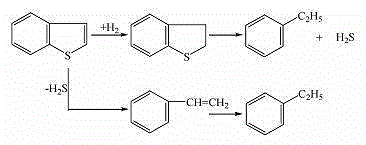
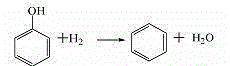
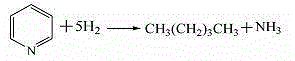A method for preparing gasoline high-octane number blending components from coking by-products
A coking by-product, high-octane technology, applied in the petroleum industry, hydrocarbon oil treatment, hydrotreating process, etc., can solve problems such as poor stability, complex composition, and low added value of products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] The heavy fraction of light oil and dephenolized phenol oil are mixed in a ratio of 2:5 to obtain raw material oil. The raw oil is mixed with hydrogen and then enters into a fixed bed reactor equipped with a hydrogenation catalyst for hydrogenation reaction. The optimal hydrogenation reaction conditions : The temperature is 260~340℃, the pressure is 2.4~3.6Mpa, the hydrogen oil ratio (volume) is 650~850:1, and the liquid space velocity is 0.9~1.0h -1 ; The reaction product is cooled by a heat exchanger, and then separated by a gas-liquid separator, and the gas is absorbed by the lye to absorb H 2 After S, hydrogen is recovered; hydrogen is recycled; the product oil is separated by a rectifying tower, the light components mainly benzene are separated from the top of the column, the heavy fractions are obtained at the bottom of the column, and the gasoline high-octane blending components are separated from the side line. In the fixed bed reactor, according to the directio...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The three-mixed dephenolized phenol oil and heavy benzene are mixed into a raw material oil in a ratio of 1:3. The raw material oil is mixed with hydrogen and then enters a fixed bed reactor equipped with a hydrogenation catalyst for hydrogenation reaction. The optimal hydrogenation reaction Conditions: Temperature is 330~420℃, pressure is 4.0~4.6Mpa, hydrogen oil ratio (volume) is 1200~1400:1, liquid space velocity is 0.2~1.0h -1 ; The reaction product is cooled by a heat exchanger, and then separated by a gas-liquid separator to obtain a different oil, and the gas absorbs H through the lye 2 After S, hydrogen is recovered; hydrogen is recycled; the product oil is separated by a rectifying tower, the light components mainly benzene are separated from the top of the column, the heavy fractions are obtained at the bottom of the column, and the gasoline high-octane blending components are separated from the side line. According to the direction of the material in the fixe...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The heavy fraction of light oil and heavy benzene are mixed into feedstock oil at a ratio of 1:2. The feedstock oil is mixed with hydrogen and then enters a fixed bed reactor equipped with a hydrogenation catalyst for hydrogenation reaction. The optimal hydrogenation reaction conditions: temperature The temperature is 270~390℃, the pressure is 1.8~3.8Mpa, the hydrogen oil ratio (volume) is 650~1500:1, and the liquid space velocity is 0.2~1.2h -1 ; The reaction product is cooled by a heat exchanger, and then separated by a gas-liquid separator to obtain oil, and the gas absorbs H through lye 2 After S, hydrogen is recovered; hydrogen is recycled; the product oil is separated by a rectifying tower, the light components mainly benzene are separated from the top of the column, the heavy fractions are obtained at the bottom of the column, and the gasoline high-octane blending components are separated from the side line. In the fixed bed reactor, according to the direction of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com