Method for manufacturing zinc-oxide-based p-type materials
A zinc oxide-based, p-type technology, applied in the direction of final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability and low repeatability, and achieve good temperature stability and high repeatability , the effect of increasing the ionization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
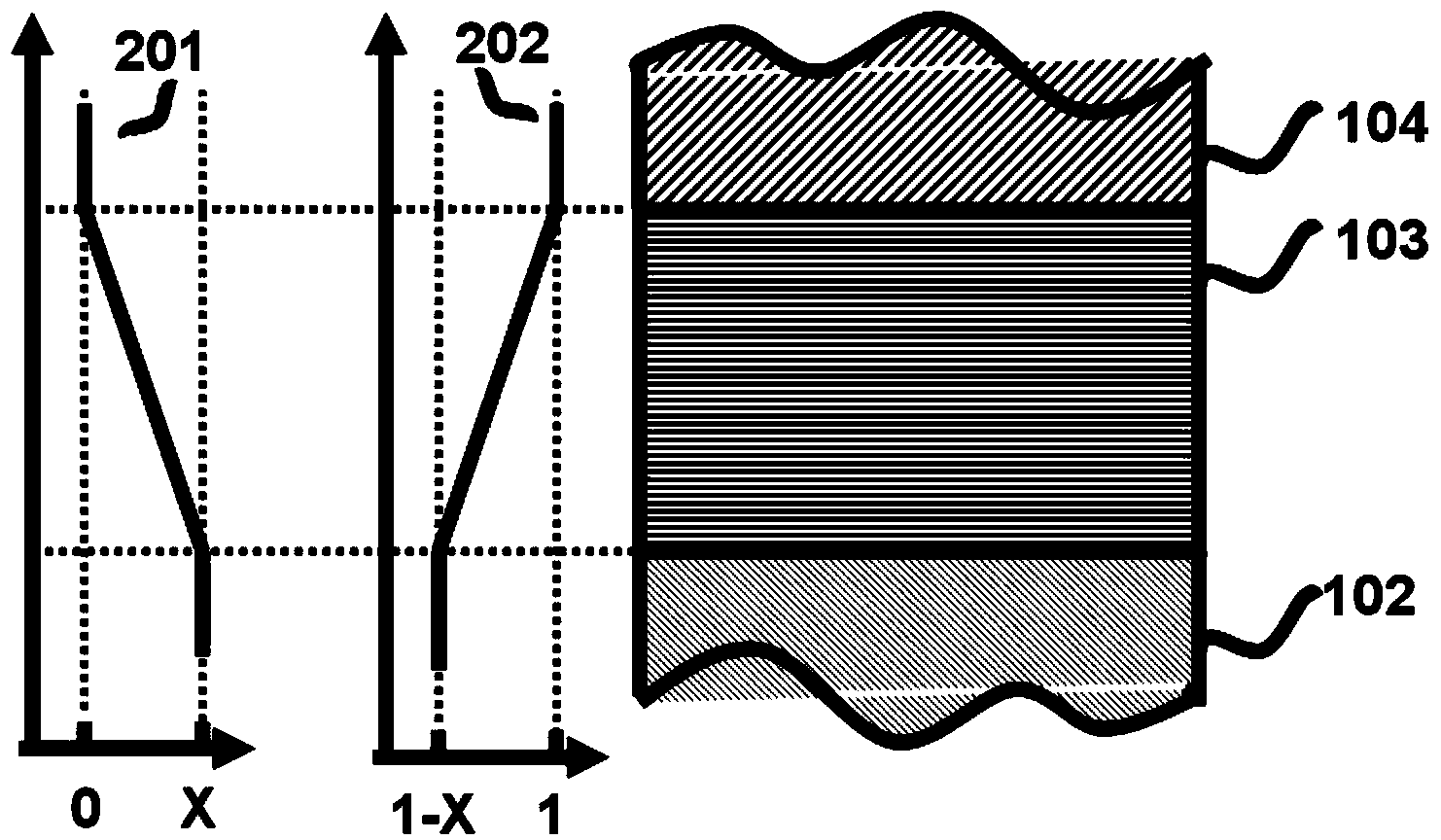
[0023] The invention provides a method for preparing a zinc oxide-based p-type material, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0024] Prepare a gradient layer 103 on the base layer 102;
[0025] Prepare a cover layer 104 on the gradient layer 103;
[0026] The base layer 102 is Mg on the oxygen polar surface x Zn 1-x O material, the thickness of the base layer is not less than 5nm, preferably 20-50nm, and it must have a complete structure to control the polarity of the subsequent structure;
[0027] The gradient layer 103 has a composition gradient structure, and the Mg composition of the gradient layer gradually decreases from x (0.6≥x≥0.2) in the base layer to 0 as the thickness changes, and its structure can be expressed as Mg from bottom to top x Zn 1-x O / Mg x-δ Zn 1-(x-δ) O / Mg x-2δ Zn 1-(x-2δ) O / … / Mg x-(n-1)δ Zn 1-[x-(n-1)δ] O / Mg x-nδ Zn 1-(x-nδ) O(ZnO) (δ→0, n is a natural number; nδ=x; abbreviated as graded-MgZnO), δ is a value close to 0 betwee...
Embodiment 1
[0035] The specific implementation method of preparing polarization-induced p-type ZnO material by MOCVD
[0036] Zinc source adopts diethyl zinc, magnesium source adopts dimethyl dimagnesocene, oxygen source adopts oxygen, zinc source and magnesium source are contained in bubble bottles, and the active ingredients in the bubble bottles are carried by carrier gas (nitrogen) It can be seen that the organic source pipeline of the MOCVD system in this embodiment is a standard pipeline, so the amount of the source passed into the reaction chamber is related to the temperature of the source and the flow rate of the carrier gas (the higher the temperature of the source, the greater the flow rate of the carrier gas, the greater the flow rate of the carrier gas through the greater the amount of source that enters the reaction chamber).
[0037] Step 1, substrate preparation: clean the C-plane sapphire substrate of oxygen polarity, and place it in the MOCVD reaction chamber (correspond...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com