Adaptive line loss compensation circuit for DC-DC (direct current) converter
A DC-DC, line loss compensation technology, applied in the direction of converting DC power input to DC power output, instruments, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve, limited process, and high performance requirements, to reduce process costs and simplify compensation. The effect of simple circuit and circuit structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
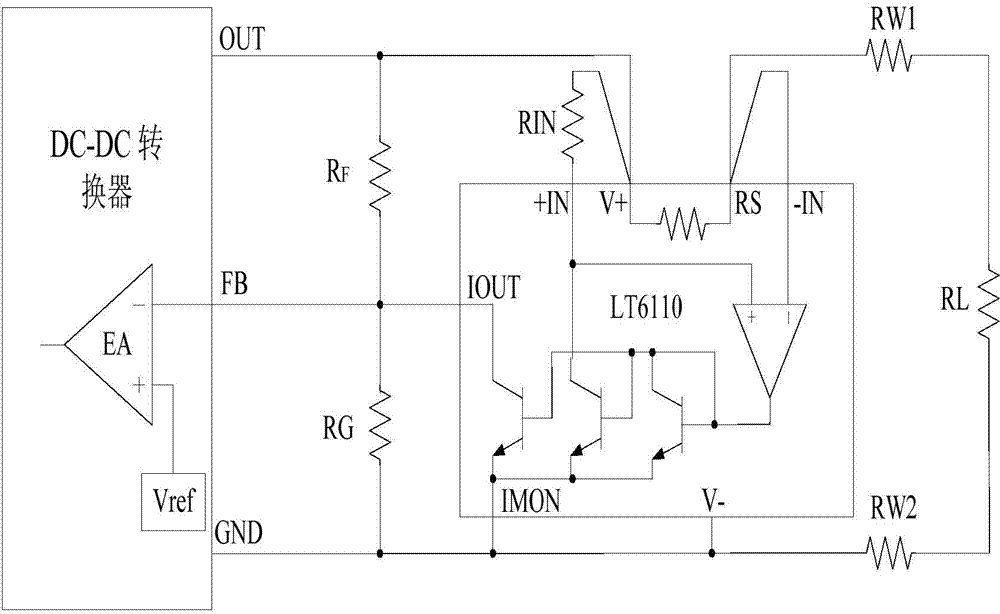
Embodiment 1
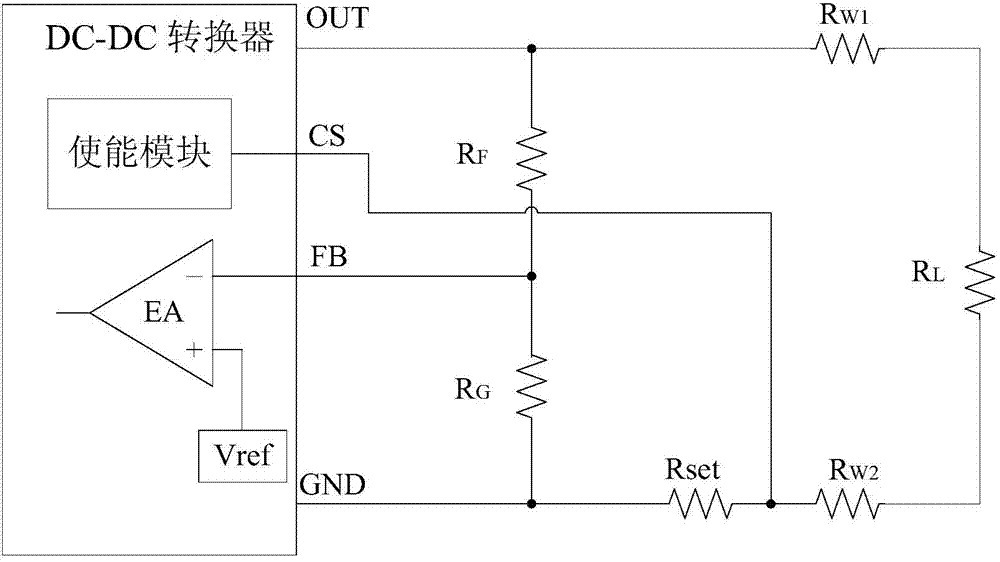
[0035] The circuit structure of the DC-DC converter adopted in the present invention is as image 3 shown with an external current limiting resistor. Among them, R W1 , R W2 Is the resistance of the power line, Rset is an external current limiting resistor, it can detect the load current, and output a CS terminal voltage signal proportional to the load current. When the load current exceeds the preset threshold, the CS signal will turn off the DC-DC converter to protect the DC-DC converter. When the DC-DC converter works normally, the signal voltage at the FB terminal is equal to the reference voltage Vref. When using this converter, the output voltage OUT can be set by adjusting the ratio of the voltage dividing resistors RF and RG.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the line loss compensation circuit of the present invention includes an operational amplifier A, an NMOS transistor M, a low-side current sampling resistor Rset and a compensation resistor Rcom. One end of the low-side current sampling resistor Rset and the compensation resistor Rcom are commonly grounded, the other end of Rset is connected to the CS terminal, and the other end of Rcom is connected to the Vcom terminal; the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier A is connected to the CS terminal, and the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier A The terminal is connected to the Vcom terminal, and the output terminal of the operational amplifier A is also connected to the gate of the NMOS transistor M; the source of the NMOS transistor M is connected to the Vcom terminal, and the drain of the NMOS transistor M is connected to the FB terminal.
[0038] When the DC-DC converter works normally, the signal voltage ...
Embodiment 3
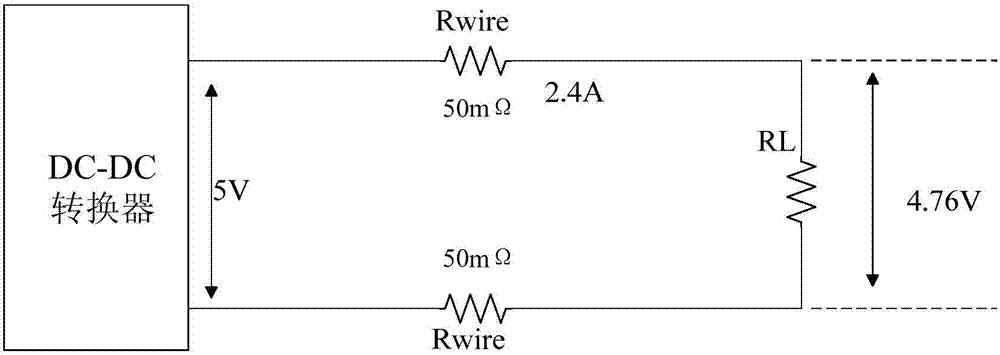
[0043] The circuit of the present invention is applied to a current mode, PWM control, step-down DC-DC converter. The input voltage of the converter is 12V, the output voltage is set to 5V, Rset=100mΩ, R W1 =R W2 =50mΩ, when the load current jumps from 0.5A to 3A, the voltage at both ends of the load before and after line loss compensation is as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0044] Load regulation is defined as the change of output voltage caused by the change of unit load current, and its mathematical expression is based on Figure 5 Based on the simulation results, the load regulation rate before and after compensation can be calculated.
[0045] Before compensation: LR 0 = 4.93 V - 4.42 V 3.00 A - 0.50 A = 0.204 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com