O type foot and mouth disease virus-like particle vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
A foot-and-mouth disease virus and particle technology, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and immunology, can solve the problems of poor safety and unsatisfactory use effect, and achieve the effect of good stability, favorable for popularization and use, and good safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of O-type foot-and-mouth disease virus antigen VP1 gene
[0039] The O-type foot-and-mouth disease virus antigen VP1 gene was constructed by PCR amplification. First, the upstream and downstream primers were synthesized, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0040] Upstream primer: 5'-GGGTCGAC ATGACCACTTCGACGGGCGAGTCGGCTG- 3';
[0041] Downstream primer: 5'-CCCTCGAG CAAGGACTGCTTTACAGGCGCCACT- 3'.
[0042] Among the above-mentioned upstream and downstream primer sequences, the underlined part is the sequence complementary to the VP1 gene, and the bold italic part is the introduced XhoI and SalI restriction sites. The specific fragment amplified by PCR is reclaimed after 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to obtain the O-type foot-and-mouth disease virus antigen VP1 gene fragment with XhoI and SalI restriction sites. The nucleotide sequence of the VP1 gene fragment is as follows: Sequence 2 in the sequence listing (the nucleotide sequ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Construction of recombinant expression vector plasmid pET30-FMD-VP1
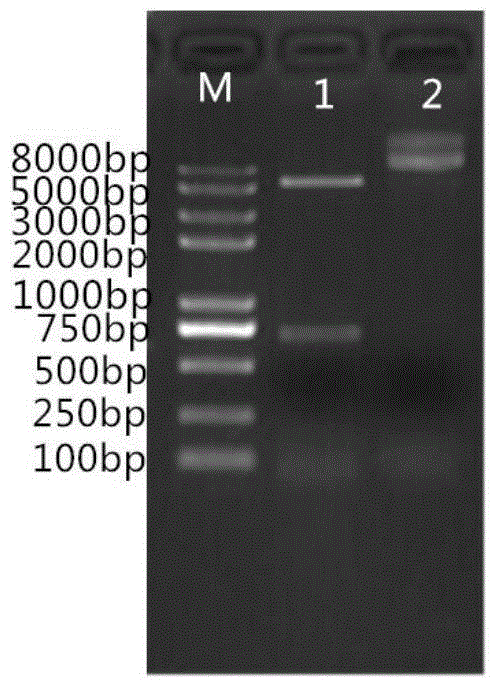
[0044] The O-type foot-and-mouth disease virus antigen VP1 gene fragment (that is, the complete reading frame containing the O-type foot-and-mouth disease virus VP1 gene) obtained in Example 1 with XhoI and SalI restriction sites is inserted into the prokaryotic treated by XhoI and SalI double enzyme digestion On the multi-cloning enzyme cutting site of the expression vector pET30a, the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, and the white clone was picked from the resistance plate for SalI / XholI double enzyme digestion sequencing identification, the results are as follows figure 2 As shown, it was confirmed by sequencing that the connection was successful, that the VP1 virus coding frame was correct, and that the restriction site used for the connection was mutated, and that the sequenced correct clone was named the recombinant expression vector plasmid pET30-FMD-VP1. ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: VP1 protein expression, identification and purification
[0046] Transform the correct recombinant expression vector plasmid pET30-FMD-VP1 obtained in Example 2 into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the recombinant genetically engineered bacteria, and inoculate the obtained recombinant genetically engineered bacteria into the LB liquid with kana resistance In the culture medium, shake culture to about OD600=0.6, add IPTG to a final concentration of 1mmol / L, induce the expression of recombinant genetically engineered bacteria, the induction conditions are: temperature 37°C, rotation speed 180r / min, induction 6h; The bacterial cells were collected, and the expression of the target protein was detected by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis; the expression of the bacterial protein induced by IPTG and the negative control (uninduced empty cells) were subjected to SDS-PAGE electrophoresis detection. The result is as image 3 As shown, compared with the uninduced rec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com