A new use of a maize-derived transcription factor and its coding gene
A transgenic plant, gene technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, application and other directions, can solve problems such as low nitrogen utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
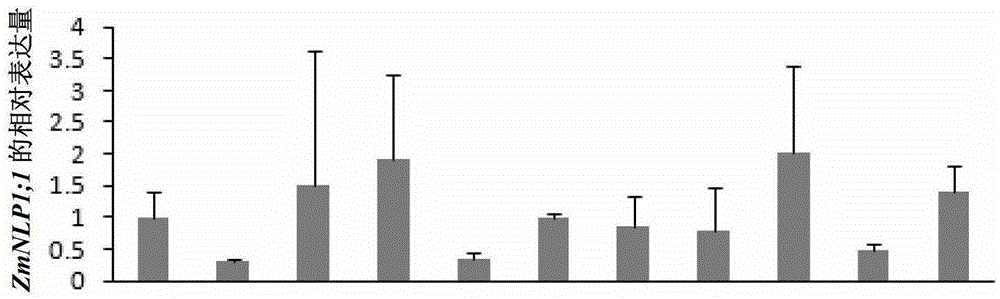
[0067] Example 1. Real-time quantitative PCR (Real-TimePCR) analysis of the expression characteristics of maize ZmNLP1;1 gene tissues
[0068] The maize inbred line B73 (Germplasm Resource Center, Crop Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) was selected. Extract seedling corn roots, seedling corn shoots, new leaves before pollination, old leaves before pollination, panicle leaves before pollination, ear ears before pollination, tassels before pollination, new leaves 15 days after pollination, and 15 days after pollination Total RNA was extracted from old leaves, 15-day post-pollination panicle leaves, 15-day post-pollination cobs, and 15-day-pollination grain samples. The resulting total RNA was removed by DNaseI enzyme (TaKaRa Company) after DNA contamination in the total RNA was removed, and M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega Company) and oligod (T) were used to 18 Reverse transcribe into cDNA first strand. Utilize the method of Real-timePCR, use primers P2...
Embodiment 2
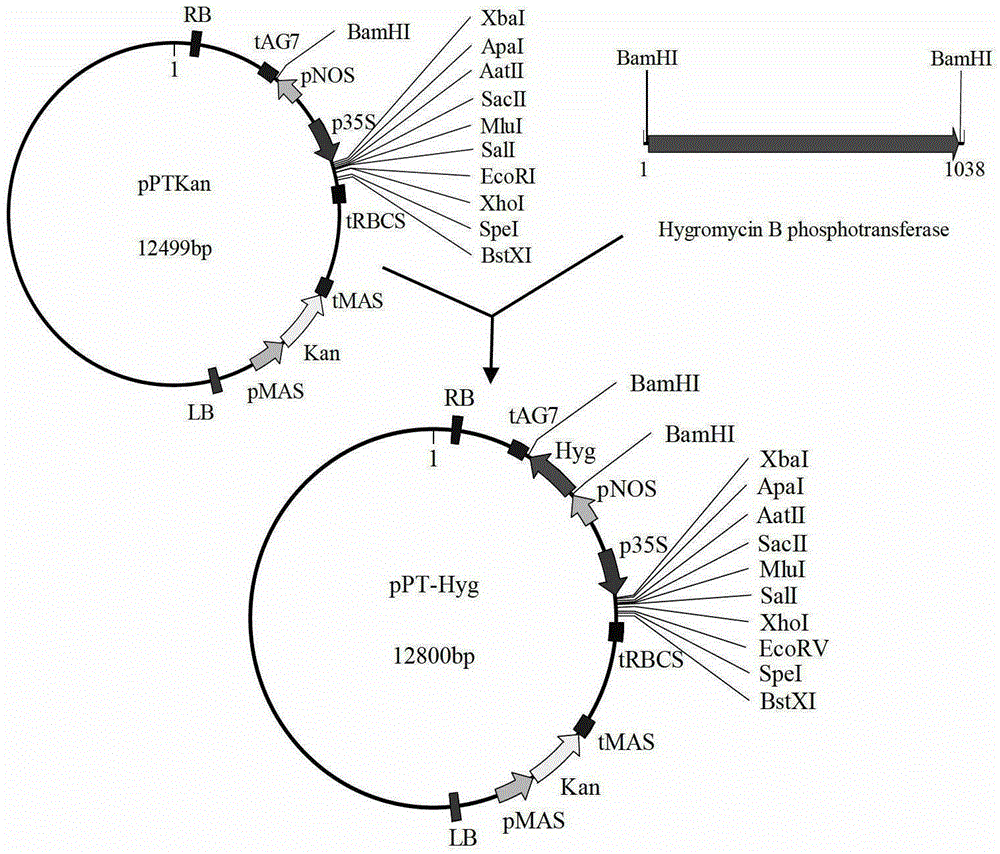
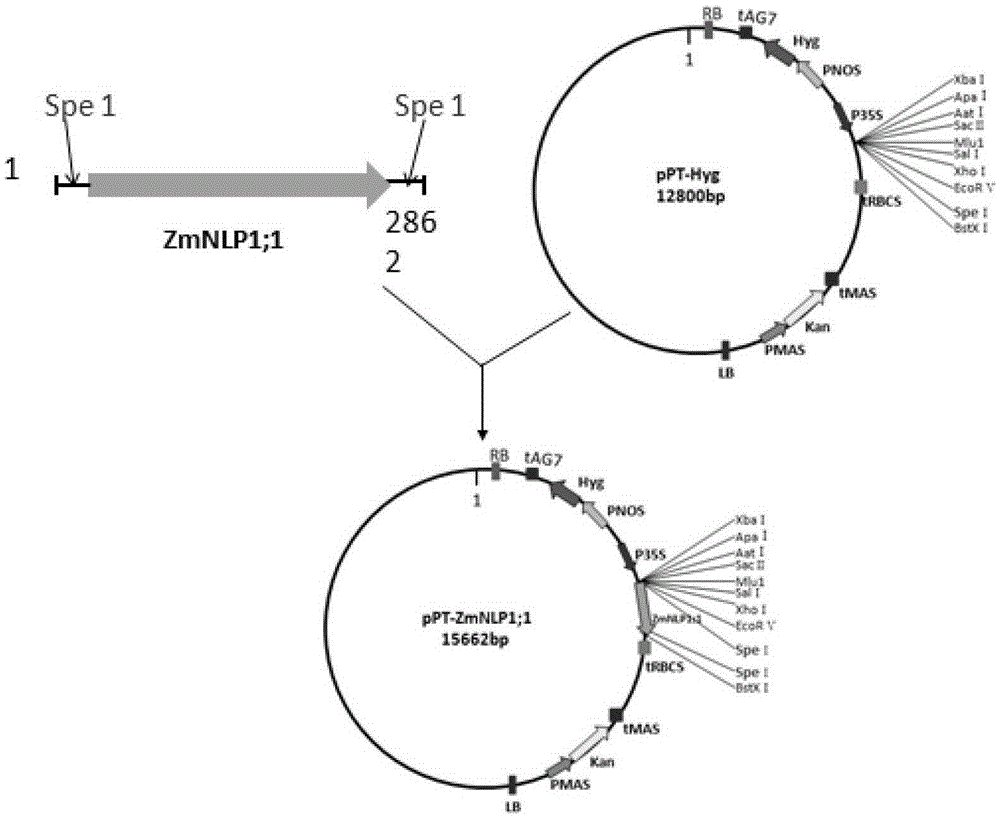
[0091] Embodiment 2, cultivating trans ZmNLP1; 1 gene Arabidopsis
[0092] 1. Amplification of full-length ZmNLP1;1 gene cDNA
[0093] Design a pair of primers P1-F (5'-ATGGAGCAGGCGCCGCAGAC-3') and P1-R (5'-TTACTGCATACAAACCAATCC-3'), where P1-F just contains the translation start codon ATG, and P1-R contains the translation stop codon The sub-TAA; using the cDNA library of reverse transcription of the total RNA of the corn inbred line B73 as a template, was amplified using the high-fidelity PrimerSTAR enzyme to obtain the ZmNLP1;1 gene fragment containing the complete open reading frame (the nucleotide sequence of which is sequence 1 From the 355th to the 3216th nucleotide of the 5' end). Wherein, the reaction system is as follows:
[0094]
[0095] PCR reaction conditions: 98°C pre-denaturation for 2 minutes; then 98°C for 10 seconds, 65°C for 10 seconds, 72°C for 3 minutes and 30 seconds, 30 cycles; then add 1 μl Taq enzyme, 72°C for extension and tailing for 20 minutes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com