Preparation method and application of fluorescent marker gene chip reagent for detecting ToRCH (toxopasma, rubella virus, cytomegalo virus and herpes virus)
A fluorescent labeling and gene chip technology, applied in the field of medical testing and biochips, can solve the problems of long operation time, complicated reagents, unfavorable test results of patients, etc., and achieve the effect of short time consumption and short time consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] 1. Target sequence determination:
[0081] The present invention uses the following target sequences: According to the gene sequences of Toxopasma (Toxopasma), Rubella Virus (RubellaVirus), Cytomegalo Virus (Cytomegalo Virus), Herpes Simplex Virus Type I and Type II (Herpes Virus I / II), select a section The gene sequence with better specificity and appropriate fragment length is used as the target sequence for detection;
[0082] After the selected target sequence is searched by homology comparison, it is considered to be a sequence with high specificity;
[0083] Preferably, the present invention introduces the human actin β-action gene as a housekeeping gene to perform quality control on the inspection process, and the sequence is as follows:
[0084] TACCACTGGCATCGTGATGGACTCCGGTGACGGGGTCACCCACACTGTGCCCATCTACGAGGGGTATGCCCTCCCCCATGCCATCCTGCGTCTGGACCTGGCTGGCCGGGACCTGACTGACTACCTCATGAAGATCCTCACCGAGCGCGGCTACAGCTTCACCACCACGGCCGAGCGGGAAATCGTGCGTGACATTAAGGAGAAGCTG
[0085] ...
Embodiment 2
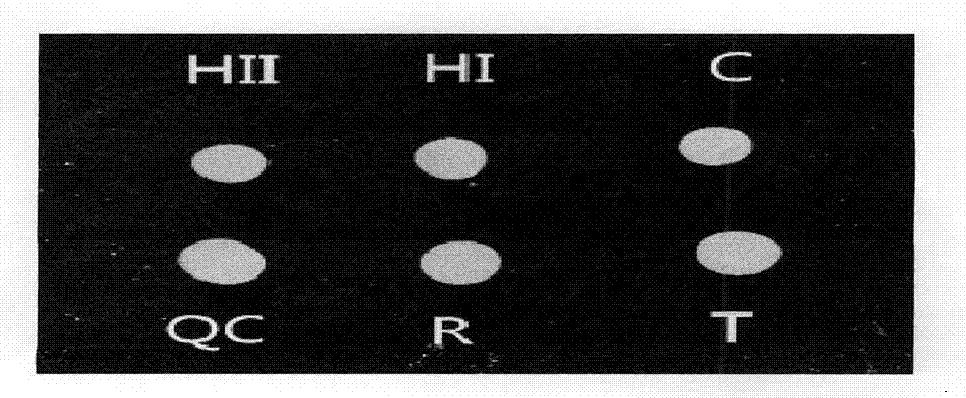
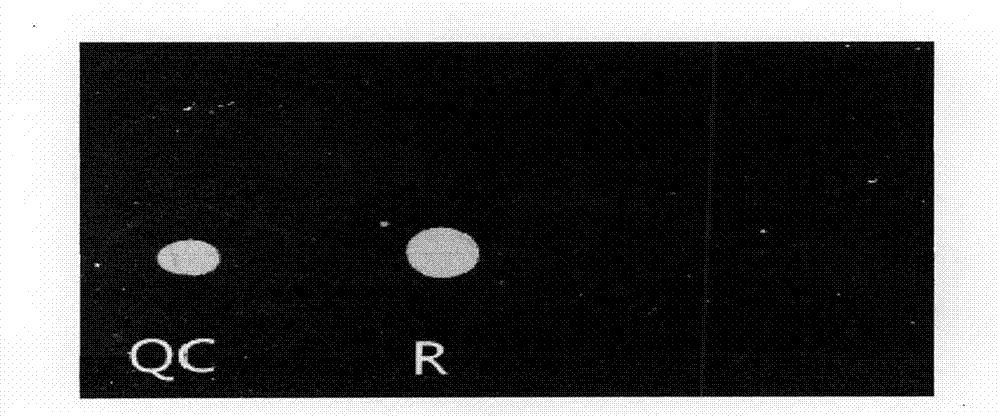
[0122] Using coxsackie virus, treponema pallidum, parvovirus, hepatitis B virus, HIV virus, chlamydia virus, toxoplasma gondii, rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus type I / II and other pathogen samples as templates, The primers and probes designed in this experiment were used for probe in situ hybridization, and the results showed that only Toxopasma, Rubella Virus, Cytomegalo Virus, Herpes Simplex virus I and II I / II) Fluorescent signal is generated, and the detection result is shown in Figure 2 to Figure 6 . Prove that the reagent prepared by the preparation method of the present invention has the ability to detect Toxopasma (Toxopasma), Rubella Virus (Rubella Virus), Cytomegalo Virus (Cytomegalo Virus), Herpes Simplex Virus I and Type II (Herpes Virus I / II) specificity.
Embodiment 3
[0124] In order to determine the detection sensitivity of the present invention, the above-mentioned gene fragment of the quality control gene human actin β-action is also subjected to a concentration gradient test. The β-action gene fragment was artificially synthesized in Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd., the synthetic concentration was 1000ng / ml, and the known concentration of the gene fragment was diluted 10×, that is, diluted to 100ng / ml, 10ng / ml, 1ng / ml ml, 0.1ng / ml, 0.01ng / ml, 0.001ng / ml total 6 concentration gradients. Use the designed primers labeled with 5'cy3 to carry out fluorescent incorporation labeling PCR amplification. After diluting the aminated probe to 50pmol / ul with deionized water, take 0.5ul and add it dropwise on the aldehyde-based substrate, let it stand overnight at room temperature, and wash it successively with eluent I (5×SSC, 1% SDS), then Elute with dehydration II (0.25×SSC, 1% SDS) for 5 min each to elute unfixed probes, then centrifuge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com