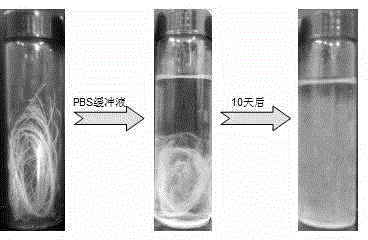
Absorbable antibacterial alginate fibers
A technology of seaweed fiber and sodium alginate, applied in fiber treatment, fiber chemical characteristics, alginate man-made filament, etc., can solve the problems of cytotoxicity of antibacterial agents, complicated preparation process, and non-lasting antibacterial effect, and achieve good Antibacterial properties, simple preparation process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A kind of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber, its technical scheme comprises the steps:
[0023] (1) Preparation of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: Sodium alginate was dissolved in deionized water to obtain a sodium alginate solution with a mass percentage of 1.5% and a viscosity of 10000 mPa; a mass percentage of 4.0% calcium chloride The coagulation bath is used for conventional wet spinning at 20°C. The resulting as-spun fibers are post-stretched by 1 time, washed with water at 30°C, and then heat-treated at 100°C to obtain absorbable antibacterial seaweed fibers.
[0024] (2) Modification of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: 1 g of the seaweed fiber obtained in step (1) was immersed in 200 mL of 1.0% glutaraldehyde solution by weight and cross-linked for 30 min. The breaking strength of the modified absorbable antibacterial algae fiber was 1.7 cN / dtex, and the breaking elongation was 4.5%. The antibacterial rates of the obtained seaweed fiber agai...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A kind of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber, its technical scheme comprises the steps:
[0027] (1) Preparation of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: Dissolve sodium alginate in deionized water to obtain a 2.5% sodium alginate solution with a viscosity of 15000 mPa; 2.5% calcium chloride by mass It is a coagulation bath, and conventional wet spinning is carried out at 30°C. The resulting as-spun fibers are post-stretched 1.5 times, then washed at 40°C, and then heat-treated at 60°C to obtain absorbable antibacterial seaweed fibers.
[0028] (2) Modification of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: 1 g of the seaweed fiber obtained in step (1) was immersed in 500 mL of 1.0% glutaraldehyde solution by weight and cross-linked for 60 min. The breaking strength of the modified absorbable antibacterial algae fiber was 2.0 cN / dtex, and the breaking elongation was 5.0%. The antibacterial rates of the obtained seaweed fiber against Staphylococcus aureus and Escheric...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A kind of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber, its technical scheme comprises the steps:
[0031] (1) Preparation of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: Sodium alginate was dissolved in deionized water to obtain a 3.5% sodium alginate solution with a viscosity of 20,000 mPa; 1.5% calcium chloride by mass It is a coagulation bath, and conventional wet spinning is carried out at 55°C. The obtained as-spun fibers are post-stretched twice, then washed at 50°C, and then heat-treated at 60°C to obtain absorbable antibacterial seaweed fibers.
[0032] (2) Modification of absorbable antibacterial seaweed fiber: 1 g of the seaweed fiber obtained in step (1) was immersed in 1000 mL of 1.0% glutaraldehyde solution by weight and cross-linked for 120 min. The breaking strength of the modified absorbable antibacterial algae fiber was 1.9 cN / dtex, and the breaking elongation was 4.0%. The antibacterial rates of the obtained seaweed fiber against Staphylococcus aureus and Esche...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com