Device for improving rotary table chopper Q-switch laser performance and a Q-switch laser
A technology of lasers and laser beams, applied in the field of lasers, can solve problems such as unfavorable laser Q-switching fast switching process, optical frequency breakdown, and reduce the volume of laser oscillation modes, so as to maintain the selection characteristics of transverse modes, expand the volume of fundamental modes, Avoid the effect of optical frequency breakdown
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
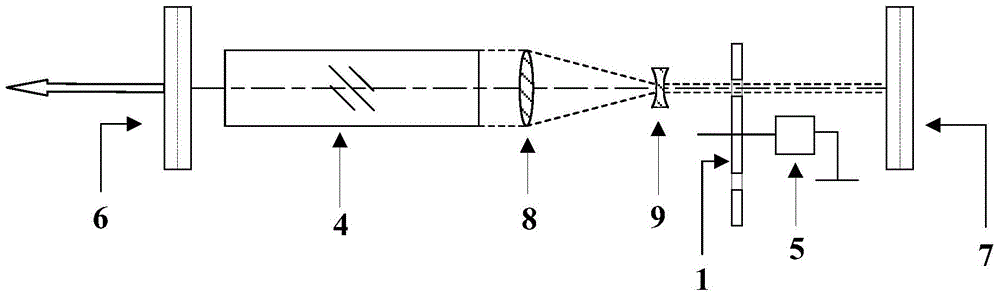
[0032] figure 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a Q-switched laser according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, in the parallel plane cavity composed of the output mirror 6 and the total reflection mirror 7, the laser medium 4, the first Galilean telescope device, and the turntable chopper Q-switching device are sequentially distributed. The turntable chopper Q-switching device includes a high-speed motor 5 and a chopper turntable 1 driven by the high-speed motor 5 to rotate. On the edge of the chopper turntable 1, light holes 3 for the passage of laser beams are arranged at equal intervals in a circular array. The first Galilean telescope device consists of a convex lens 8 and a concave lens 9 . Driven by the high-speed motor 5, the chopper turntable 1 rotates to change the Q value of the cavity, and the chopper turntable 1 periodically opens or blocks the optical path to realize Q-switching. The Galilean telescope device does...
Embodiment 2
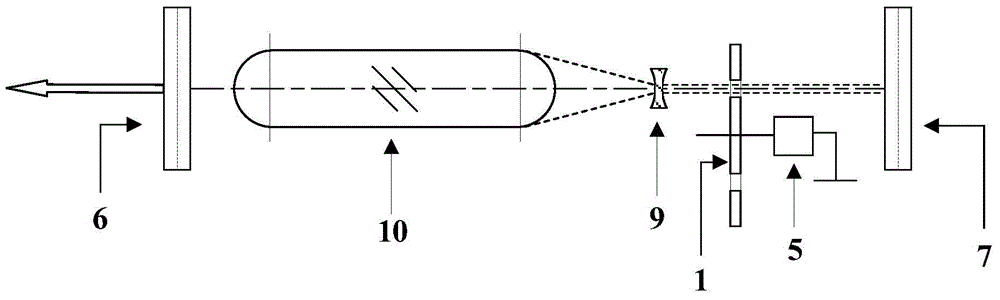
[0035] figure 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a Q-switched laser according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 2 As shown, its structural principle is the same as figure 1 The first shown embodiment is similar, except that the thermal lens formed by the thermal lens effect of the laser medium is used to replace the function of the convex lens in the first Galilean telescope device. In this embodiment, the laser medium (equivalent thermal lens) 10 and concave lens 9 form a light beam compression device, which simplifies the structure and reduces additional insertion loss.
Embodiment 3
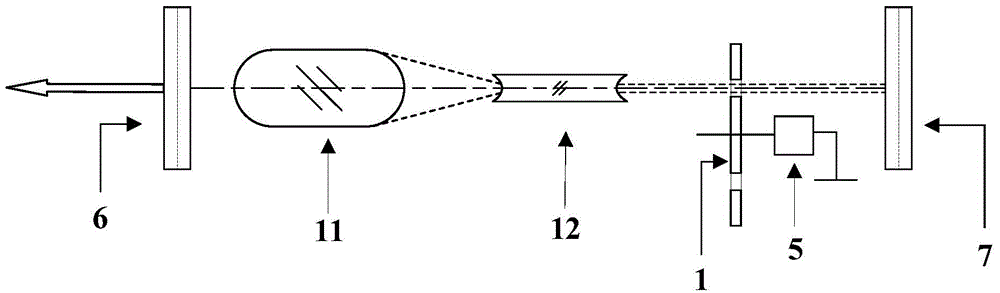
[0037] image 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a Q-switched laser according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, in the parallel plane cavity composed of the output mirror 6 and the total reflection mirror 7, the double-convex curvature end face laser medium 11, the double-concave curvature laser medium 12 and the turntable containing the chopper turntable 1 and the high-speed motor 5 are distributed in sequence chopping Q-switching device. The method of rotary disk chopping Q-modulation is the same as that of the first embodiment. The first Galilean telescope device is composed of a double convex curvature end face laser medium 11 and a double concave curvature end face laser medium 12 . The double-convex curvature end laser medium 11 has a positive curvature radius processed on both ends to achieve the optical effect of a convex lens, and the double-concave curvature end laser medium 11 has a negative curvature radius processe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com