Method for extracting Humulus scandens (Lour.) Merr. leaf protein and total flavonoids in graded manner simultaneously from fresh and tender stems and leaves of Humulus scandens (Lour.) Merr.
A technology for fractional extraction and total flavonoids, which is applied in the preparation method of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of inability to use Humulus japonicus resources in depth, time-consuming, repeated processing, etc., and achieve extraction The process conditions are accurate and reliable, and the effect of improving the value of development and utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
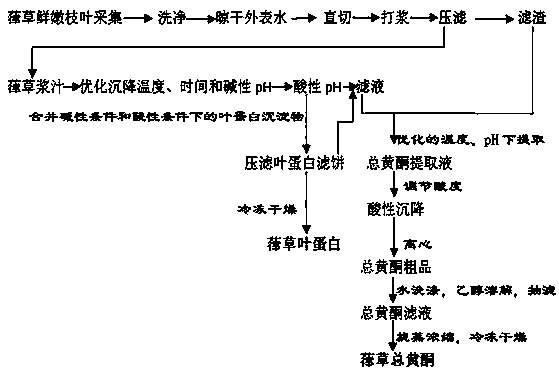
[0017] refer to figure 1 As shown, the method for extracting Humulus leaf protein and total flavonoids simultaneously from the fresh and tender stems and leaves of Humulus comprises the following steps:
[0018] Step 1, take the fresh and tender humulus stems and leaves collected in August, wash them with distilled water, dry the surface water at room temperature, measure their water content and weight, and cut them into about 0.5cm long fragments;
[0019] Step 2, adding the stems and leaves of Humulus japonicus obtained in step 1 to 10 times the weight of water, making it into a homogenized form with a high-speed homogenizer, and then completely filtering out the juice;
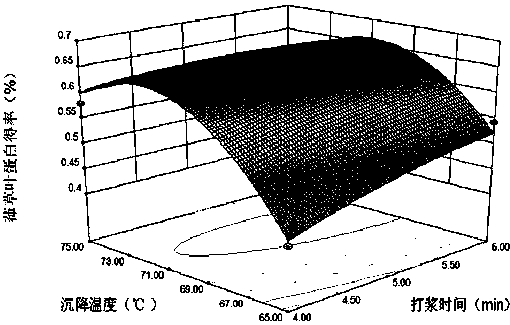
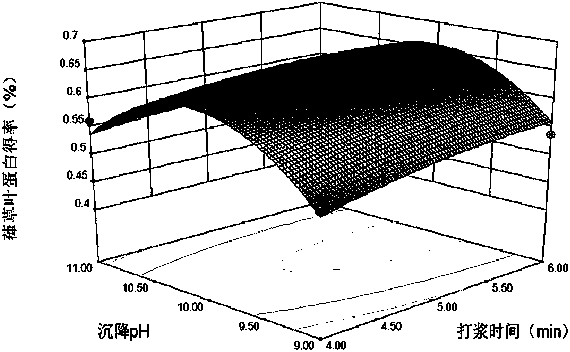
[0020] Step 3, on the basis of the single factor experiment, according to the central combination design principle of Box-Behnken, take beating time, leaf protein sedimentation temperature and leaf protein sedimentation pH three factors as independent variables (respectively with X 1 , X 2 , X 3 Indicate...
Embodiment 2
[0088] The method for extracting humulus leaf protein and total flavonoids simultaneously and fractionally from the fresh and tender stems and leaves of Humulus japonicus comprises the following steps:
[0089] Step 1, wash 10Kg of the fresh and tender branches and leaves of Humulus humulus collected in August with distilled water, dry the surface water at normal temperature, then measure its water content, and its water content is 75%. Weigh (wet weight) the stems and leaves of Humulus humulus taken, and cut them straight into about 0.5cm length fragments as a basis for measurement, and set aside for later use.
[0090] Step 2: add the stems and leaves of Humulus japonicus treated in step 1 into distilled water with a weight 10 times higher, beat for 5.5 minutes with a high-speed homogenizer, make it into a homogenized slurry, and then filter out the juice completely.
[0091] In step 3, the humulus juice obtained in step 2 is subjected to alkaline precipitation at 71°C and p...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Step 1, wash 12Kg of fresh and tender branches and leaves of Humulus humulus collected in September with distilled water, dry the surface water at normal temperature, then measure its water content, and its water content is 73%. Weigh (wet weight) the stems and leaves of Humulus humulus taken, and cut them straight into about 0.5cm length fragments as a basis for measurement, and set aside for later use.
[0102] Step 2: add the stems and leaves of Humulus japonicus treated in step 1 into distilled water with a weight 10 times higher, beat for 5.5 minutes with a high-speed homogenizer, make it into a homogenized slurry, and then filter out the juice completely.
[0103] In step 3, the humulus juice obtained in step 2 is subjected to alkaline precipitation at 71°C and pH 10 for 10 minutes, and then centrifuged to obtain supernatant and precipitate, and the precipitate is freeze-dried to obtain Humulus leaf protein. Finally, 813.6 g of humulus leaf protein was obtained, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com