A culture medium and culture method of liver stem cells
A technology of hepatic stem cells and culture methods, applied in non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems of long time of liver tissue, accompanied by spontaneous differentiation, stem cell pollution, etc., to accelerate cell proliferation and avoid culture. The effect of prolonging the cycle and reducing cell damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1) Obtain liver tissue:
[0041] Pregnant rats were sacrificed by dislocation, sterilized by 75% ethanol and transferred to an ultra-clean workbench, and the fetal liver was aseptically removed.
[0042] 2) Separation and extraction of liver stem cells
[0043] Fetal liver was rinsed several times with PBS, shredded, digested with 0.02% type I collagenase and 0.02% type II collagenase at 4°C overnight, and the digested tissue was filtered with a 200-mesh sieve, and the obtained cell suspension was centrifuged at 200g After 5 min, the cell pellet was washed twice with PBS. The cells were separated by immunomagnetic beads, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0044] 1. Prepare a single cell suspension (filter with a 30um nylon mesh to avoid clogging the column) (wet the filter with buffer before filtering)
[0045] 2. Add buffer to wash the cells, and centrifuge (300g, 10min) (4-8°C) 3: Add buffer to reselect the cell single-cell suspension,
[0046] 3. Filter ag...
Embodiment 2
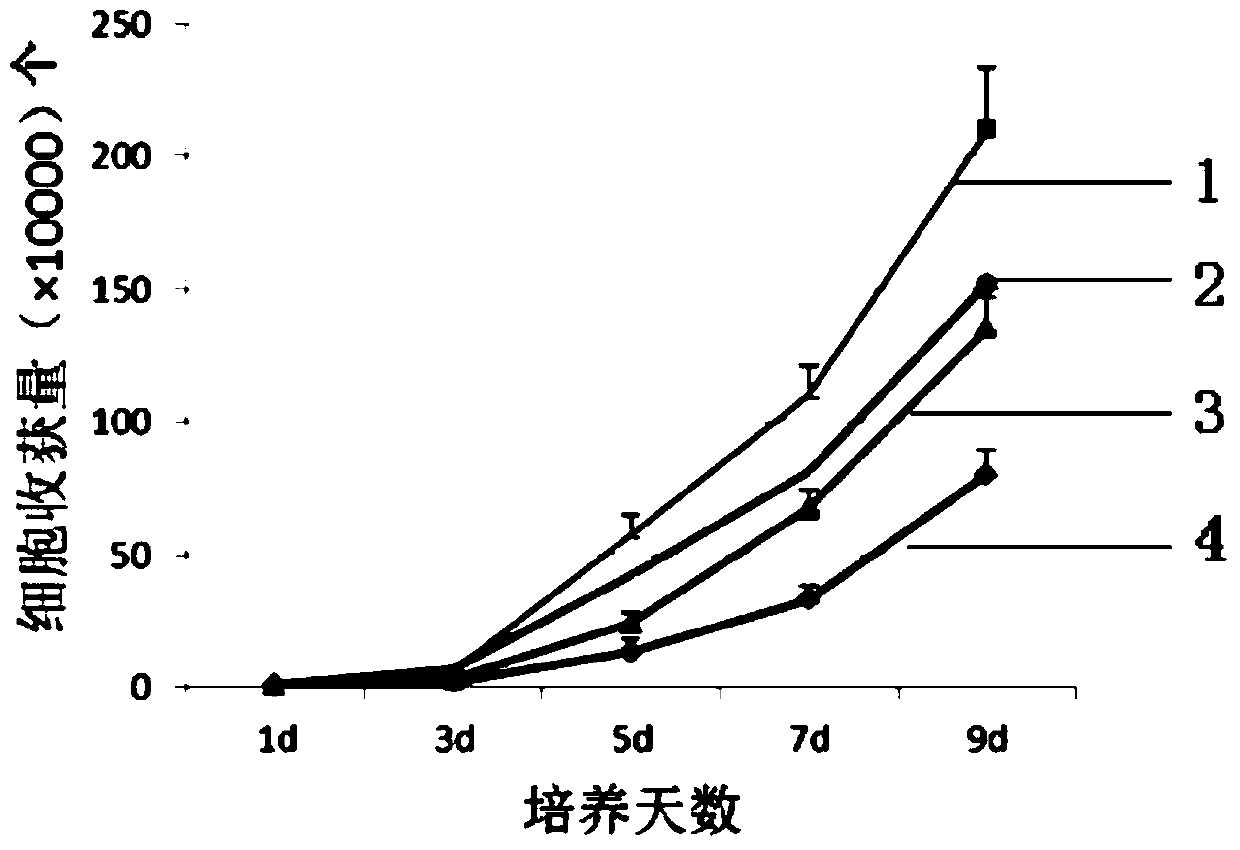
[0060] In the cell precipitation medium (the medium formula is shown in Table 1), the final concentration was prepared to be 1 × 10 5 ml of cell suspension. Add the cell suspension to the 25cm 2 culture flask at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator. After 48 h, the cell growth reached the logarithmic phase, and the cell growth was observed under an inverted phase-contrast microscope and photographed ( Figure 1-a ). After the cells grew to more than 80% confluence, the microscopic observation was carried out again ( Figure 1-b ), and then added 0.25% trypsin and 0.02% EDTA to digest and carry out repeated subculture for 3 times to obtain hepatic stem cells. During the culture process, the number of cells was recorded every day, and the growth curves were drawn for the stem cells cultured in different media. The results are shown in figure 2 .
[0061] Table 1 medium formula
[0062]
[0063] Microscopic observation results showed that hepatic stem cells grew adhe...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The hepatic stem cells cultured in different media in Example 2 were tested by flow cytometry, specifically:
[0067] Take hepatic stem cells in the logarithmic growth phase and adjust the cell density to 1×10 6 Take 2.5 μL of monoclonal antibodies against human CD34, CD44, CD105, and HLA-ABC respectively, add 500 μL of cell suspension, incubate at room temperature in the dark for 20 minutes, set up a blank isotype control at the same time, and centrifuge at 1500 r / min for 5 minutes , discard the supernatant, wash 2 times with PBS containing 10% FBS, resuspend with 500 μL 1640 and test on the machine. The statistical results of the data are shown in Table 2:
[0068] Table 2: Flow Cytometry Results
[0069]
[0070] Among them, the detection results of the hepatic stem cells cultured in medium 3 are as follows: Figure 3-a~Figure 3-b As shown, liver stem cells are a kind of mesenchymal stem cells, and mesenchymal stem cells have low expression of HLA-ABC and CD34 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com