Organic electroluminescent device and manufacturing method thereof
An electroluminescence device and luminescence technology, applied in organic light-emitting devices, organic light-emitting device structures, organic semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of low cathode luminescence brightness, low cathode, and inconsistent luminance brightness of the light-emitting surface, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
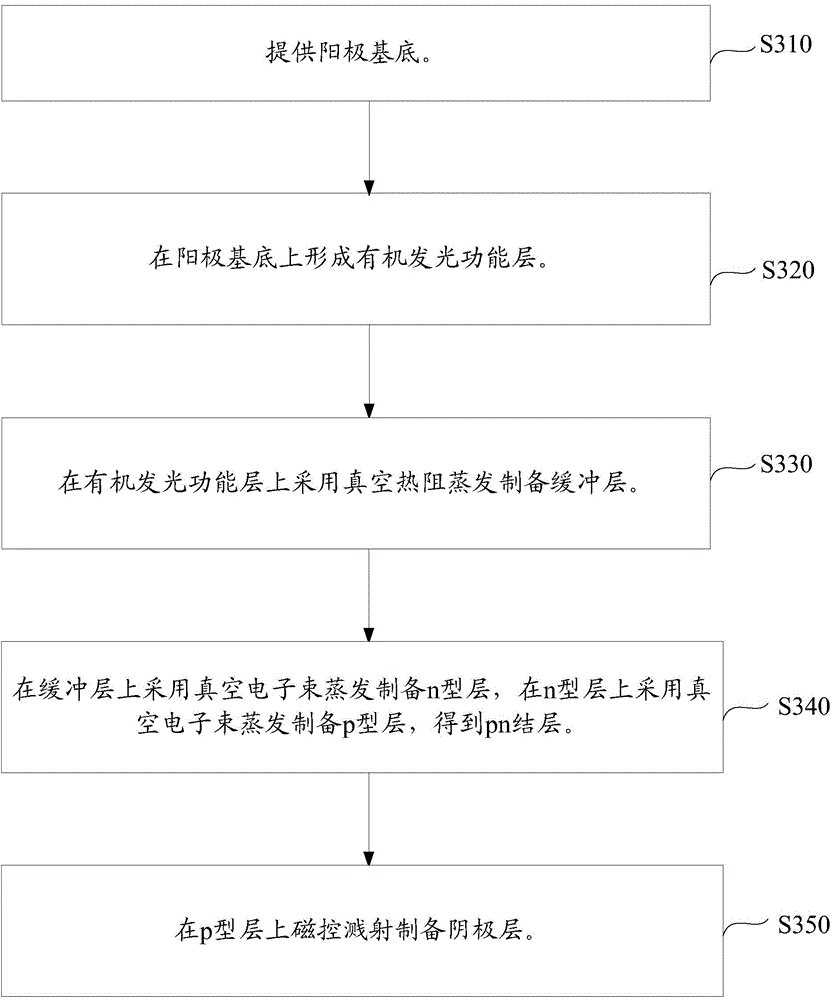
[0051] Such as image 3 As shown, a method for preparing an organic electroluminescent device in one embodiment includes the following steps:
[0052] Step S310: providing an anode substrate. Wherein, the anode substrate is transparent conductive glass. The transparent conductive glass may be indium tin oxide conductive glass (ITO), aluminum zinc oxide conductive glass (AZO) or indium zinc oxide conductive glass (IZO); preferably indium tin oxide glass (ITO); and indium tin oxide The sheet resistance of the conductive glass is 5Ω / □~100Ω / □.
[0053] Step S320: forming an organic light-emitting functional layer on the anode substrate.
[0054] Among them, the steps of forming the organic light-emitting functional layer on the anode substrate are: preparing a hole transport layer by vacuum evaporation on the anode substrate, preparing a light-emitting layer by vacuum thermal resistance evaporation on the hole transport layer, and using vacuum thermal evaporation on the light-e...
Embodiment 1
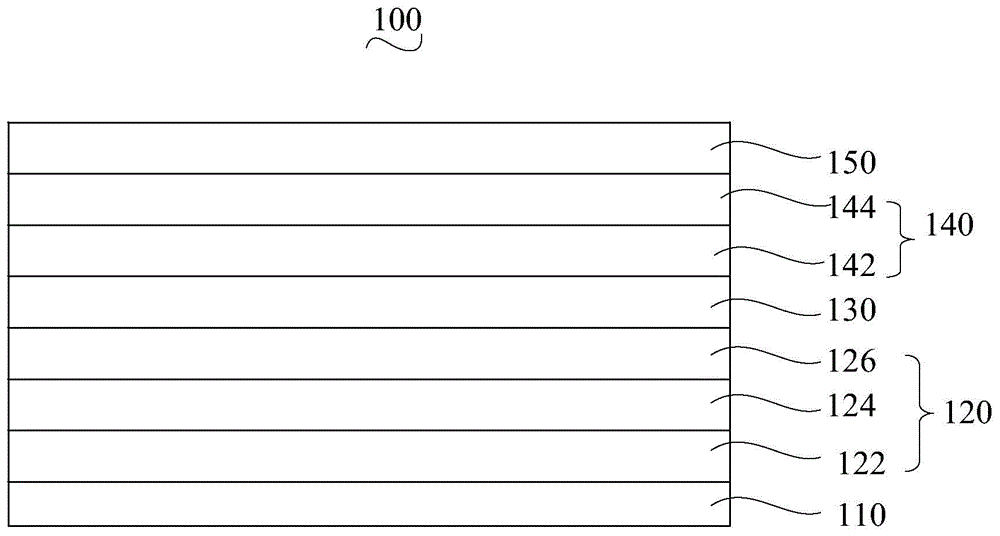
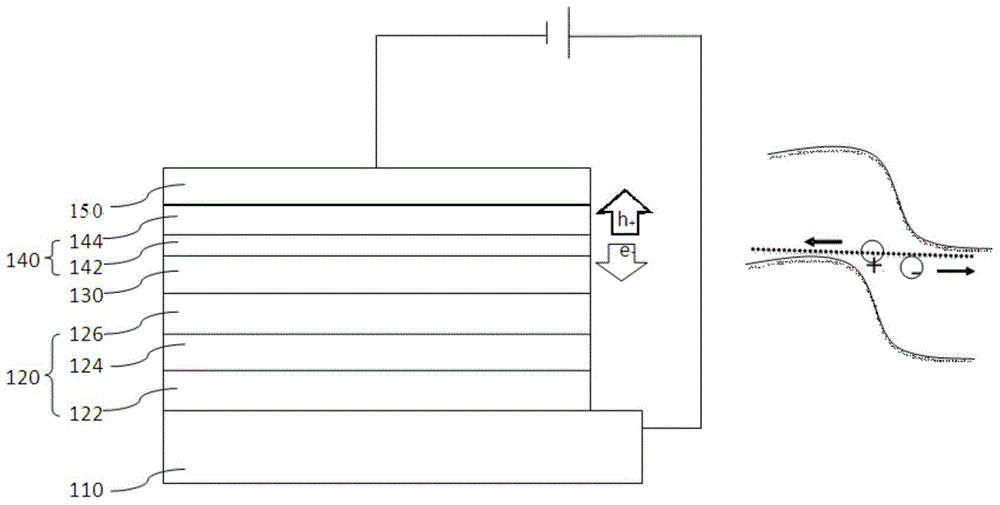
[0071] The structure of the organic electroluminescent device of the present embodiment is: ITO / NPB / NPB:Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac) / Bphen / LiF / ZnO / CuO / ITO.
[0072] The preparation of the organic electroluminescence device of this embodiment is as follows:
[0073] (1) Provide an ITO anode substrate and clean it, wherein the square resistance of the ITO anode substrate is 5Ω / □, and the ITO anode substrate is expressed as: ITO.
[0074] (2) Form an organic light-emitting functional layer on the anode substrate: in a vacuum of 1×10 -5 In the vacuum coating system of Pa, the hole transport layer is prepared by vacuum evaporation on the anode substrate, the thickness of the hole transport layer is 20nm, and the material is N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-bis(1-naphthalene base)-1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (NPB), the evaporation rate is 0.1nm / s, and the hole transport layer is expressed as: NPB;
[0075] In a vacuum of 1×10 -5 In the vacuum coating system of Pa, the light-emitting layer is prepared on t...
Embodiment 2
[0087] The structure of the organic electroluminescence device of the present embodiment is: ITO / MeO-TPD / Alq 3 :DCJTB / TPBi / CsF / SnO 2 / NiO / AZO.
[0088] The preparation of the organic electroluminescence device of this embodiment is as follows:
[0089] (1) Provide an ITO anode substrate and clean it. The sheet resistance of the ITO anode substrate is 100Ω / □, and the ITO anode substrate is expressed as: ITO.
[0090] (2) Form an organic light-emitting functional layer on the anode substrate: in a vacuum of 1×10 -3 In the vacuum coating system of Pa, the hole transport layer is prepared by vacuum evaporation on the anode substrate. The thickness of the hole transport layer is 60nm, and the material is (N,N,N',N'-tetramethoxyphenyl)- For p-diaminobiphenyl (MeO-TPD), the evaporation rate is 1nm / s, and the hole transport layer is expressed as: MeO-TPD;
[0091] In a vacuum of 1×10 -3 In the vacuum coating system of Pa, the light-emitting layer was prepared on the hole transpor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com