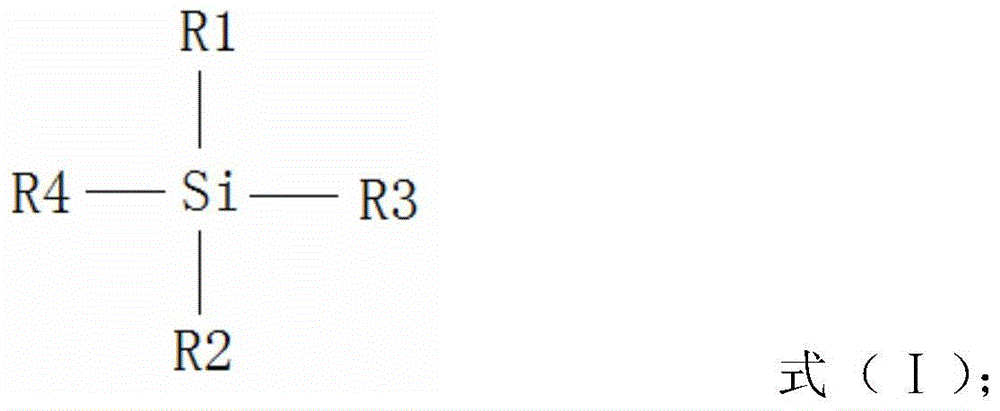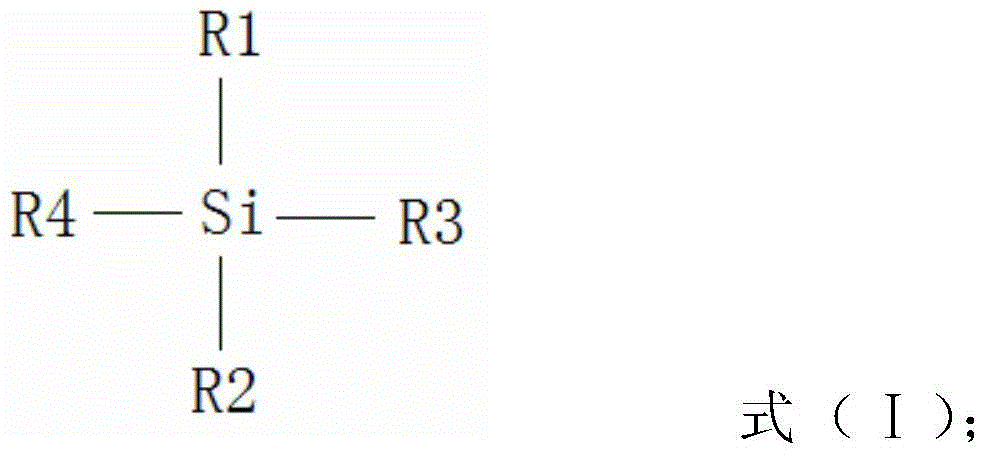Method for extracting and separating l-lactic acid from ammonium lactate fermentation feed liquid
A technology for fermentation material and ammonium lactate, applied in the field of L-lactic acid extraction, can solve the problems of low yield, high production cost, large energy consumption and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] In this embodiment, the method for extracting and separating L-lactic acid from the ammonium lactate fermentation feed liquid comprises the following steps:
[0035] (1) Pretreatment of ammonium lactate fermentation feed liquid: use membrane filtration or centrifuge to pretreat the ammonium lactate fermentation feed liquid, remove the bacteria and nutrients in the fermentation feed liquid, and return the separated bacteria and nutrients to lactic acid The fermentation process continues to participate in the fermentation to realize the recycling of bacteria.
[0036] (2) Sulfuric acid acidolysis of ammonium lactate: join the sulfuric acid solution that mass fraction is 96% in the ammonium lactate fermentation feed liquid that obtains after pretreatment, make the pH=1.5 of feed liquid acidolysis end point, and concentrate or add water to dilute, Make the mass fraction of L-lactic acid in the acidolysis feed solution be 25%.
[0037] (3) Add the acidolysis feed liquid and...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the coupling adsorbent is composed of 25 kg of coupling agent, 100 kg of loading solvent and 8 kg of coupling accelerator. The coupling agent is polydimethylsiloxane, the loading solvent is oleyl alcohol, and the coupling accelerator is soybean lecithin.
[0045] At 24 degrees Celsius, the coupling adsorbent of this embodiment and the lactic acid acid hydrolysis solution with a mass fraction of L-lactic acid of 25% were added to the centrifugal extractor respectively, and the mass ratio of the coupling adsorbent to the lactic acid acid hydrolysis solution was 1: 3. The aqueous phase and the organic phase are separated, and the mass percentage content of L-lactic acid in the aqueous phase is detected. The results showed that 82.1wt% of L-lactic acid in the lactic acid acid hydrolysis solution was extracted by the coupled adsorbent.
[0046]After reverse-coupling adsorption separation of L-lactic acid in th...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the coupling adsorbent is composed of 35 kg of coupling agent, 100 kg of loading solvent and 15 kg of coupling accelerator. The coupling agent is dimethylsiloxane with hydroxyl groups.
[0049] The dimethylsiloxane with hydroxyl is shown in formula (I):
[0050]
[0051] In formula (I): R3 and R4 are both CH 3 O-, R1 is CH 3 -, R2 is HOCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 -. The loading solvent is methyl acetate, and the coupling accelerator is soybean lecithin.
[0052] At 24 degrees Celsius, the coupling adsorbent of this embodiment and the lactic acid acid hydrolysis solution with a mass fraction of L-lactic acid of 25% were added to the centrifugal extractor respectively, and the mass ratio of the coupling adsorbent to the lactic acid acid hydrolysis solution was 1: 3. The aqueous phase and the organic phase are separated, and the mass percentage content of L-lactic acid in the aqueous phase is detected. The resu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com