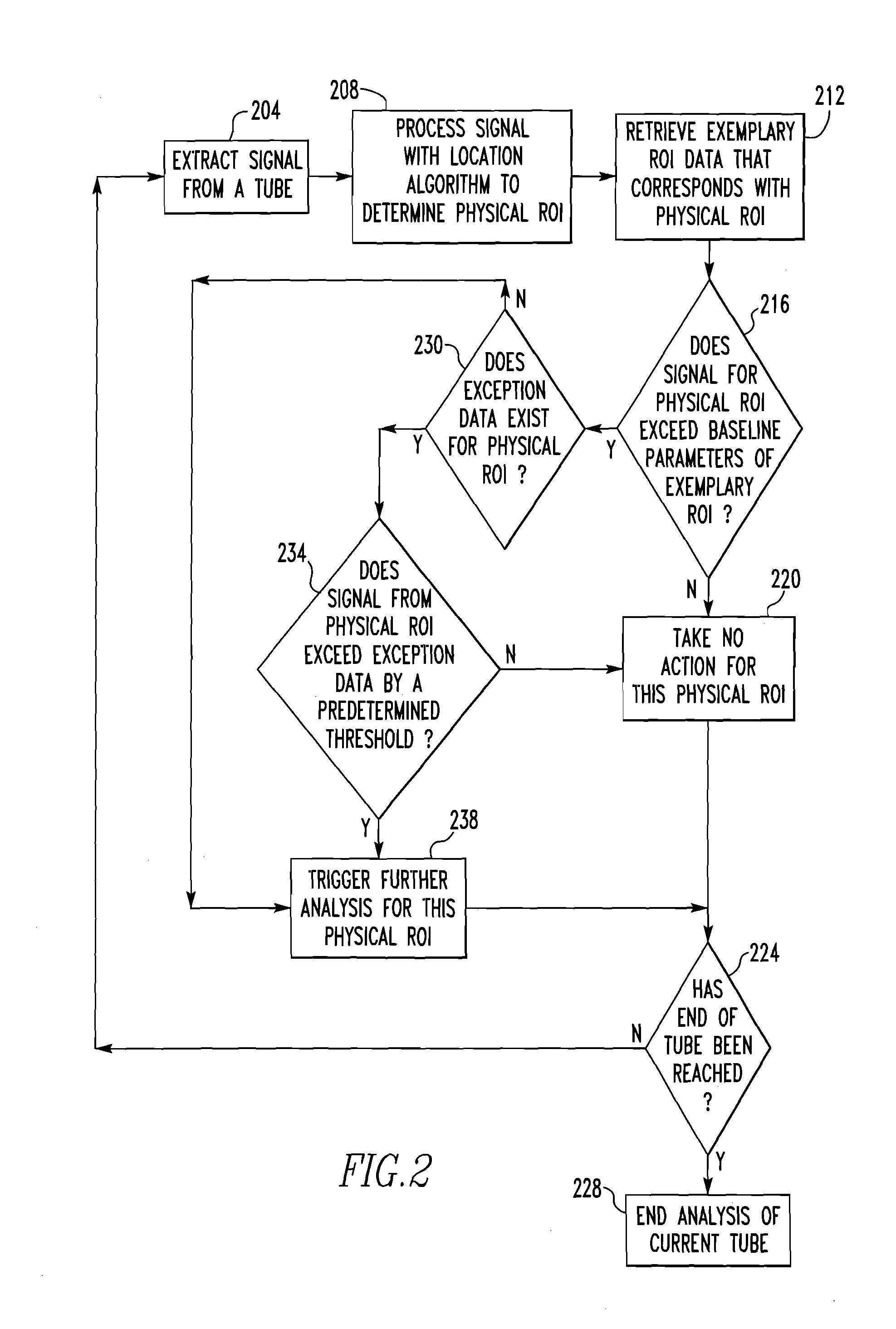
Method of Processing Steam Generator Tubes of Nuclear Power Plant
ActiveUS20110172964A1Reduce effortImprove accuracySteam generation heating methodsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorImproved method
An improved method of inspecting the tubes of a steam generator of a nuclear reactor involves collecting historic data regarding the tube sheet transition regions of each tube for use during a subsequent analysis to create a new simpler signal from which historic artifacts have been removed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Pressurized-water-cooled nuclear reactor with compact steam generators
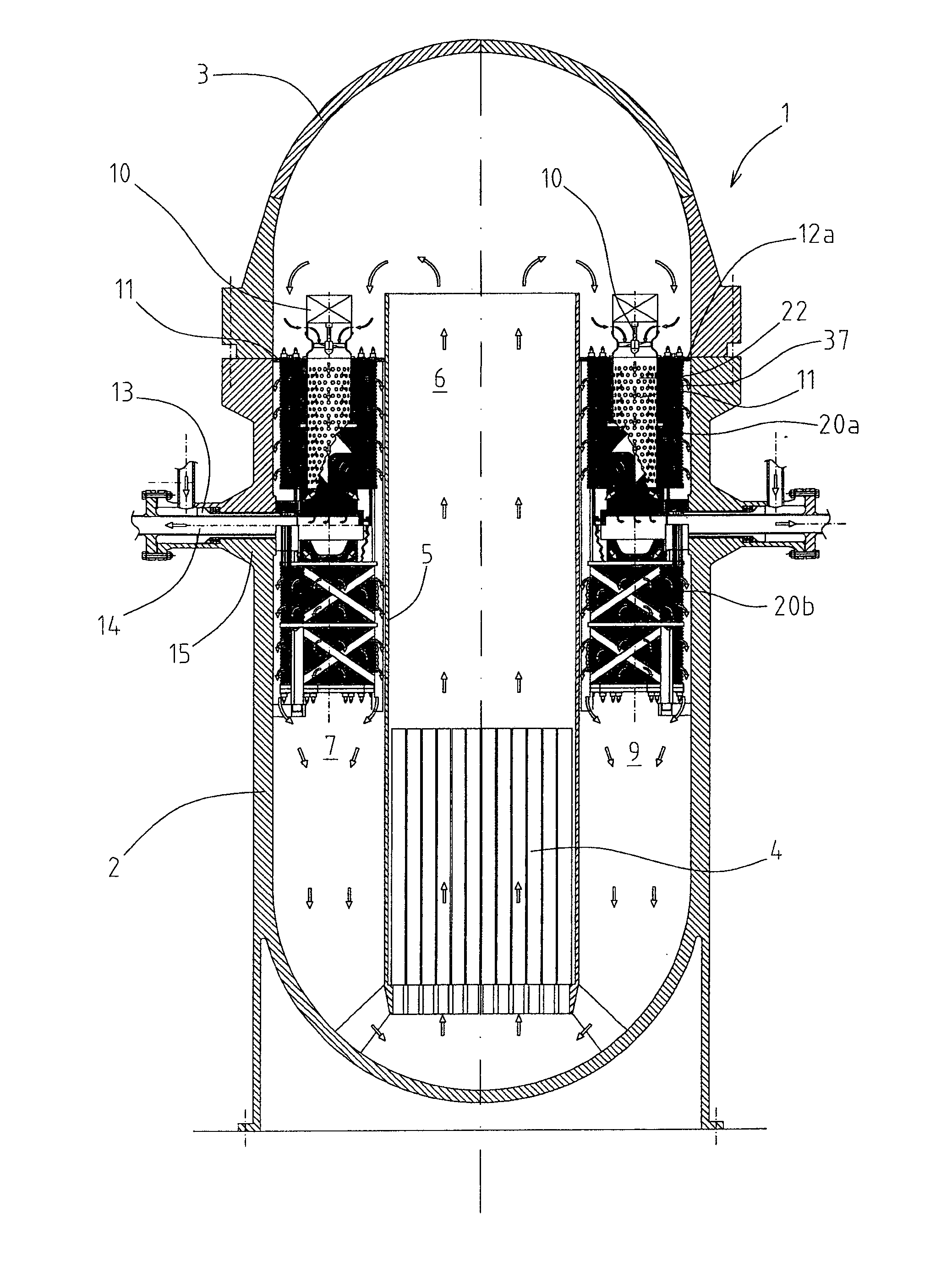
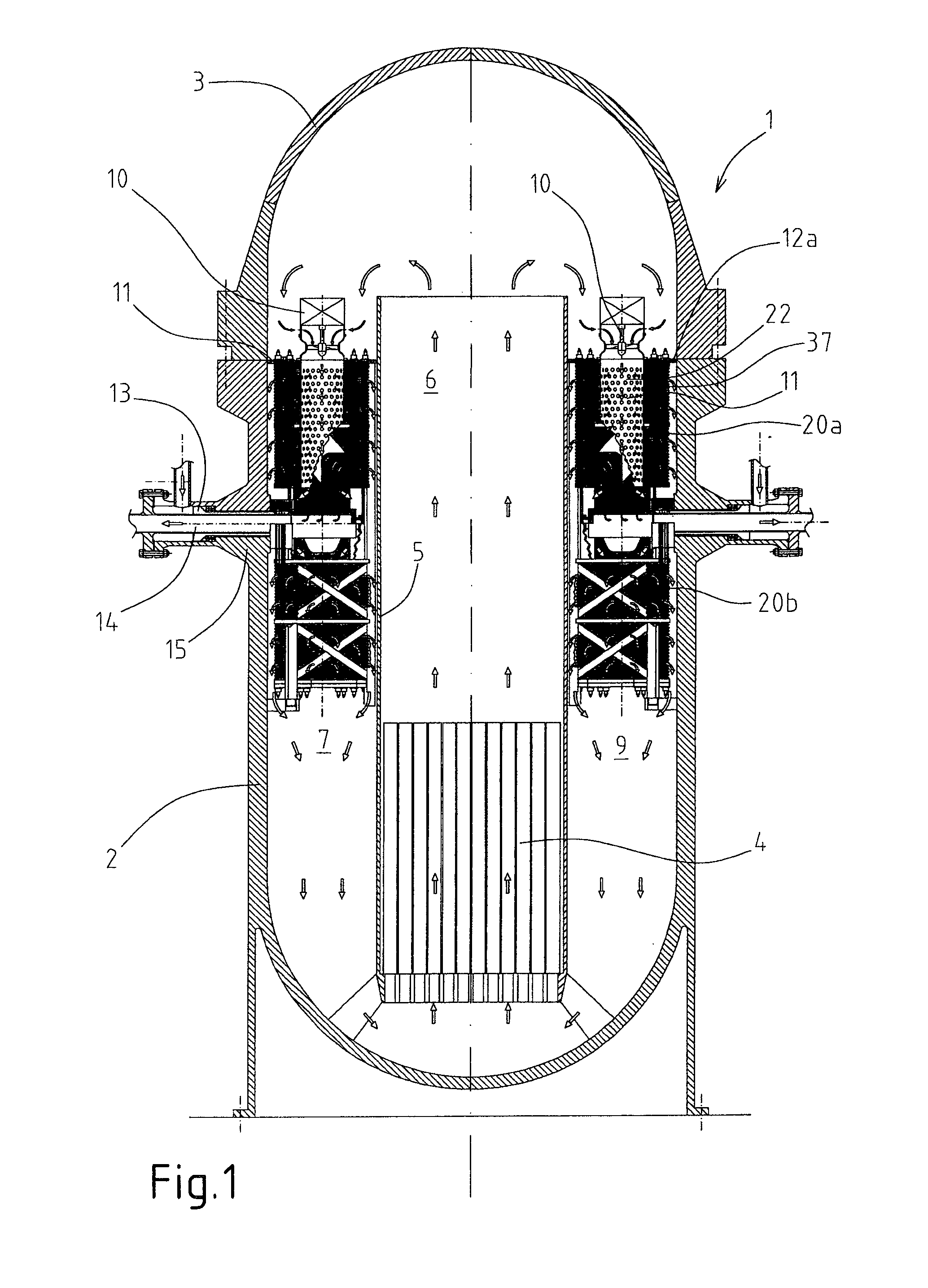
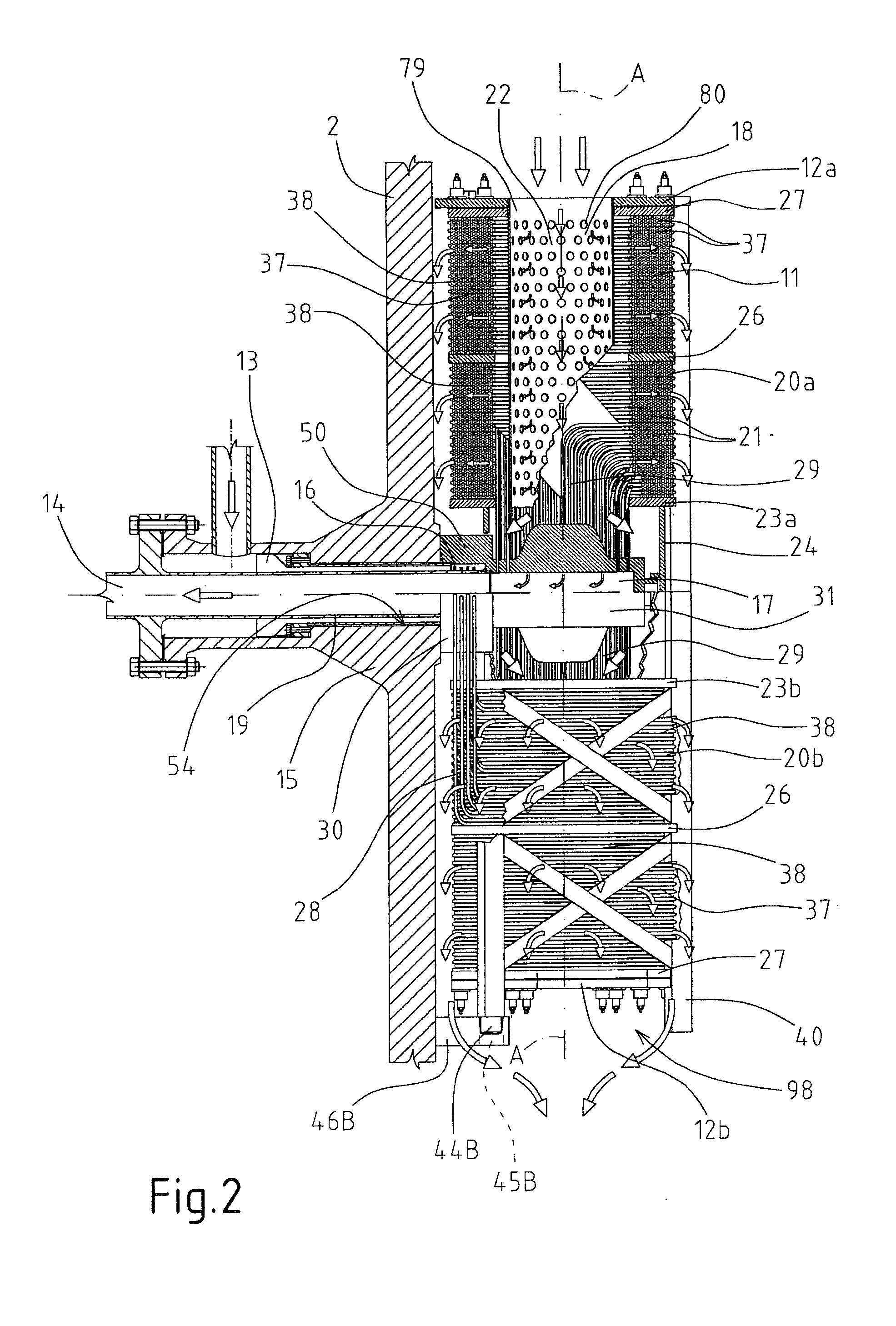
A nuclear reactor cooled with pressurized water, having a pressurized tank installed in which are compact steam generators; each steam generator comprises a plurality of heat-exchange tubes having respective spiral portions set in levels on top of one another to form at least one annular tube bundle delimiting a substantially cylindrical internal central zone, pre-arranged for supply from above with primary water, which then traverses the tube bundle radially.
Owner:NEWCLEO LTD
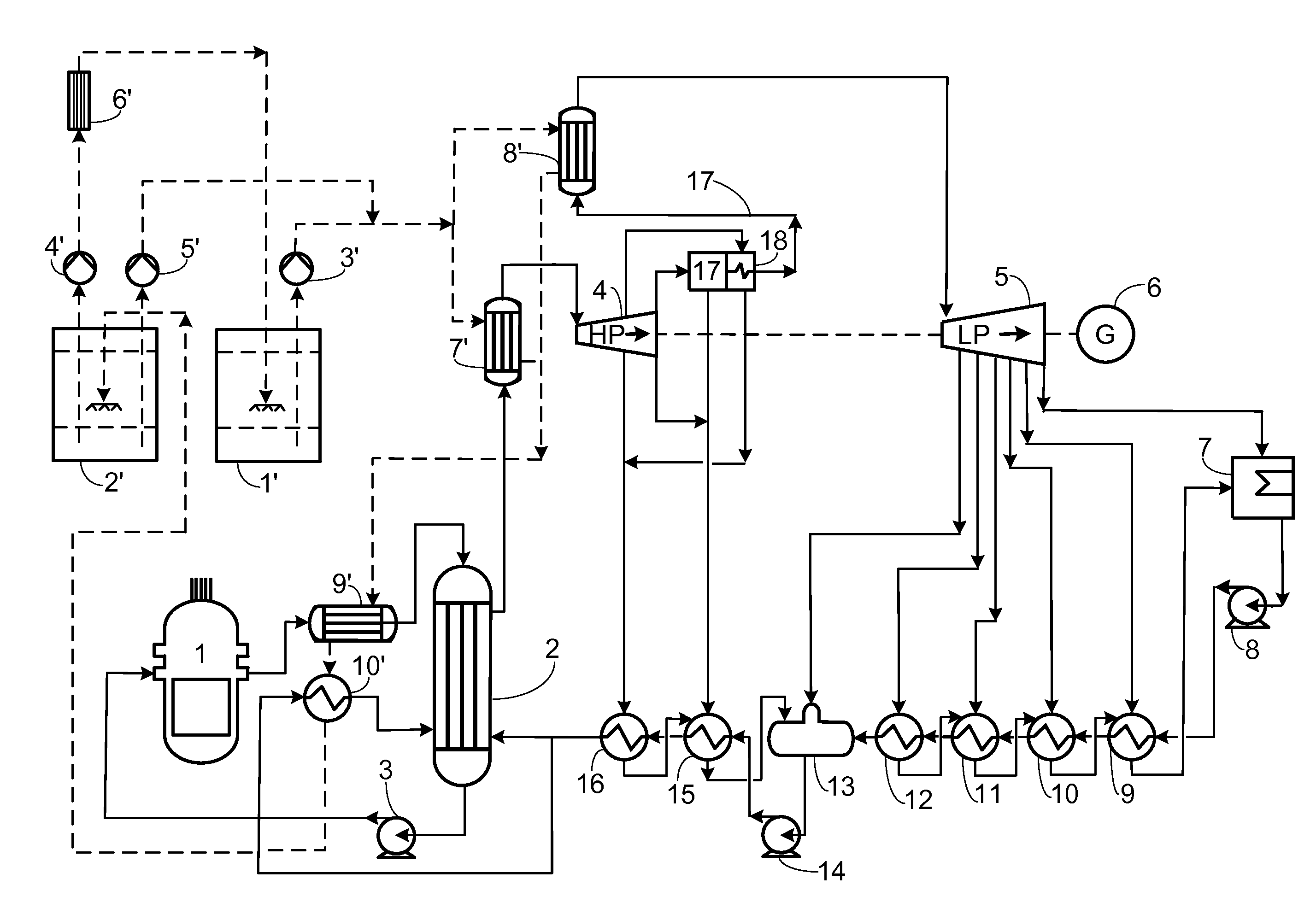
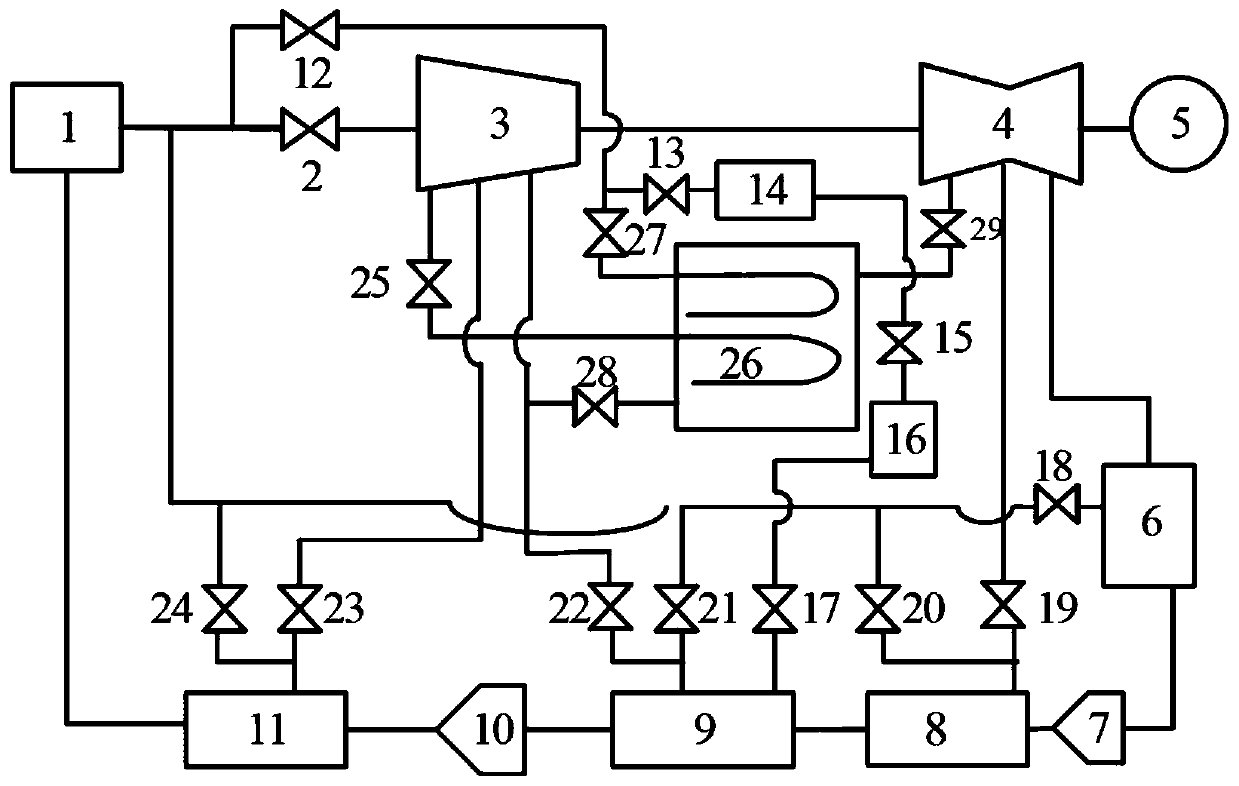
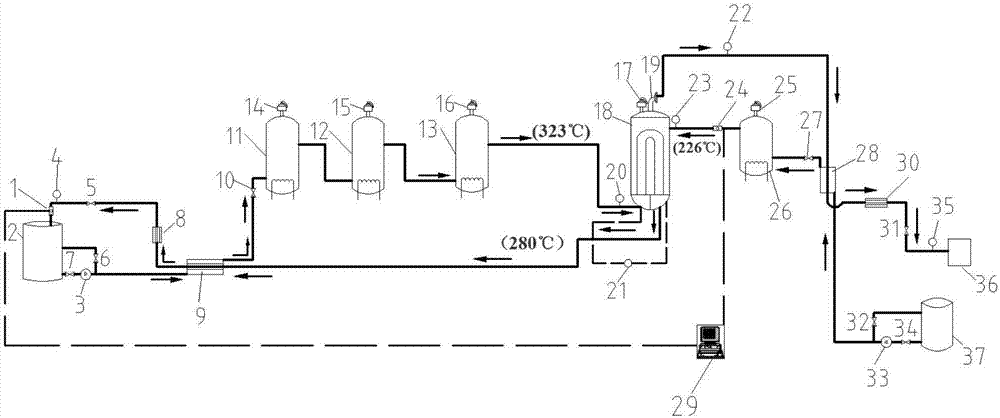
Pressurized water reactor nuclear power unit secondary circuit thermodynamic system self-adaptive steam supply system and method
PendingCN110259532AReduce startup timeSafe and stable operationNuclear energy generationSteam generator primary sideStart stopPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a pressurized water reactor nuclear power unit secondary circuit thermodynamic system self-adaptive steam supply system and method. By means of the system and the method, a main steam bypass can be self-adaptively put into use or cut out to supply a heating steam source to a low-pressure heater, a deaerator and a high-pressure heater according to secondary circuit thermodynamic parameters in the unit start-stop and normal running process, the defect of long-time hot stand-by duty of an auxiliary boiler is avoided, energy cascade recycling is achieved, meanwhile the reliability, stability and safety are high, and the power consumption is low.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD
Miniature steam generator thermal hydraulic analysis testing system
ActiveCN107293340AReduce high pressureSimple structureNuclear energy generationSteam generator primary sideNuclear reactorNuclear power
The invention discloses a miniature steam generator thermal hydraulic analysis testing system, and belongs to the technical field of nuclear power station steam generator equipment. The miniature steam generator thermal hydraulic analysis testing system comprises a first loop unit, a second loop unit, a steam generator and a data acquisition unit. The first loop unit and the second loop unit are connected with the steam generator through pipelines, and fluid in the first loop unit can be used for heating fluid in the second loop unit. The data acquisition unit is used for acquiring the temperature, pressure and flow of fluid of the first loop unit and the second loop unit and flowing into steam generator, the first loop unit heats cooling water by means of a heat regenerator and a heating water tank which replace a nuclear reactor being of a complex structure. With respect to the first loop unit and the second loop unit, heat regenerators are employed to lead in a regenerative cycle, energy is saved, and the energy utilization rate of the system is increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Passive reactor cooling system
ActiveUS20140321596A1Avoid warpingNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactorCoolant flow
A nuclear reactor cooling system with passive cooling capabilities operable during a reactor shutdown event without available electric power. In one embodiment, the system includes a reactor vessel with nuclear fuel core and a steam generator fluidly coupled thereto. Primary coolant circulates in a flow loop between the reactor vessel and steam generator to heat secondary coolant in the steam generator producing steam. The steam flows to a heat exchanger containing an inventory of cooling water in which a submerged tube bundle is immersed. The steam is condensed in the heat exchanger and returned to the steam generator forming a closed flow loop in which the secondary coolant flow is driven by natural gravity via changes in density from the heating and cooling cycles. In other embodiments, the cooling system is configured to extract and cool the primary coolant directly using the submerged tube bundle heat exchanger.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC
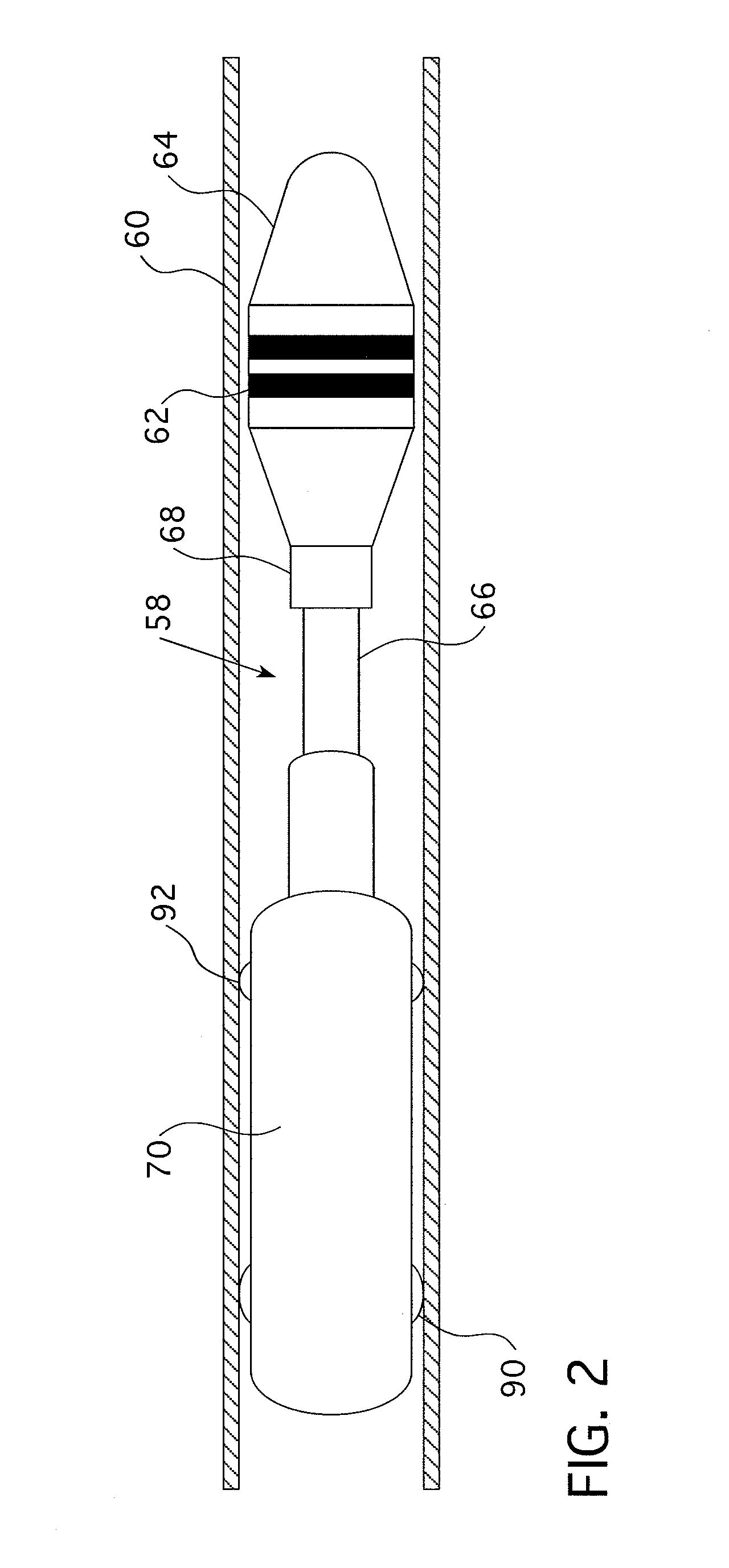
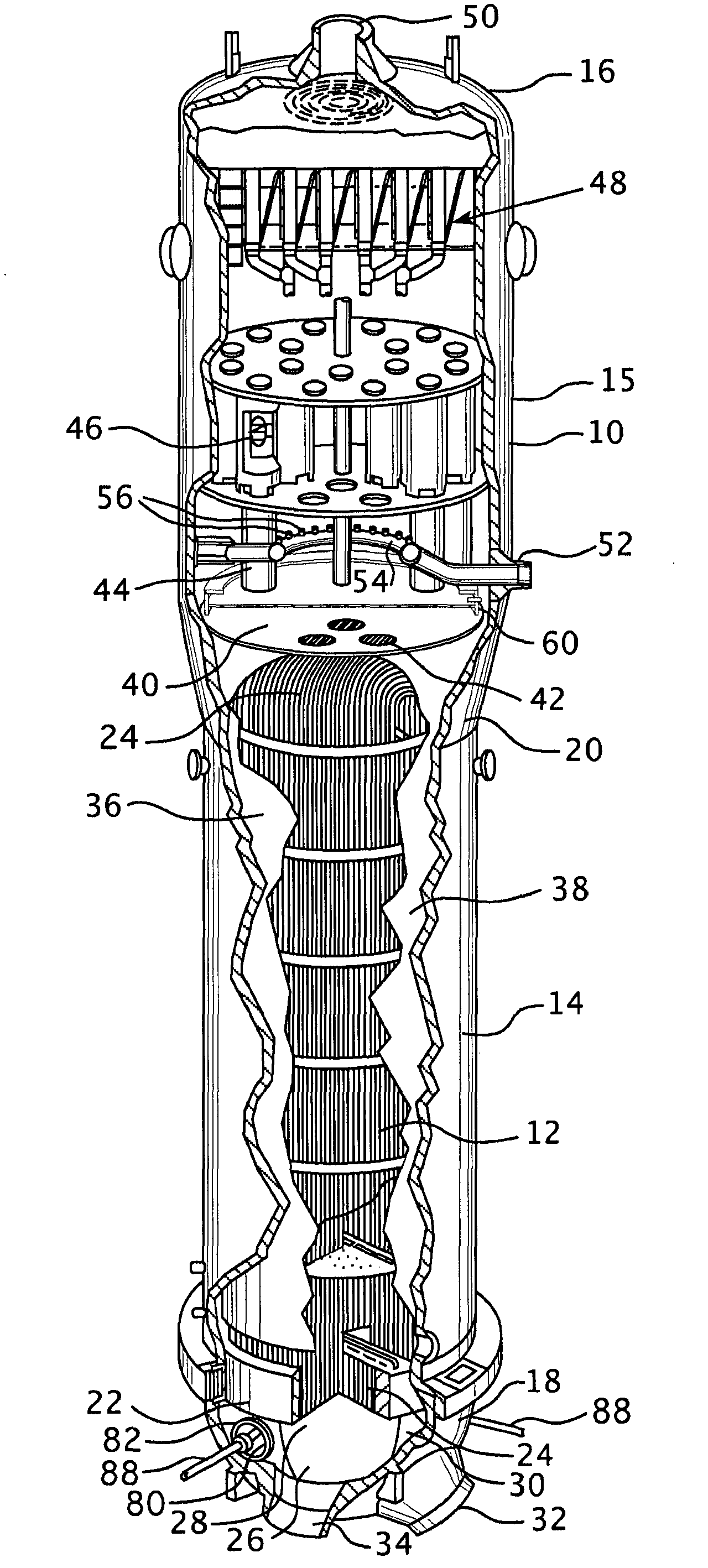
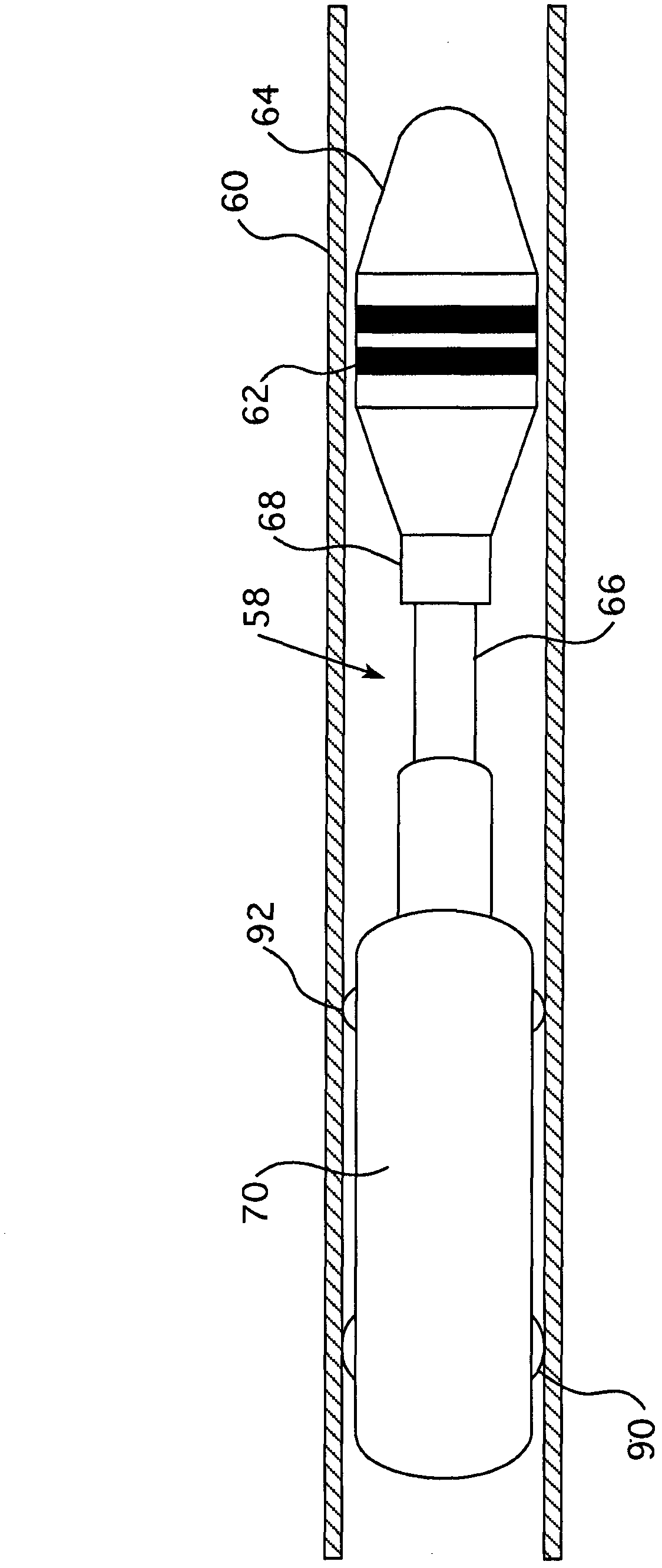
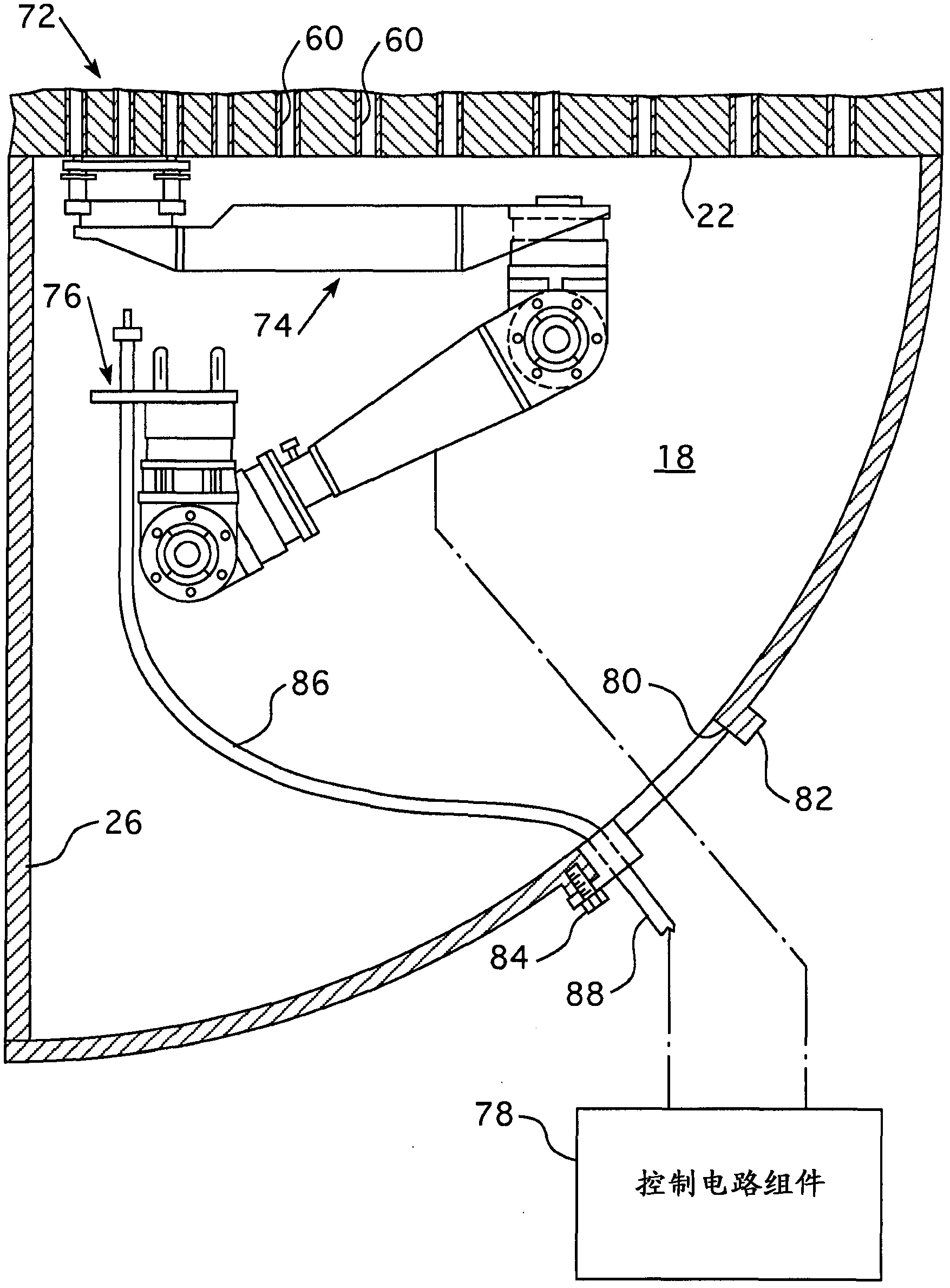
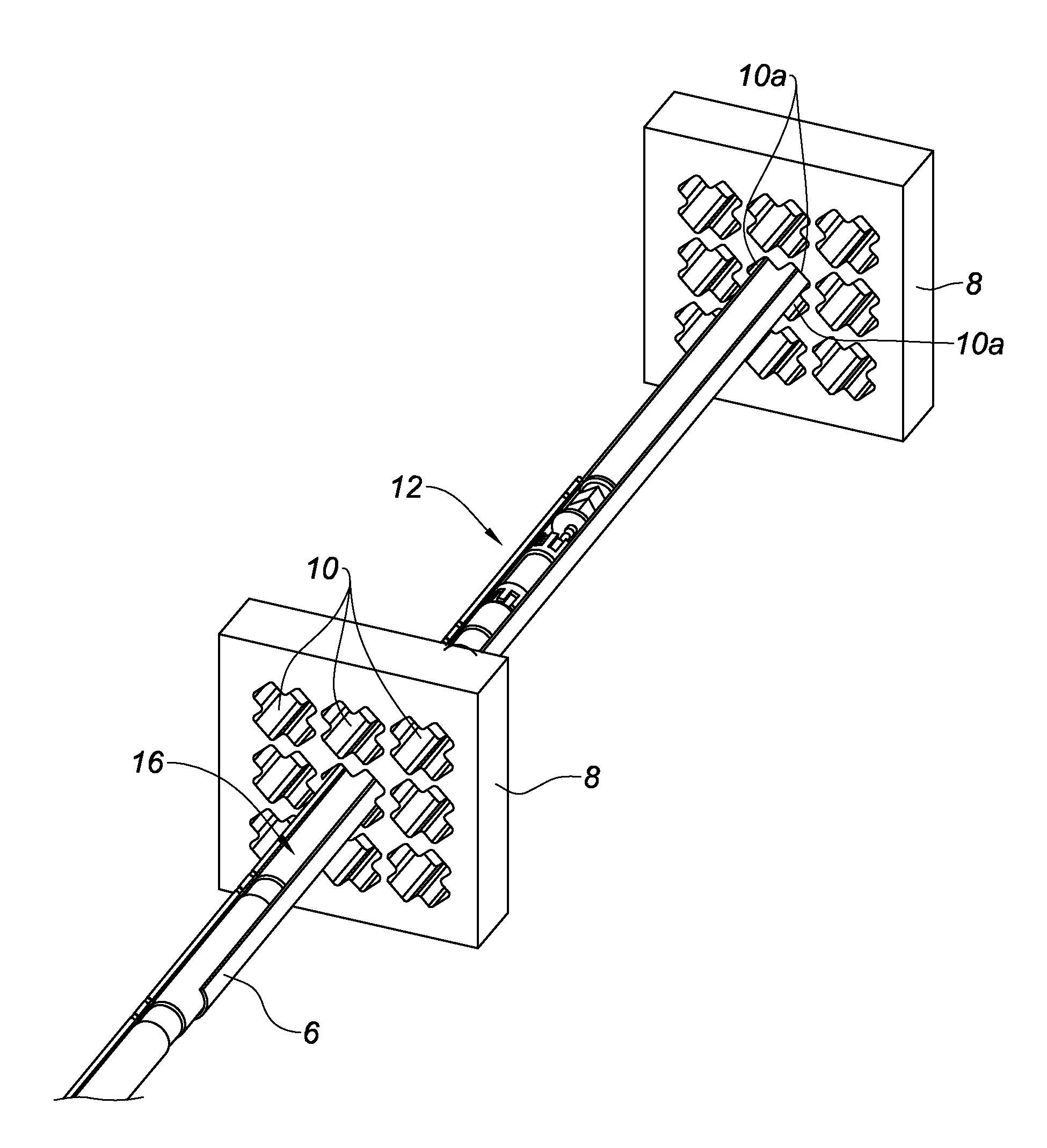
Device for inspecting a steam generator
An inspection device for inspecting a steam generator having a first long and flexible video probe intended to be inserted inside the housing of the steam generator and configured to be moveable through a fluid passage orifice defined by a spacer plate and a flow tube, all arranged inside the housing. The first video probe includes at least one ferromagnetic element. The inspection device also includes a second long and flexible probe to be inserted into a flow tube, the second probe including at least one permanent magnet arranged to cooperate with the at least one ferromagnetic element of the first probe so that the first probe can be driven along the exterior surface of a flow tube by the second probe when the second probe is inserted into the flow tube and moved therein, and when the first probe is inserted into the housing of the steam generator and positioned near the exterior surface of the flow tube in which the second probe is inserted.
Owner:SRA SAVAC
Low row steam generator inspection probe
InactiveUS20120006133A1Minimize resistance against movementNuclear energy generationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiomedical engineeringHead parts
An inspection assembly for insertion inspection of an elongate tubular member. The inspection assembly includes a probe head with a sensor. The assembly also includes a flexible shaft connected to the probe head and transmitting a motive force to the probe head to move the probe head within the elongate tubular member. The probe head includes at least one characteristic to minimize resistance against movement of the probe head along a torturous path within the tubular member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
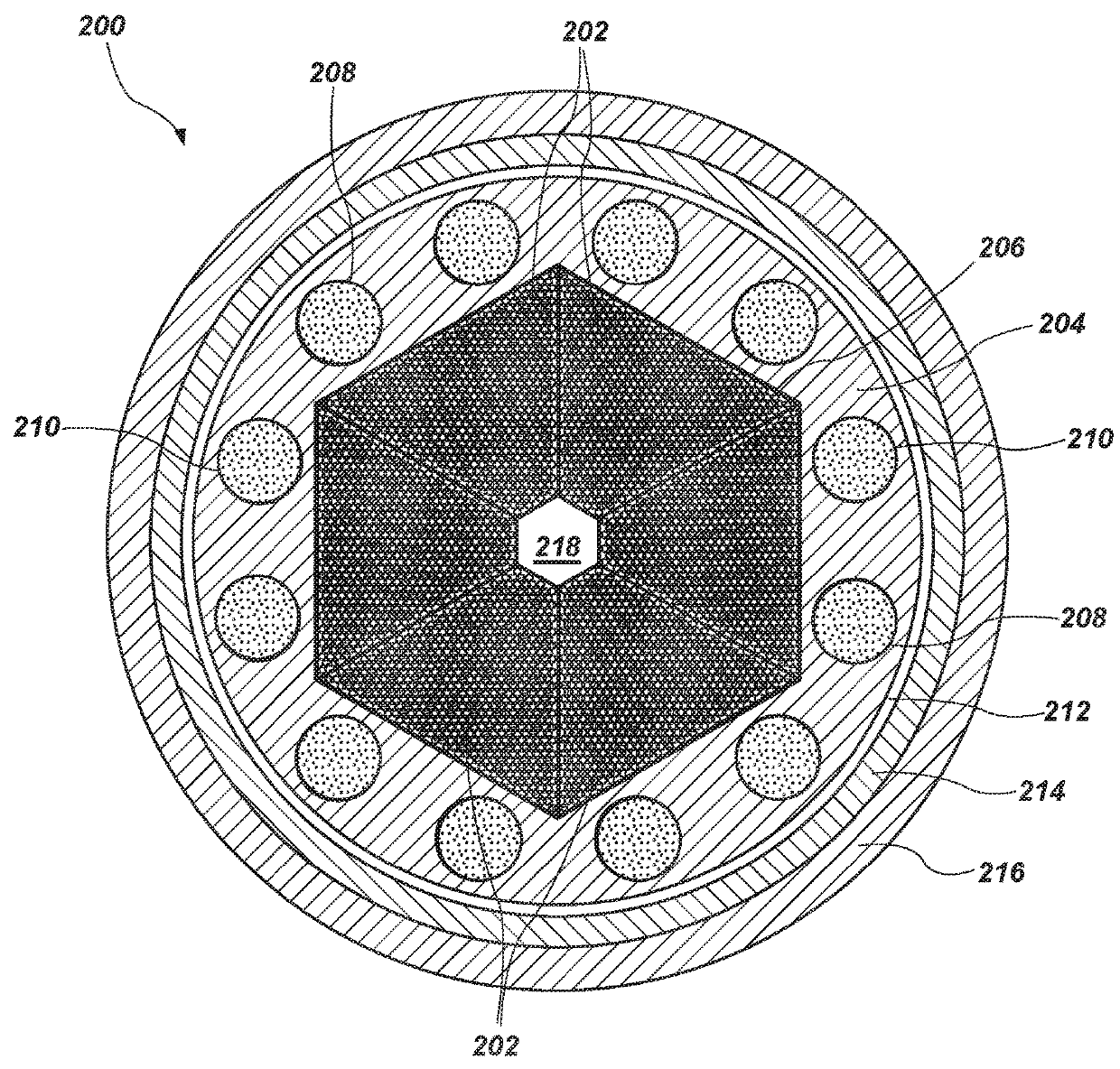
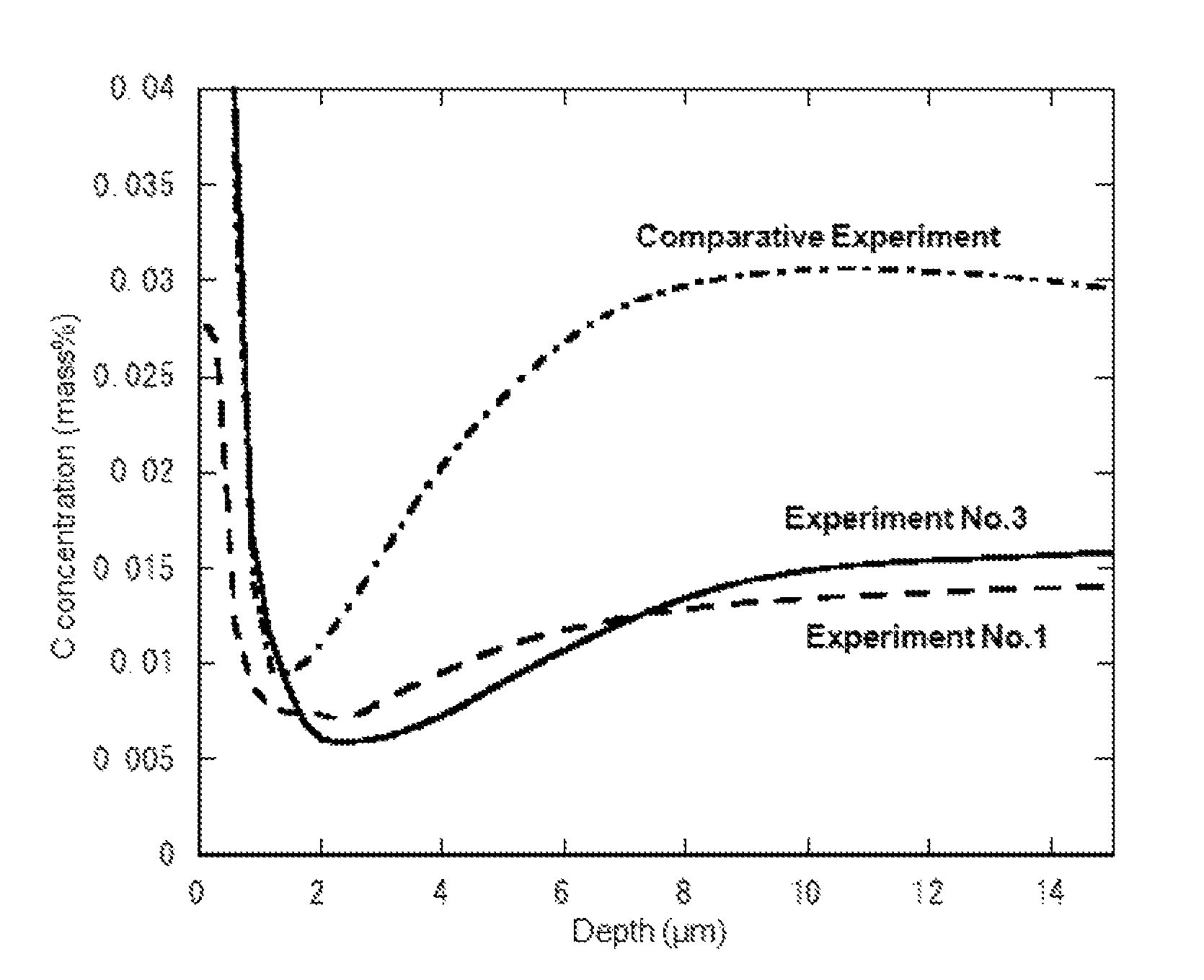
Cr-containing austenitic alloy tube and method for producing the same
ActiveUS9255319B2Low costUniformlyNuclear energy generationSolid state diffusion coatingAlloyAustenite
There is provided a Cr-containing austenitic alloy tube, wherein a chromium oxide film with a thickness of 0.05 to 1.5 μm having the relationship defined by Formula (i) is formed on the inner surface of the tube, wherein the average concentration of C in the depth range of 5 to 10 μm from the inner surface is lower than the concentration of C in a base metal;0.4≦δ1 / δ2≦2.5 (i)wherein δ1 and δ2 are thicknesses (μm) of the chromium oxide film at both ends of tube, respectively.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Nuclear steam supply system
ActiveUS20150110236A1Reduced fretting damage rateAvoid failureNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsWorking fluidCoolant flow
A nuclear steam supply system utilizing gravity-driven natural circulation for primary coolant flow through a fluidly interconnected reactor vessel and a steam generating vessel. In one embodiment, the steam generating vessel includes a plurality of vertically stacked heat exchangers operable to convert a secondary coolant from a saturated liquid to superheated steam by utilizing heat gained by the primary coolant from a nuclear fuel core in the reactor vessel. The secondary coolant may be working fluid associated with a Rankine power cycle turbine-generator set in some embodiments. The steam generating vessel and reactor vessel may each be comprised of vertically elongated shells, which in one embodiment are arranged in lateral adjacent relationship. In one embodiment, the reactor vessel and steam generating vessel are physically discrete self-supporting structures which may be physically located in the same containment vessel.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC
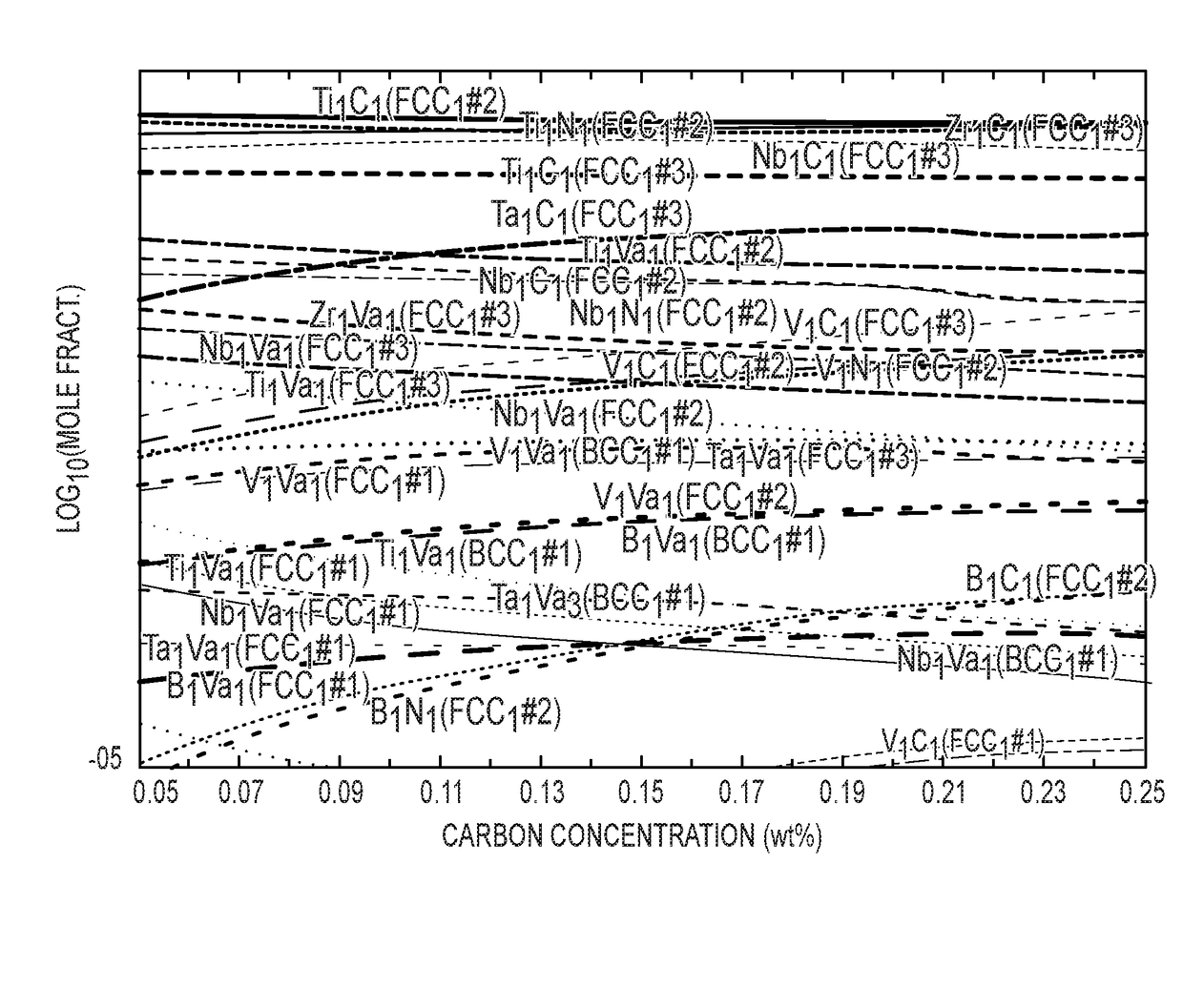
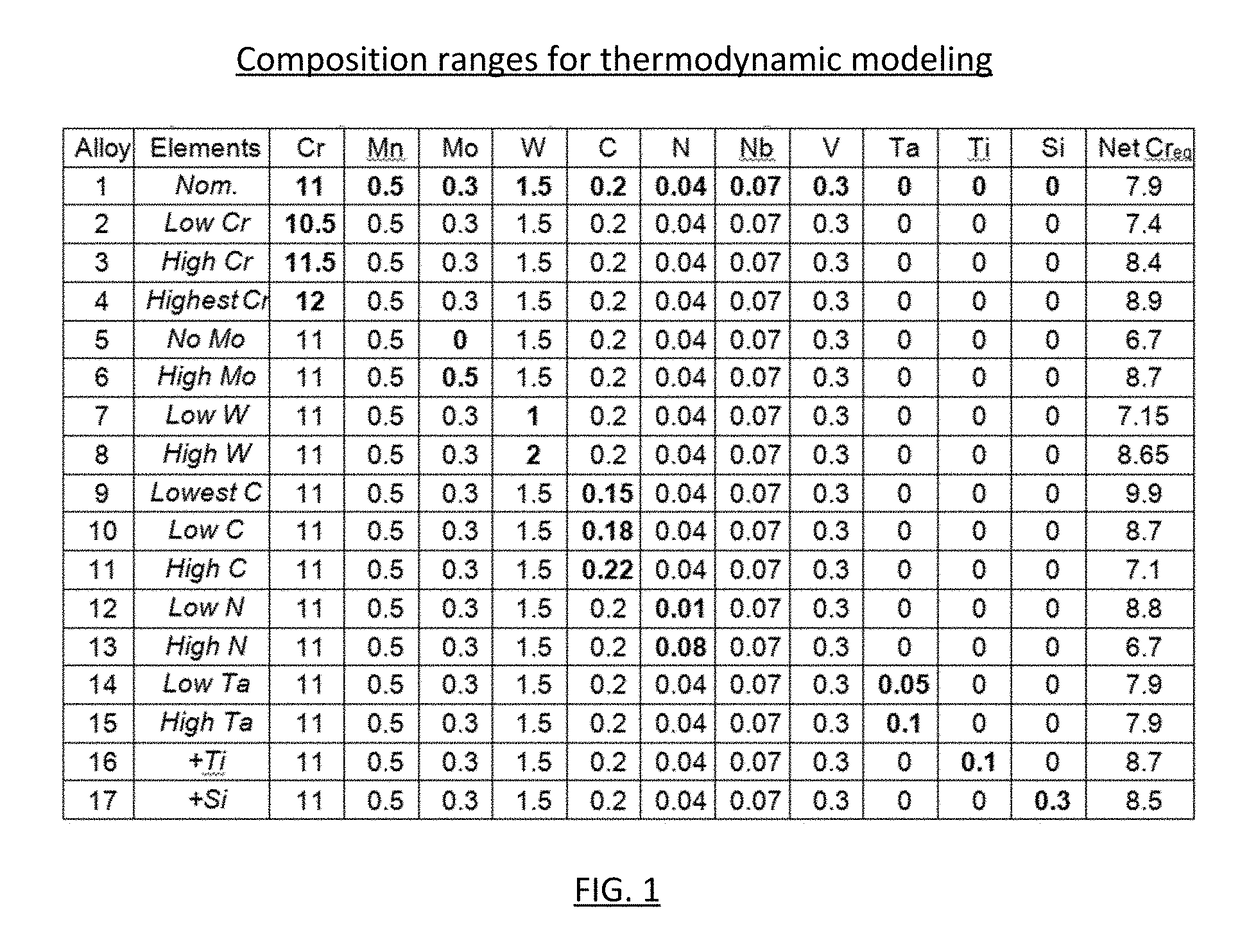
High temperature, radiation-resistant, ferritic-martensitic steels
InactiveUS20170292179A1Improve fracture toughnessReduced thermal creep and swellingOptical rangefindersPump componentsRadiation resistantThermal creep
This disclosure describes new high temperature, radiation-resistant, ferritic-martensitic steel compositions. The new steels generally contain 9.0-12.0 wt. % Cr, 0.001-1.0 wt. % Mn, 0.001-2.0 wt. % Mo, 0.001-2.5 wt. % W, and 0.1-0.3 wt. % C, with the balance being primarily Fe. More specifically, steels having from 10.0-12.0 wt. % Cr are considered particularly advantageous. Small amounts of N, Nb, V, Ta, Ti, Zr, and B may or may not also be present, depending on the particular embodiment. Impurities may be present in any embodiment, in particular impurities of less than 0.01 wt. % S, less than 0.04 wt. % P, less than 0.04 wt. % Cu, less than 0.05 wt. % Co, and less than 0.03 wt. % As are contemplated. Examples of these steels exhibit improved fracture toughness and reduced thermal creep and swelling.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
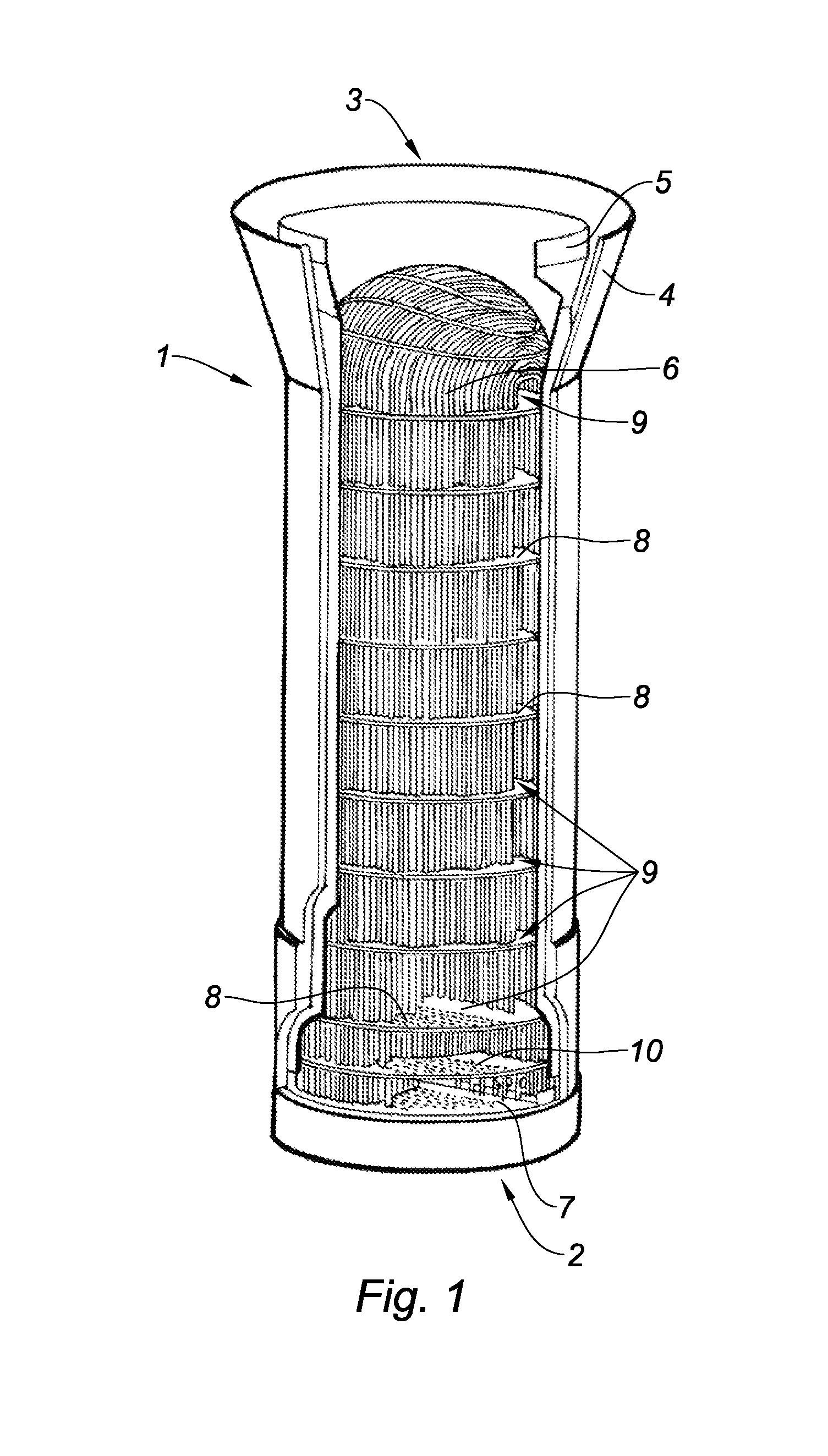
Steam generator dual system sludge and loose parts collector
A U-tube steam generator having a dual system for collecting loose parts and sludge. A loose parts collector having a water overflow edge is disposed between a feedwater inlet and a tube bundle of the steam generator. A sludge collector having a water outlet is disposed downstream of the overflow edge of the loose parts collector and maintains a pressure differential between a water inlet of the sludge collector and the water outlet.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
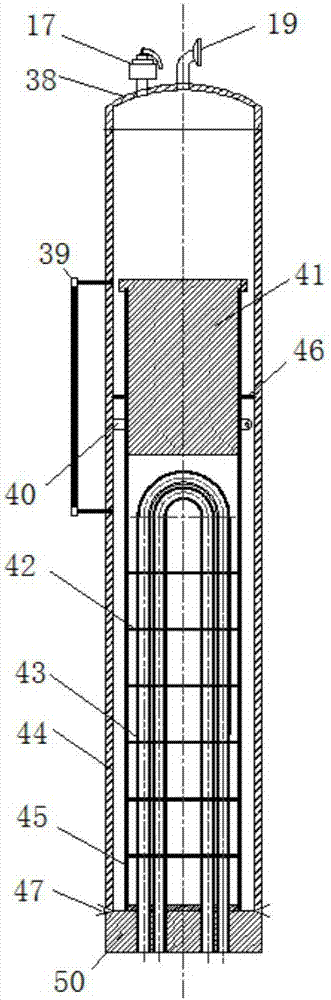
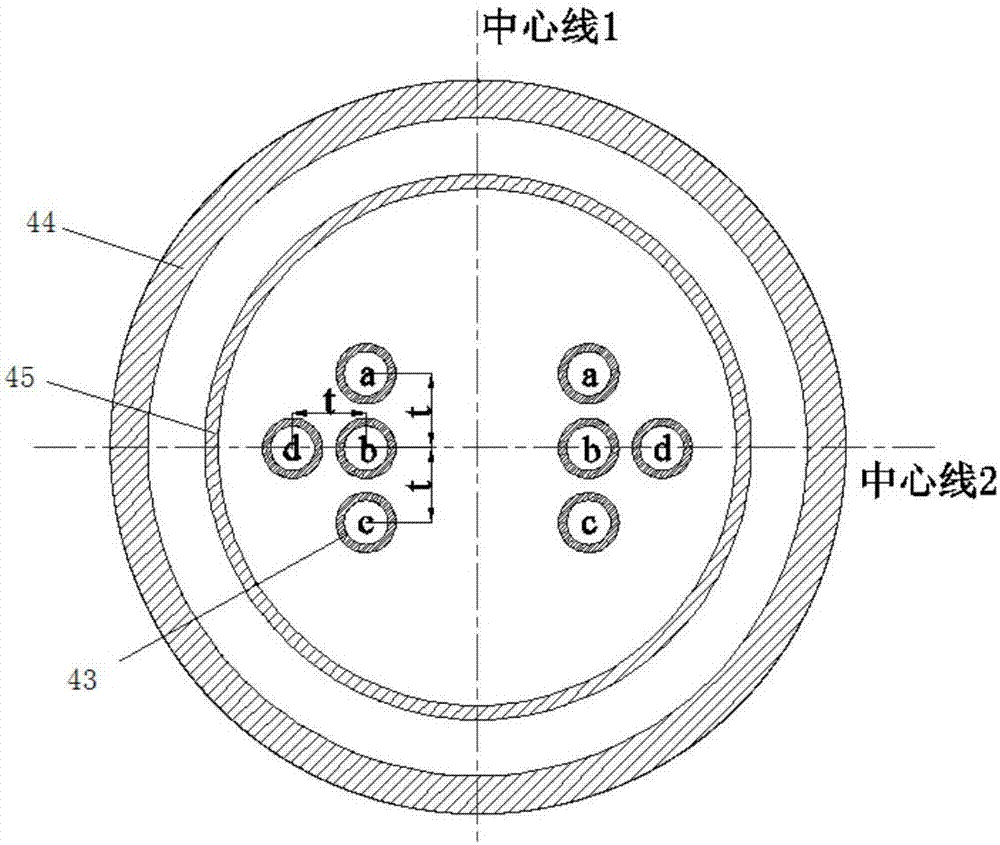
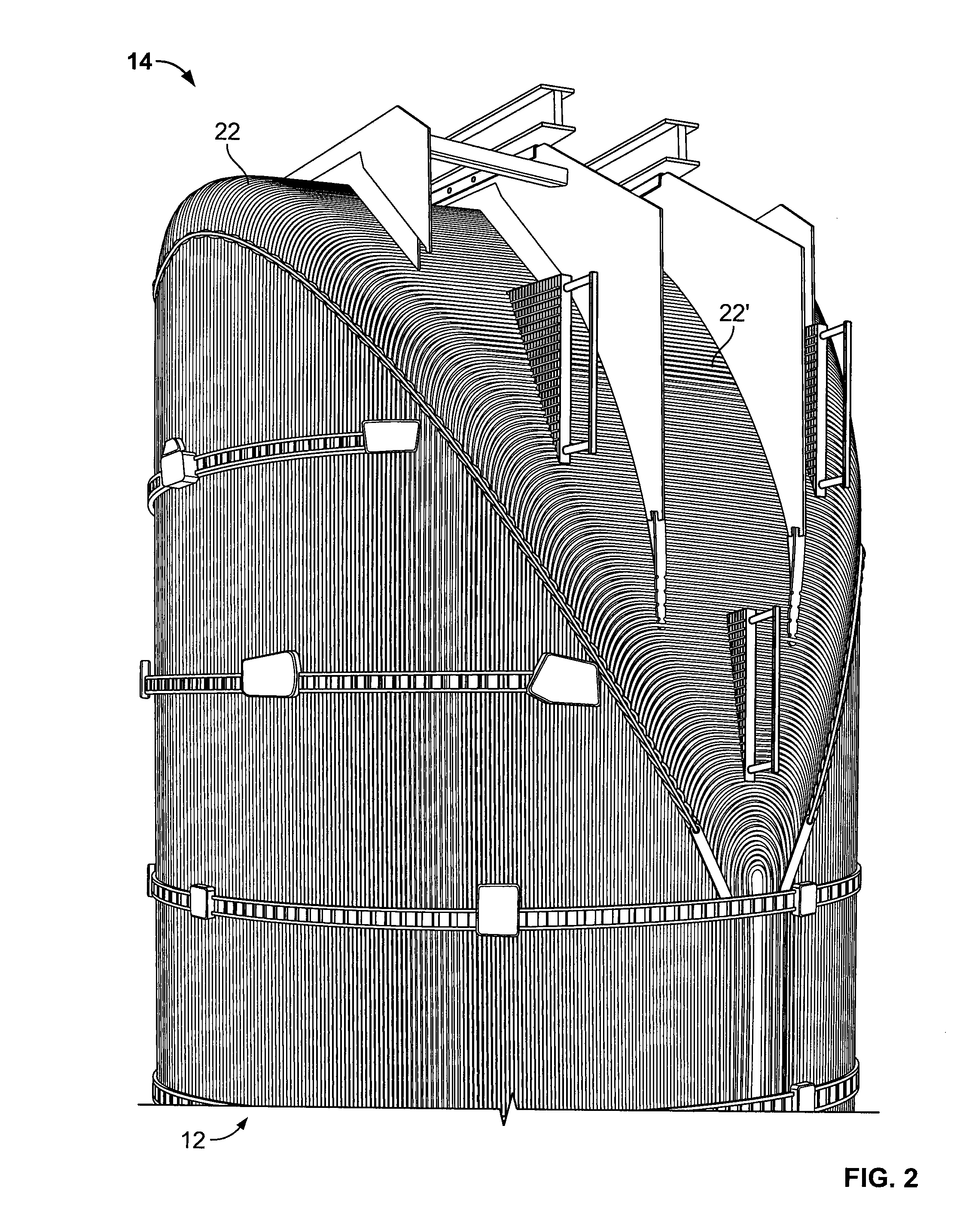
Flexible tube sheet structure for nuclear power plant steam generator
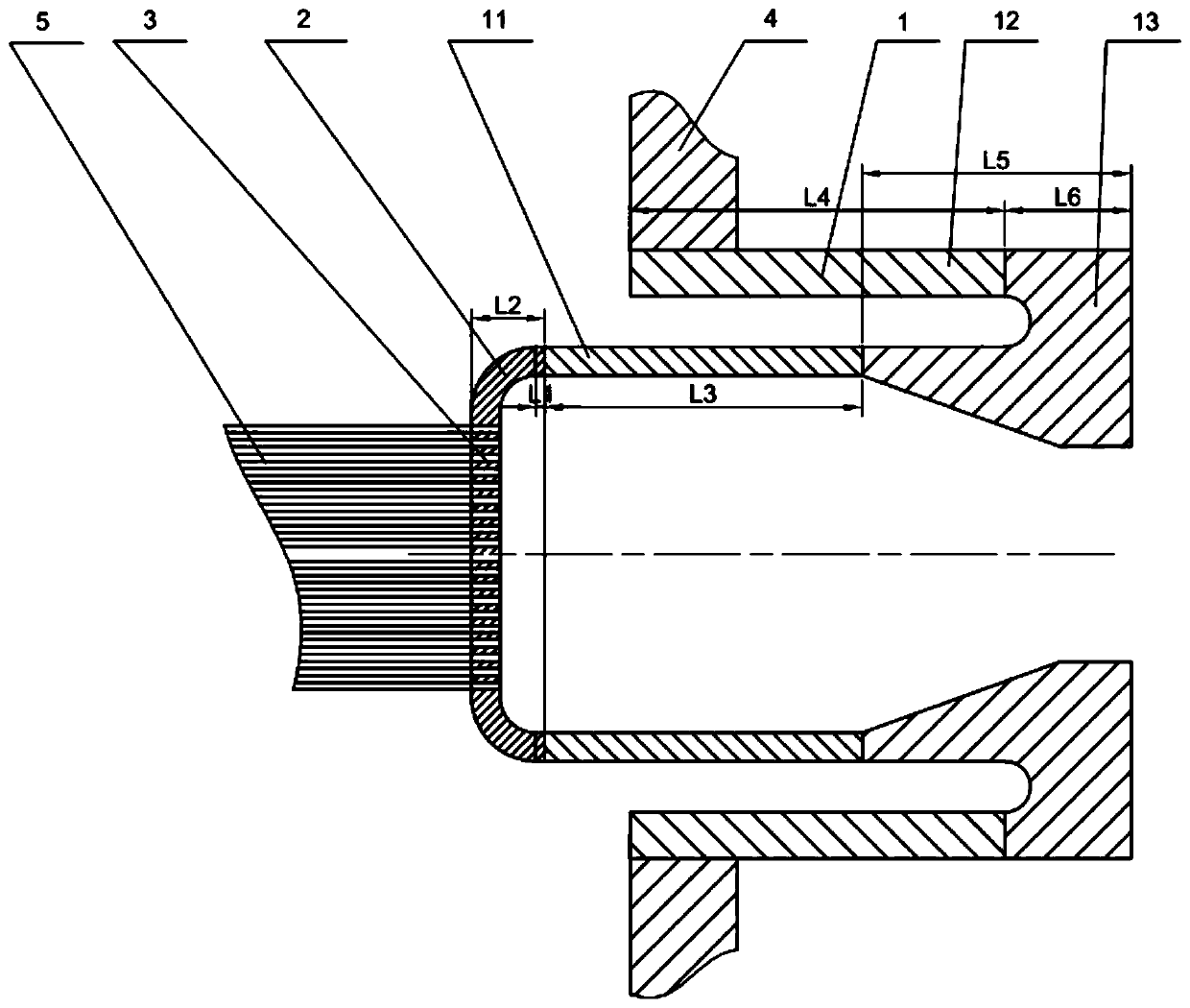
PendingCN110345464ALow costReduced thermal bending stressNuclear energy generationSteam generator primary sideBarrel ShapedEngineering
The invention relates to a flexible tube sheet structure for a nuclear power plant steam generator. The flexible tube sheet structure comprises a thermal expansion buffer section and a flexible tube sheet; the two ends of the flexible tube sheet are connected with the thermal expansion buffer section through a transition section; the thermal expansion buffer section is in a barrel shape in the whole and is composed of an inner barrel, an outer barrel and a connection flange, wherein the inner barrel and the outer barrel are different in thickness, a cavity serving as a fluid dead zone is formed between the inner barrel and the outer barrel, the two ends of the connection flange are welded to one end of the inner barrel and one end of the outer barrel, the other end of the inner barrel is welded to the end of the transition section, and the side wall of the other end of the outer barrel is welded to a steam generator barrel body; the flexible tube sheet and the transition section are subjected to primary forging forming, the transition section is a circular-arc-shaped rotation body, and heat exchange tube holes are uniformly and densely distributed in the flexible tube sheet; and the flexible tube sheet, the transition section and the inner barrel of the thermal expansion buffer section are equal in effective thickness. Through the flexible tube sheet structure, the thickness ofa tube sheet can be decreased, thermal stress of the two sides of the tube sheet is decreased, in addition, the tube sheet has certain flexibility, and the thermal expansion difference between the heat exchange tube and the steam generator barrel body can be decreased to a certain extent.
Owner:CHINERGY CO LTD
Thermotechnical design method suitable for sodium water once-through steam generator
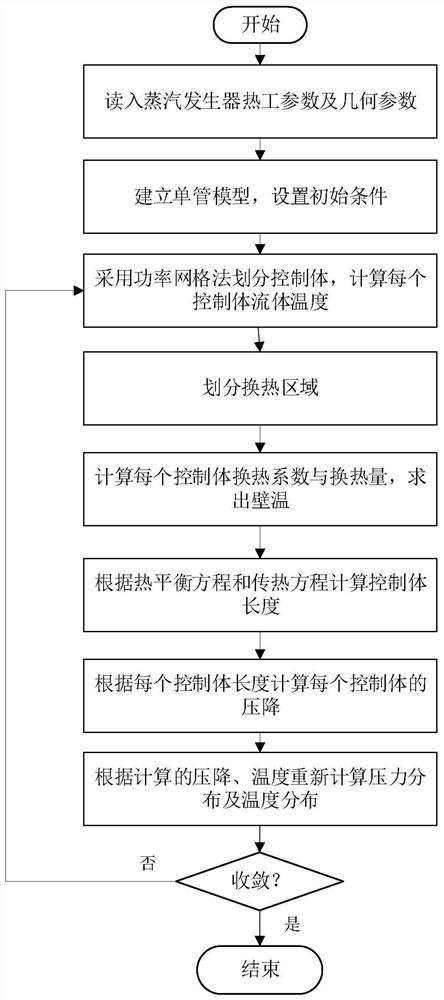
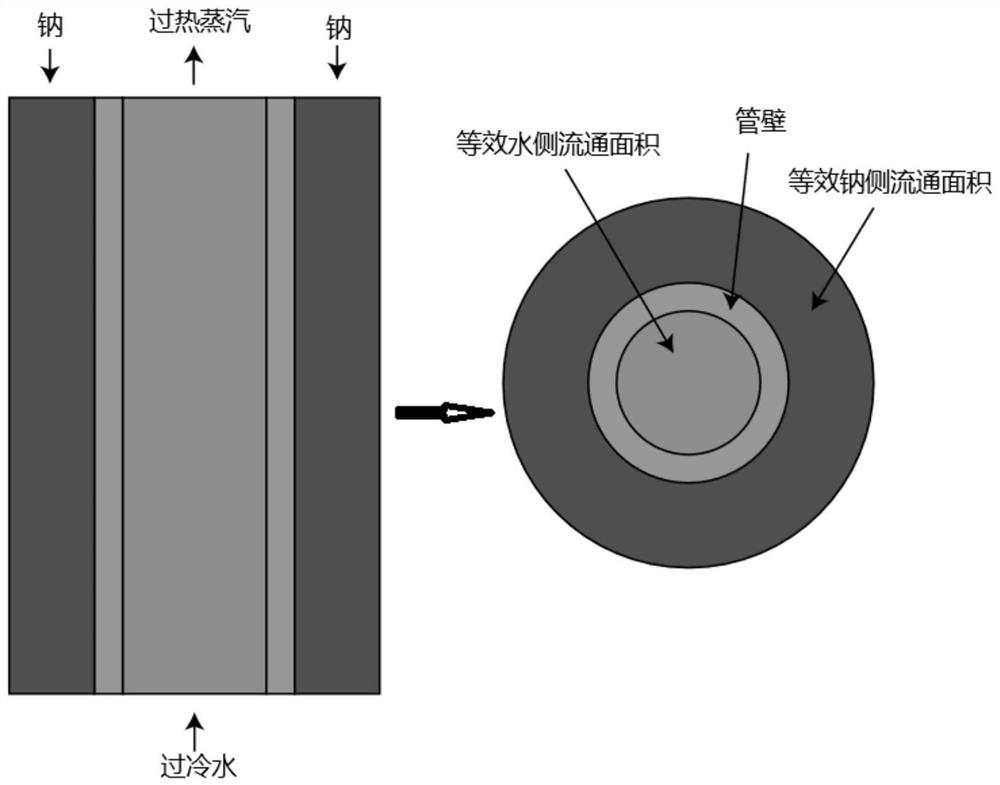
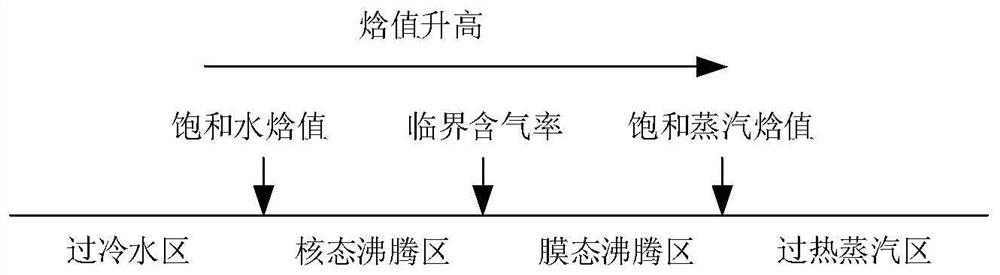
ActiveCN111680417ASuitable for a wide range of objectsAvoid being in two heat exchange areas at the same timeNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationFluid controlPower grid
The invention discloses a thermotechnical design method of a sodium water once-through steam generator. The method comprises the following steps: determining thermal parameters of the sodium water once-through steam generator and geometrical parameters except the length of a heat transfer tube; establishing a steam generator single-tube model, and setting the initial pressure and temperature of the steam generator; obtaining the fluid temperature of each fluid control body by using a power grid method; dividing a heat exchange area to calculate a heat exchange coefficient and a heat exchange amount, and solving a wall temperature according to an energy balance relation of heat conduction and convective heat exchange; solving the length of each fluid control body on the heat transfer pipe according to the heat balance equation and the heat transfer equation; calculating the pressure drop of each fluid control body to obtain new pressure distribution. The invention relates to a universalthermal design calculation method for a sodium-water once-through steam generator. The method is convenient to operate, high in universality, flexible to use and high in precision, the thermal designcalculation requirement of the sodium-water once-through steam generator can be met, and a software basis can be provided for independent design of the sodium-cooled fast reactor in China.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com