Chromic acid wastewater treatment method and system
A technology for wastewater treatment and chromic acid, which is applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of poor adsorption effect of cation exchange resin, low concentration and high transportation cost. The effect of saving equipment investment, simple operation procedures and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
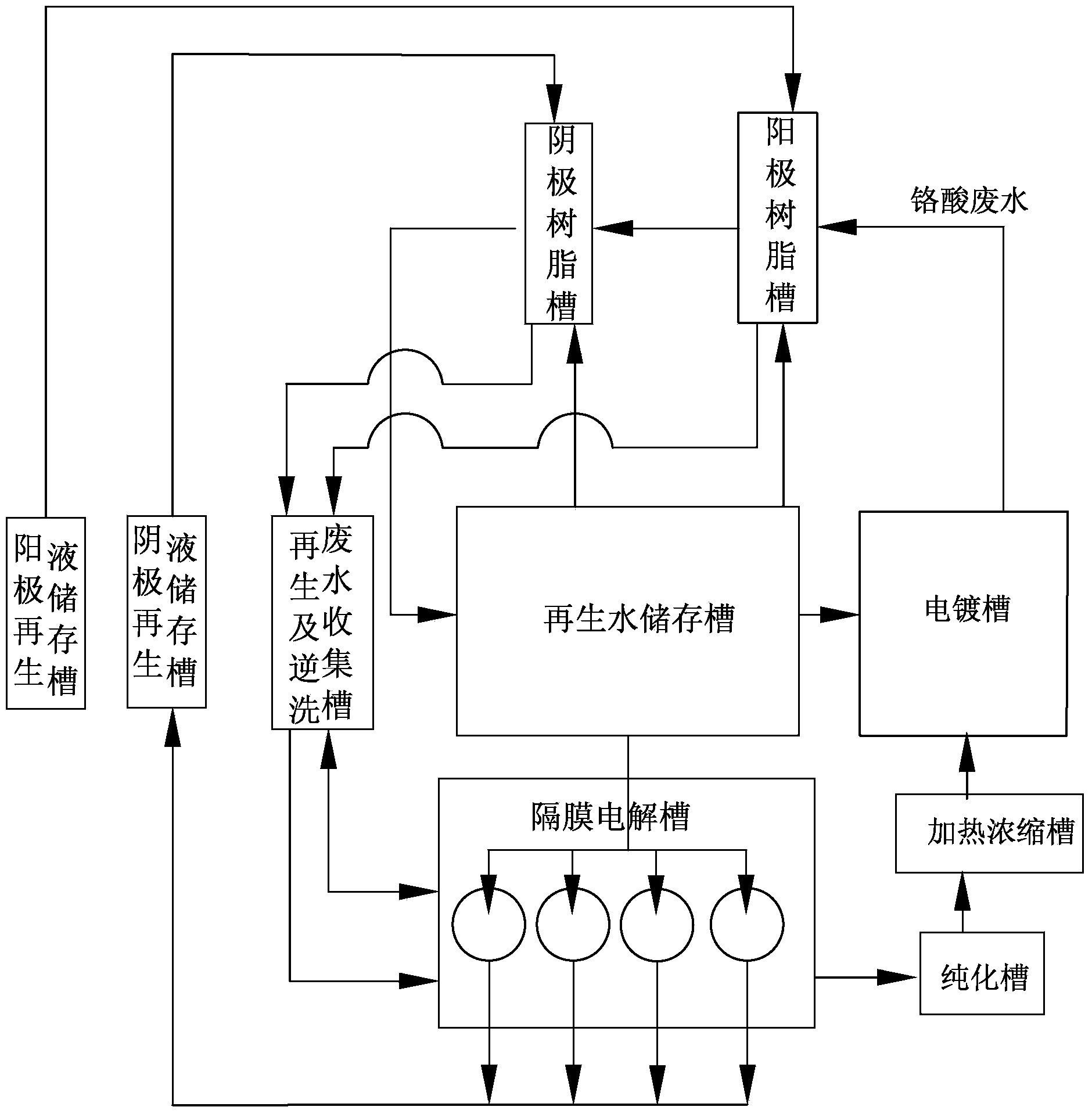
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] First, the chromic acid wastewater is injected into the anode resin tank equipped with cation exchange resin for ion exchange, and then the chromic acid wastewater flowing out of the anode resin tank is injected into the anion resin tank equipped with anion exchange resin, and the chromic acid wastewater becomes in line with the discharge standard regenerated water, the regenerated water is input into the regenerated water storage tank for standby; when the exchange capacity of the cation exchange resin through ion exchange is close to or reaches saturation, stop inputting chromic acid waste water to the anode resin tank, and use the cation exchange resin with a concentration of 1 to 4wt% The sulfuric acid solution soaks the cation exchange resin for more than 48 hours. At this time, the sulfuric acid solution becomes the anode regeneration waste liquid. The anode regeneration waste liquid is collected for treatment, and the cation exchange resin is backwashed with regene...
Embodiment 2
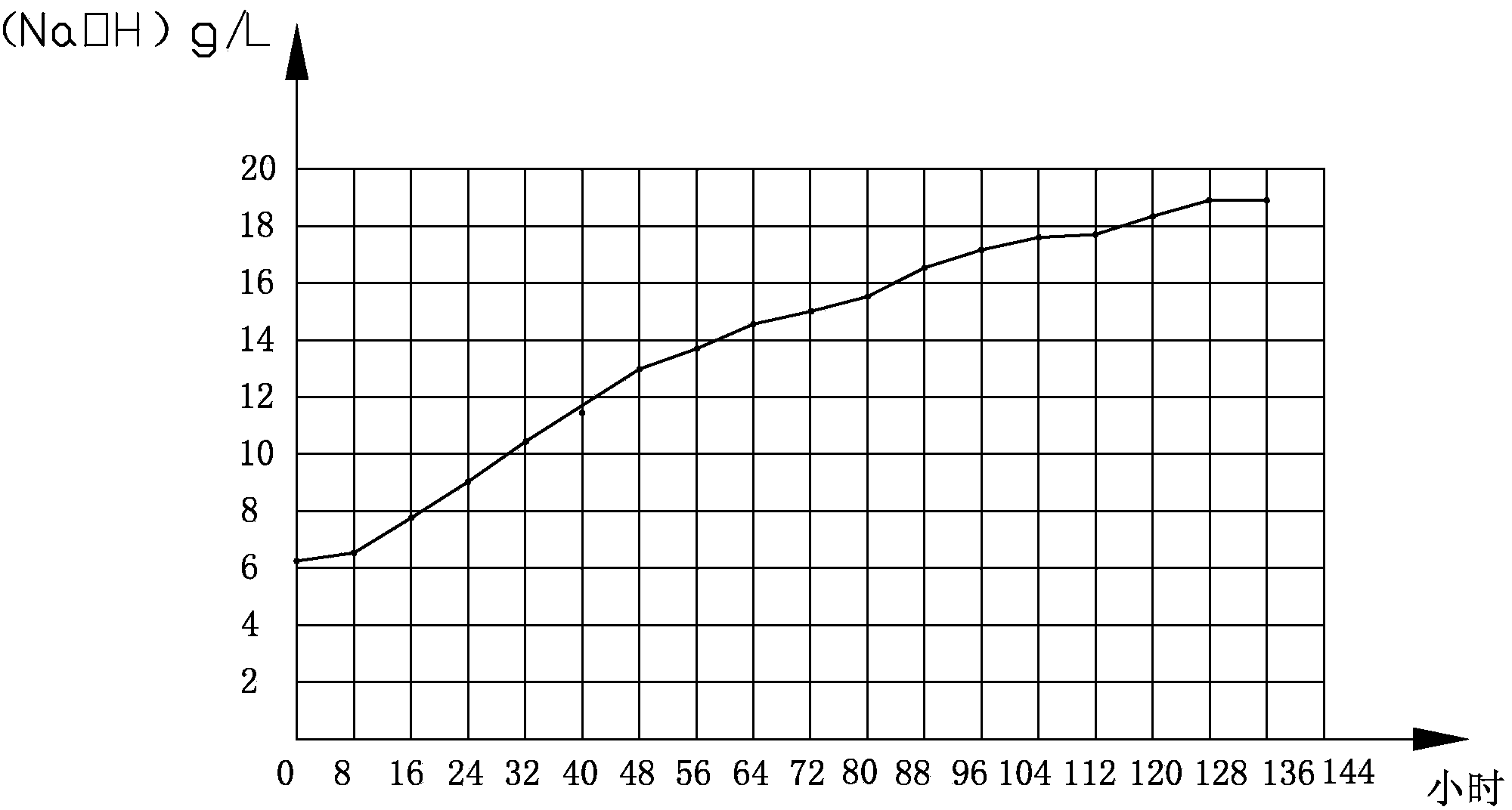
[0092] time h Concentration g / L 0 6.33 8 6.5 16 8 24 9.8 32 11.6 40 12.4 48 15.2 56 16.3 64 17.1 72 18 80 18.3 88 18.5 96 18.9 104 19.1 112 19.3 120 19.3 128 19.3
[0093] Gained cathode sodium hydroxide concentration graph sees figure 1 .
[0094] At the beginning of electrolysis, the current was very small because the temperature was low. As the time of electrolysis increased, the temperature continued to rise. At the beginning, the concentration of sodium hydroxide in the ceramic cylinder was only 1%, but after 16 hours, the current increased rapidly. The concentration of sodium hydroxide also increased sharply, but the current dropped significantly after 72 hours, and the increase rate of the concentration of sodium hydroxide also slowed down. After 96 hours, the current almost dropped to zero, and the bubbles produced by the cathode plate were also very small, which means ...
Embodiment 3
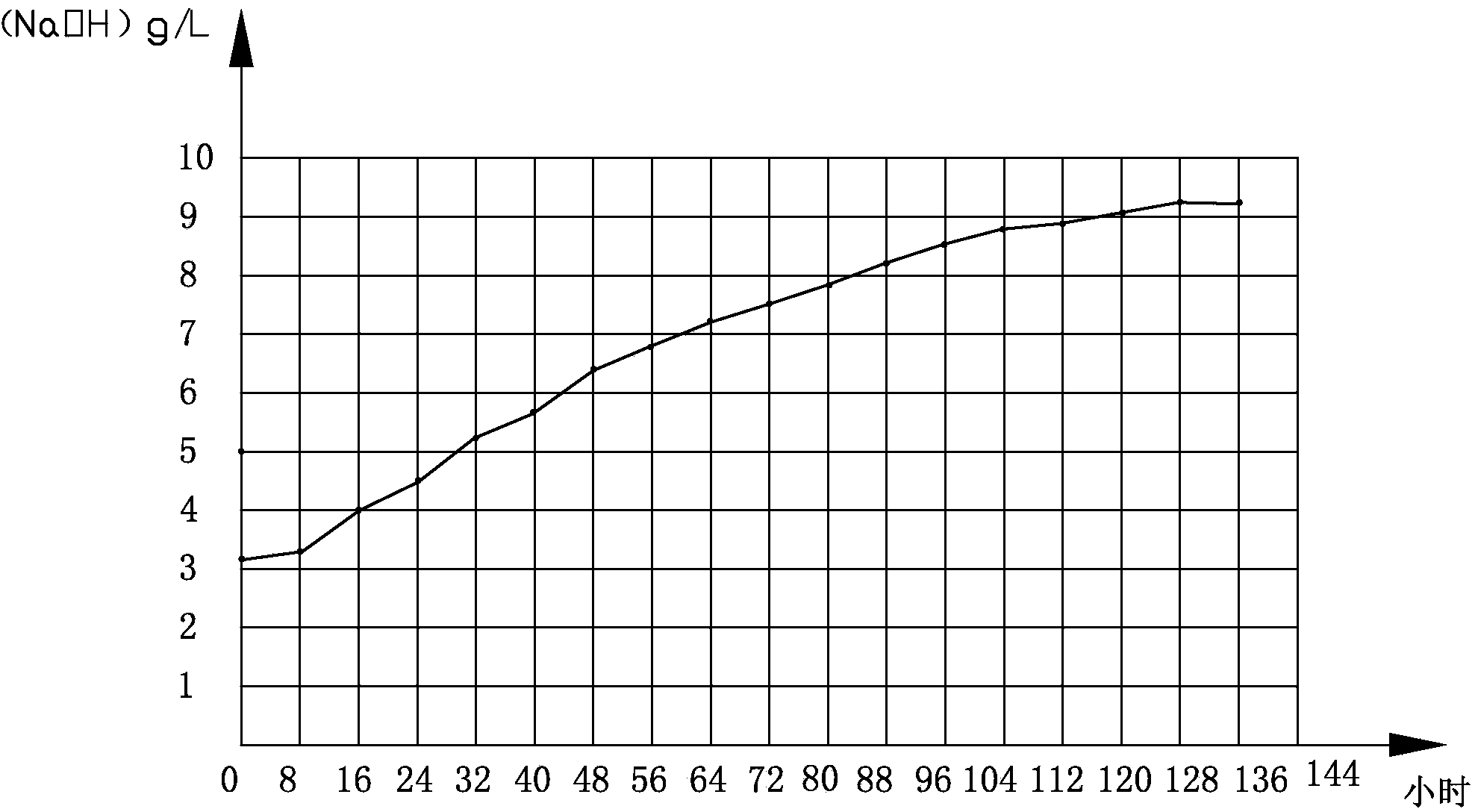
[0096] time h Concentration g / L 0 3.1 8 3.2 16 3.9 24 4.5 32 5.2 40 5.7 48 6.4 56 6.8 64 7.2 72 7.5 80 7.8 88 8.2 96 8.6 104 8.8
[0097] 112 8.9 120 9.1 128 9.3 136 9.3
[0098] Gained cathode sodium hydroxide concentration graph sees figure 2 .
[0099] There are a lot of oxides attached to the outer wall of the ceramic cylinder. The analysis results are as follows:
[0100]
[0101] Compared with the second embodiment of the treatment method of chromic acid wastewater, the biggest difference between this embodiment is that the outer wall of the ceramic cylinder in this embodiment produces a large amount of attachments, which can be easily scraped off.
[0102]The examples of the three chromic acid wastewater treatment methods show that only the ionization concentration of sodium hydroxide in the inner tank should be paid attention to during operation, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com