Nucleic acid amplification method
A nucleic acid and nucleotide sequence technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA preparation, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of low amplification efficiency, low non-specific products, low amplification efficiency, and increased non-specific products, etc. problem, to avoid the effect of reducing the amplification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
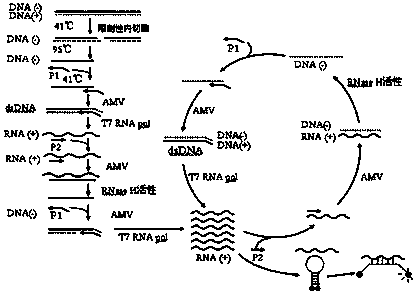
[0087] Example 1: Respectively use restriction endonuclease and restriction nickase to amplify nucleic acid with different concentrations, compare detection sensitivity and specificity of amplified products
[0088] 1. According to the method of Chinese patent CN02807389.4, use restriction endonucleases to amplify nucleic acids with different concentrations (control group):
[0089] Reaction conditions: A conservative restriction endonuclease XbaI is encoded in the conserved region of S-gen of HBV DNA (according to nt244-285 of the EcoRI site). When this portion of the S-region is capable of becoming single-stranded DNA of negative polarity, oligonucleotides ("restriction primers" (RP)) complementary to the region containing the sequence Forms a double-stranded restriction site. Use the HBV quality control product nucleic acid (including the site to be tested, single-stranded DNA) developed by our company for gradient detection, and use 5 μL of extract for each measurement (a...
Embodiment 2
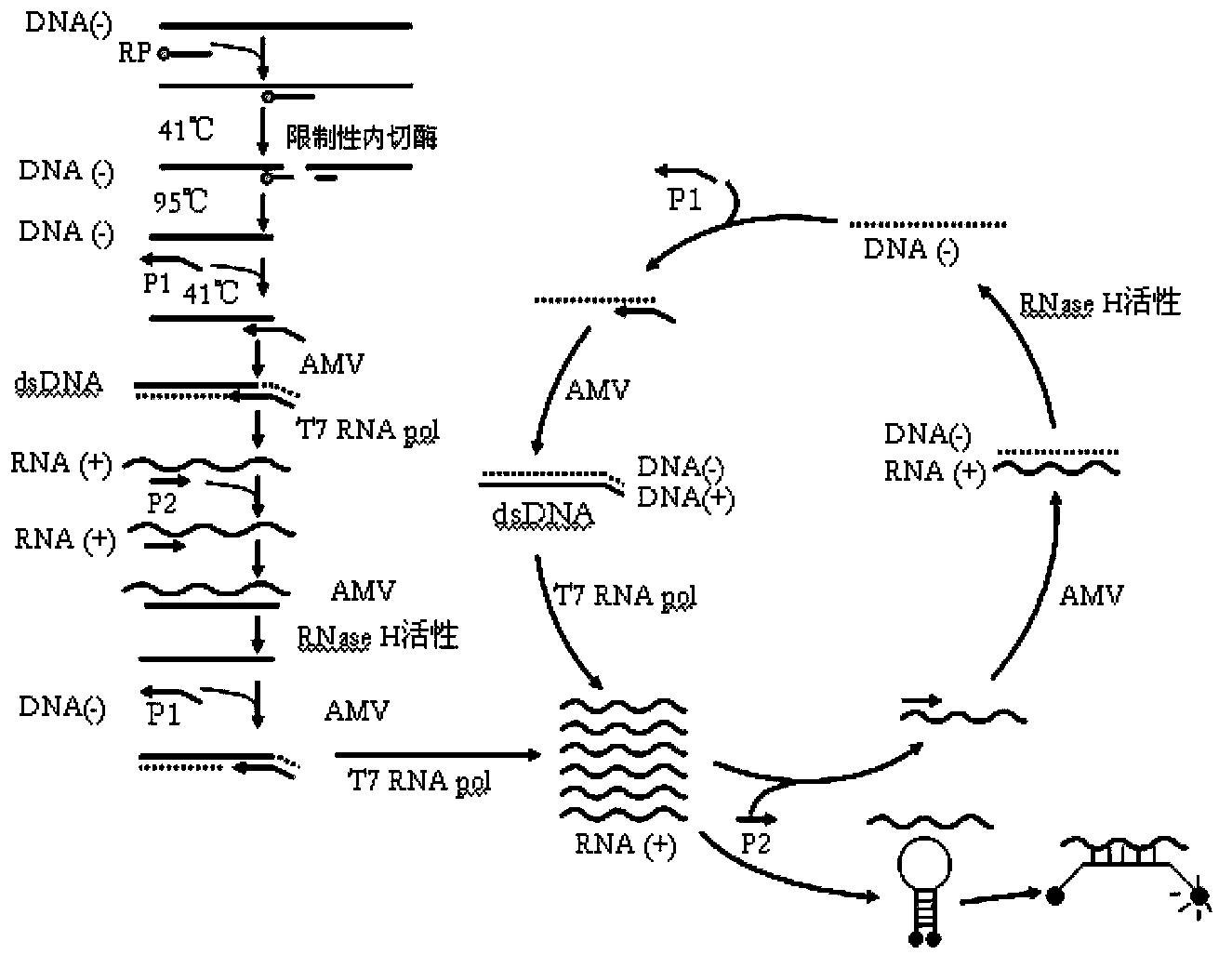
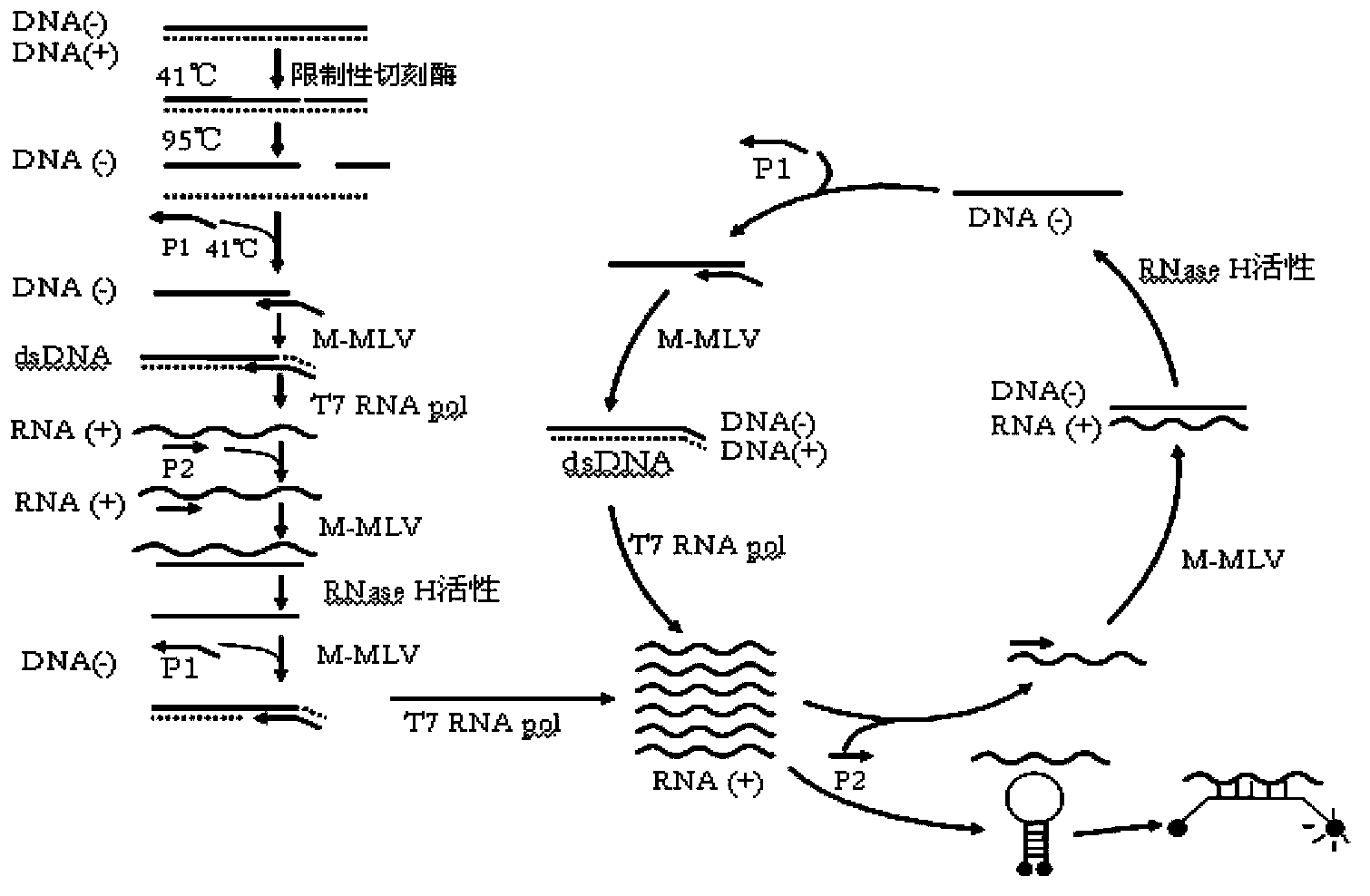
[0099] Embodiment 2: Amplification of HBV DNA (template is single-stranded DNA)
[0100] A conserved restriction nickase Nt.CviPII is encoded in the conserved region of S-gen of HBV DNA (according to nt257-262 of the EcoRI site, --TGGˇTGGˇA--). When this part of the S-region is capable of becoming single-stranded DNA of negative polarity, a promoter primer is added, in this method a promoter primer is used whose 3' part contains a sequence exactly complementary to the 3' end at the cut site, and The 5' end contains a promoter sequence that can be recognized by RNA polymerase (such as T7). Double-stranded restriction sites are thereby formed for all genomic DNA present. 6 μL of extract was used for each assay. Restriction enzyme digestion was carried out under the following conditions: TMA buffer 50mM Tris-HCl pH8.5, 8.66mM MgCl 2 , 70mM KCl, 11%v / vDMSO, 3.3mM DTT, 1.25mM of various dNTPs and NTPs, 0.1μM promoter primer F201111-1 in Table 5, 0.1μM reverse primer R708 in Tabl...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3: Amplification of Treponema pallidum (treponema pallidum, TP) DNA (template is double-stranded DNA)
[0114] A conserved restriction nickase Nb.BtsI site is encoded in the conserved region of DNA polymerase I gene (polA) of TP DNA. On the negative strand, the restriction site is 3`-CGTCACˇNN-5`. TP DNA in its natural state is double-stranded, and 6 μL of TP DNA solution is used for each determination. Restriction enzyme digestion was carried out under the following conditions: TMA buffer (50mM Tris-HCl pH8.5, 8.66mM MgCl 2 , 70 mM KCl, 11% v / v DMSO, 3.3 mM DTT, 1.25 mM of various dNTPs and NTPs, 0.1 μM promoter primer F400806 in Table 7, 0.1 μM reverse primer R400806-3 in Table 7, 0.067 μM Molecular beacon probe MBP3 and 2U restriction nickase Nb.BtsI in Table 7 (experimental results show that there is no significant difference in the amplification effect of the nickase in the range of 1U-5U, and the effect of 2U is slightly better) . After incubating at 41...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com