Vitamin D oxime derivative and synthetic method and application thereof
A synthesis method and technology of derivatives, applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve problems such as application limitations, and achieve the effects of high yield, easy availability of synthetic raw materials, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of compound 1.2
[0037] Vitamin D 2 (500mg, 1.26mmol), aluminum isopropoxide (510mg) were dissolved in toluene, acetone (50mL) was added, and the reaction was refluxed. After TLC traced the reaction, dilute hydrochloric acid was slowly added to the reaction solution to terminate the reaction, extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer was combined, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated. The material was subjected to column chromatography (SiO 2 , PE:EA=20:1) to obtain compound 1.2 (0.15 g, 30.17%) as a white solid. 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3)δ7.26(s,1H),5.92(s,2H),5.41(s,3H),5.33(s,3H),5.29–5.07(m,7H),4.94(s,3H),3.15(t ,J=6.9Hz,6H),2.72(t,J=6.9Hz,7H),2.50(d,J=7.2Hz,10H),2.06–1.91(m,11H),1.85(d,J=6.4Hz ,5H),1.66(t,J=18.6Hz,24H),1.54–1.39(m,15H),1.35–1.20(m,22H),1.01(d,J=6.6Hz,13H),0.92(d, J=6.8Hz,11H),0.84(dd,J=15.9,8.6Hz,22H),0.56(s,10H). 13 C NMR (126MHz,...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of compound 1.3
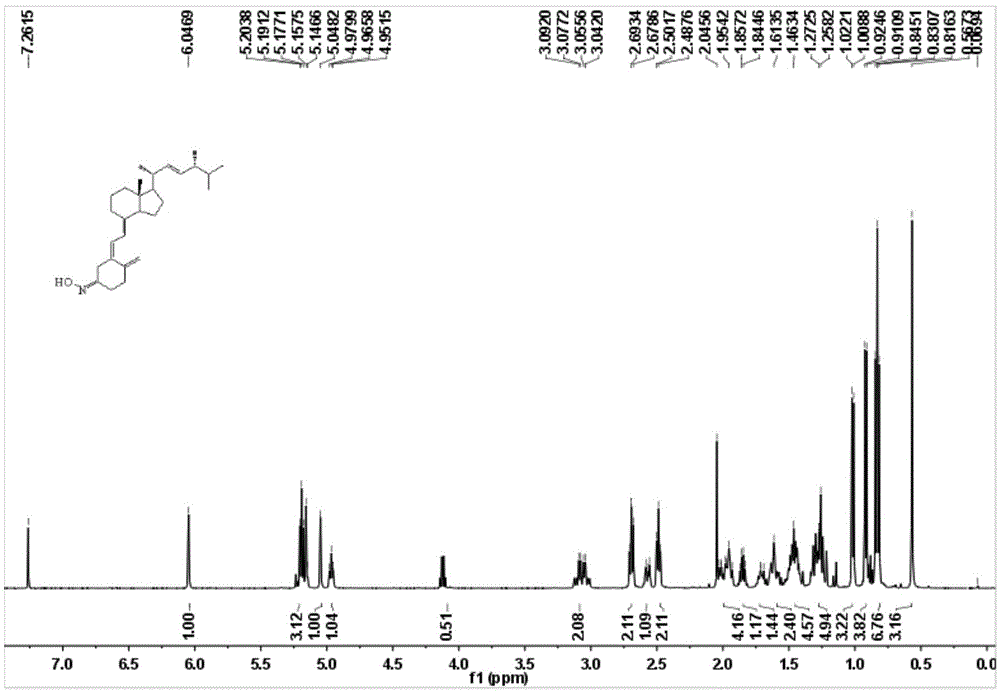
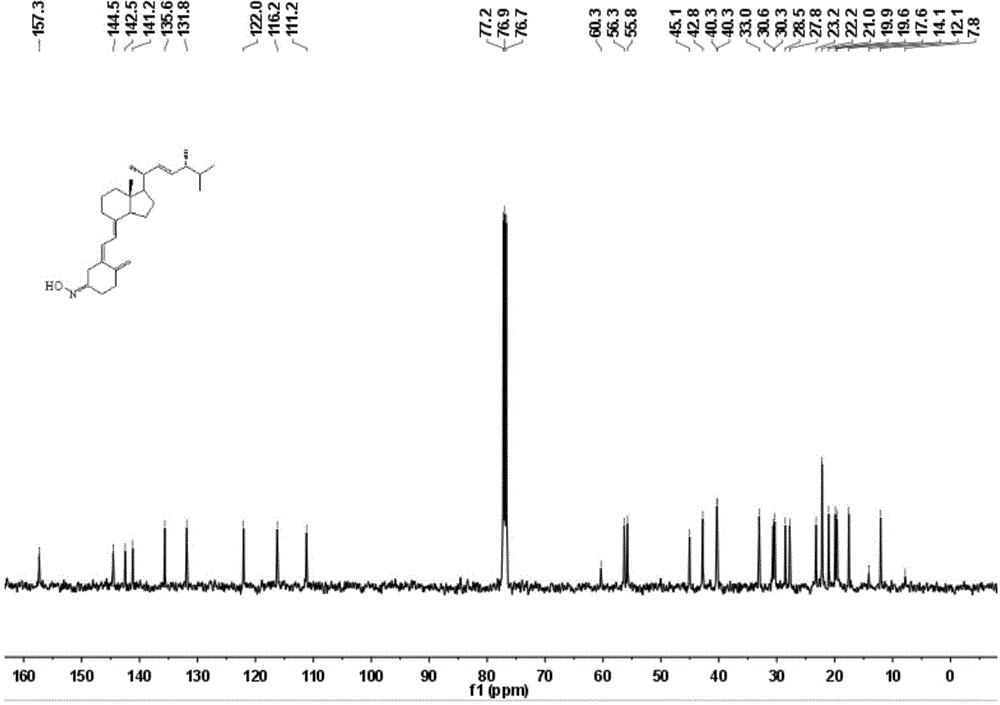
[0039] Compound 1.2 (500mg, 1.27mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (106mg, 1.52mmol), and triethylamine (2mL) were dissolved in ethanol, heated to reflux and stirred, and TLC was followed. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was cooled and added to the reaction system Ethyl acetate and water, extracted with ethyl acetate, combined organic layers, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and spin-dried to obtain a yellow oil. After column separation (SiO 2 , PE:EA=20:1) to obtain light yellow viscous 1.3 (270mg, 51.90%). 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.26(s,1H),6.05(s,2H),5.25–5.11(m,6H),5.05(s,2H),4.97(t,J=7.1Hz,2H),4.11(t,J =7.1Hz,1H),2.69(d,J=7.4Hz,4H),2.49(s,4H),2.05(s,2H),1.46(s,4H),1.32–1.20(m,8H),1.02 (d, J=6.6Hz, 6H), 0.92(d, J=6.9Hz, 7H), 0.83(t, J=7.2Hz, 13H), 0.57(s, 6H). See figure 1 13 C NMR (126MHz, CDCl 3 )δ157.32,144.55,142.47,141.16,1...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of compound 1.4
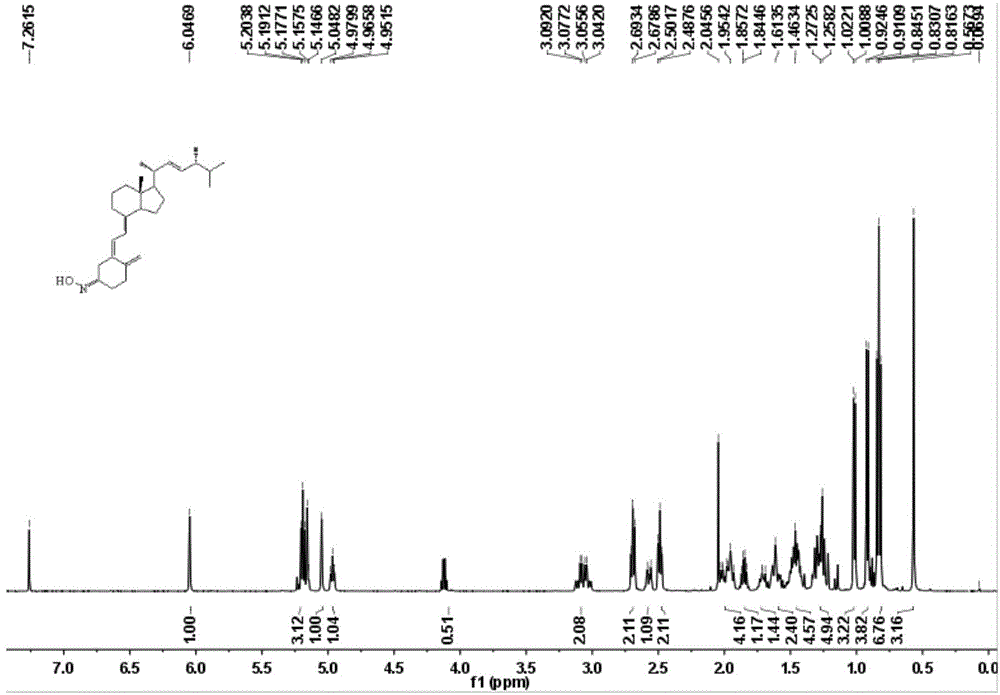
[0041] Compound 1.2 (500mg, 1.27mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (106mg, 1.52mmol), and triethylamine (2mL) were dissolved in ethanol, heated to reflux and stirred, and TLC was followed. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was cooled and added to the reaction system Ethyl acetate and water, extracted with ethyl acetate, combined organic layers, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and spin-dried to obtain a yellow oil. After column separation (SiO 2 , PE:EA=20:1) to obtain light yellow viscous 1.4 (170mg, 32.68%). 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ6.77(s,1H),5.24(s,1H),5.19(t,J=6.7Hz,2H),5.09(s,1H),4.97(s,1H),3.14(d,J=7.4 Hz,2H),2.65–2.50(m,3H),2.45(dd,J=8.4,5.1Hz,2H),2.10–1.90(m,5H),1.85(d,J=6.3Hz,2H),1.02 (d, J=6.6Hz, 4H), 0.58(s, 4H). See image 3 13 C NMR (126MHz, CDCl 3 )δ153.86,147.04,142.45,141.18,135.63,131.84,116.28,114.72,112.85,77.20,76....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com