Method for producing zaltoprofen and derivative thereof
A manufacturing method and technology of derivatives, applied in the direction of drug combinations, active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, antipyretics, etc., can solve problems such as dimers not being removed, purity that cannot be said to be sufficient, toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
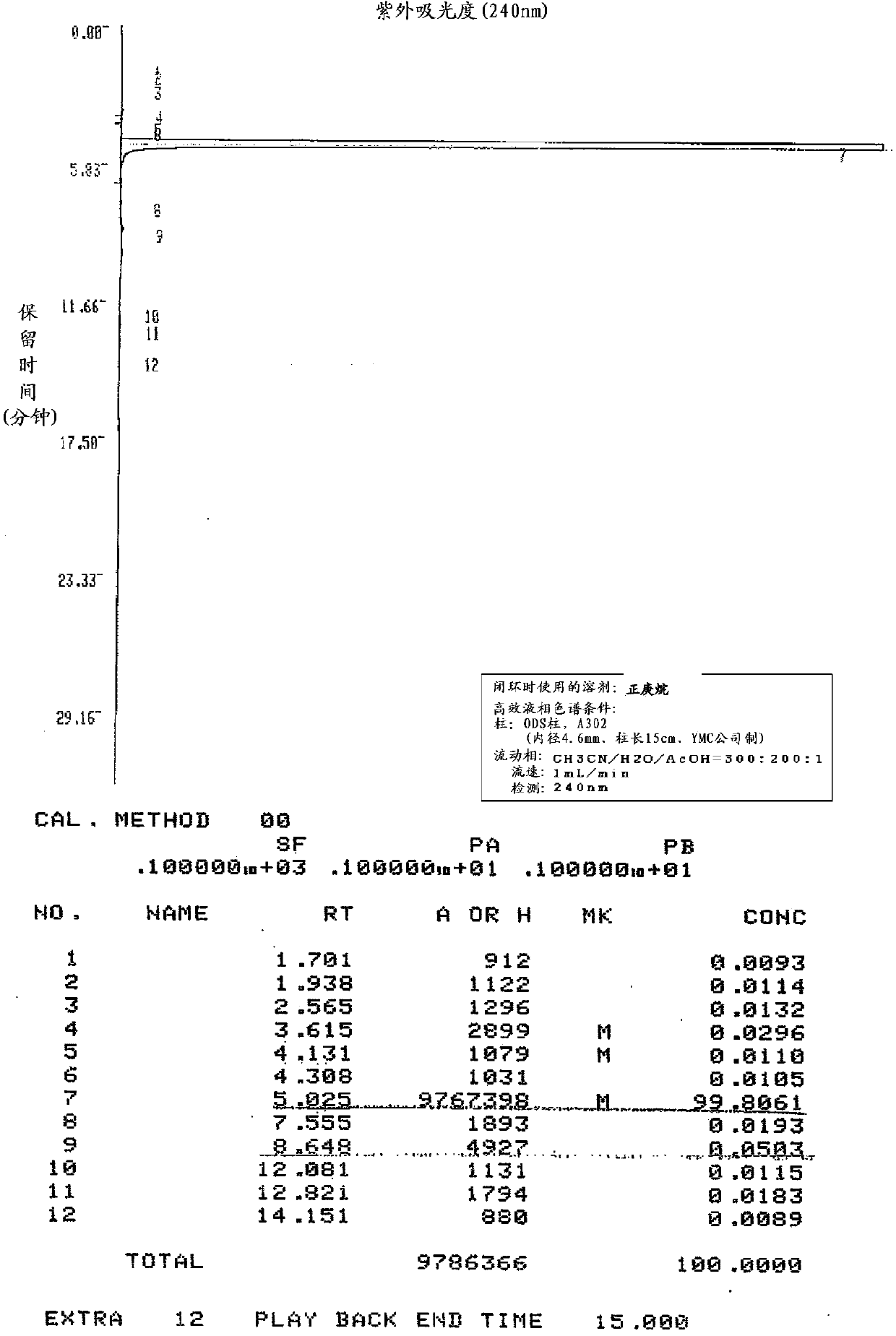
[0146] Production of zaltoprofen by ring closure in the presence of methylcyclohexane
[0147] In the 5-(1-carboxyethyl)-2-phenylthiophenylacetic acid shown in the following formula (IV) of 50g (0.158mol), add the polyphosphoric acid of 250g degree of condensation 105% and the methyl Cyclohexane was stirred at an internal temperature of 90 to 95°C for 3.5 hours while slowly heating. Thereafter, heating was stopped, and when the internal temperature reached 45° C., 250 mL of water and 250 mL of ethyl acetate were simultaneously added dropwise, and the organic solvent layer was fractionated. The aqueous layer was extracted with 150 mL of ethyl acetate, the separated ethyl acetate and the organic solvent layer were combined, 200 mL of water and 200 mL of brine were added, and the organic solvent layer was separated and washed. After adding 50 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to the fractionated organic layer for dehydration, the organic solvent was distilled off under reduced pre...
Embodiment 2
[0151] Production of zaltoprofen by ring closure in the presence of n-heptane
[0152] In the 5-(1-carboxyethyl)-2-phenylthiophenylacetic acid shown in the following formula (IV) of 100g (0.316mol), add the polyphosphoric acid of 500g degree of condensation 105% and the n-heptyl of 120mL alkane, and stirred at an internal temperature of 98° C. for 4.5 hours while heating slowly. Thereafter, heating was stopped, and when the internal temperature reached 45° C., 500 mL of water and 500 mL of ethyl acetate were simultaneously added dropwise with an internal temperature of 60° C. as the upper limit, and the organic solvent layer was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with 300 mL of ethyl acetate, combined with the above organic solvent layer, and after adding 500 mL of water and 500 mL of saline, the organic solvent layer was separated and washed. After adding 50 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to the fractionated organic layer for dehydration, the organic solvent was dis...
Embodiment 3
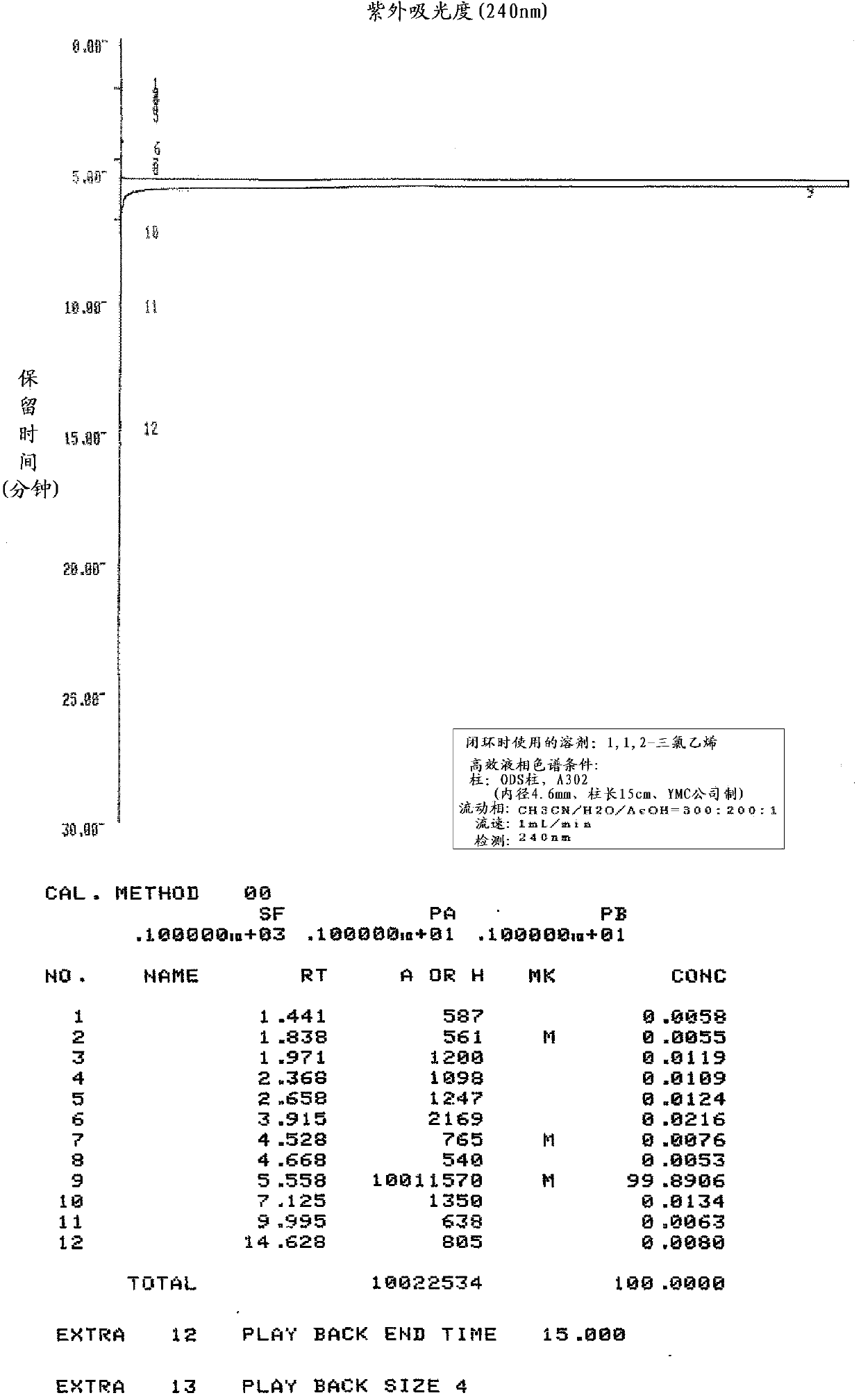
[0156] Production of zaltoprofen by ring closure in the presence of 1,1,2-trichloroethylene
[0157] In 5-(1-carboxyethyl)-2-phenylthiophenylacetic acid shown in the following formula (IV) of 5.20g (16.4mmol), add polyphosphoric acid and 8.0mL polyphosphoric acid of 33.5g degree of condensation 105% 1,1,2-trichloroethylene was stirred at an internal temperature of 89° C. for 3 hours while slowly heating. Thereafter, heating was stopped, and when the internal temperature reached 40° C., 25 mL of water and 25 mL of ethyl acetate were simultaneously added dropwise with an internal temperature of 60° C. as the upper limit, and the organic solvent layer was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with 15 mL of ethyl acetate, and the separated ethyl acetate was combined with the above organic solvent layer to obtain the zaltoprofen fraction. After adding 30 mL of water and 30 mL of saline to the zaltoprofen portion, the organic solvent layer was separated and washed. After ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com