Cytoplasmic male sterility restorer gene in rice and application thereof
A technology for male sterility and gene recovery, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering to achieve the effects of improving selection efficiency, speeding up the breeding process, and eliminating the need for test crosses.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
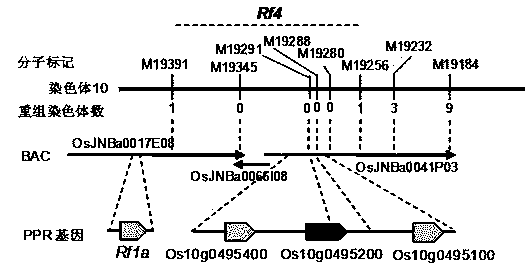
[0044] Example 1 Restoration gene in rice Rf4 positioning and cloning
[0045] The present invention is cloned by map-based cloning Rf4 Gene.
[0046] Firstly, the rice wild-abrupt cytoplasmic male sterile line Zhenshan 97A was crossed with the restorer line Minghui 63 to establish a F 2 Separate the population and select about 2000 sterile plants for Rf4 position. According to the reported preliminary location on chromosome 10 of rice Rf4 The approximate location of the site (Zhang et al., 1997; Zhang Qunyu et al., 2002; Ahmadikhah and Karlov, 2006), in which multiple polymorphic molecular markers as shown in Table 1 were created. with these marks and the F 2 Infertile populations were subjected to linkage analysis to construct a Rf4 The linkage map of locus regions, namely figure 1 . There are 2 marks in the picture namely M19391 and M19256 with Rf4 There is only 1 recombination event between loci, and 4 markers with Rf4 Complete co-segregation, ie zero re...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2 Rf4 Transformation and functional testing of candidate genes
[0052] According to Os10g0495200 upstream and downstream sequence design gene-specific PCR amplification oligonucleotide primers, its primer sequence is as SEQ ID NO:11 (underline is restriction endonuclease Kpn I cut point) and SEQ ID NO:12 (underlined as Xba I cut point).
[0053] SEQ ID NO: 11: 5'-ACTTAT ggtacc TAGCAACTGCGAACACACCCTCAAT-3'
[0054] SEQ ID NO: 12: 5'-CGGTCA tctaga ACCAGCAACCTCCCAACCATGACTAT-3'
[0055] A 7.8 kb genomic fragment containing the promoter, coding region, and downstream termination sequence was amplified from the restorer line Minghui 63 by PCR. The PCR reaction system and reaction conditions are as follows: 1 x reaction buffer, 200 μM dNTPs, 100 ng Minghui 63 genomic DNA, 0.3 μM primers, 1.0 U KOD FX polymerase in a 50 μl reaction. 30 cycles: 97°C 15S, 68°C 6 min. restriction endonuclease Kpn I and Xba Clone into the plant binary transformation v...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Rf4 gene sequence analysis
[0058] The functional types of five wild-type restorer lines Minghui 63, IR24, HNF-W1, HNF-W2, and HNF-W8 were analyzed by PCR amplification and sequencing Rf4 Allele ( Rf4-M, Rf4-I, Rf4-W1, Rf4-W2, Rf4-W8 ) and two non-functional CMS lines Zhenshan 97A and Jin 23A rf4 allele (rf4-Z, rf4-J ). Among them, HNF-W1, HNF-W2, HNF-W8 Rf4 allele ( Rf4-W1, Rf4-W2, Rf4-W8 ) is derived from common wild rice and obtained by crossing and backcrossing an indica rice line with a different common wild rice strain. The sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 are respectively Minghui 63 and IR24 Rf4-M and Rf4-I Genomic DNA fragments of alleles (including the sequence of the promoter region, CDS, and 3' untranslated region); the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:3 to SEQ ID NO:5 are HNF-W1, HNF-W2, HNF-W8 Rf4-W1, Rf4-W2, Rf4-W8 Allele CDS sequence. These functional Rf4 The open reading frame of the allele has 2349 nucleotides,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com