Method for quickly detecting extracellular respiratory activity of microorganisms
A microbial and external respiration technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of detecting extracellular respiration activity and achieve high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
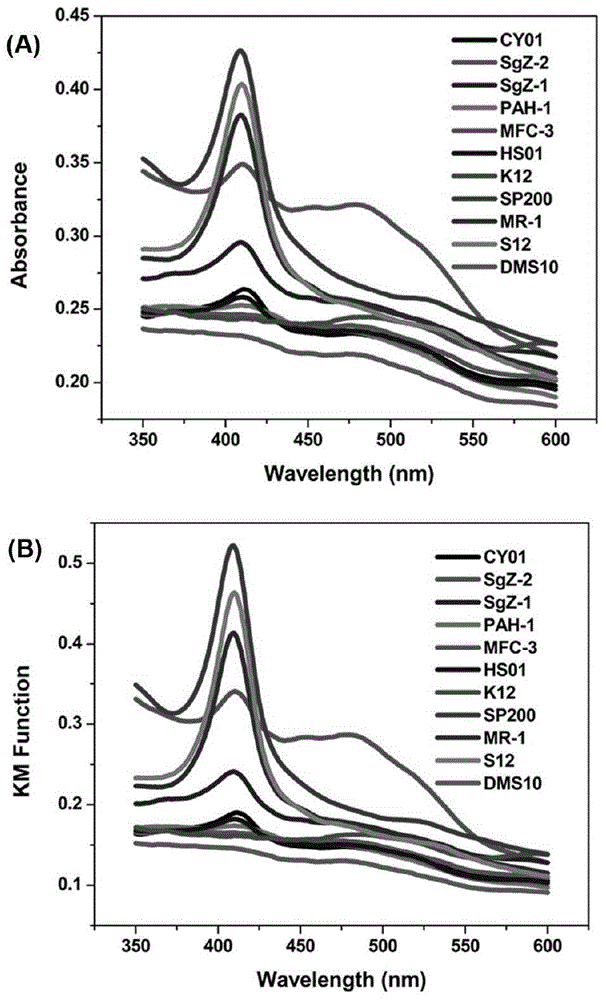
[0046] Example 1: Microbial Cytochrome c Diffuse Reflectance Spectrum Scanning
[0047] (1) Preparation of microbial suspension
[0048] Inoculate the microbial preservation solution in a test tube containing 5ml of sterile LB medium at a ratio of 1:50, culture at 30°C with shaking at 180rpm until the logarithmic growth phase; centrifuge the culture solution at 7000g for 5min, and pour off the supernatant Collect the precipitate and wash it 3 times with HEPES buffer; adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution to OD600 of about 0.5 (about 2.5×10 8 CFU / mL), store at 4°C until use.
[0049] (2) Diffuse reflectance spectrum scanning
[0050] Take a quartz cuvette with 1cm optical path and 1ml volume, and use 1ml HEPES buffer as a blank to calibrate the diffuse reflectance absorption spectrum of the integrating sphere; Reflection Absorption Spectrum. According to the Kubelka-Munk equation F(R)=(1-R∞) 2 / (2R∞)=K / S Calculate the content of microbial cytochrome c. ...
Embodiment 2
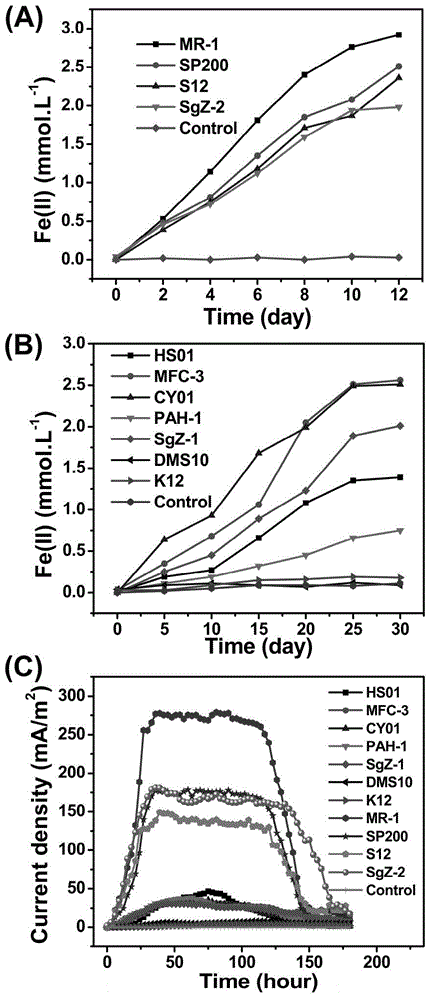
[0051] Embodiment 2: the method for rapid detection microbial extracellular respiration activity
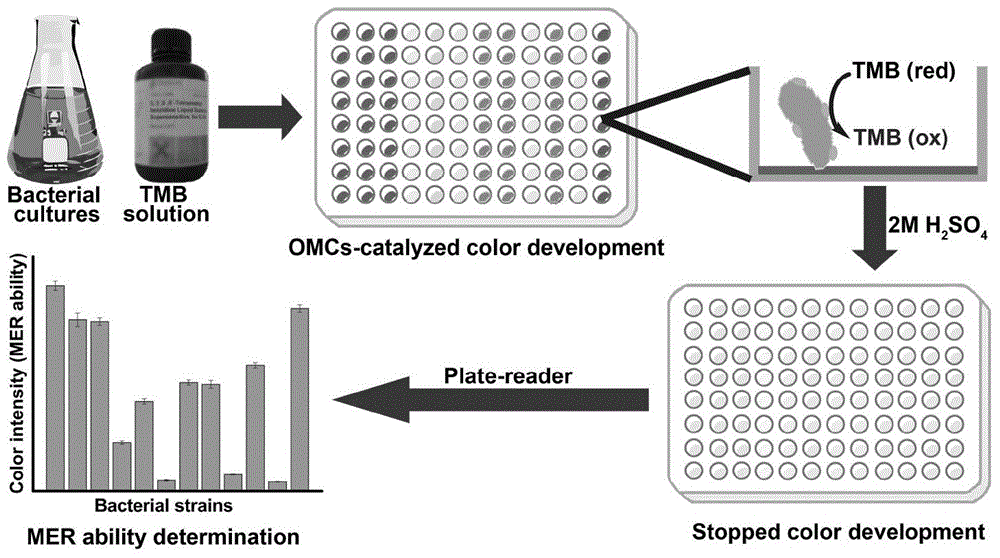
[0052] rapid detection of microorganisms ( Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, Shewanella putrefaciens SP200, Shewanella decolorationis S12, Pantoea agglomerans MFC-3, Aeromonas hydrophila HS01, Comamonas guandongensis CY01, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAH-1, Fontibacter ferrireducens SgZ-2, Thauera humireducens SgZ-1, Escherichia coli K12 and Bacillus subtilis DMS10) Schematic diagram of the extracellular respiration activity method as shown in figure 1 As shown, the specific operation steps are:
[0053] 1) Add 100 μL to a 96-microwell plate to prepare the bacterial suspensions of the above-mentioned microorganisms according to the method described in Example 1;
[0054]2) Then add 100 μL of chromogenic solution (100 mM sodium citrate, 200 mM disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.32 mM tetramethylbenzidine and 2 mM hydrogen peroxide, pH 4.3) to the above 96-well plate, r...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3 The method for rapid detection of microbial extracellular respiration activity
[0085] 1) Preparation of the microbial suspension to be tested
[0086] microbes Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 preservation solution was inoculated in a test tube containing 5ml of sterile LB medium at a ratio of 1:50, cultured at 30°C with shaking at 180rpm to logarithmic growth phase; centrifuged at 7000g for 5min, and poured off the supernatant The precipitate was collected from the solution, and washed three times with normal saline; the concentration of the bacterial solution was adjusted to 2.5×10 8 About CFU / mL, which is the microbial suspension to be tested, stored at 4°C for later use;
[0087] 2) Add the chromogenic solution to the microbial suspension to be tested for color reaction
[0088] Add the above-prepared bacterial suspension into a 96-well plate, 100 μL per well; use an 8-channel pipette to absorb 100 μL of the chromogenic solution and add it to the 96-wel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com