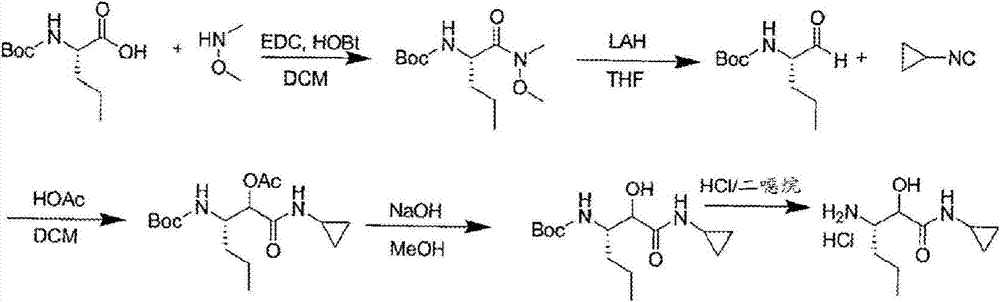
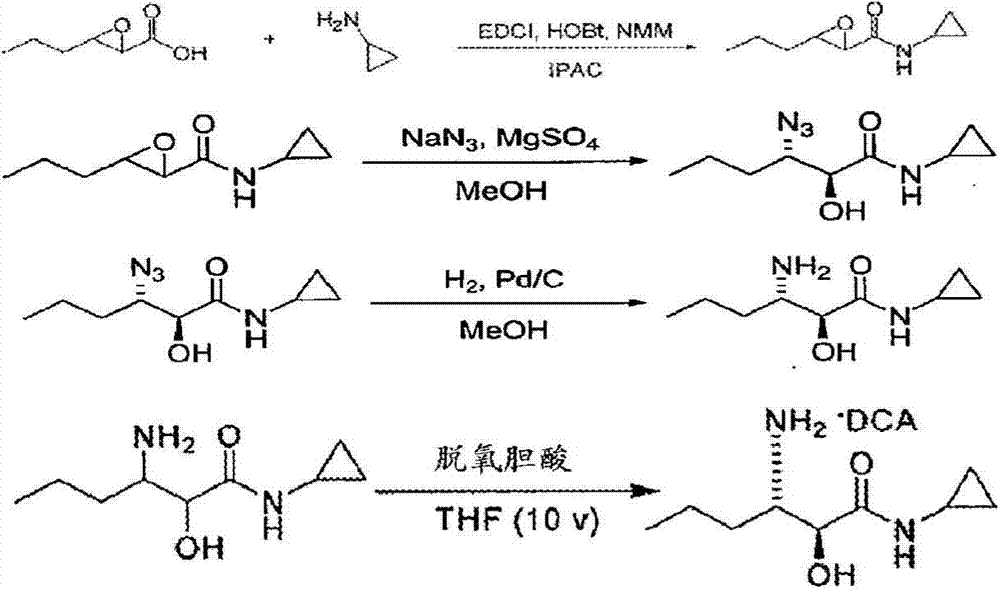
A method for the preparation of 3-amino-n-cyclopropyl-2-hydroxyl-hexanamide
A technology of cyclopropyl and hexamide, applied in the field of preparing pharmaceutical intermediates, can solve the problems of difficult handling, strict reaction conditions, expensive reaction conditions and the like, and achieves the effects of low equipment requirements, simple operation and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0128] Example 1. To a 1 L reaction flask was added 400 g of water, then trans-2-hexenoic acid (45.7 g, 0.4 mol) and cetylpyridinium chloride (13.6 g, 0.04 mol) were added with stirring. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6 with 30% sodium hydroxide solution. 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide (91 g, 0.8 mol) was added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was then heated to 50°C and allowed to react for 6 hours until completion. The reaction mixture was collected to room temperature and the pH was adjusted to 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The mixture was extracted twice with 400 g of dichloromethane. The extract was concentrated until dry. 48.6 g of 3-propyloxirane-2-carboxylic acid were obtained in a yield of 92%. The molecular weight of this compound was confirmed by GC-MS.
[0129] In the above examples, if the sodium hydroxide solution is replaced by ammonia water, sodium carbonate solution, potassium carbonate solution, potassium hydroxide solution, sodi...
example 2
[0130] Example 2. To a 1 L reaction flask was added 130 g of water and then trans-2-hexenoic acid (45.7 g, 0.4 mol) and sodium tungstate (26.4 g, 0.08 mol) were added under stirring. The pH of the mixture was adjusted to about 5 with sodium carbonate solution. 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide (91 g, 0.8 mol) was added to the reaction mixture at room temperature. The reaction mixture was then heated to 60°C and allowed to react for a further approximately 5 hours until the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and the pH was adjusted to about 1 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The mixture was extracted twice with 400 g of dichloromethane. The extract was concentrated until dry. 47.5 g of 3-propyloxirane-2-carboxylic acid were obtained in a yield of 90%. The molecular weight of this compound was confirmed by GC-MS.
example 3
[0131] Example 3. To a 1 L reaction flask was added 400 g of water and trans-2-hexenoic acid (45.7 g, 0.4 mol) and cetylpyridinium chloride (20.4 g, 0.06 mol) were added with stirring. The pH of the mixture was adjusted to about 6 with 30% sodium hydroxide solution and then 30% hydrogen peroxide (102.3 g, 0.9 mol) was added to the mixture. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 50 °C and allowed to react for a further 5.5 hours until the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and the pH was adjusted to about 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The mixture was extracted twice with 400 g of dichloromethane. The extract was concentrated until dry. 49.4 g of product were obtained in a yield of 93.5%.
[0132] Preparation of Methyl 3-Propyloxirane-2-carboxylate (III)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com