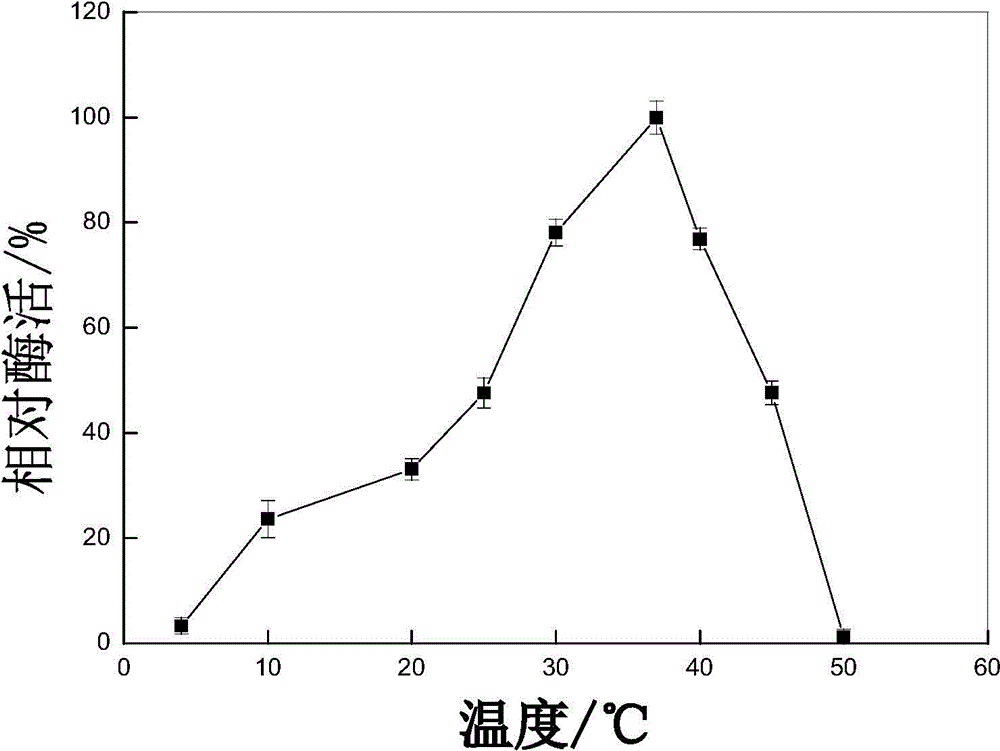
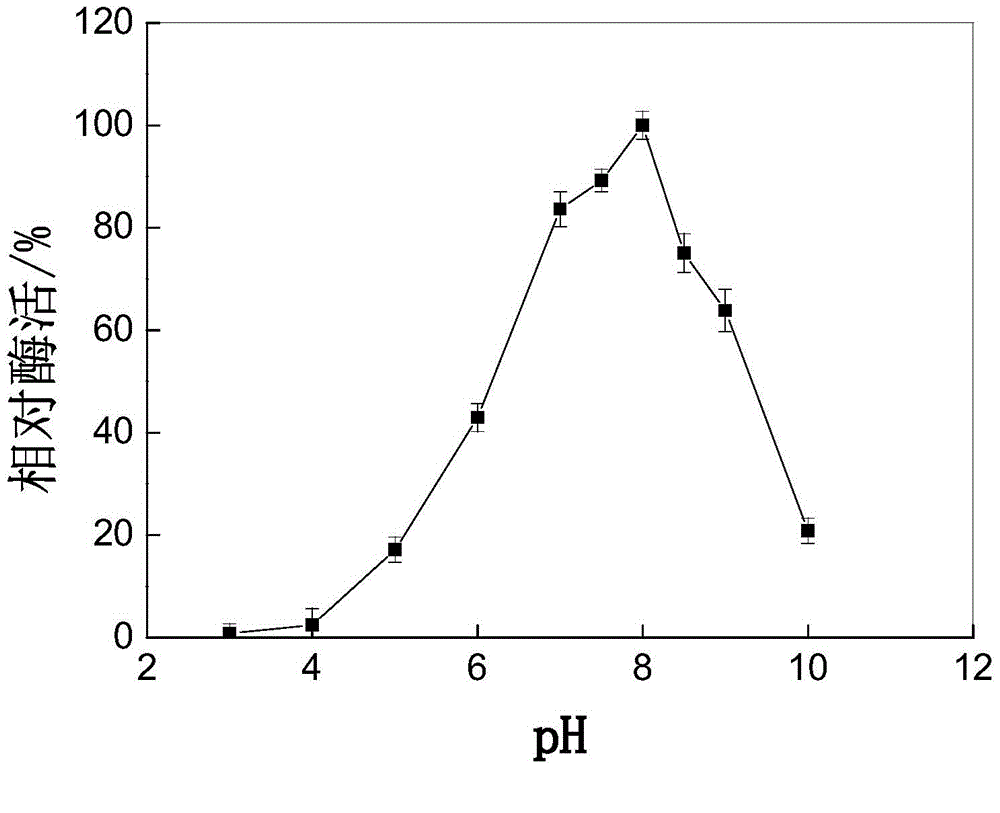
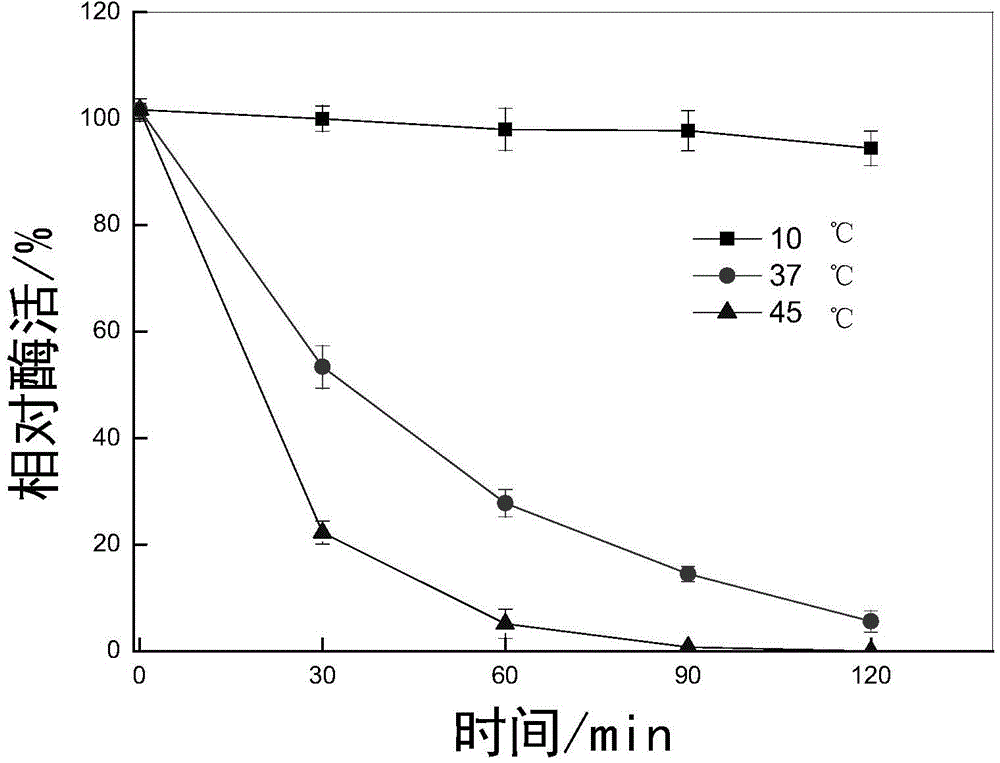
Low temperature protease production strain, low temperature protease produced by the same and gene of enzyme
A low-temperature protease and bacteria-producing technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve problems such as poor stability, and achieve the effects of short fermentation cycle, fast growth, and easy control of fermentation conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] Five, the preparation method of low temperature protease crude product
[0038] The low-temperature protease produced by the strain is a secreted protein, which mainly exists in the supernatant of the fermentation broth. First, the method of filtration or centrifugation is used to obtain the supernatant or filtrate from the culture medium, and then the method of salting out, conventional desalination, freeze-drying or spray-drying is used to obtain the crude low-temperature protease.
Embodiment 1
[0041] Fermentation of Low Temperature Protease-Producing Bacillus Motility Coccus TCCC11813
[0042] ⑴ Inoculate the slant of the fermentation strain into 50mL (250mL Erlenmeyer flask) 2216E liquid medium (5g peptone, 1g yeast extract, 0.01g ferric phosphate, 1000ml seawater, pH value 7.6-7.8), 20°C, 200rpm shaking culture 24 hours,
[0043] (2) Then inoculate 50mL (500mL Erlenmeyer flask) fermentation medium (5g of peptone, 1g of yeast extract, 1000mL of seawater, pH value 7.0-8.0) at a volume ratio of 2%, respectively, at different temperatures (15°C, 20°C, 25°C, ℃), shake culture at 200r / min for 72h, take samples regularly, and measure the enzyme activity.
[0044] The results showed that the optimum growth temperature of the strain was consistent with the optimum enzyme production temperature, both at about 20°C + 5°C, and the enzyme production peak could be reached in about 48 hours of fermentation culture, and the enzyme production amount was about 280U / mL.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Low temperature protease activity assay method
[0047] Take 1mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution (50mmol / L Tris.HCl, pH8.0), incubate at 37°C for 2min, add the substrate at the same temperature (prepared with 50mmol / L Tris.HCl, pH8.0 buffer 1.0% casein) 1 mL, reacted at 37° C. for 10 min, and added 2 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid to terminate the reaction. Centrifuge statically, take 1mL supernatant, add 5mL0.4mol / LNa 2 CO 3 Solution, 1mL Folin’s phenol reagent, mix well, keep warm at 40°C for 20min, measure the absorbance A 680 . The inactivated enzyme solution reaction system was used as a blank control.
[0048] The enzyme activity unit is defined as: per milliliter of enzyme solution, under the conditions of 37°C and pH 8.0, the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μg of tyrosine per minute is 1 enzyme activity unit (U / mL)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com