Amphiphilic anticancer photosensitizer with big two-photon absorption section as well as preparation and application thereof
A two-photon absorption and amphiphilic technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low two-photon absorption efficiency, poor biocompatibility and tumor targeting, and achieve good tumor cell permeability and good two-photon cell imaging. Effect, effect of strong killing ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
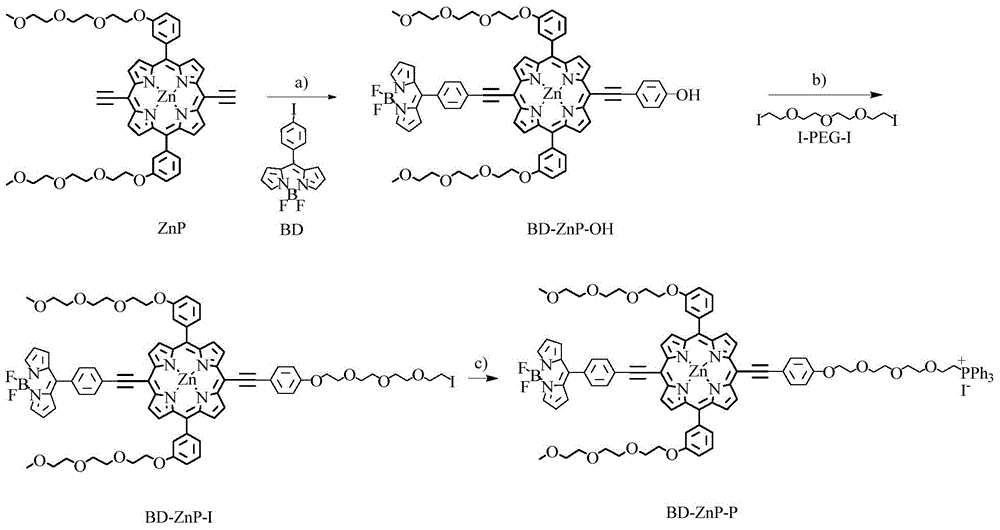
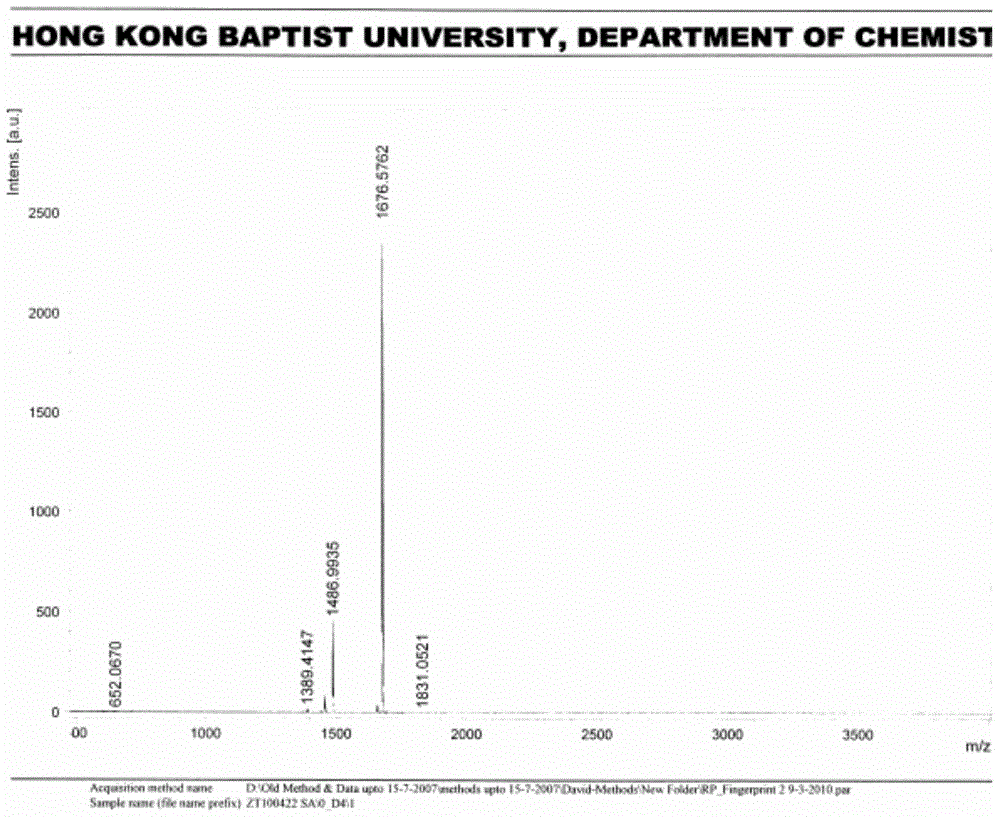
[0041] (1) Under nitrogen protection, combine 499.1mg (0.5mmol) ZnP, 102.0mg (0.25mmol) BD, 55.0mg (0.25mmol) 4-iodophenol and catalyst 28.9mg (0.025mmol) tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) Palladium (Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 ), 9.5 mg (0.05 mmol) of cuprous iodide (CuI) were dissolved in 20 mL of a mixed solvent (volume ratio 1:1) of dry tetrahydrofuran and triethylamine, the temperature was raised to 45 ° C, TLC detected that the reaction was terminated, and the solvent was removed to obtain The crude product was separated by silica gel chromatography to obtain the purple porphyrin intermediate BD-ZnP-OH with a yield of 46%.
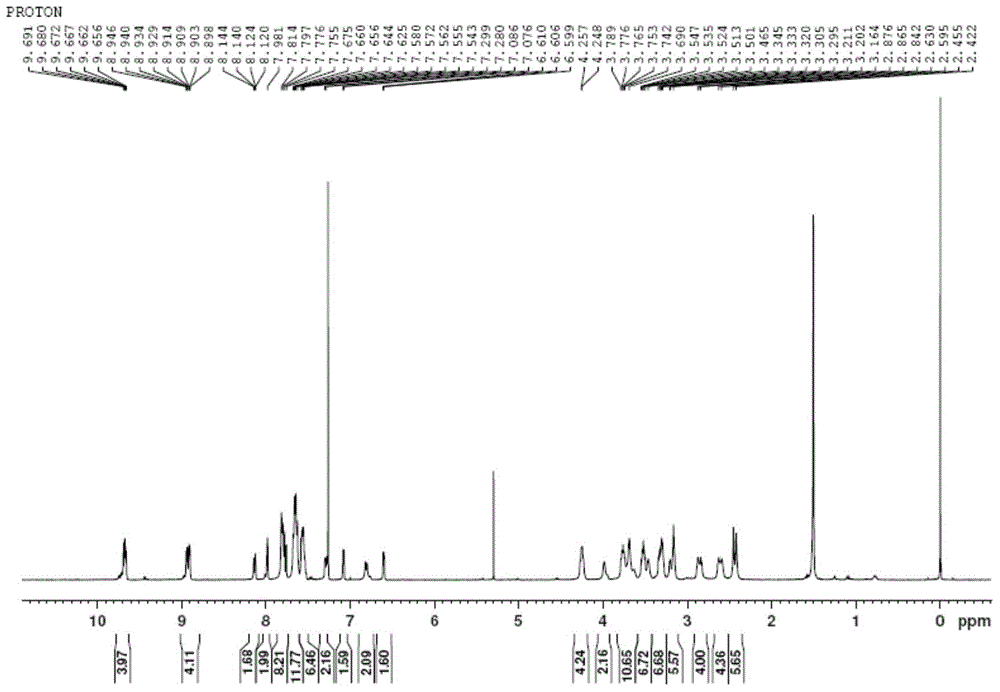
[0042] Characterization data: 1 HNMR (CDCl 3 / 5%d 5 -Pyridine): δ3.31(s,6H),3.48(q,J=4.40Hz,4H),3.62(q,J=4.92Hz,4H),3.68(t,J=4.12Hz,4H),3.77 (t, J=3.28Hz, 4H), 3.95(t, J=4.48Hz, 4H), 4.34(t, J=4.44Hz, 4H), 6.61(dd, J=1.44Hz, J=2.60Hz, 2H ),7.08(m,4H),7.34(m,2H),7.61(m,2H),7.75(m,6H),7.89(d,J=6.48Hz,2H),8.15(d,J=8.20Hz ,2H),8.87(d,J=4.56Hz,2H),8.92(d,J=4.56Hz,2H)...
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) Under nitrogen protection, combine 499.1mg (0.5mmol) ZnP, 102.0mg (0.25mmol) BD, 55.0mg (0.25mmol) 4-iodophenol and catalyst 57.8mg (0.05mmol) tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) Palladium (Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 ), 19.0mg (0.1mmol) of cuprous iodide (CuI) was dissolved in 20mL of a mixed solvent (volume ratio 1:1) of dry tetrahydrofuran and triethylamine, the temperature was raised to 45°C, TLC detected that the reaction was terminated, and the solvent was removed to obtain The crude product was separated by silica gel chromatography to obtain the purple porphyrin intermediate BD-ZnP-OH with a yield of 48%.
[0055] (2) Under nitrogen protection, 62.5 mg (0.05 mmol) of the purple porphyrin intermediate obtained in step (1) BD-ZnP-OH, 207.0 mg (0.5 mmol) of diiodotriethylene glycol (I-PEG -I)( figure 1 shown in ) and 138mg (1mmol) potassium carbonate (K 2 CO 3 ) was dissolved in 5 mL of anhydrous DMF, the temperature was raised to 65°C, the reaction was terminated by TLC detec...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Under nitrogen protection, combine 499.1mg (0.5mmol) ZnP, 102.0mg (0.25mmol) BD, 55.0mg (0.25mmol) 4-iodophenol and catalyst 57.8mg (0.05mmol) tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) Palladium (Pd(PPh 3 ) 4), 19.0mg (0.1mmol) of copper iodide (CuI) was dissolved in 20mL of a mixed solvent (volume ratio 1:1) of dry tetrahydrofuran and triethylamine, the temperature was raised to 65°C, TLC detected that the reaction was terminated, and the solvent was removed to obtain The crude product was separated by silica gel chromatography to obtain the purple porphyrin intermediate BD-ZnP-OH with a yield of 42%.
[0059] (2) Under nitrogen protection, 62.5mg (0.05mmol) of the purple porphyrin intermediate obtained in step (1) BD-ZnP-OH, 103.5mg (0.25mmol) of diiodotriethylene glycol (I-PEG -I)( figure 1 shown in ) and 69mg (0.5mmol) of potassium carbonate (K 2 CO 3 ) was dissolved in 5 mL of anhydrous DMF, the temperature was raised to 85°C, the reaction was terminated by TLC detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com