Sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet based on crystal grain recombination and manufacturing method
A manufacturing method and permanent magnet technology, which is applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, permanent magnets, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of easy oxidation of the base material, affecting product yield and particle size distribution, and affecting the particle size of powder making, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
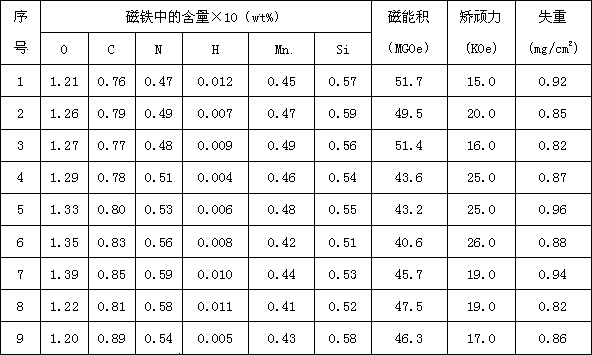
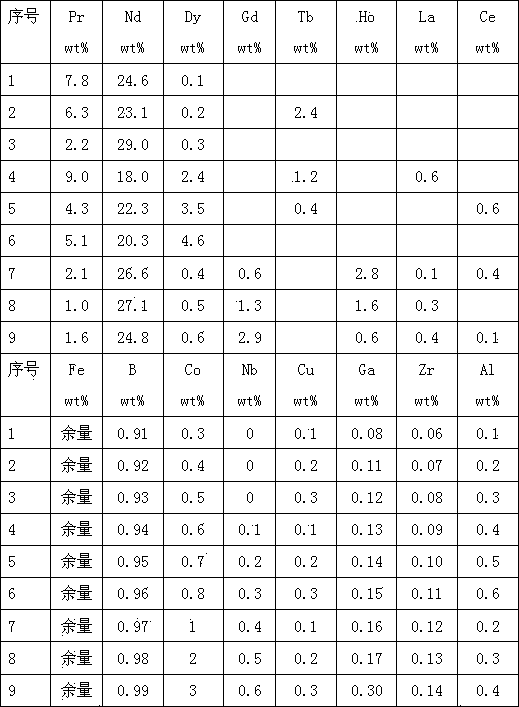
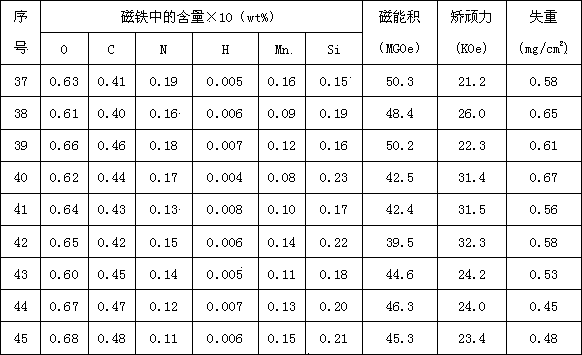
[0048] Raw materials containing Pr and Nd are batched according to serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into vacuum melting and quick-setting equipment to prepare vacuum quick-setting alloy flakes as the first alloy; the average grain size of the alloy flakes of the first alloy is greater than 1.6 μm , less than 3.9 μm; then the raw materials containing Pr, Nd, and Dy components are batched according to the serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into the vacuum quick-setting alloy sheet prepared by the vacuum melting quick-setting equipment as the second alloy; the second alloy The average grain size of the alloy sheet is greater than 1.1 μm and less than 2.9 μm; the first and second alloy smelting are both carried out in a vacuum Mn removal process, and the Mn removal process controls the heating temperature in the range of 400-1500 ° C and controls the vacuum degree to 5×10 3 Pa to 5×10 -2 Pa range, holding time 10-240 minutes; then c...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The raw materials containing Pr and Nd are batched according to the serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into the double-roller cooled vacuum melting quick-setting equipment to prepare double-sided cooled quick-setting alloy flakes as the first alloy; the alloy flakes of the first alloy The average grain size is greater than 2.6 μm and less than 3.0 μm; then the raw materials containing Pr, Nd, and Dy are batched according to the serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into the double-roller cooling vacuum melting and quick-setting equipment to prepare double-sided cooling Quick-setting alloy flakes are used as the second alloy; the average grain size of the alloy flakes of the second alloy is greater than 2.5 μm and less than 2.9 μm; the first and second alloy smelting are all carried out in a vacuum de-Mn process, and the de-Mn process controls the heating temperature 400-1450°C range, control vacuum 5×10 3 Pa to 5×10 -1 Pa ran...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The raw materials containing Pr and Nd are batched according to the serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into the double-roller cooled vacuum melting quick-setting equipment to prepare double-sided cooled quick-setting alloy flakes as the first alloy; the alloy flakes of the first alloy The average grain size is greater than 2.6 μm and less than 3.0 μm; then the raw materials containing Pr, Nd, and Dy are batched according to the serial numbers 1-9, and then the raw materials are loaded into the double-roller cooling vacuum melting and quick-setting equipment to prepare double-sided cooling Quick-setting alloy flakes are used as the second alloy; the average grain size of the alloy flakes of the second alloy is greater than 1.1 μm and less than 1.5 μm; the first and second alloy smelting are all carried out in a vacuum de-Mn process, and the de-Mn process controls the heating temperature 500-1400℃ range, control vacuum degree 5×10 1 Pa to 5×10 -1 P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com