Method for efficiently extracting polysaccharide of lycium barbarum leaves
A technology of wolfberry leaves and polysaccharides, which is applied in the field of polysaccharide extraction, can solve the problems of long extraction time, limited extraction range, and high operating costs, and achieves benefits for modern industrial production and continuous production, saving raw materials and time, and low operating costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
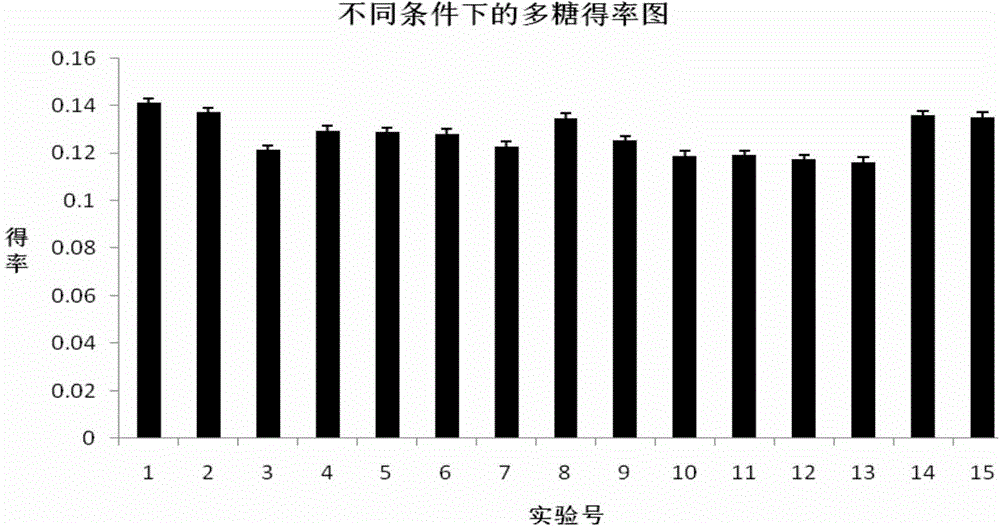
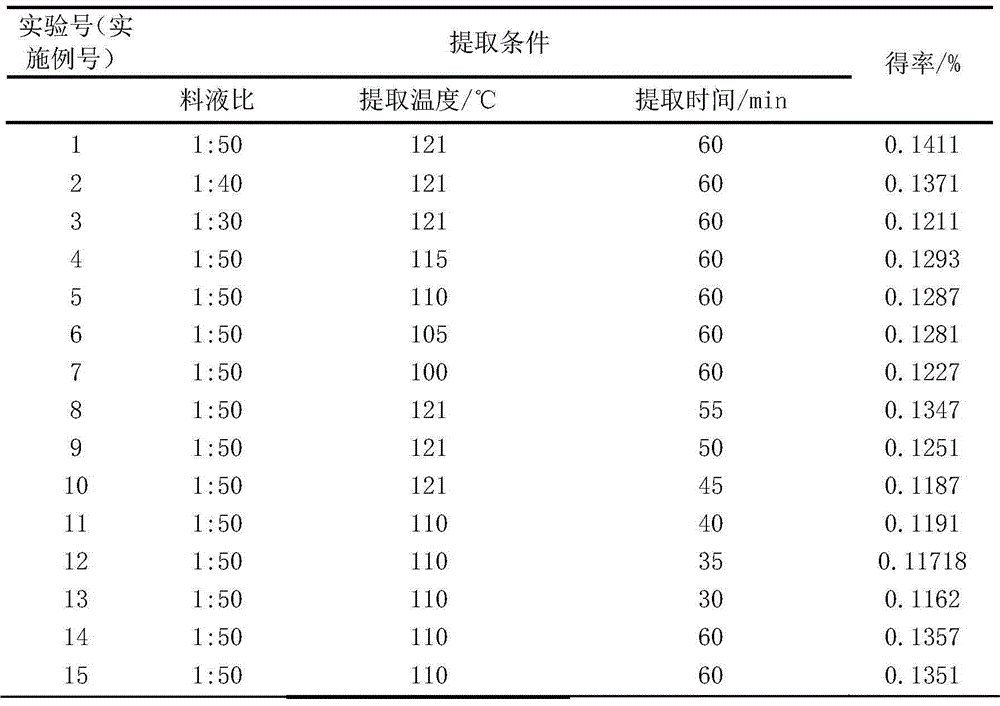
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1. Wash wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry at 50°C for 7 hours, grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0028] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add 300ml of ether, stir for 20min and then suction filter.
[0029] 3. Move the filter cake into a beaker, add 2.5L of distilled water, put it in a sterilizing pot, treat it under the conditions of 121°C and 0.25MPa for 60 minutes, and filter it with suction. Extract the filter cake twice under the same conditions, and combine the filtrates.
[0030] 4. Concentrate the filtrate to 1 / 10 of the original volume in a vacuum distillation device, add 2 times the volume of savage solution (chloroform:n-butanol=4:1, volume ratio), shake it for 20 minutes and then place it in a centrifuge at 1500r / Centrifuge for 20 minutes, remove the intermediate protein layer, add absolute ethanol until the volume fraction of ethanol reaches 80%, and let stand for 6 hours to precipitate.
[0031] 5. The filter cake ob...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1. Wash wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry at 40-60°C for 6-8 hours, grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0034] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add 300ml of ether and stir for 20min, then suction filter.
[0035] 3. Transfer the filter cake into a beaker, add 2.0L of distilled water, put it in a sterilizing pot, treat it at 121°C and 0.25 MPa for 60 minutes, and filter it with suction. Extract the filter cake twice under the same conditions, and combine the filtrates.
[0036] 4. Concentrate the filtrate to 1 / 10 of the original volume in a vacuum distillation device, add 2 times the volume of savage (chloroform: n-butanol = 4:1, volume ratio) solution, shake (no special requirements) for 20 minutes and then in Centrifuge at 1500r / min for 20min in a centrifuge, remove the intermediate protein layer, add absolute ethanol until the volume fraction of ethanol reaches 80%, and let stand for 4-8h to precipitate.
[0037] 5. The filter cak...
Embodiment 3
[0039] 1. Wash wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry at 40-60°C for 6-8 hours, grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0040] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add 300ml of diethyl ether and stir for 20min, then suction filter.
[0041] 3. Move the filter cake into a beaker, add 1.5L of distilled water, put it in a sterilizing pot, treat it at 121°C and 0.25 MPa for 60 minutes, and filter it with suction. Extract the filter cake twice under the same conditions, and combine the filtrates.
[0042]4. Concentrate the filtrate to 1 / 10 of the original volume in a vacuum distillation device, add 2 times the volume of savage solution (chloroform: n-butanol = 4:1, volume ratio), shake (no special requirements) for 20 minutes and then in Centrifuge at 1500r / min for 20min in a centrifuge, remove the intermediate protein layer, add absolute ethanol until the volume fraction of ethanol reaches 80%, and let stand for 4-8h to precipitate.
[0043] 5. The filter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com