Charcoal-base polyaspartic acid slow-release urea as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of polyaspartic acid and slow-release urea, which is applied in application, fertilizer mixture, fertilization equipment, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the needs of high-quality agricultural product production, aggravate soil acidification, soil compaction, and land non-point source pollution. Achieve the effect of improving soil physical and chemical properties, promoting crop growth, and reducing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
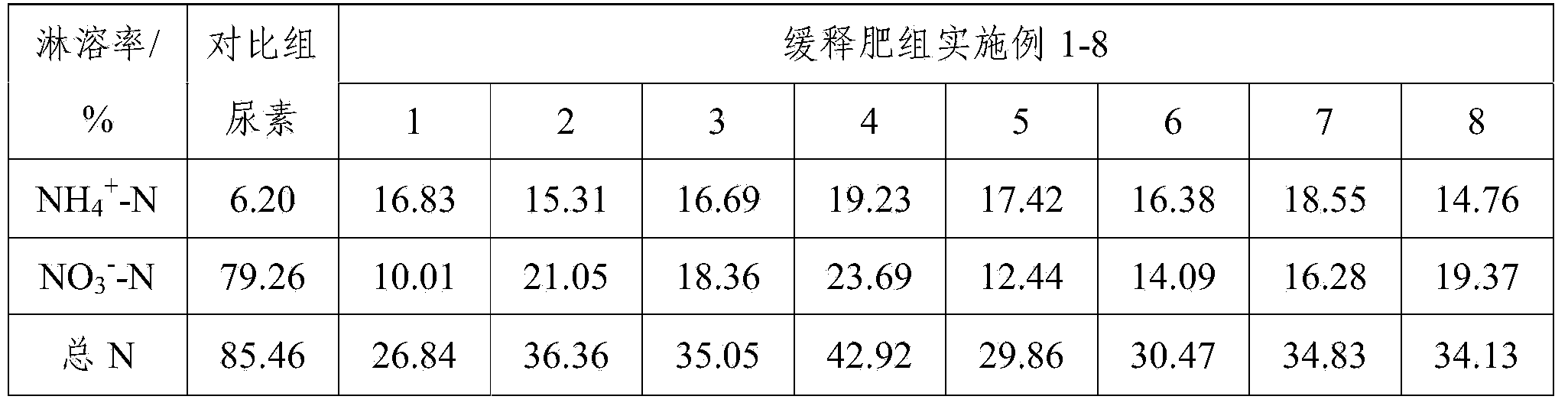
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Biochar-based polyaspartic acid slow-release urea and its preparation
[0035] Include the following steps:
[0036] 1. Use agricultural waste branches as biomass raw materials to carbonize at 500°C to form porous biochar, cool and grind through an 80-mesh sieve;
[0037] 2. Add urea and formaldehyde into the flask at a molar ratio of 1:2, adjust the pH to weak alkaline with lye, and react at 45°C for 3 hours to prepare modified urea;
[0038] 3. Add 0.12 parts of L-modified manganese polyaspartate to the solution containing 4 parts of modified urea;
[0039] 4. Soak 100 parts of biochar particles in the above solution for 10 hours, then dry;
[0040] 5. Add 3 parts of starch to 100 parts of water, add 0.3 parts of sodium hypochlorite solution dropwise at 35°C, stir and keep warm for 2 hours to make a coating solution;
[0041] 6. Add 100 parts of dried biochar granules loaded with modified urea and polytetramethylene to the oxidized starch coating solution...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Biochar-based polyaspartic acid slow-release urea and its preparation
[0043] Include the following steps:
[0044] 1. Use agricultural waste peanut shells as biomass raw materials to carbonize at 400°C to form porous biochar, which is cooled and ground through a 60-mesh sieve;
[0045] 2. Add urea and formaldehyde into the flask according to the molar ratio of 1:1.5, adjust the pH to weak alkaline with lye, and react at 40°C for 3 hours to prepare modified urea;
[0046] 3. Add 0.03 parts of sodium polyaspartate to the solution containing 10 parts of modified urea;
[0047] 4. Soak 100 parts of biochar particles in the above solution for 8 hours, then dry;
[0048] 5. Add 4 parts of starch to 100 parts of water, add 0.15 parts of sodium hypochlorite solution dropwise at 45°C, and keep stirring for 1 hour to make a coating solution;
[0049] 6. Add 100 parts of dried biochar granules loaded with modified urea and polytetramethylene to the oxidized starch coa...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Biochar-based polyaspartic acid slow-release urea and its preparation
[0051] Include the following steps:
[0052] 1. Use agricultural waste straw as biomass raw material to carbonize at 450°C to form porous biochar, which is cooled and ground through an 80-mesh sieve;
[0053] 2. Add urea and formaldehyde into the flask at a molar ratio of 1:1, adjust the pH to weak alkaline with lye, and react at 45°C for 3 hours to prepare modified urea;
[0054] 3. Add 0.06 parts of calcium polyaspartate to the solution containing 8 parts of modified urea;
[0055] 4. Soak 100 parts of biochar particles in the above solution for 3 hours, then dry;
[0056] 5. Add 2.5 parts of starch to 100 parts of water, add 0.05 parts of sodium hypochlorite solution dropwise at 40°C, stir and keep warm for 2 hours to make a coating solution;
[0057] 6. Add 100 parts of dried biochar granules loaded with modified urea and polytetramethylene to the oxidized starch coating solution, g...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com