Oxidation-resistant coking-resistant hydrocarbon cracking furnace pipe and preparation method thereof
A kind of hydrocarbon cracking furnace tube and cracking furnace tube technology, applied in non-catalytic thermal cracking, cracking, petroleum industry and other directions, can solve the problems of furnace tube matrix damage, easy peeling, cumbersome steps, etc., to reduce catalytic coking and carburizing , The effect of reducing excessive oxidation and prolonging the operating cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
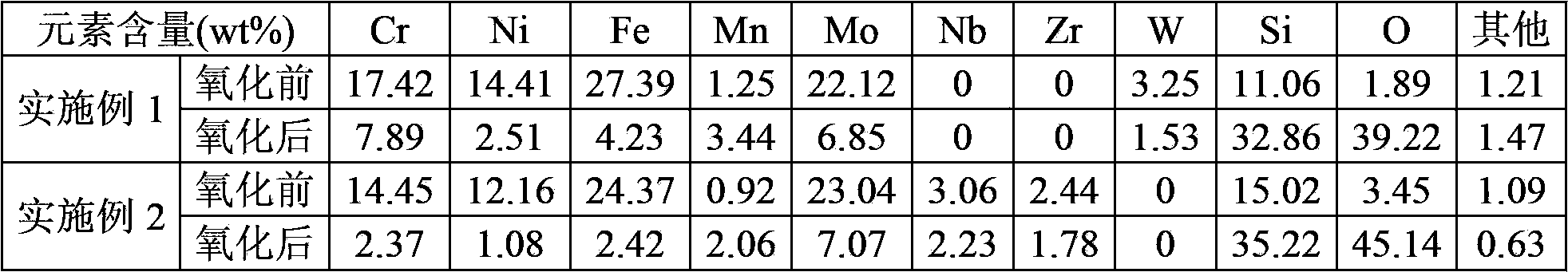
[0027] A coupon with the same size and material as that of Comparative Example 1 was used to prepare the coating according to the method provided by the present invention. Put the coupon and 60% elemental molybdenum, 30% elemental silicon, and 10% elemental tungsten in a low vacuum of 0.5Pa and a barrel-shaped cathode filled with argon to infiltrate molybdenum ions, silicon ions, and tungsten ions, the temperature is 900°C, and the temperature is kept for 5 hours, and MoSi with gradient concentration changes is formed on the surface of the coupon. 2 +W's Composite Penetration Layer. The coupon containing the coating was heated to 1200°C at a rate of 20°C / min in the air atmosphere and then oxidized at a constant temperature for 20 hours, with a weight loss of 3.83%. X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (Energy Dispersive Spectrometer referred to as EDS) was used to analyze the surface element composition of the coupons before and after oxidation, and the results are shown in T...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A coupon with the same size and material as that of Comparative Example 1 was used to prepare the coating according to the method provided by the present invention. Put the coupon and 60% elemental molybdenum, 30% elemental silicon, 5% elemental niobium, and 5% zirconia in a low vacuum of 0.5Pa and filled with argon in a barrel-shaped cathode to infiltrate the molybdenum Ions, silicon ions, niobium ions, zirconium ions, oxygen ions, temperature 800 ℃, heat preservation for 6 hours, formed a gradient concentration of MoSi on the surface of the coupon 2 +Nb+ZrO 2 composite permeable layer. The coupon containing the coating was heated to 1200°C at a rate of 20°C / min in the air atmosphere, and then oxidized at a constant temperature for 20 hours, with a weight loss of 2.06%. X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (Energy Dispersive Spectrometer referred to as EDS) was used to analyze the surface element composition of the coupons before and after oxidation, and the results ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In this comparative example, the size is The alloy furnace tube made of HK40 is coated according to the method provided by the present invention. The furnace tube is used as a barrel-shaped cathode, and the mass percentage of 60% elemental molybdenum, 30% elemental silicon, and 10% elemental tungsten is placed in the furnace tube, at 900°C and 0.5Pa in a low-vacuum argon atmosphere After 5 hours of medium heat preservation, MoSi with gradient concentration changes was formed on the inner surface of the furnace tube. 2 +W's composite penetration layer.
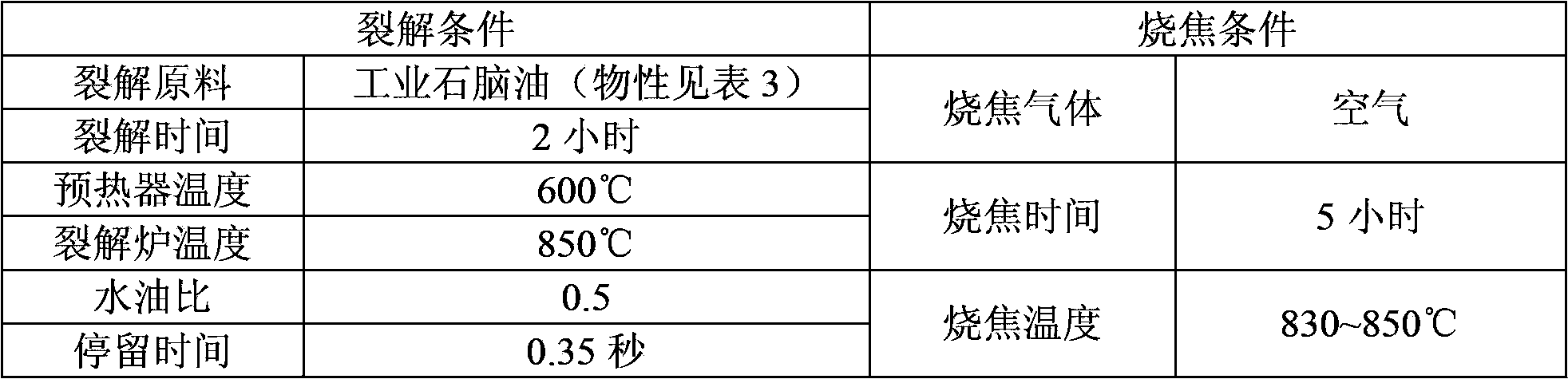
[0046] Using the pyrolysis conditions and charring conditions of Comparative Example 3, the furnace tube containing the coating of the present invention was subjected to repeated pyrolysis and charring cycle tests, and the coking amounts of different cracking times are shown in Table 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com