Method for attacking miRNAs through free radicals to cause oxidative damage to RNAs
A technology of oxidative damage and free radicals, applied in the field of RNA oxidative damage, can solve the problem of limited oxidative modification of microRNA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
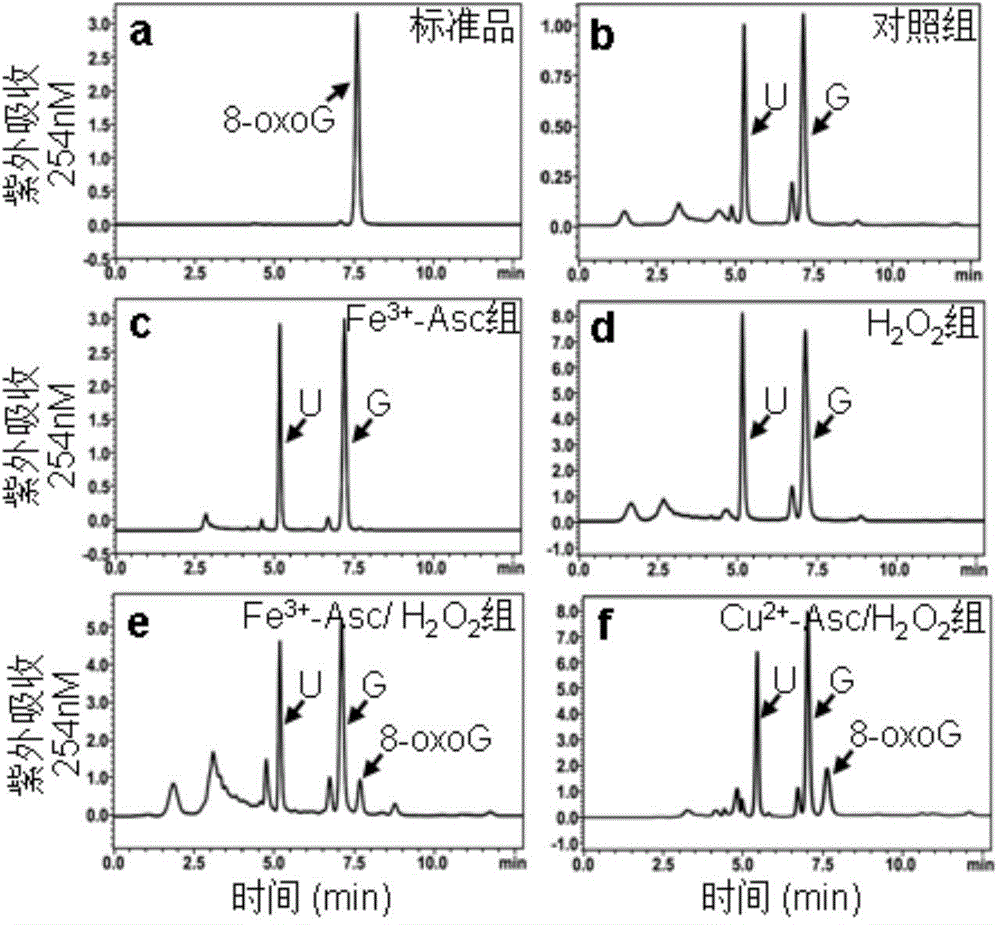
[0030] Example 1: Fenton's reagent oxidation system causes miRNA oxidative damage and produces 8-oxoguanine
[0031] Cu in this example + / Fe 2+ with H 2 o 2 The Fenton’s reagent oxidation system has a very strong oxidation ability, and is the main reaction for organisms to produce OH (hydroxyl radicals); this reaction system is used to oxidize chemically synthesized double-stranded miRNA mimics samples (hsa-let-7a-1: 5'-UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU-3'SEQ ID NO:12), namely miRNA (80μg) and 0.5mM ferric citrate (Fe 3+ ) or copper sulfate (Cu 2+ ), 5mM ascorbic acid (Asc) and 2mM H 2 o 2 , in 10mM NaH 2 PO 4 / Na 2 HPO 4 Buffer (pH 7.4) system, incubated at 37°C for 1h. After the incubation, 10 μl of 100 mM deferoxamine methanesulfonate (iron ion scavenger) or dicyclohexanone oxalyldihydrazone (copper ion scavenger) was added to terminate the reaction. Add 1 / 10 volume of 3M NaAc, 1 / 10 volume of 1 μg / ml glycogen and 2.5 volumes of ethanol to the above solution, and precipita...
Embodiment 2
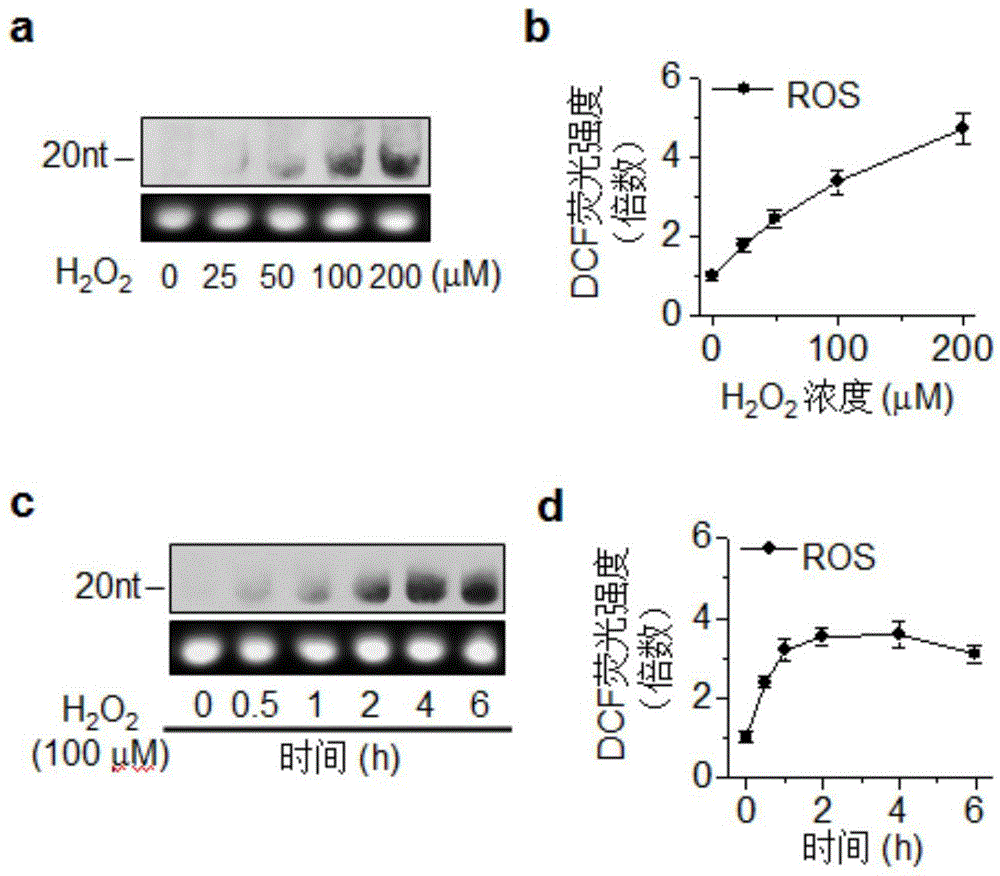
[0033] Example 2: H 2 o 2 Oxidative damage of miRNA during apoptosis induced in myocardial H9c2 cells, producing 8-oxoguanine
[0034] This embodiment is to detect H 2 o 2 The degree of miRNA oxidative damage in the process of inducing myocardial H9c2 cell apoptosis (which can be obtained from American Type Culture Collection); 2 o 2 H9c2 cells were treated, and cells were collected after 3h for reactive oxygen species (Reactive oxygen species, ROS) detection (which can be obtained from Invitrogen), and flashPAGE TM The fractionator system (Ambion, Inc) was used to extract miRNA, and Northwestern Blot analysis was performed as described, and the results are shown in figure 2 a and figure 2 b.
[0035] The results of this example show that with 0mM H 2 o 2 Treatment groups were control, 25 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM and 200 μM H 2 o 2 The intracellular ROS levels of the treatment groups increased by 2.25±0.19, 3.43±0.31, 5.54±0.46, 6.72±0.57 (p2 o 2 The increase multiples ...
Embodiment 3
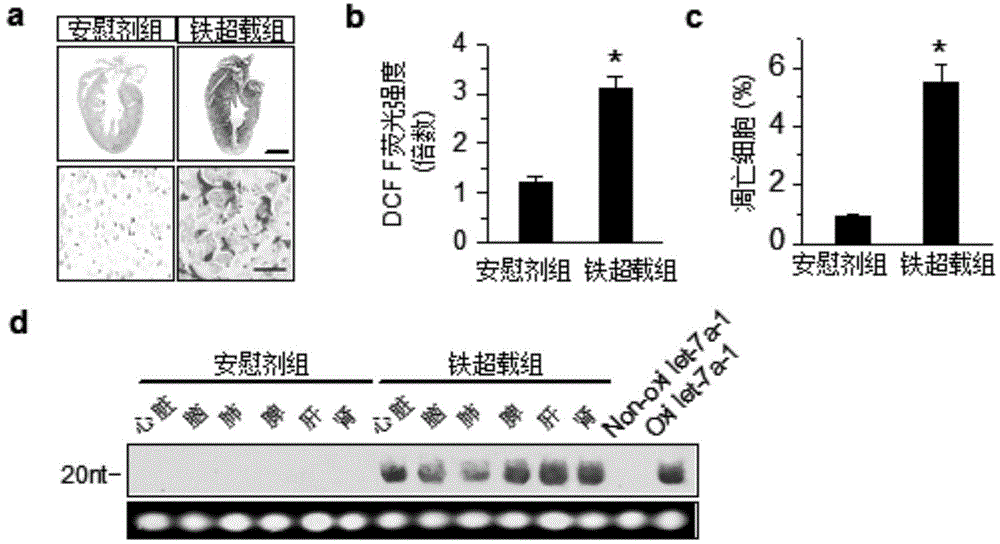
[0036] Example 3: Iron overload induces miRNA oxidative damage in a myocardial injury model, producing 8-oxoguanine
[0037] The iron overload (iron overload) in the cardiomyocytes of this embodiment can cause a significant increase in the intracellular ROS level, and cause damage to myocardial function and increased apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. Obtained from the Experimental Animal Center of the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) intraperitoneal injection of iron dextran to quickly establish an iron overload model, the dose is 12 mg / day, five days a week, and sacrificed after injection for four weeks; found that the iron overload ( In the Fe) group, blue iron particles were deposited in the cytoplasm, but in the placebo control (Plecebo) group, no iron particles were found in the cells, confirming the successful establishment of the iron overload model in mice ( image 3 a); At the same time, the levels of ROS and apoptosis in the Fe group were significantly h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com