Plant pathogen activity evaluation and bactericide high throughput screening method and kit
A plant pathogenic bacteria and kit technology, which is applied to measurement devices, material analysis by optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unstable test results, labor-intensive screening, and high costs, saving manpower, rapid operation, and repeatability. Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 Screening of plant pathogenic bacteria activity and agent evaluation targets based on fluorescent double staining
[0051] Use FDA (fluorescein diacetate) and PI (propidium iodide) as dyes to identify the spores and hyphae of plant pathogenic fungi and the spore viability of plant pathogenic bacteria, and screen the plant pathogenic bacteria that can be identified by fluorescent double staining target.
[0052] 1. Experimental method
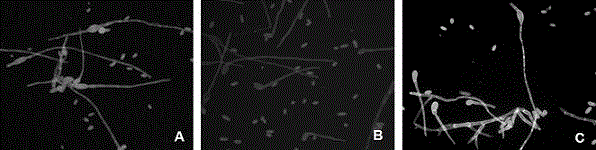
[0053] Plant pathogenic fungal spores, hyphae and plant pathogenic bacterial spores were selected as targets (Table 1), and FDA / PI double staining method was used to identify the activity of plant pathogenic bacteria.
[0054] Fluorescent staining solution configuration: Weigh 0.05 g FDA, dissolve in 1 mL acetone, add 9 mL PBS 7.4 to prepare FDA stock solution with a concentration of 5 mg / mL, store in a brown bottle at -20°C for later use, and use PBS before use Dilute to a final concentration of 100 μg / mL for use. Weigh 0....
Embodiment 2
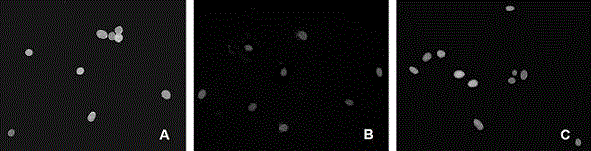
[0058] Example 2 Determination of Optimum Fluorescent Detection Time for Hoechst 33258 / PI Staining Drug Screening
[0059] A key condition for using fluorescent double staining to evaluate the activity of plant pathogens or to perform high-throughput screening of fungicides is to determine the optimal fluorescence detection time to maximize the reproducibility of the method results. Botrytis cinerea ( B. cinerea ) spore activity identification as an example, using 96-well microtiter plate and 384-well microtiter plate to conduct experiments respectively.
[0060] 1. Experimental method
[0061] Botrytis cinerea was cultured in PDA medium for 10 days, and the spore suspension was collected by the spore brush method, and divided into three groups. The spores in the first group were treated in a water bath at 95°C for 10 min to death, and the spores in the second group were treated without any treatment. Viable spores of the same group, the third group was equal mixture of h...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Quantitative analysis of the activity of plant pathogenic bacteria detected by flow cytometry
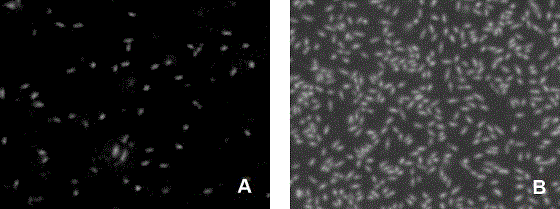
[0070] Anthracnose melons ( C. orbitale ) spores as the target, using flow cytometry to detect the spore viability of the anthracnose melons double-stained by Annexin V–FITC / PI, and quantitatively analyze the spore survival rate. At the same time, using the spore germination method as a control, the correlation between the detection results of the fluorescent double staining method and the traditional spore germination method was compared.
[0071] 1. Experimental method
[0072] Five strains of Bacillus anthracnose melons were used as experimental materials. The freshly prepared spore suspension was treated at 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, and 60°C for three times, namely 5 minutes, 10 minutes, and 20 minutes. All samples were divided into two groups, and one group was treated with Annexin After V-FITC / PI double-staining, the flow cytometer was loaded to analyze th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com