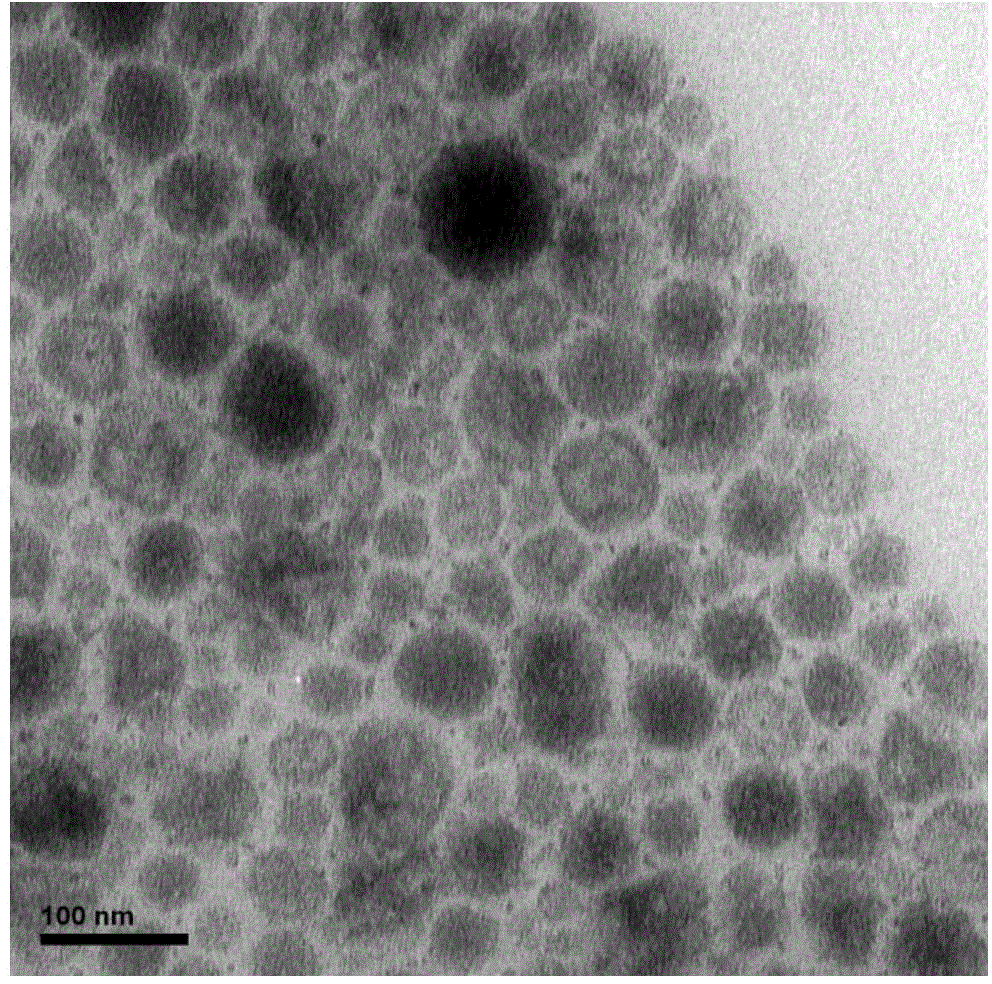
Method for preparing aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by water-soluble initiator
A technology of aggregation-induced luminescence and water-soluble initiators, which is applied in the direction of luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of complex processing and cumbersome process, and achieve the effect of simple preparation process, simple process and convenient coupling modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The emulsifier is selected from sodium lauryl sulfate, weighs 4 grams, and dissolves in 125 grams of distilled water to obtain an aqueous emulsifier solution.
[0054] 1.0 g of 1-allyl-1-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetraphenylsilole and 0.6 g of hexadecane were dissolved in 9.0 g of methyl methacrylate to obtain an oil phase solution. The obtained oil phase solution is added to the emulsifier aqueous solution, and the obtained mixed dispersion is pre-emulsified by stirring to obtain a coarse emulsion. The container containing the coarse emulsion is placed in an ice-water bath at 0°C, and ultrasonic waves with a power of 400W are used for 10 minutes to obtain Stable monomer miniemulsion.
[0055] Add 0.5 g of water-soluble initiator potassium persulfate to the above-mentioned monomer miniemulsion, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen, raise the temperature to 70° C., and react under nitrogen protection for 3 hours to obtain aggregation-induced luminescent polymer fluorescent nanoparticle e...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The emulsifier is cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, weighed 0.6 g, and dissolved in 40 g of distilled water to obtain an emulsifier aqueous solution.
[0059] 2.5 g of 1-vinyl-1-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetraphenylsilole and 1 g of n-eicosane were dissolved in 7.5 g of styrene to obtain an oil phase solution. The obtained oil phase solution is added to the emulsifier aqueous solution, and the obtained mixed dispersion liquid is stirred and pre-emulsified to obtain a coarse emulsion. The container containing the coarse emulsion is placed in an ice-water bath at 0° C., and the ultrasonic wave with a power of 125W is used for 50 minutes. A stable monomer miniemulsion is obtained.
[0060] Add 0.9 g of initiator 2,2'-azobisisobutylamidine dihydrochloride to the above-mentioned monomer miniemulsion, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen, raise the temperature to 60°C, and react for 20 hours under the protection of nitrogen to obtain Aggregation-Induced Luminescent Polymer Fluorescent Nanopart...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The emulsifier is selected from the compound emulsification system of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and OP-10, each weighing 0.5 g, and dissolving in 200 g of distilled water to obtain an aqueous emulsifier solution.
[0064] 0.5 g of the compound represented by formula (IV) (for the synthesis method, refer to the literature [Polym Chem 2014, 5, 683-688]) and 0.3 g of n-hexadecane were dissolved in 9.5 g of methyl methacrylate to obtain an oil phase solution. The obtained oil phase solution is added to the emulsifier aqueous solution, and the obtained mixed dispersion liquid is stirred and pre-emulsified to obtain a coarse emulsion. The container containing the coarse emulsion is placed in an ice-water bath at 0° C., and ultrasonic waves with a power of 600W are used for 5 minutes. A stable monomer miniemulsion is obtained.
[0065] Add 0.1 g of triethanolamine to the above-mentioned monomer miniemulsion, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen, and raise the temperature to 55°...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com