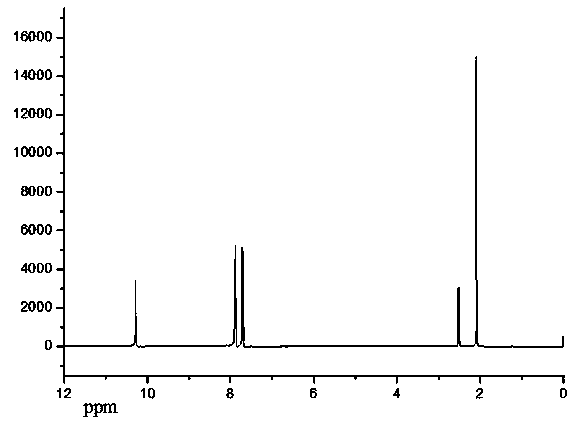
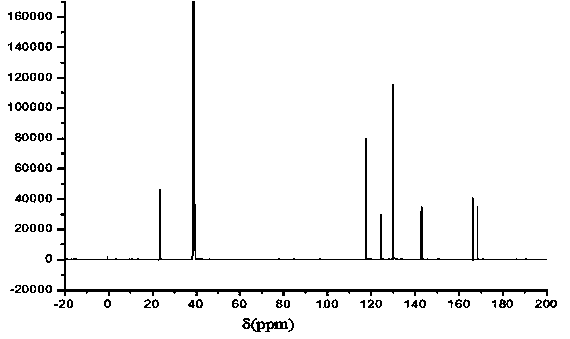
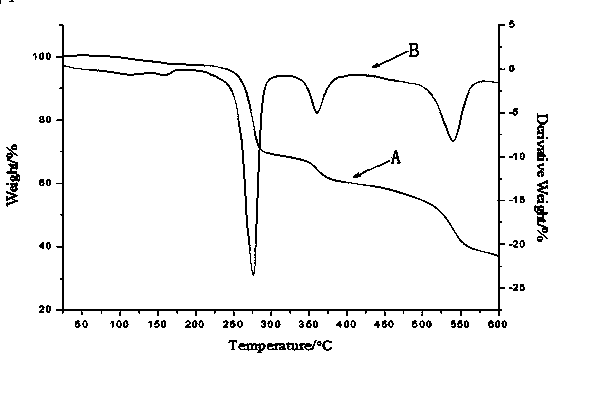
P-N expanded reaction type flame retardant and preparation method thereof
An expansion reaction, P-N technology, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve the problems of smoke, large amount of addition, affecting mechanical properties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of P-N series intumescent reactive flame retardant
[0026] (a) Add 0.13mol of acrylic acid to a 250ml three-neck flask equipped with a constant pressure low liquid funnel, stirrer and reflux device, stir magnetically at a rate of 200rpm and raise the temperature to 90°C. At this time, add 0.1mol of benzene Phosphorous dichloride, the dropping rate is controlled at 1.0ml / min, and the dropping time is 2h; after the dropping is completed, the temperature is raised to 110°C and refluxed, and the reaction is continuously stirred at 200rpm for 4h. After the reaction is completed, the solution becomes a colorless transparent liquid. It is 2-carboxyethylphenylphosphorous acid;
[0027] (b) Cool the 2-carboxyethylphenylphosphorous acid obtained in step a to 1°C in a low-temperature reaction constant temperature bath, add 0.26mol triethylamine acid-binding agent, raise the temperature to 5°C, and take 0.2mol p-aminobenzene Dissolve formic acid in glacial a...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Add 0.13 mol of acrylic acid to a 250 ml three-necked flask equipped with a constant-pressure low-liquid funnel, a stirrer and a reflux device, stir magnetically at a rate of 200 rpm and heat up to 90 ° C. The dropping rate was controlled at 1.0ml / min, and the dropping time was 2h; after the dropping was completed, the temperature was raised to 110°C for reflux, and the stirring reaction was continued at a rate of 200rpm for 4h. - Carboxyethylphenylphosphorous acid;
[0042] Place the above product in a low-temperature reaction constant temperature bath and cool it to about 1°C, add 0.26mol triethylamine acid-binding agent, heat up to 5°C, dissolve 0.19mol p-aminobenzoic acid in glacial acetic acid, add it to 2-carboxyethyl In the mixed solution of phenylphosphinic acid and triethylamine, stir the reaction at a rate of 200rpm for 2h, then raise the temperature to 80°C, and continue to stir the reaction at a rate of 200rpm for 4h; After suction filtration and drying, a ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Add 0.13 mol of acrylic acid to a 250 ml three-necked flask equipped with a constant-pressure low-liquid funnel, a stirrer and a reflux device, stir magnetically at a rate of 200 rpm and heat up to 90 ° C. The dropping rate was controlled at 1.0ml / min, and the dropping time was 2h; after the dropping was completed, the temperature was raised to 110°C for reflux, and the stirring reaction was continued at a rate of 200rpm for 4h. - Carboxyethylphenylphosphorous acid.
[0045] Put the above product in a low-temperature reaction constant temperature bath and cool it to about 1°C, add 0.26mol triethylamine acid-binding agent, heat up to 5°C, dissolve 0.21mol p-aminobenzoic acid in glacial acetic acid, add it to 2-carboxyethyl In the mixed solution of phenylphosphinic acid and triethylamine, stir the reaction at a rate of 200rpm for 2h, then raise the temperature to 80°C, and continue to stir the reaction at a rate of 200rpm for 4h; After suction filtration and drying, a wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com