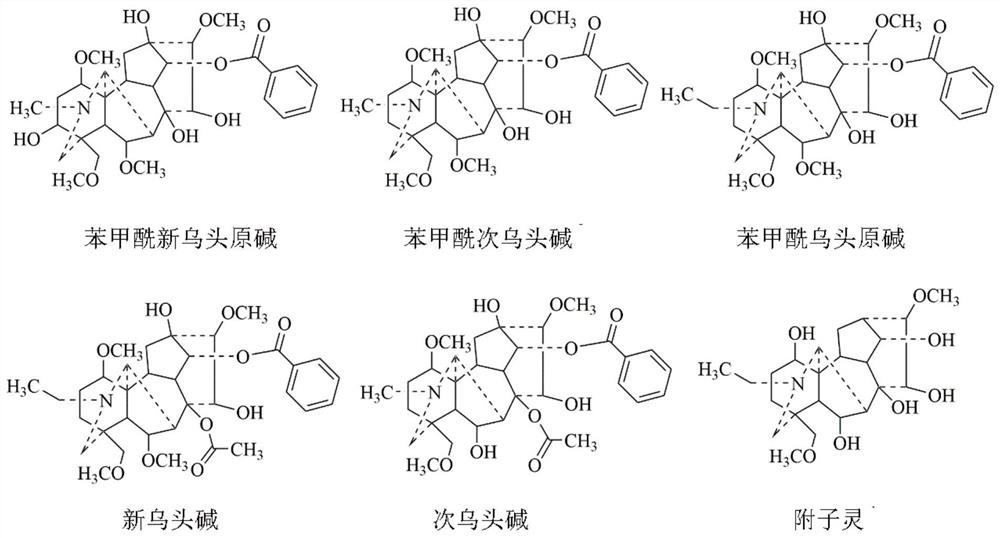
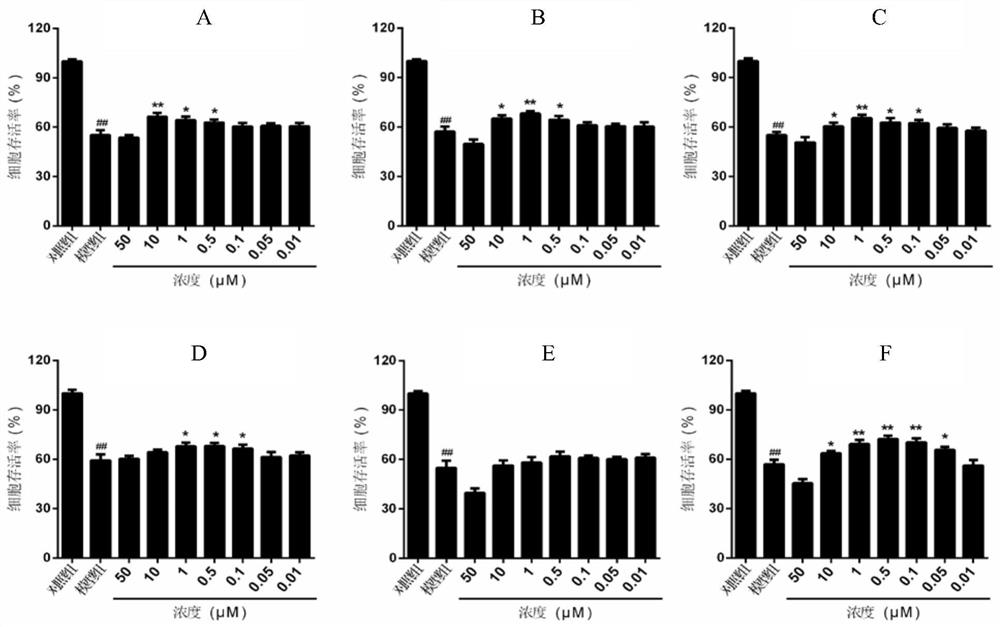
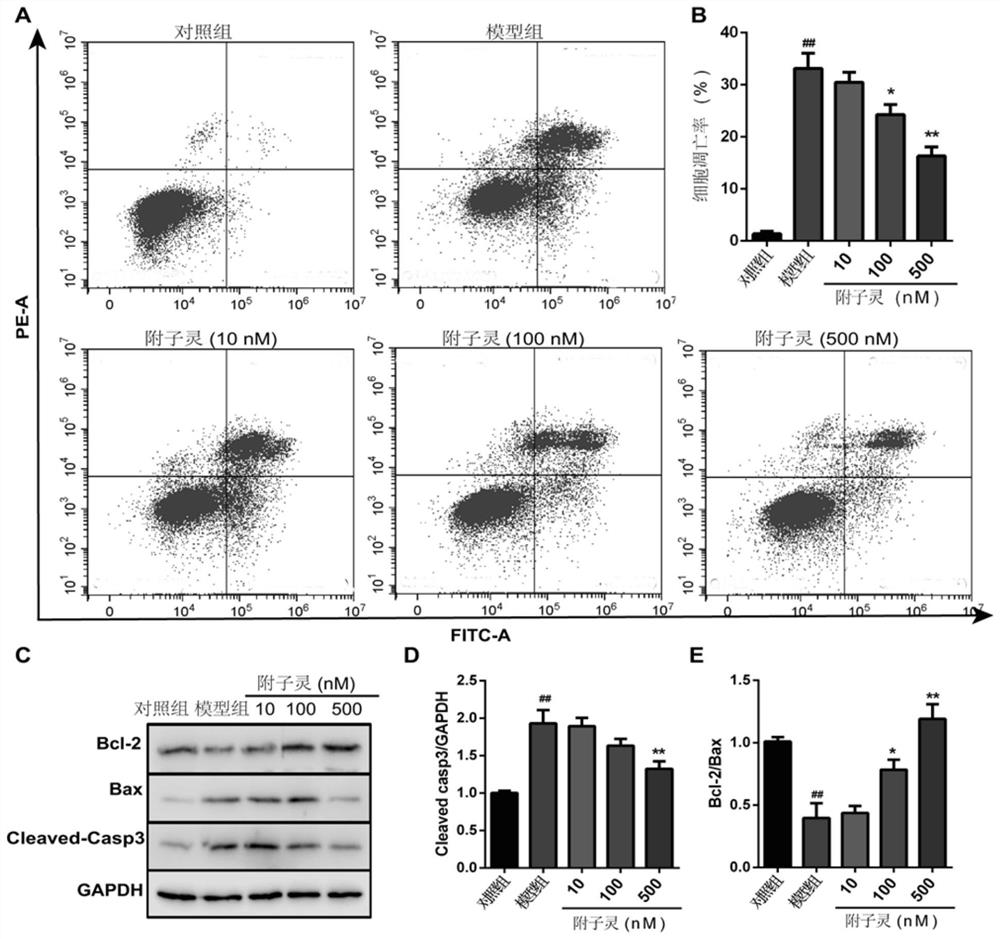
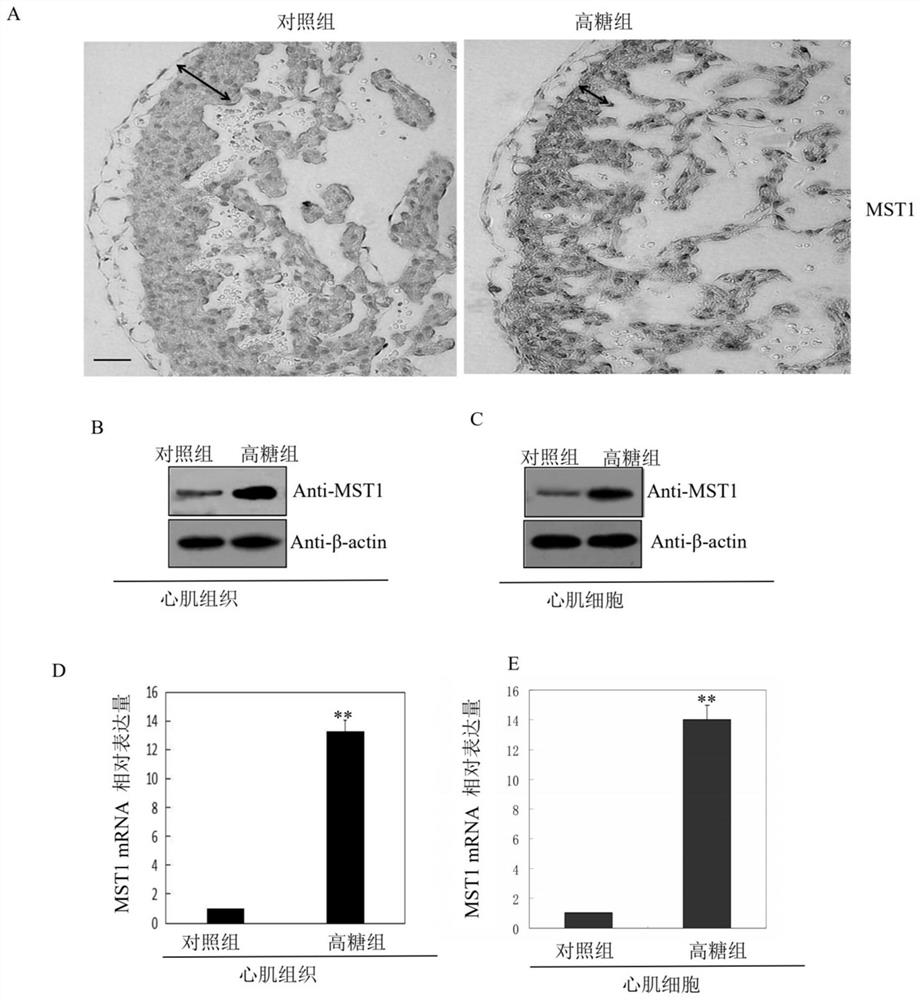
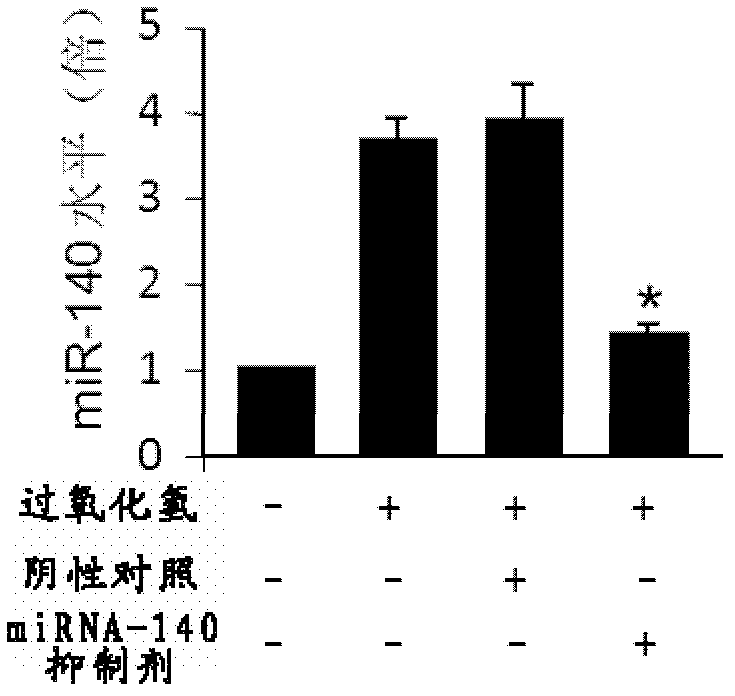Patents
Literature
42 results about "Myocardial apoptosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Myocardial apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial dysfunction is an important mechanism for the initiation and progression of heart failure. MiRNAs act as negative regulators of gene expression and play a vital role in the development of heart failure.
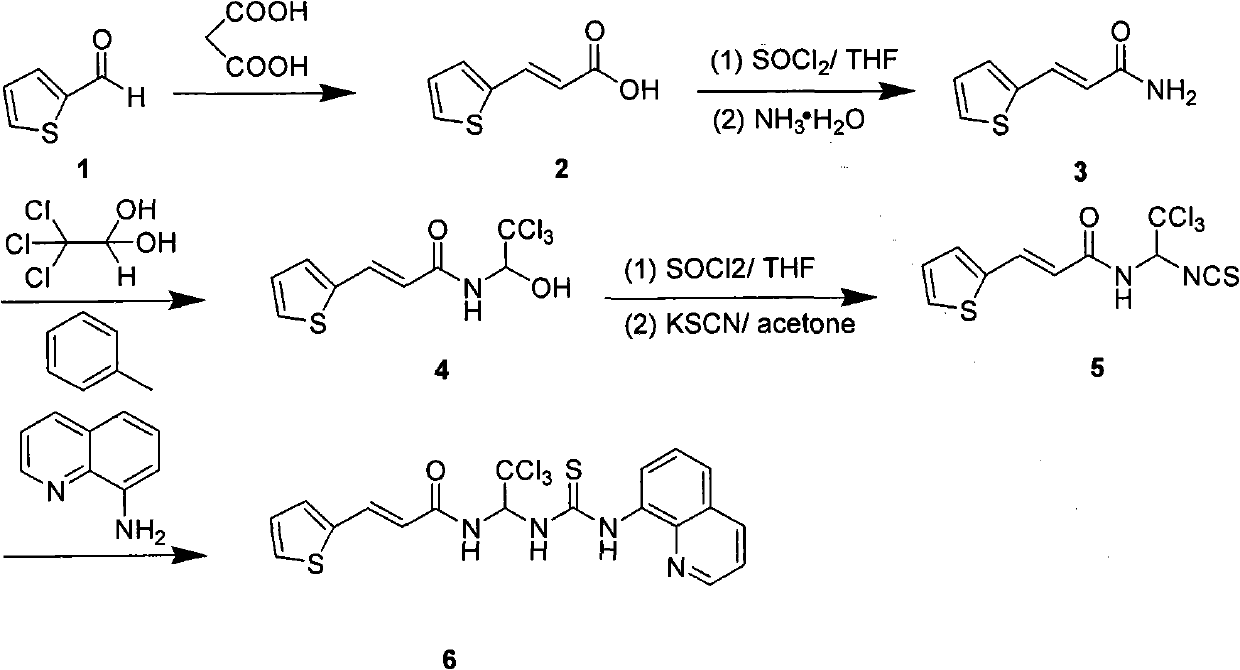
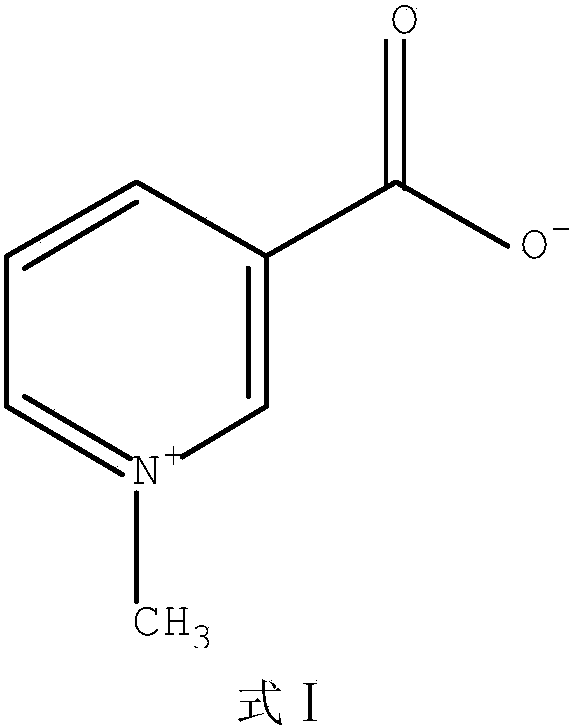
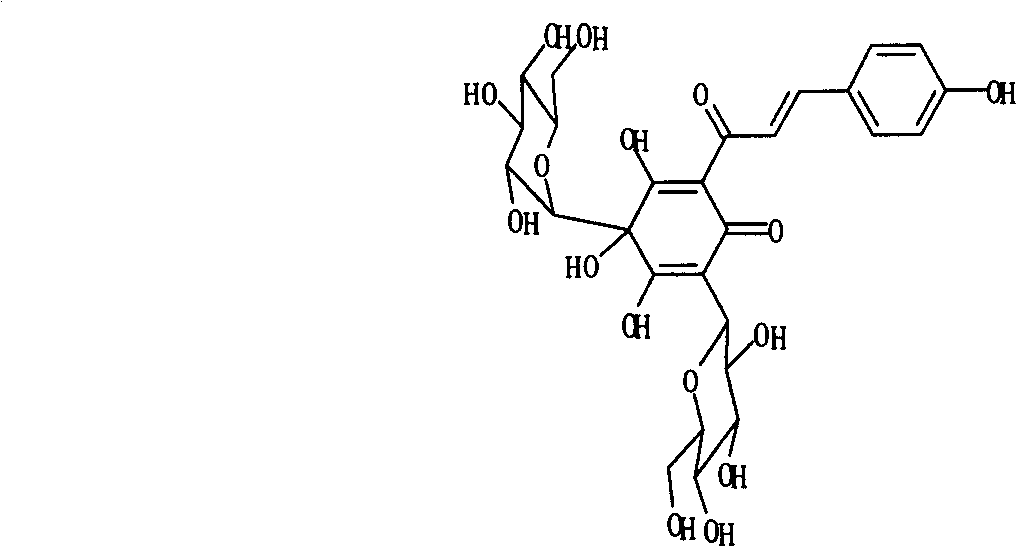
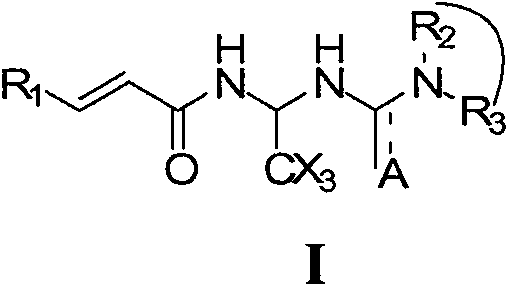
Acrylamide compounds and medicinal uses thereof
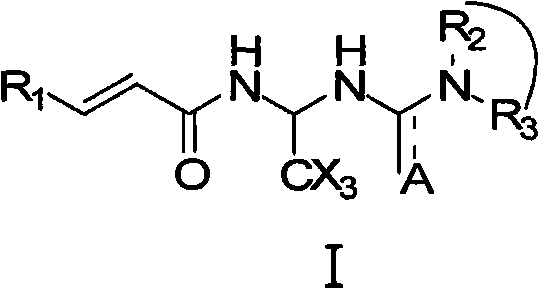
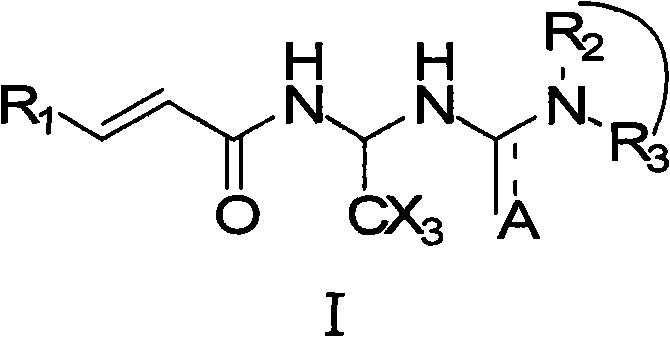
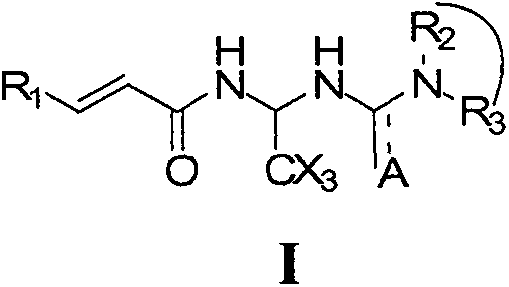
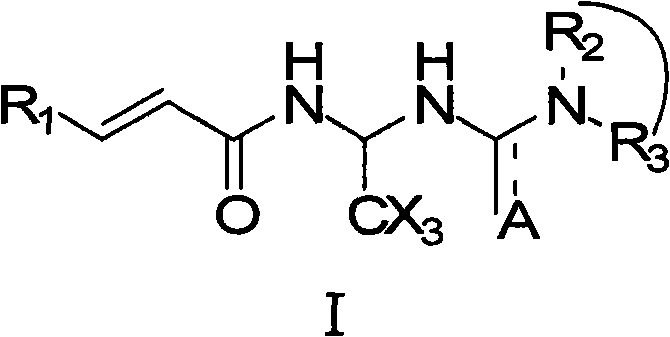
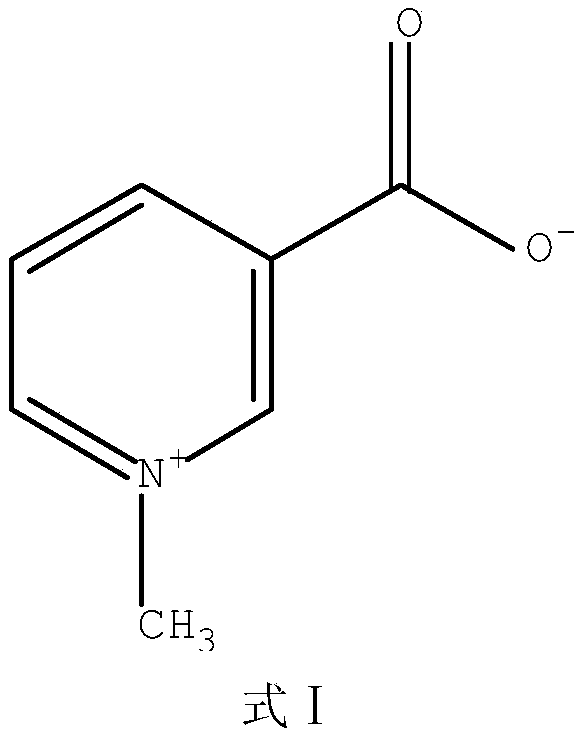
The invention relates to compounds of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates. The invention also relates to compositions containing the compounds shown of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates, and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, excipients or diluents. The invention further relates to uses of the compounds shown of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates in resisting cell apoptosis and preventing or treating of diseases or symptoms related to cell apoptosis, and especially in protecting cardiac muscle cells and preventing or treating diseases or symptoms related to cardiac muscle cell apoptosis.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Recombinant protein and application thereof
InactiveCN106243212AInhibit apoptosisPrevent leakagePeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationCardiac fibrosisCardiac fibroma
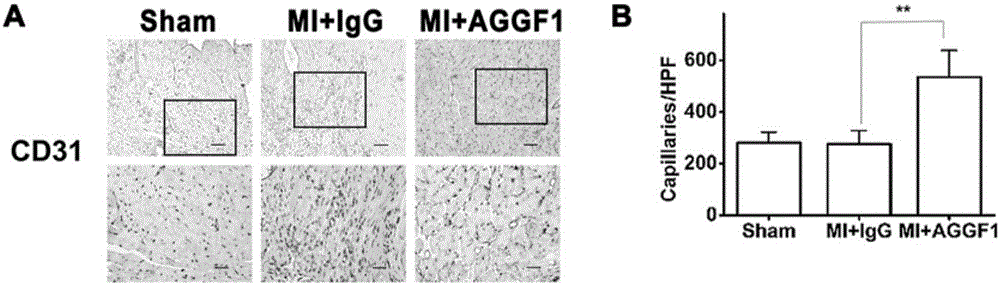
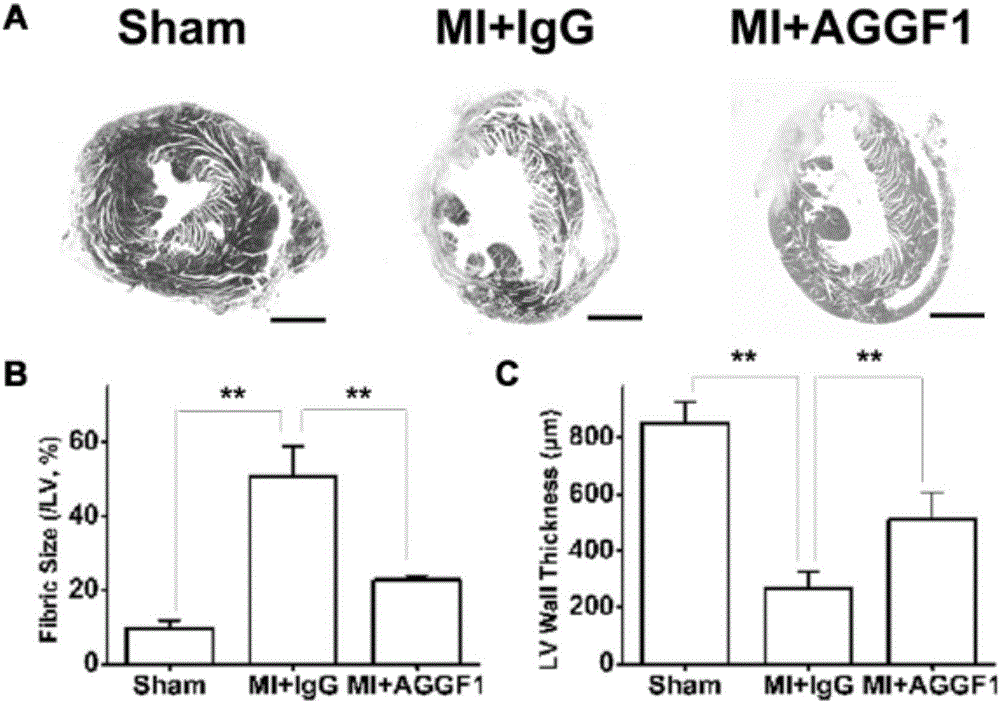
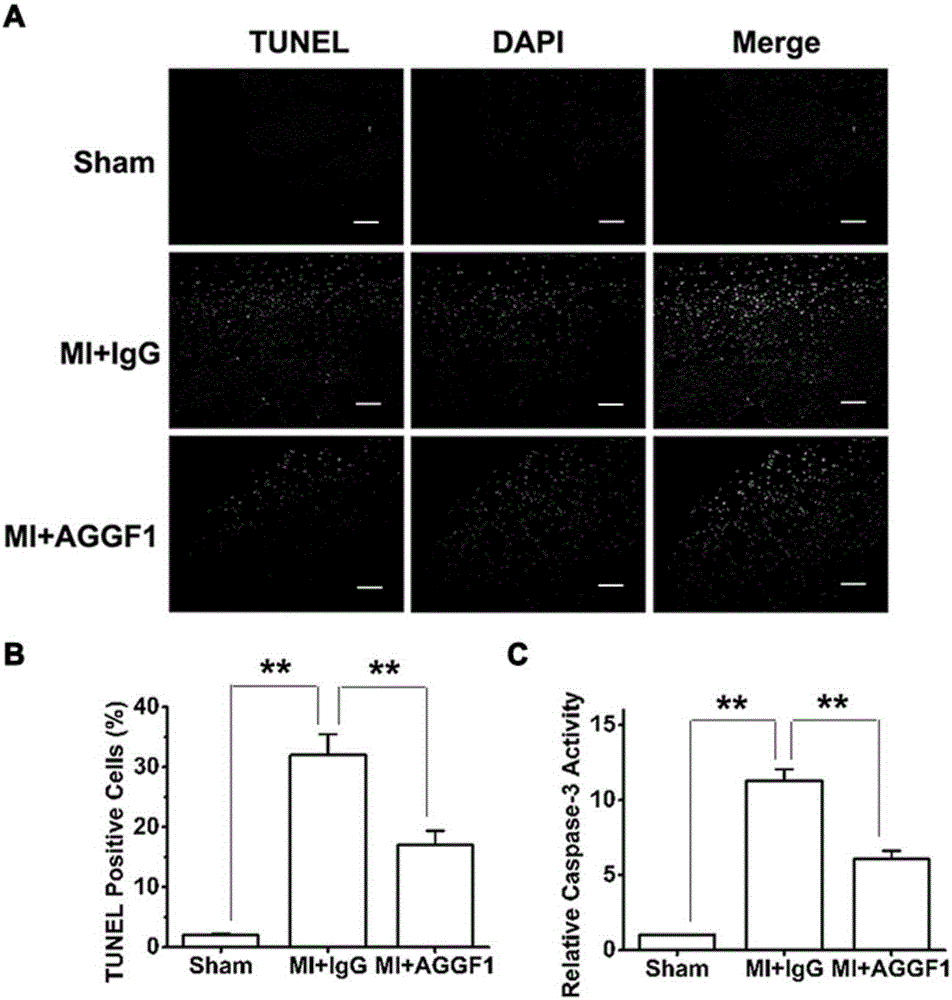
The invention discloses a recombinant protein AGGF1. The recombinant protein AGGF1 can improve the cardiac function of a mouse with acute myocardial infarction and inhibit myocardial apoptosis and cardiac fibrosis by promoting angiogenesis in the heart of the mouse. Thus, the recombinant protein AGGF1 can be used for preparation of angiogenesis promoting drugs for treatment of ischemic diseases. Meanwhile, the recombinant protein AGGF1 can improve the cardiac function of the mouse and inhibit cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting vascular leakage and oedema in cardiac muscles after the operation of cardiac ischemia reperfusion. Thus, the recombinant protein AGGF1 provided by the invention can be used for preparation of drugs for inhibiting vascular leakage to treat vascular leakage, oedema and dysfunction caused by cardiac ischemia reperfusion.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of gynesine in preparing medicine or food for treating or preventing hypoxic damage
ActiveCN108014109ATreat or prevent hypoxic injuryHypoxic damage protectionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNerve cellsObserved Survival
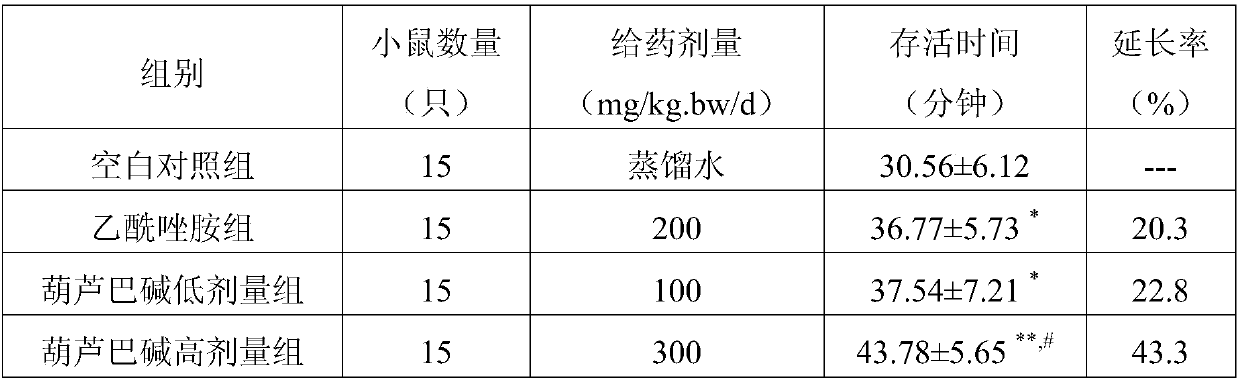
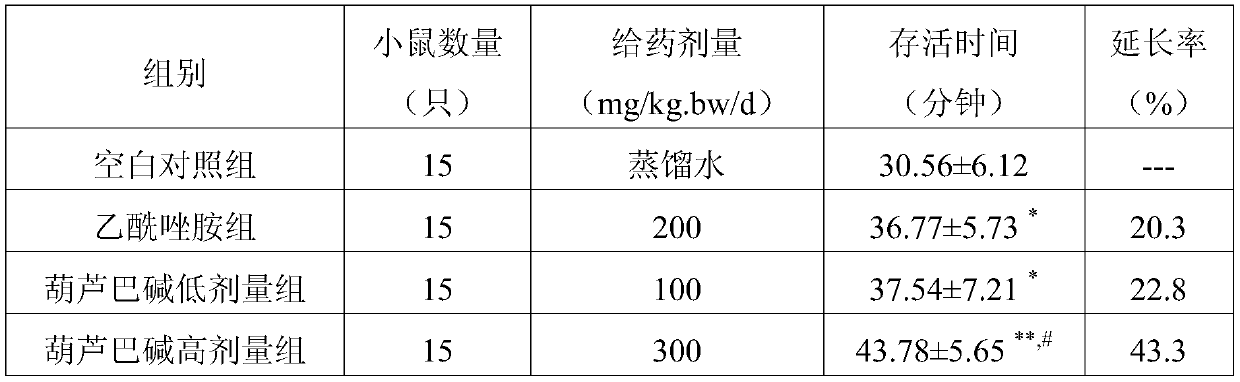
The invention discloses new application of gynesine, namely application of the gynesine in preparing a medicine or food for treating or preventing hypoxic damage, and the medicine or the food preparedfrom the gynesine and used for treating or preventing hypoxic damage. The research finds that the gynesine has a function of treating or preventing hypoxic damage, and can be used for preparing the medicine or the food for treating or preventing hypoxic damage; a cell experiment and an animal experiment prove that the gynesine can be beneficial to protecting hypoxic nerve cell damage, reducing myocardial apoptosis caused by hypoxia, prolonging the survival time of rats in a normal pressure anoxia tolerance test, and increasing the survival rate of the rats in an acute low pressure hypoxia test.
Owner:杭州方回春堂健康科技有限公司
Application of curcumin metabolite in preparation of medicine for treating myocardial ischemia related injury
ActiveCN113456621AAlleviate pathological manifestationsImprovement effect is slightly betterEther/acetal active ingredientsKetone active ingredientsDiseaseTissue fibrosis
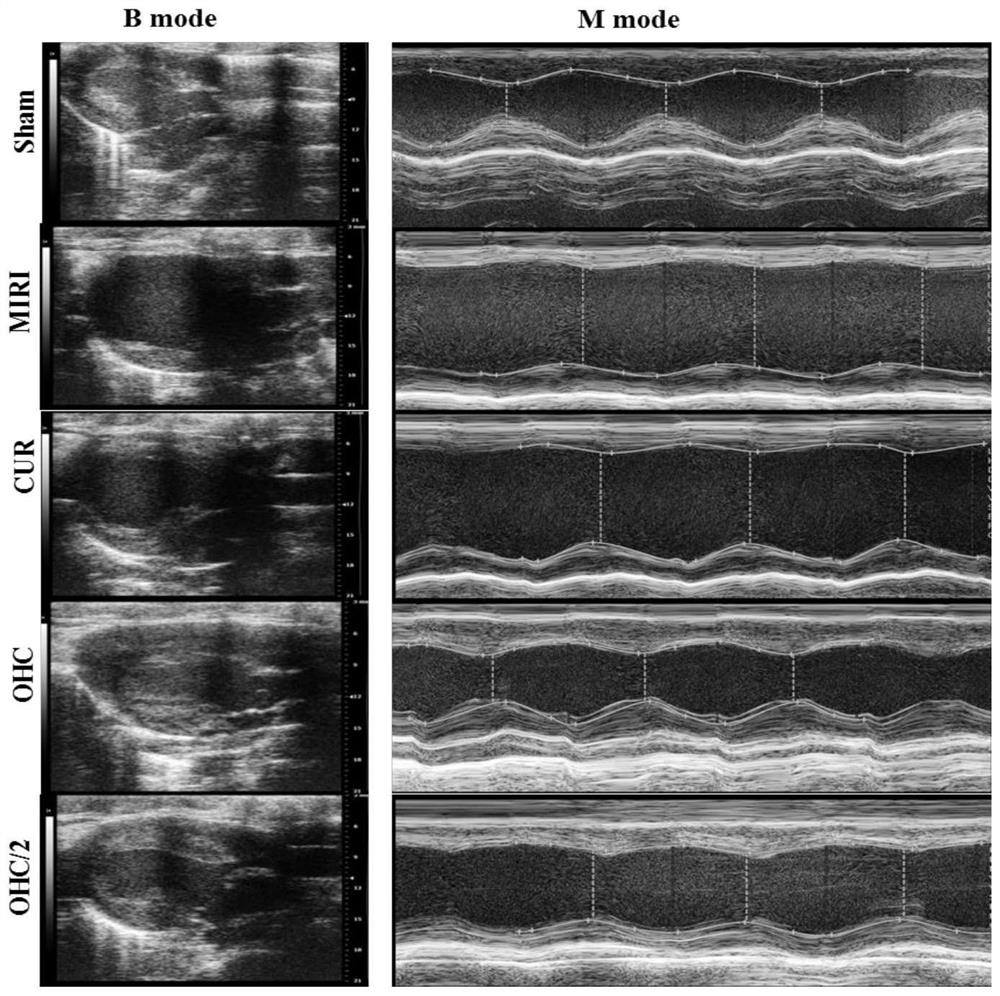
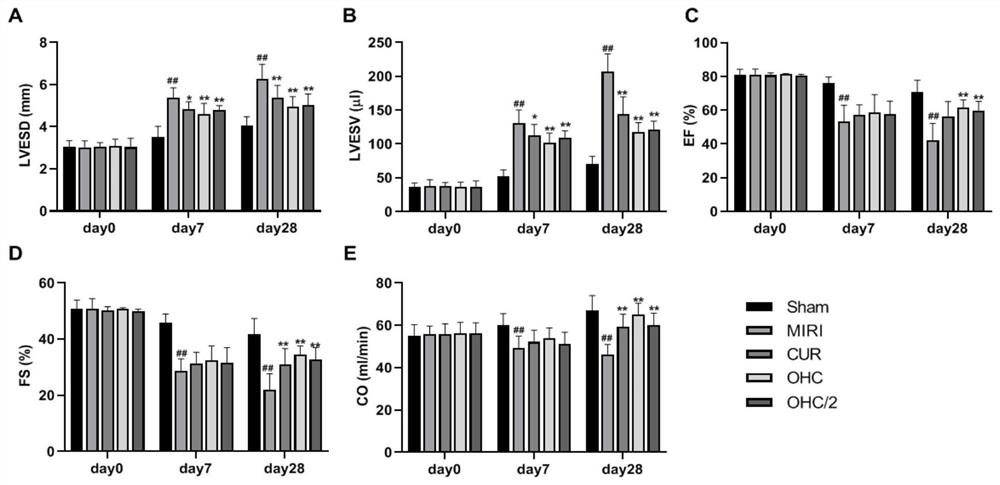
The invention provides an application of curcumin metabolite in preparation of a medicine for treating myocardial ischemia related injury. The research on the intervention effect of a rat MIRI model finds that both CUR and OHC can improve the impaired heart function and serum myocardial enzyme expression, relieve the ventricular enlargement degree, reduce myocardial cell apoptosis and tissue fibrosis-like change and relieve the pathological expression of MIRI, and the improvement effect of OHC is slightly excellent. Therefore, the molecular mechanism of the MIRI disease process can be known, and a valuable scientific basis is provided for explaining the pharmacodynamic action mechanism of the CUR and the active metabolite OHC of the CUR.
Owner:GUANGDONG HOSPITAL OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
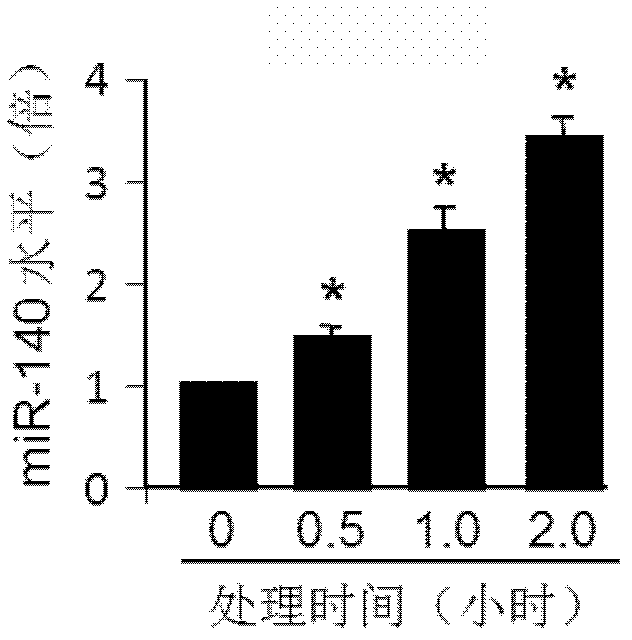
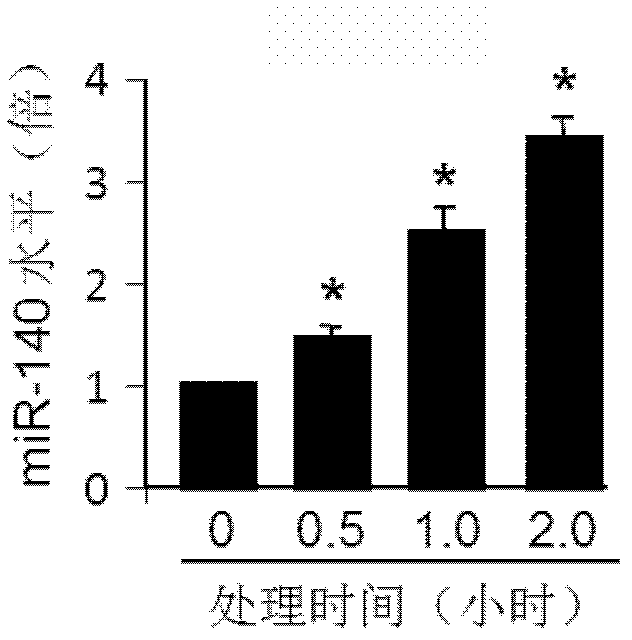
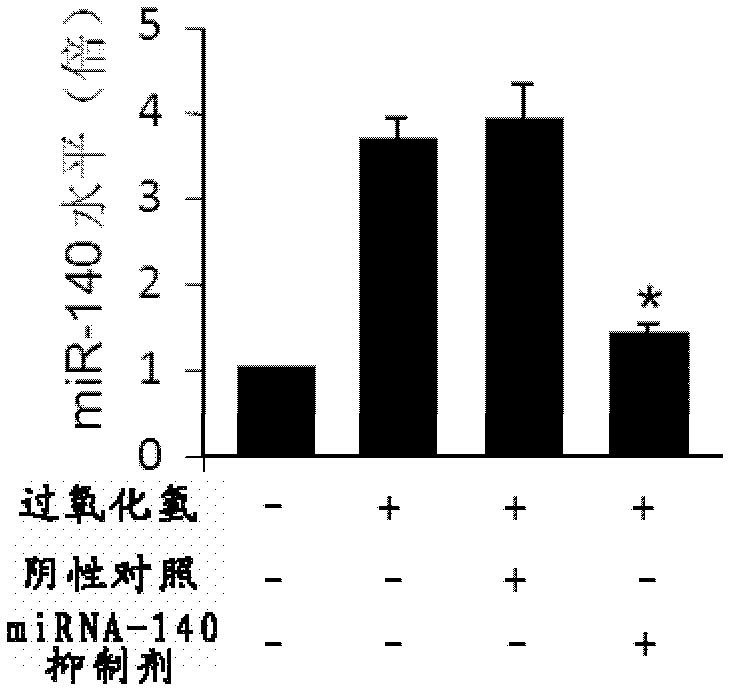
MiRNA-140 inhibitor and applications thereof
ActiveCN103243091AFunction increaseImprove heart functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention provides a miRNA-140 inhibitor and applications thereof, wherein a sequence of the inhibitor has at least 90% of homology with a nucleotide sequence showing in the following SEQ ID NO:1: 5'-CUACCAUAGGGUAAAACCACUG-3', wherein each basic group is modified by 2'-O-methyl; and the miRNA-140 inhibitor is used for preparing a medicament or a kit for diagnosing, preventing, treating and / or prognostically evaluating heart diseases. The miRNA-140 inhibitor is changed in treatment of myocardial ischemia injury and myocardial apoptosis and has a myocardial preservation effect.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
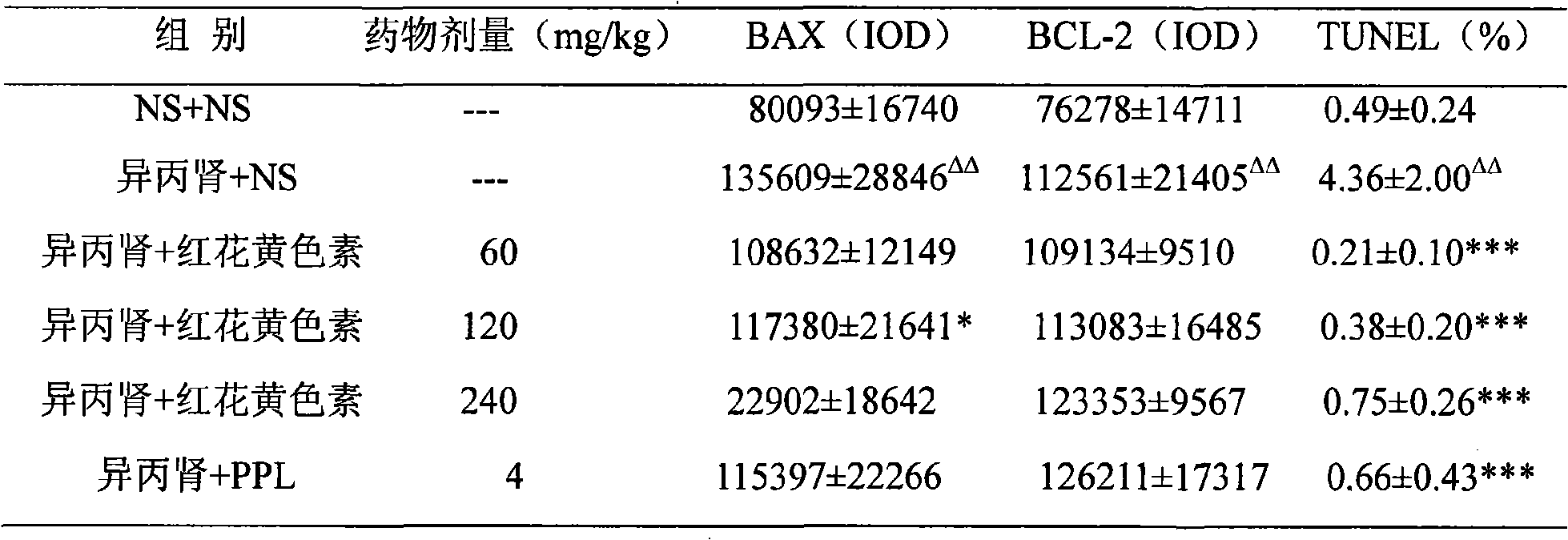
Use of carthamus tinctorius yellow colour in preparing medicine for treating and/or preventing myocardial apoptosis
InactiveCN101357127AReduce apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCarthamusSafflowers
The invention discloses the new application of carthamus tinctorius yellow colour which is prepared by extracting traditional Chinese safflower, namely, the new application on preparing medicines which cure and / or prevent the death of cardiac muscle cells; the invention also discloses medicines prepared by the carthamus tinctorius yellow colour and formulations thereof.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEART LUNG & BLOOD VESSEL DISEASES
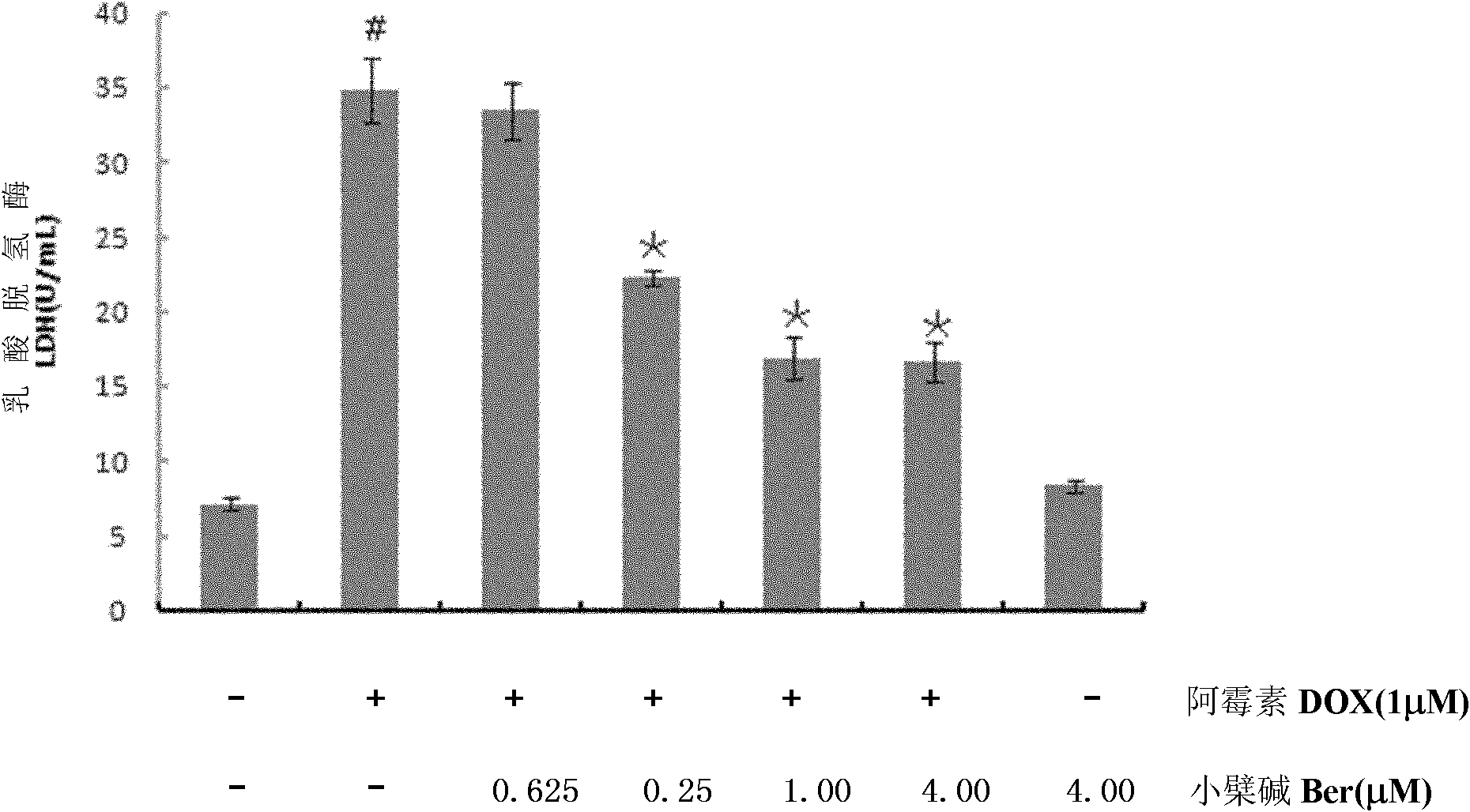
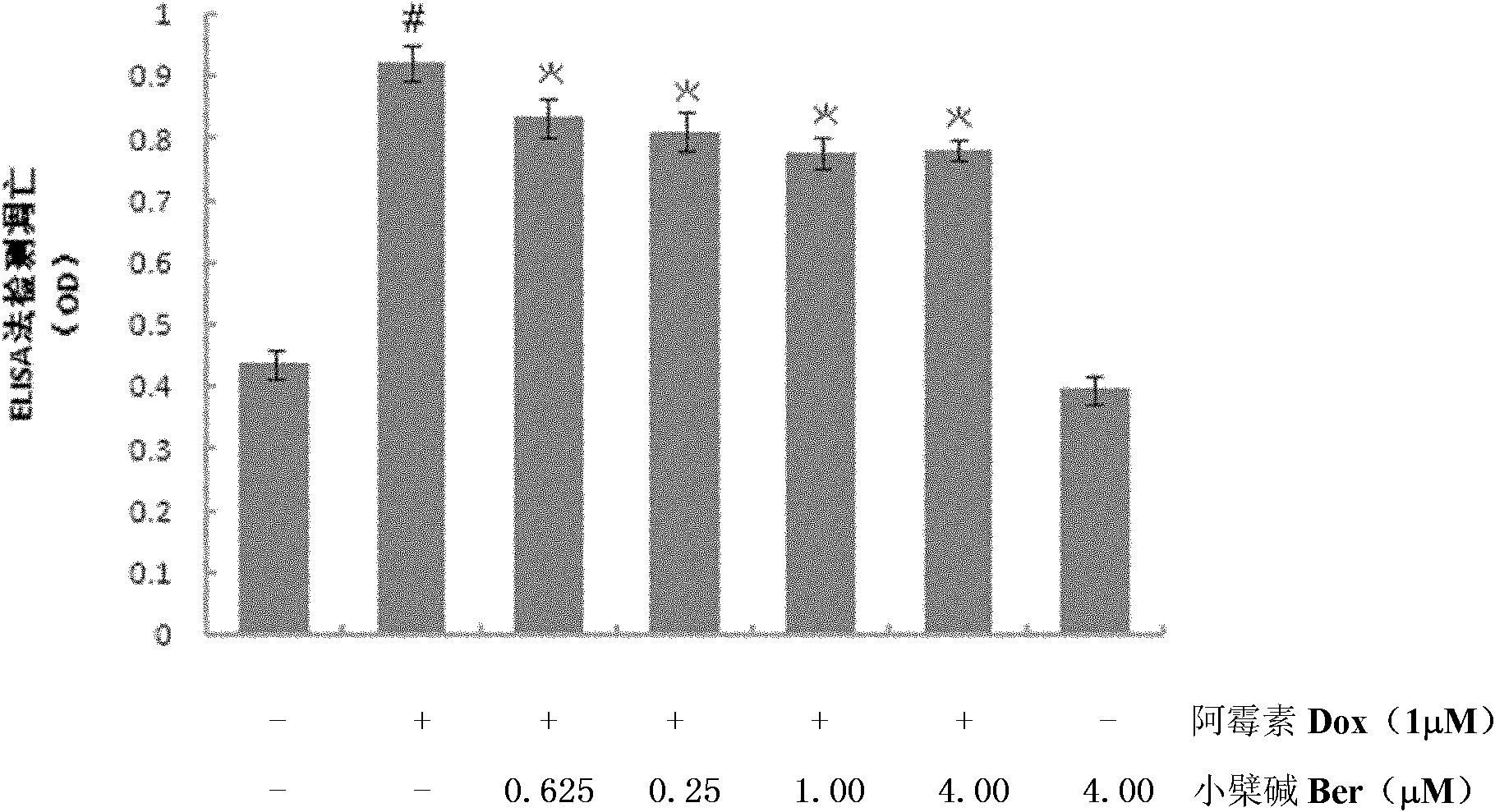
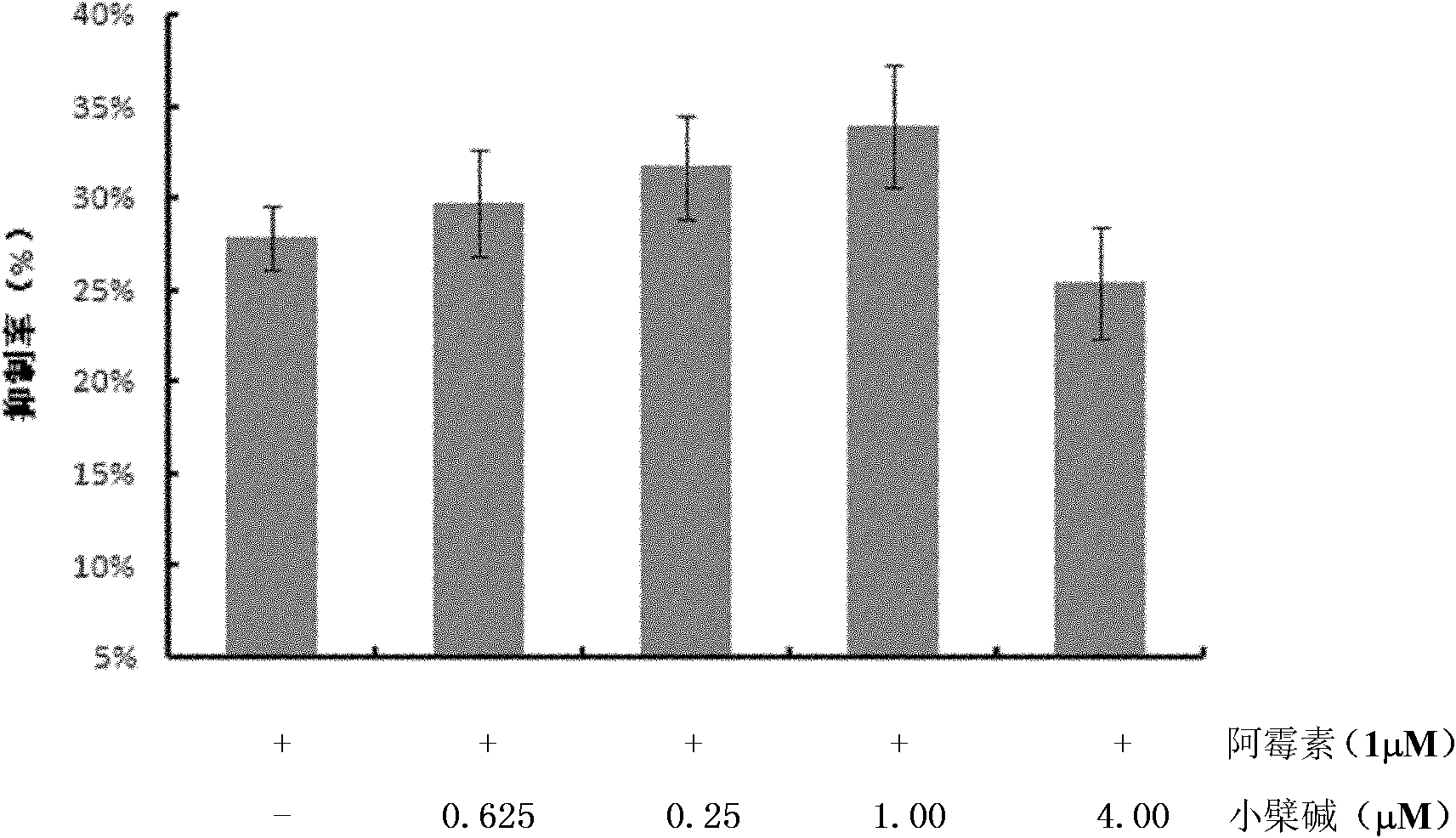
Application of berberine and doxorubicine mixed preparation in preparation of medicament against doxorubicine cardiac dysfunction or tumor
InactiveCN102008495AImprove survival rateHigh inhibition rateOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBerberineCardiac dysfunction
The invention discloses application of a berberine and doxorubicine mixed preparation in preparation of a medicament against doxorubicine cardiac dysfunction or tumor. The molar concentration ratio of the berberine to the doxorubicine in the medicament is (0.625-4): 1, and the optimal ratio is 1:1. The medicament is an oral preparation or an injection preparation. The combined use of the berberine and the doxorubicine can lighten myocardial damage caused by the doxorubicine, also can play a role in inhibiting myocardial apoptosis caused by the doxorubicine, and does not weaken, even enhance the anti-tumor effect of the doxorubicine at the same time.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing human myocardial cell apoptosis model
PendingCN111411075AInduce apoptosisGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMedicineApoptosis
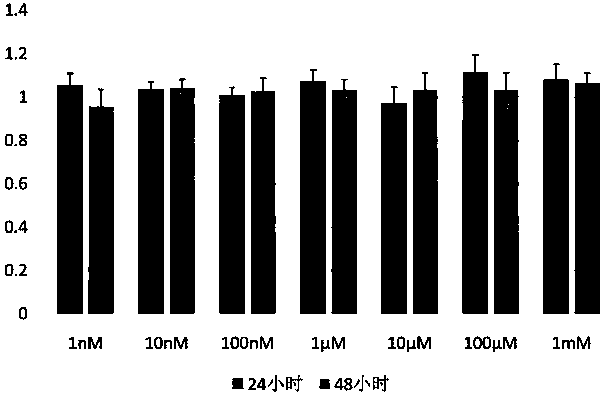
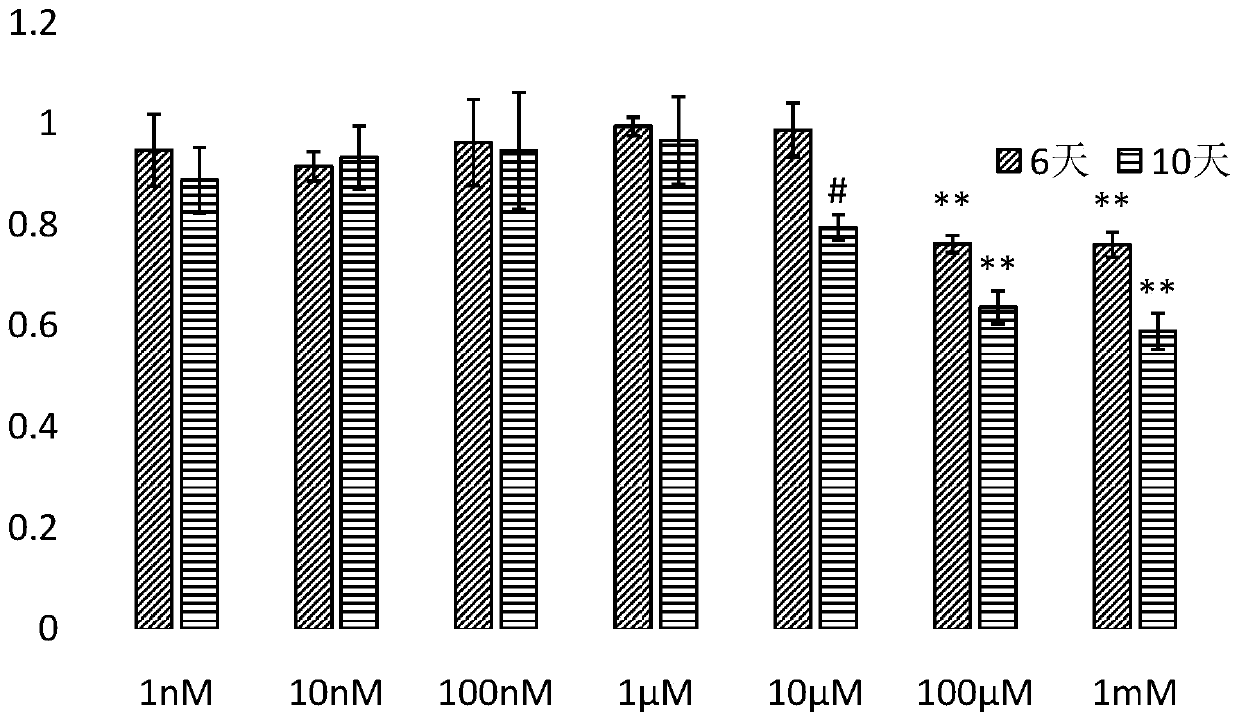
The invention discloses a method for constructing a human myocardial cell apoptosis model. The inventor accidentally finds that after angiotensin II with a certain concentration is used for treating hiPSC-CM for a certain time, the apoptosis of hiPSC-CM can be effectively induced. According to some examples of the invention, the angiotensin II is used for inducing the apoptosis of human myocardialcells, and the myocardial cell apoptosis model closer to the human body is constructed, so that a powerful tool and method are provided for subsequent pharmacological experiments.
Owner:GUANGDONG BEATING ORIGIN REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
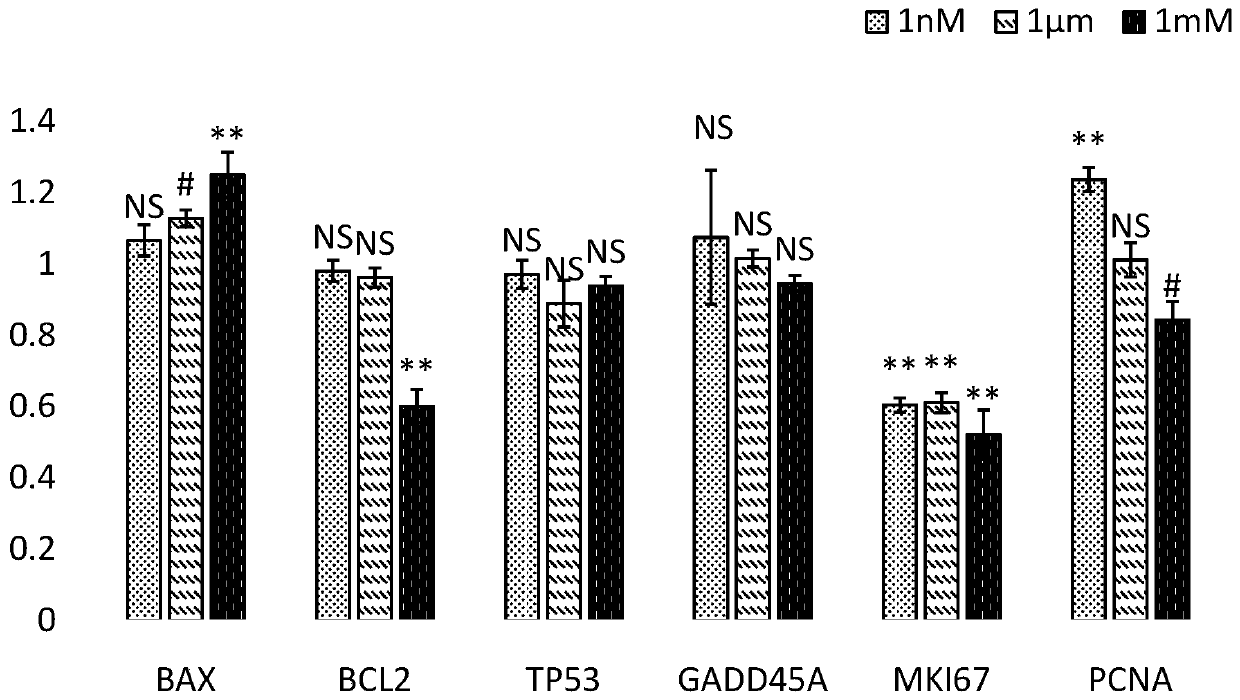
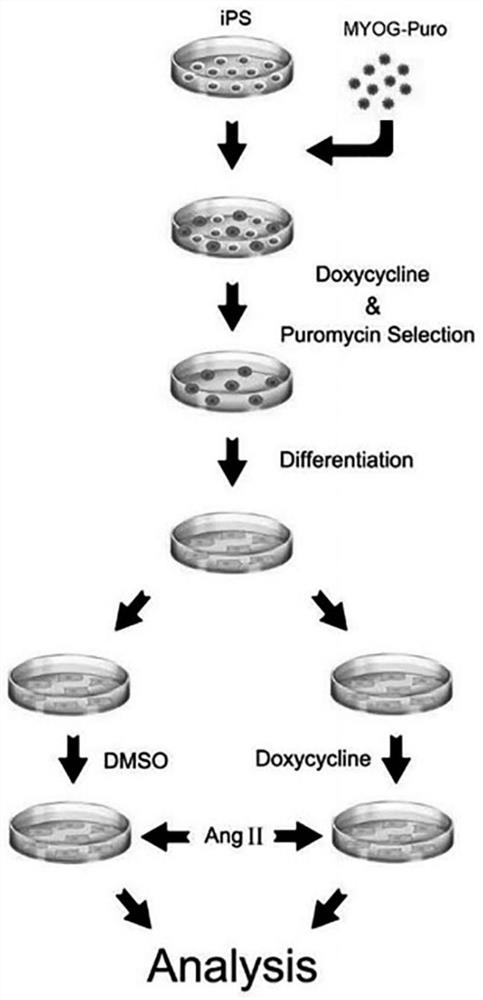
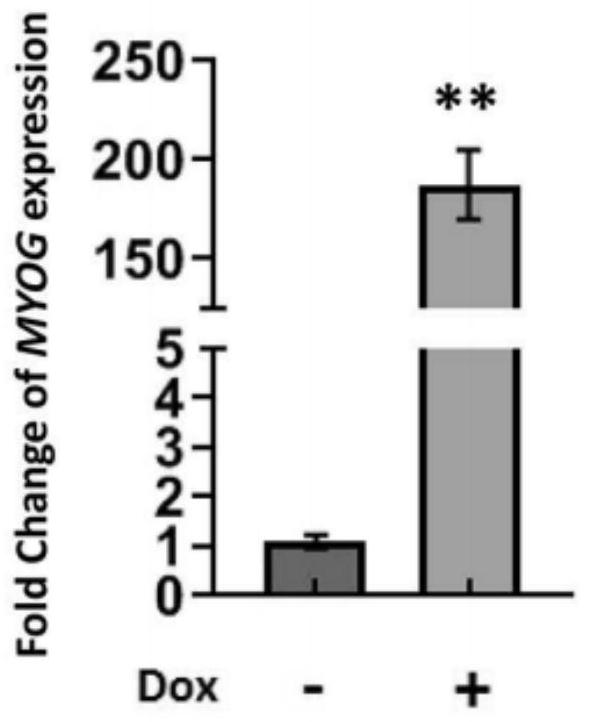
Application of MYOG gene as target point in preparation of drugs for treating cardiovascular diseases related to myocardial cell apoptosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, and particularly relates to application of an MYOG gene as a target point in preparation of drugs for treating cardiovascular diseases related to myocardial cell apoptosis. According to the invention, an angiotensin II induced human induced pluripotent stem cell differentiation myocardial cell apoptosis model is constructed in vitro, the effect of a transcription factor MYOG in inhibiting myocardial cell apoptosis is disclosed for the first time, and a theoretical basis and a scientific basis are provided for research and development of drugs for cardiovascular diseases related to myocardial cell apoptosis, thereby being a new target for research and development of cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:GUANGDONG BEATING ORIGIN REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
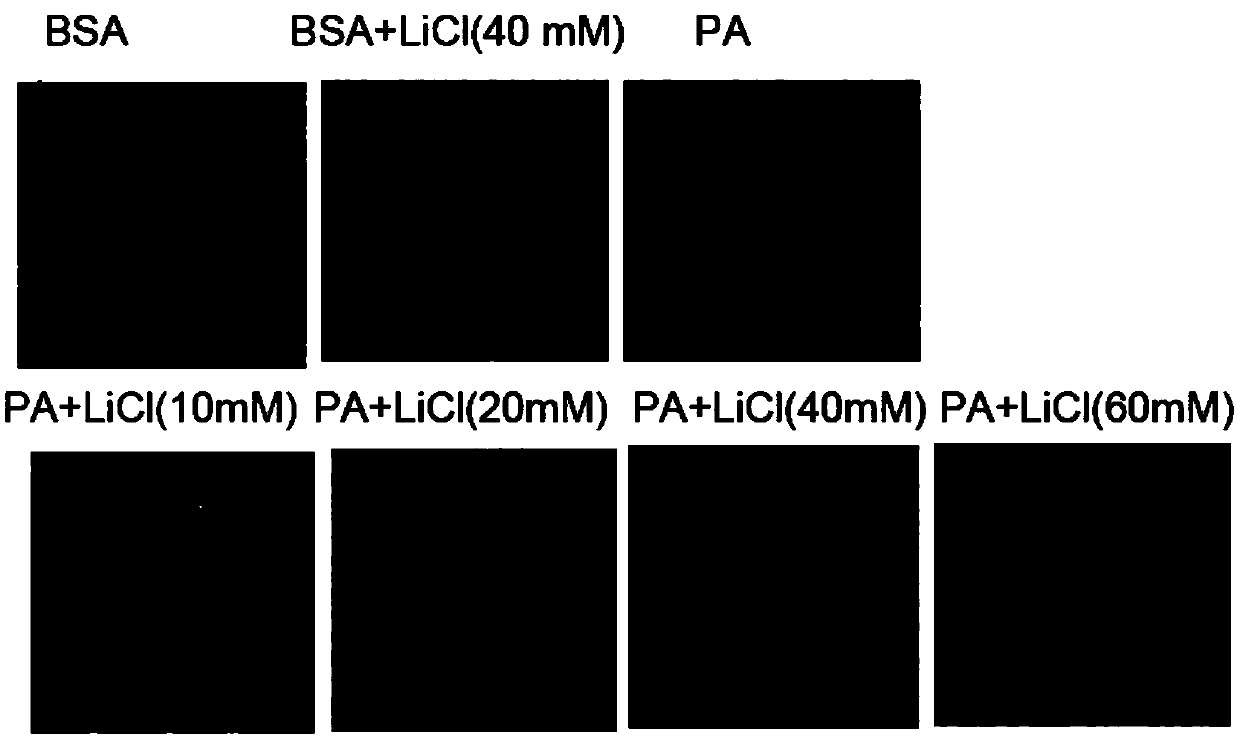
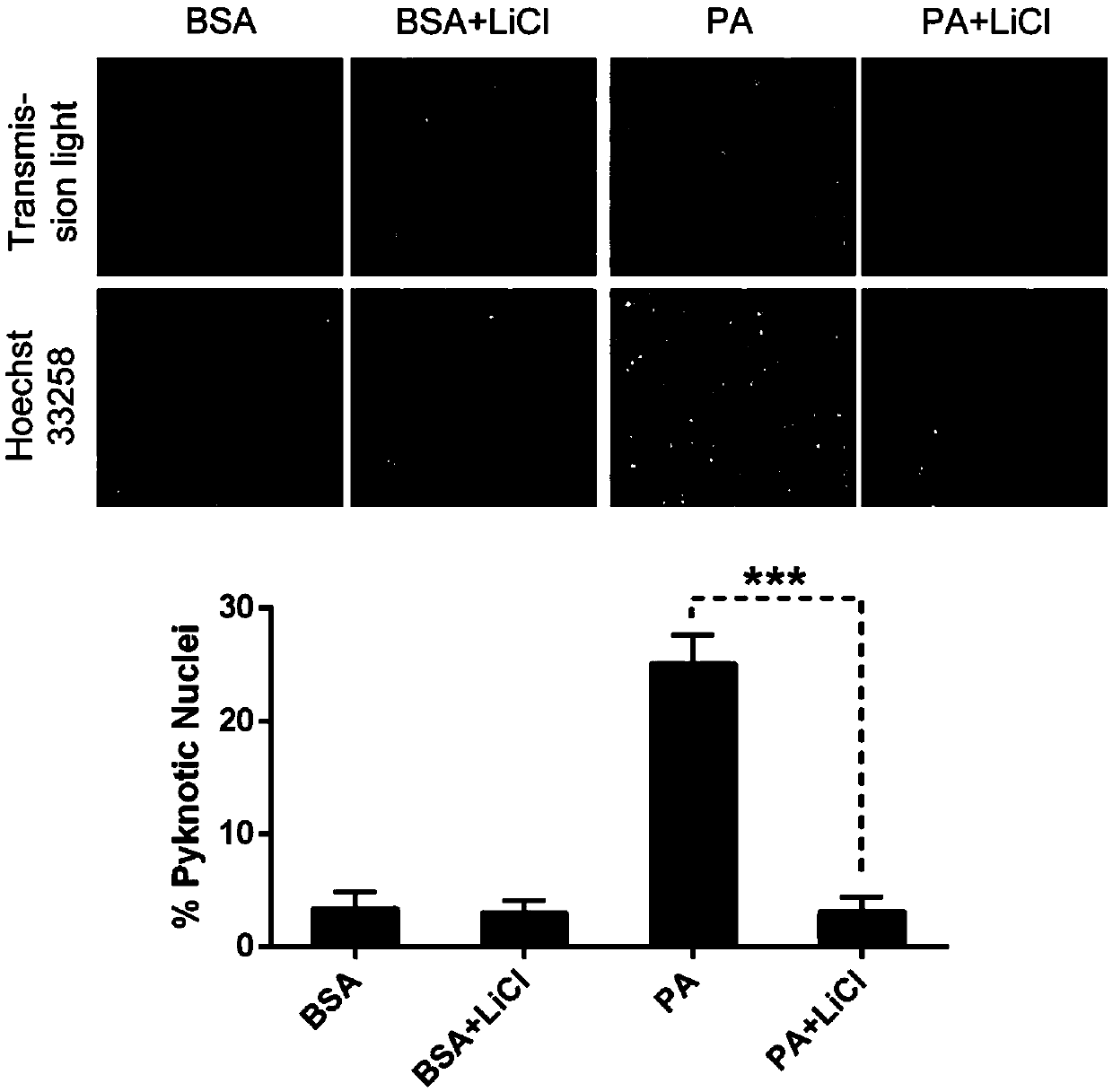
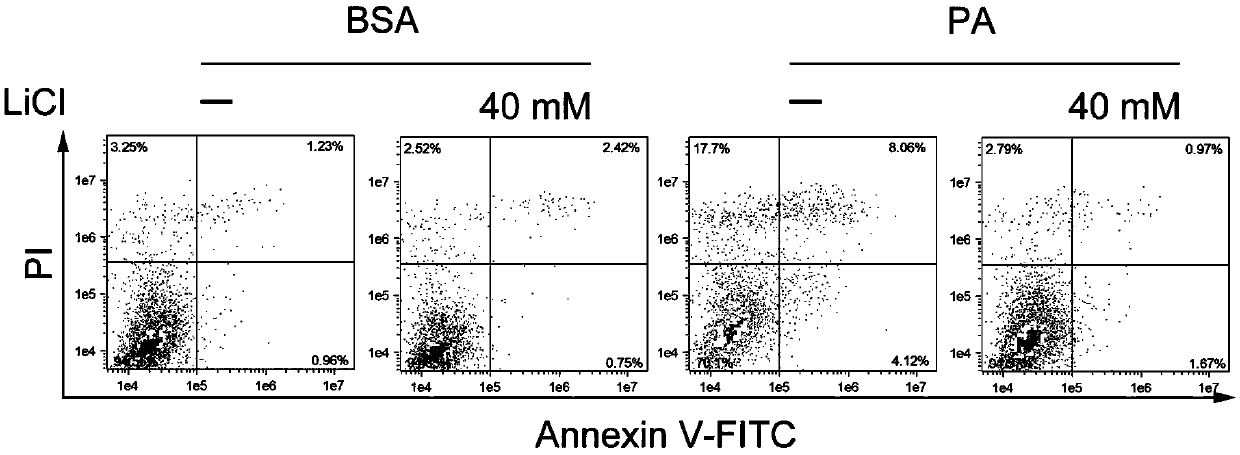
Application of LiCl in preparation of drug for resisting myocardial apoptosis induced by excessive accumulation of lipids
InactiveCN105497060AInhibit apoptosisAlkali/alkaline-earth metal chloride active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseasePyknosis
The invention discloses an application of LiCl in preparation of a drug for resisting myocardial apoptosis induced by excessive accumulation of lipids. Experiments prove that LiCl can effectively inhibit myocardial apoptosis induced by long-chain saturated fatty acid palmitate, specifically, LiCl inhibits cutting of palmitate induced apoptosis executor caspase 3 precursors, and the apoptosis rate of cells and pyknosis of nucleus chromatin are remarkably reduced; the experiments further determine that 40 mM concentration can be taken as drug concentration for effectively and specifically inhibiting palmitate induced H9c2 myocardial apoptosis by LiCl, and LiCl is expected to be applied to the preparation of the drug for treating the myocardial apoptosis induced by excessive accumulation of the lipids accompanied by diseases such as obesity, diabetes mellitus and the like in clinical research and has broad scientific research and clinical development prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating sepsis heart failure and preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine composition
InactiveCN109125591AReduce fatalityReduce apoptosisAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticMotherwortTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to the field of treatment of sepsis heart failure, in particular to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating sepsis heart failure and a preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine composition. The traditional Chinese medicine composition consists of 25-35 parts of radix astragali, 15-25 parts of poria cocos, 15-25 parts of radix salviae miltiorrhizae, 5-15 parts of Chinese magnoliavine fruits, 10-20 parts of radix ophiopogonis, 10-20 parts of tansymustard seeds, 15-25 parts of motherwort and 35-55 parts of princesplume ladysthumb fruits and fructus aurantii, wherein the mass ratio of the added princesplume ladysthumb fruits to the added fructus aurantii is 1.25-3.5 to 1. The lethality caused by sepsis can be reduced, the myocardial damage canbe reduced, and the traditional Chinese medicine composition can resist inflammation, restrain myocardial apoptosis and the like, and has better treatment effects on the sepsis heart failure.
Owner:BEIJING CHINESE MEDICINE HOSPITAL AFFILIATED CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Application of traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and/or treating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
InactiveCN111514209AGood biocompatibilityImprove targetingUnknown materialsCardiovascular disorderMyocardial ischaemiaPharmacology
The invention relates to application of a traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of a medicine for preventing and / or treating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from radix rehmanniae praeparata, rhizoma coptidis, radix paeoniae alba, radix scutellariae, colla corii asini and poria. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can obviously control the weight gain of a rat after ovariectomy and can obviously reduce the infarction area of the rat under myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury after ovariectomy; the levels of serum LDH and serum CK after myocardial ischemia reperfusion are remarkably reduced, and myocardial damage is reduced; and according to the application, the expression of GRP78 protein, CHOP protein, Active-caspase12 protein and the Active-caspase3 protein after the myocardial ischemia reperfusion can be significantly inhibited and reduced, so as to inhibit the apoptosis of the myocardial cells after the myocardial ischemia reperfusion.
Owner:GUIYANG XINTIAN PHARMA CO LTD
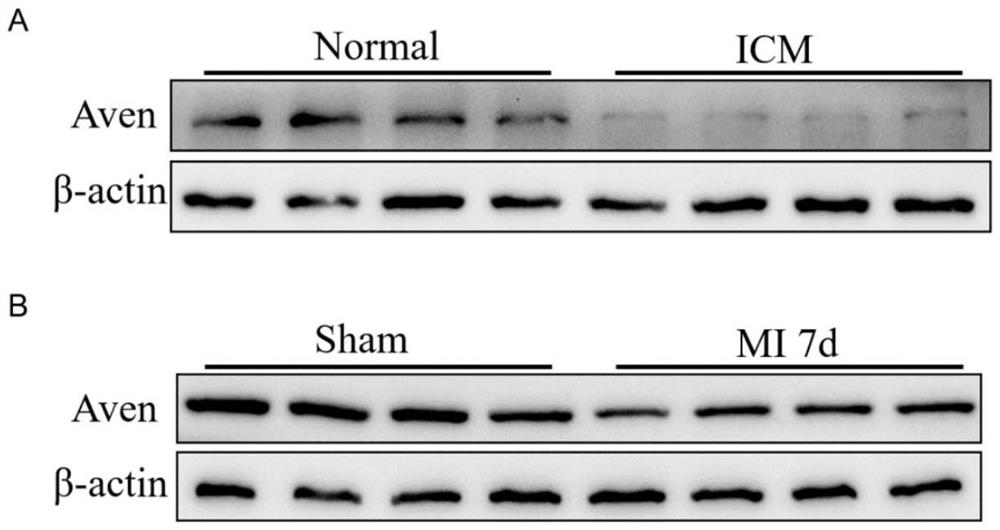
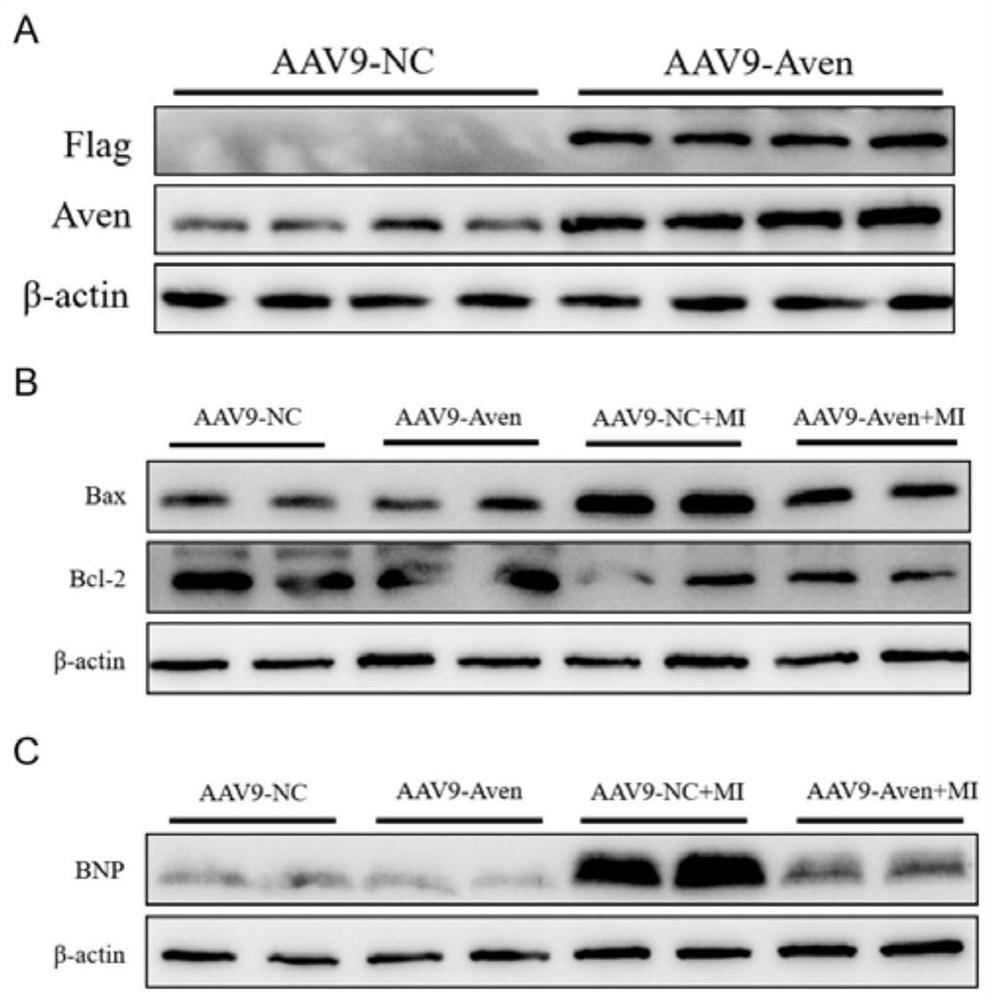
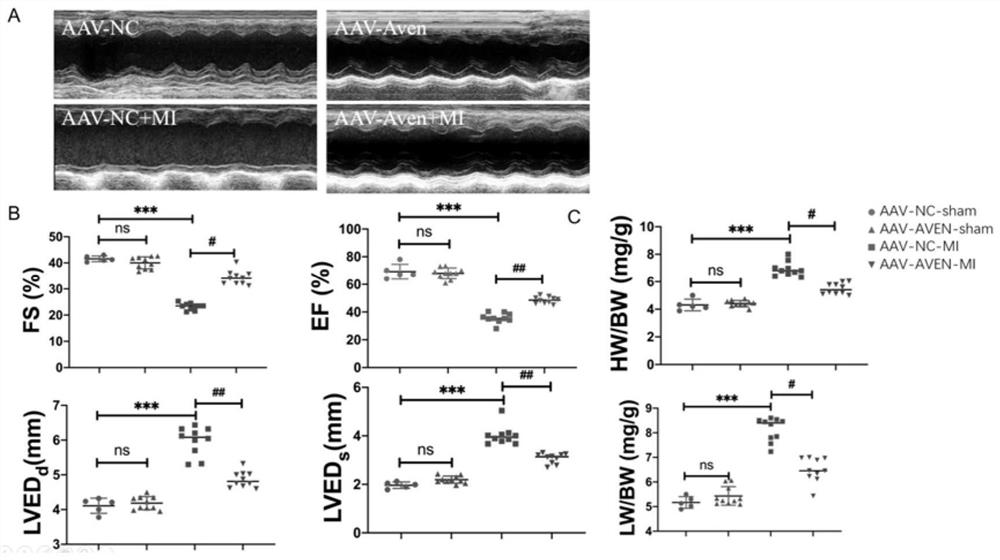
Application of AVEN gene in ischemic heart disease
ActiveCN114425091AEasy to shrinkFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisApoptosisBiology
The invention discloses an application of an AVEN gene in ischemic heart disease. Through analysis, the invention finds that the AVEN gene is obviously reduced in myocardial infarction patients and mouse myocardial infarction models, which may be an important reason for myocardial apoptosis and heart failure. The AVEN is overexpressed in a mouse myocardial infarction model by using the adeno-associated virus, and the result shows that the overexpression of the AVEN can inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis and obviously improve the left ventricular function. According to the application of the AVEN gene in preventing and treating the ischemic heart disease, AVEN adeno-associated virus gene therapy is given to a patient suffering from myocardial infarction clinically, myocardial cell apoptosis can be inhibited, the cardiac contraction and relaxation functions are improved, and the living quality and long-term prognosis of the patient are improved; a new target and strategy are provided for clinically preventing and treating the ischemic heart disease.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
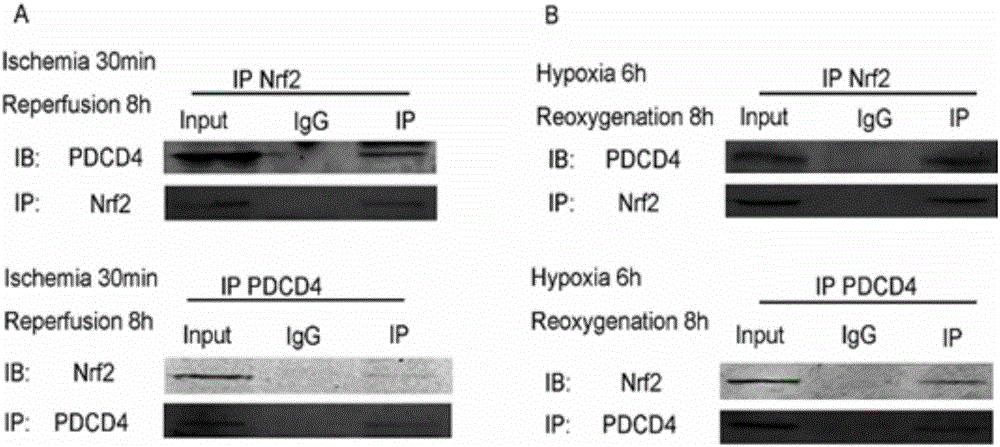
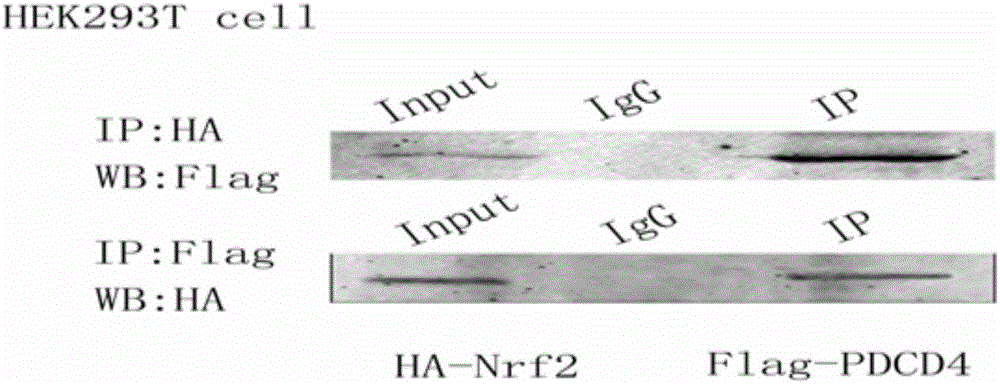
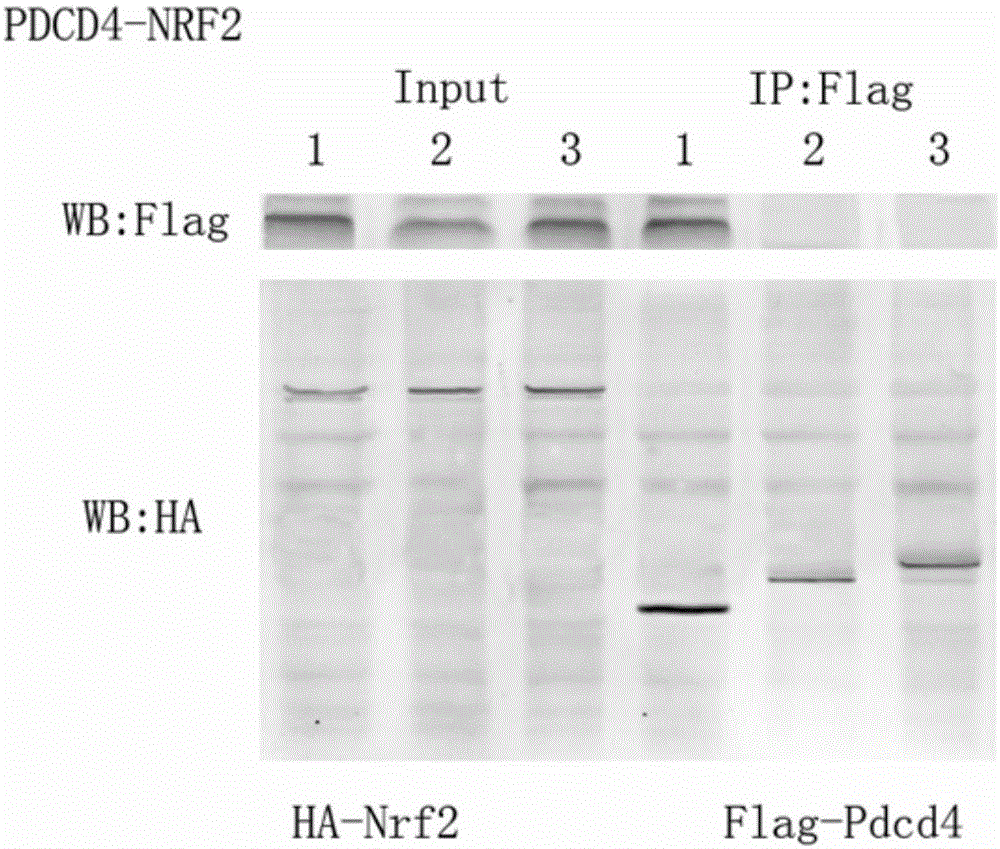
Small molecular polypeptide inhibiting MIRI and vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105906701AAchieve reorganizationInhibit apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis related proteinsSequence analysisEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses small molecular polypeptide inhibiting MIRI and a vector and application thereof. A bioengineering technology is utilized, a section of sequence corresponding to polypeptide analogue is genetically recombined to a p3XFLAG-CMV eukaryotic expression vector; after it is proved that recombination is successful through enzyme digestion and sequential analysis, plasmid corresponding to the eukaryotic expression polypeptide analogue is transfected into myocardium cells, protein expression of polypeptide is proved through immunoblotting, and polypeptide recombination is achieved. It is proved through co-immunoprecipitation that the polypeptide analogue can promote interaction of PDCD4 and Nrf2, it is shown through cell biology experiments that the polypeptide analogue has the capacity of inhibiting myocardium cell apoptosis caused by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injuries and the functions of resisting oxidative stress and apoptosis of the myocardium cells and inhibiting occurrence and development of MIRI.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
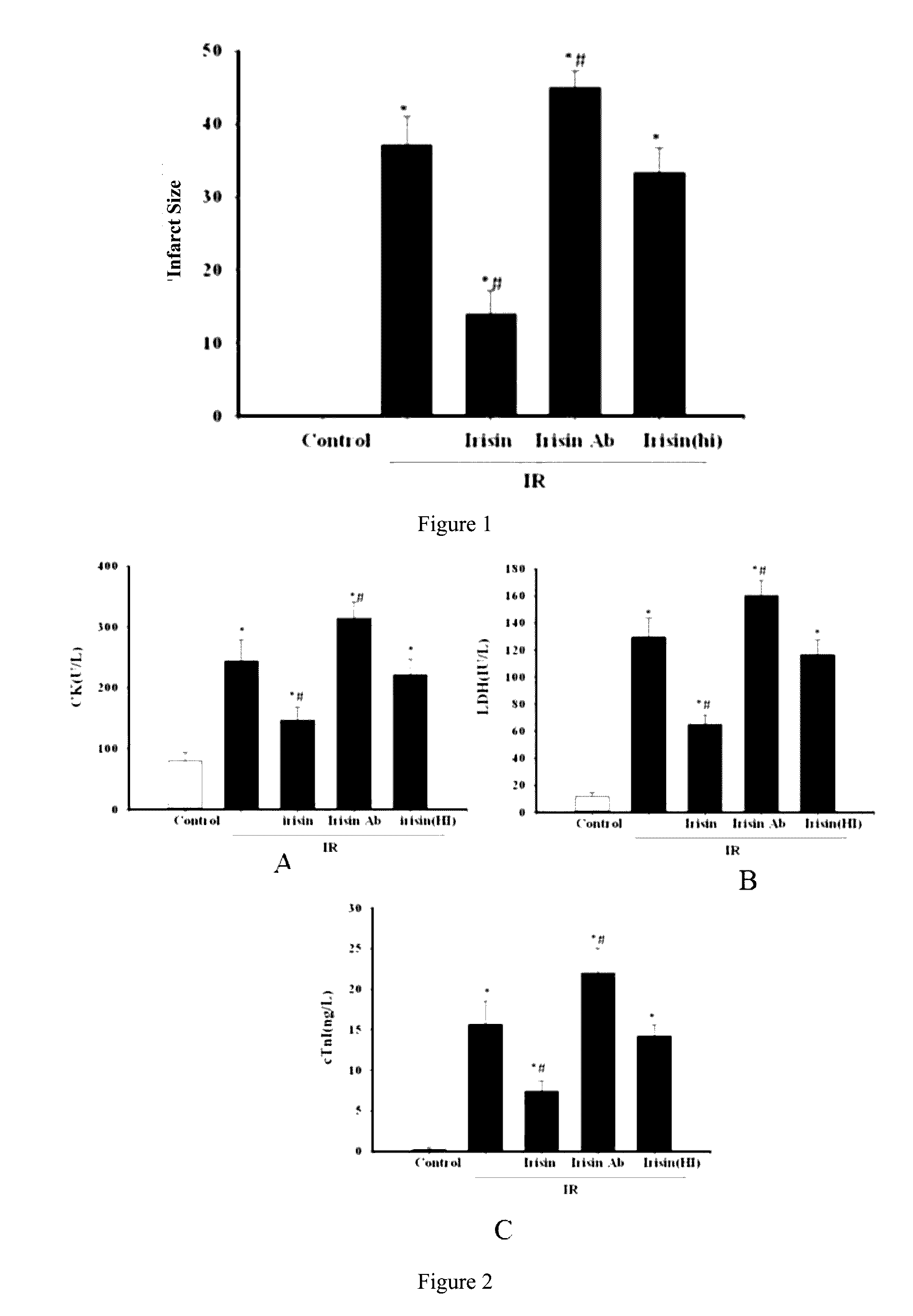
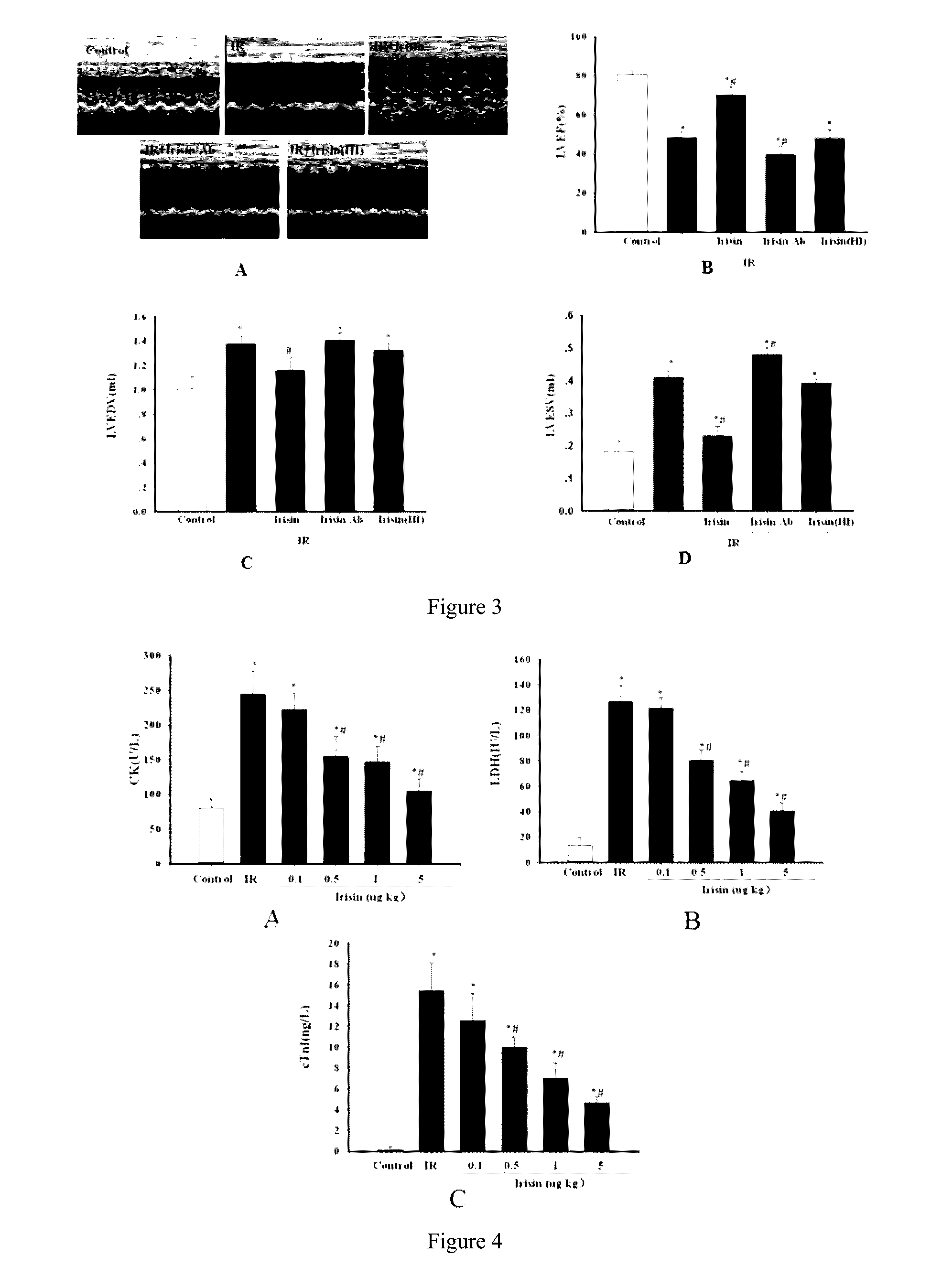
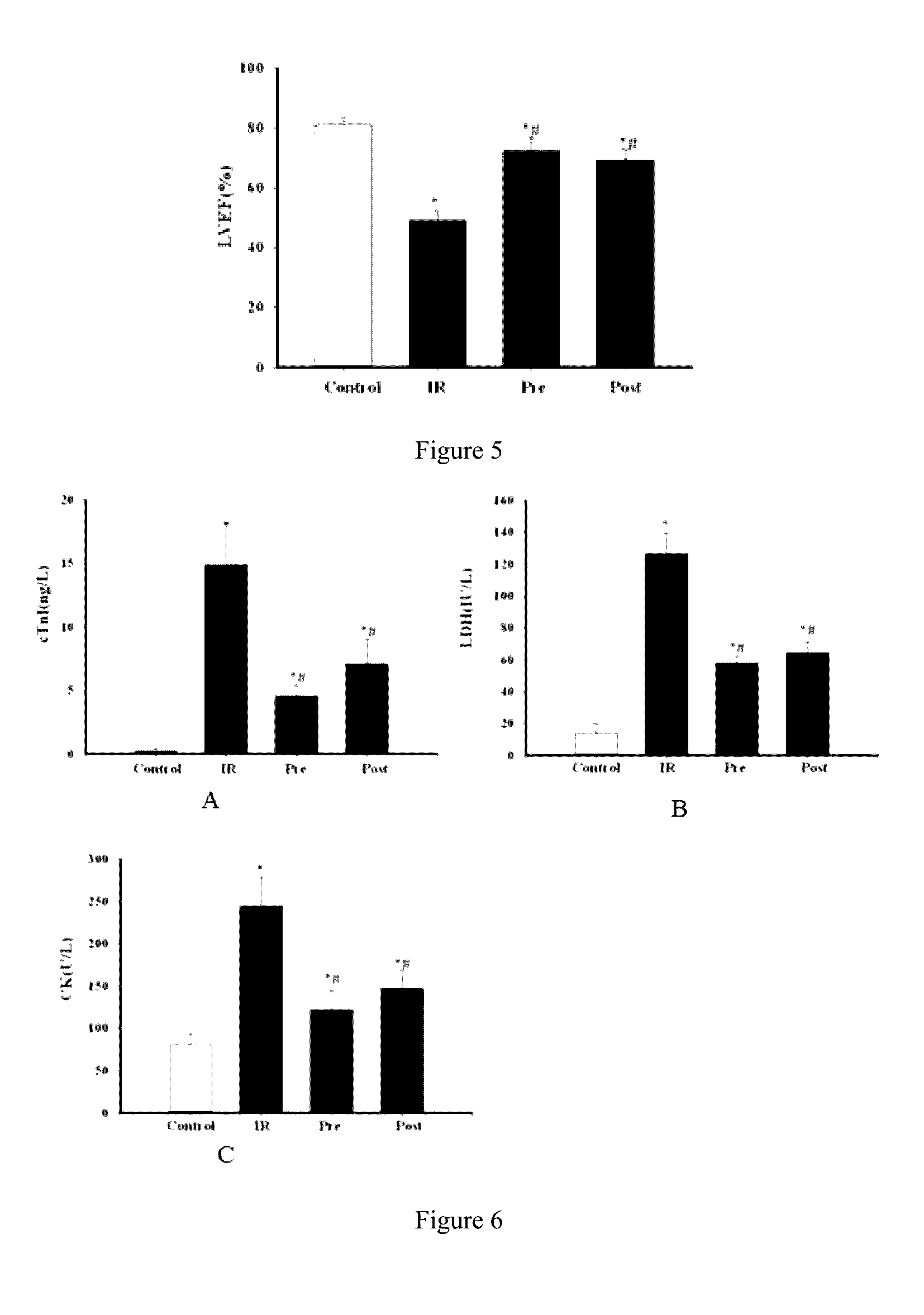
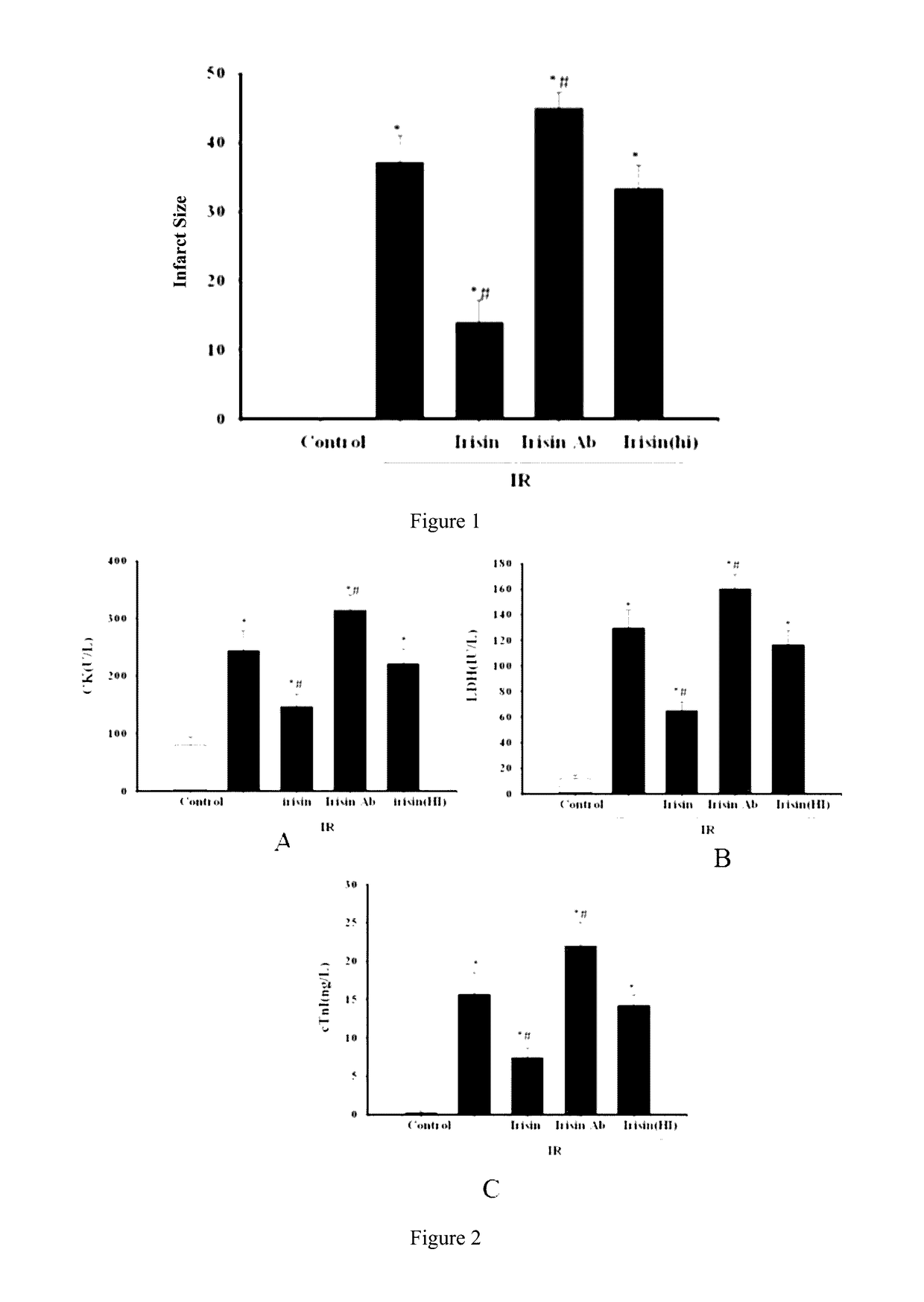
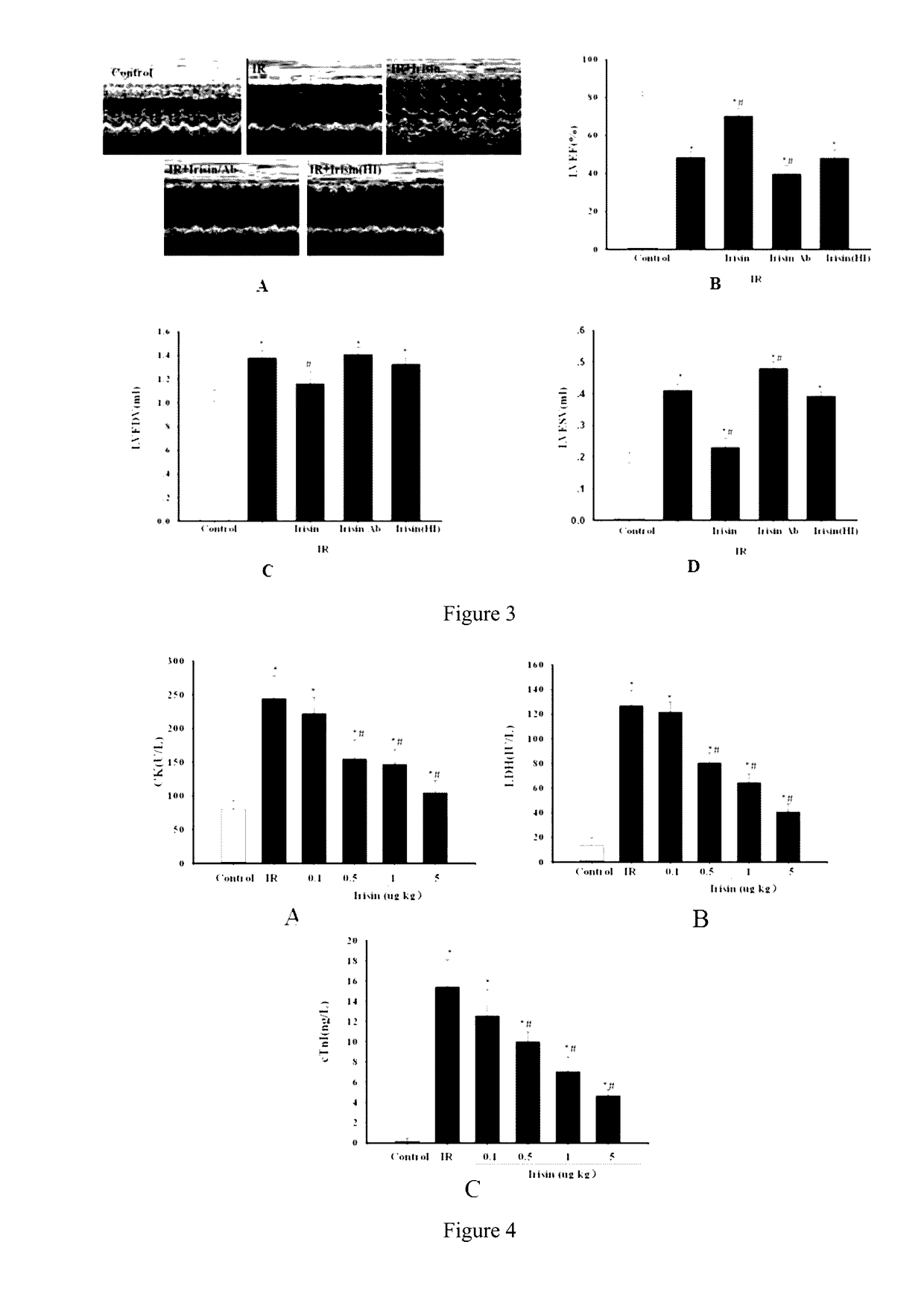
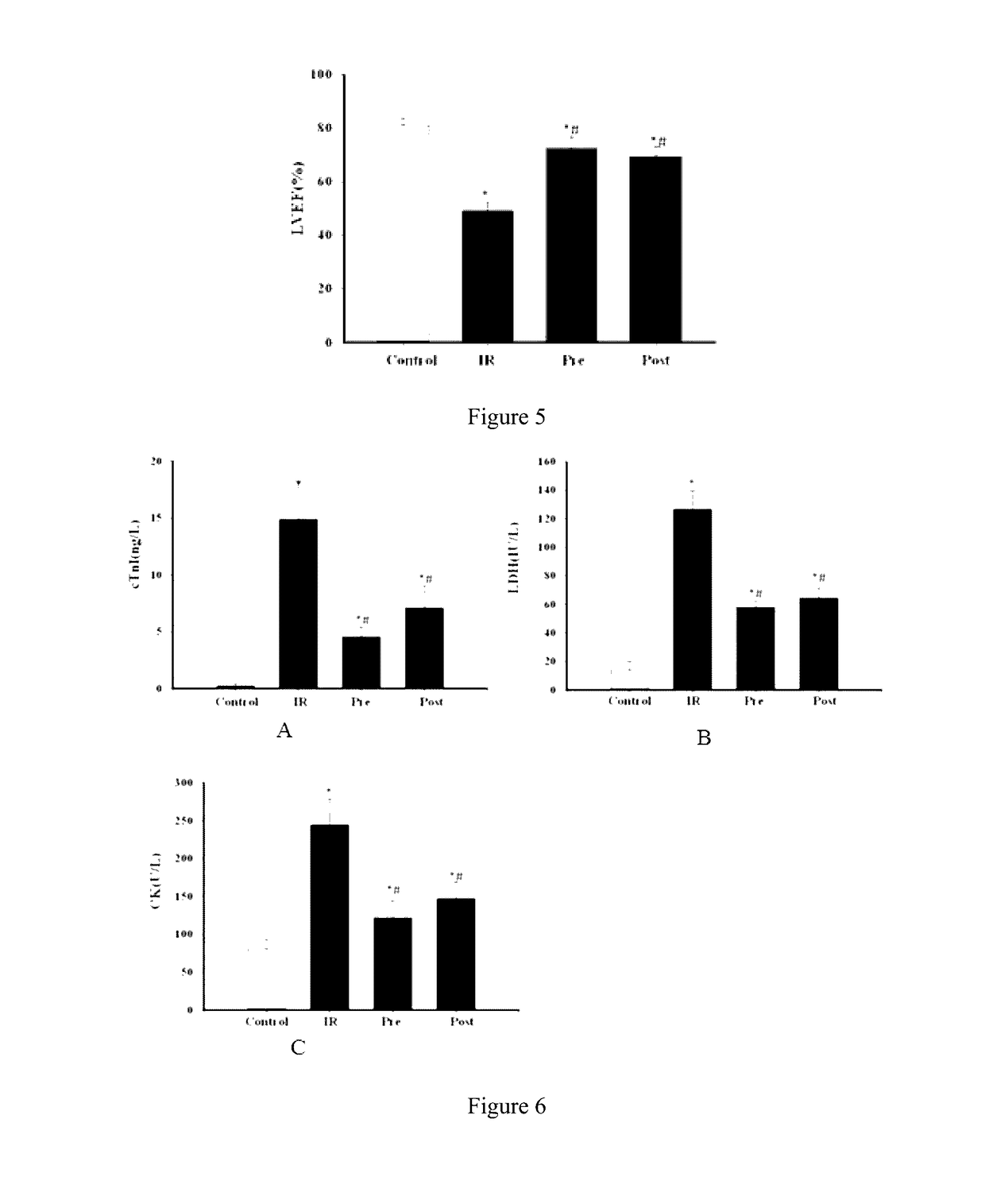
Application of irisin in the preparation of drugs for preventing myocardial ischemia reperfusion injuries
ActiveUS20160296598A1Inhibit oxidative stressDecrease the enlargement of the myocardial infarction areaHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsCreatine kinaseMyocardial reperfusion
The invention discloses application of irisin in the preparation of drugs for preventing myocardial ischemia reperfusion injuries. Experimental results show that irisin can decrease the myocardial infarction area caused by ischemia reperfusion, reduce the increase of the contents of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponin (cTnI), creatine kinase (CK), and other myocardial enzyme markers caused by ischemia reperfusion, meanwhile reducing the inflammatory response, myocardial apoptosis, and oxidative stress response caused by myocardial ischemia reperfusion, promote peroxysome proliferator-activated receptor γ nuclear translocation, and inhibit nuclear transcription factor NF-κB nuclear translocation and accordingly decrease myocardial structure injuries and load increase caused by ischemia reperfusion. Therefore, irisin can be used for preventing and decreasing myocardial reperfusion injuries and has important clinical significance on the treatment of myocardial ischemia.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Acrylamide compounds and medicinal uses thereof
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Application of a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell
ActiveCN105769910BImproved flow dynamicsProtect against pathological changesUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac functioningAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses application of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of a preparation for treating a myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury generated after cardiopulmonary bypass.In the myocardial ischemia reperfusion process after the cardiopulmonary bypass, the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can effectively prevent myocardial cells from being injured in myocardial ischemia reperfusion, obviously improve the cardiac functions, lower the levels of myocardial injury specific marker protein lactic dehydrogenase, creatine kinase isoenzyme and troponin I, lower the levels of a plasma inflammatory factor interleukin-8 and a tumor mecrosis factor-alpha, increase the content of the plasma inflammatory factor interleukin-10, obviously improve pathological changes of the myocardial tissue, reduce myocardial cell apoptosis, lower the expression level of cell apoptosis promoting protein, increase the expression quantity of anti-apoptoasis protein and can protect the functions of myocardial cell mitochondria.By preparing the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells into an injection for treatment on the myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury generated after the cardiopulmonary bypass, the cardiac functions can be effectively protected, and postoperative complications of the cardiopulmonary bypass are relieved.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
Application of fuziline in preparation of medicine for preventing and/or treating diseases caused by myocardial cell apoptosis
InactiveCN112891347AInhibit apoptosisInhibition of stress injuryOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderReticulum cellApoptosis
The invention discloses application of fuziline in preparation of a medicine for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by myocardial cell apoptosis. The invention discovers for the first time that fuziline has an effect of protecting myocardial cells, can inhibit the myocardial cell apoptosis caused by ISO by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress injury of the myocardial cells by reducing ROS generation, and can be used for preparing the medicine for preventing and / or treating the diseases caused by the myocardial cell apoptosis; and the invention also discovers that a composition of ginsenoside Rb1 and fuziline and a composition of tanshinone IIA and fuziline can obviously improve the survival rate of the myocardial cells compared with the single effect of fuziline. The fuziline disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the field of medicines, and can provide a new medicine source for treatment of the diseases caused by the myocardial cell apoptosis.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
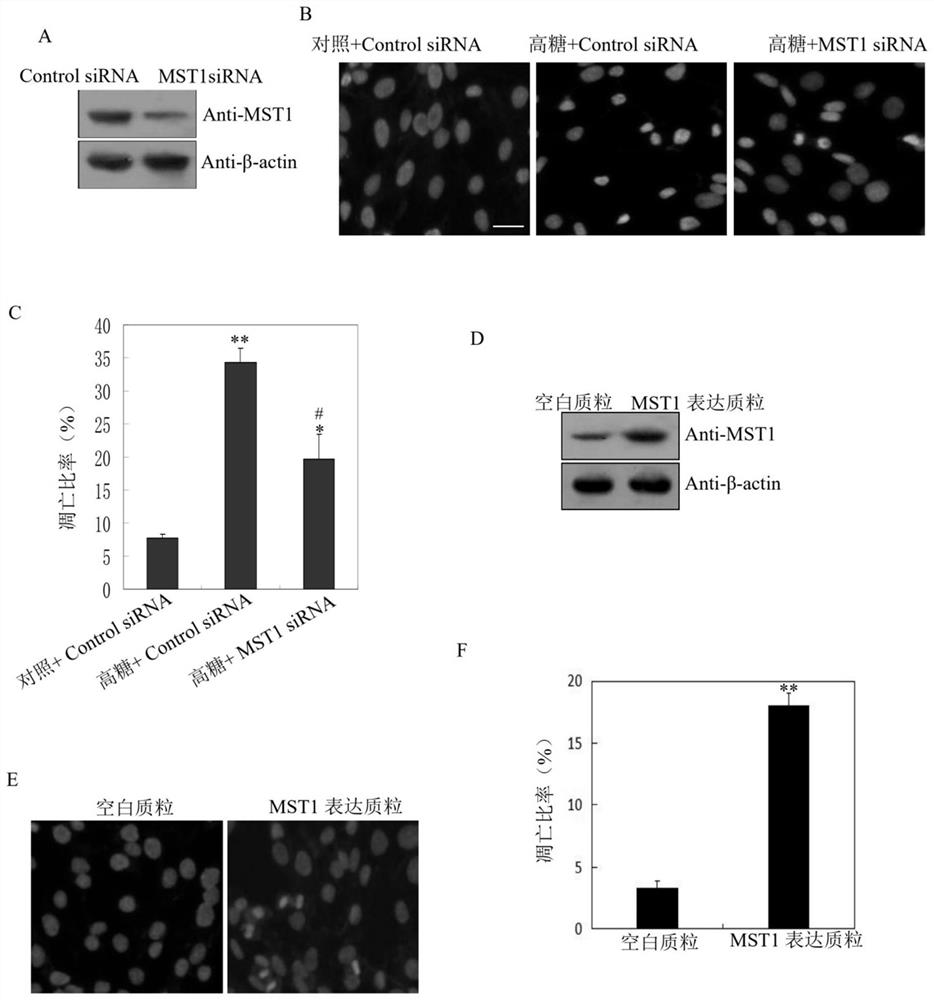
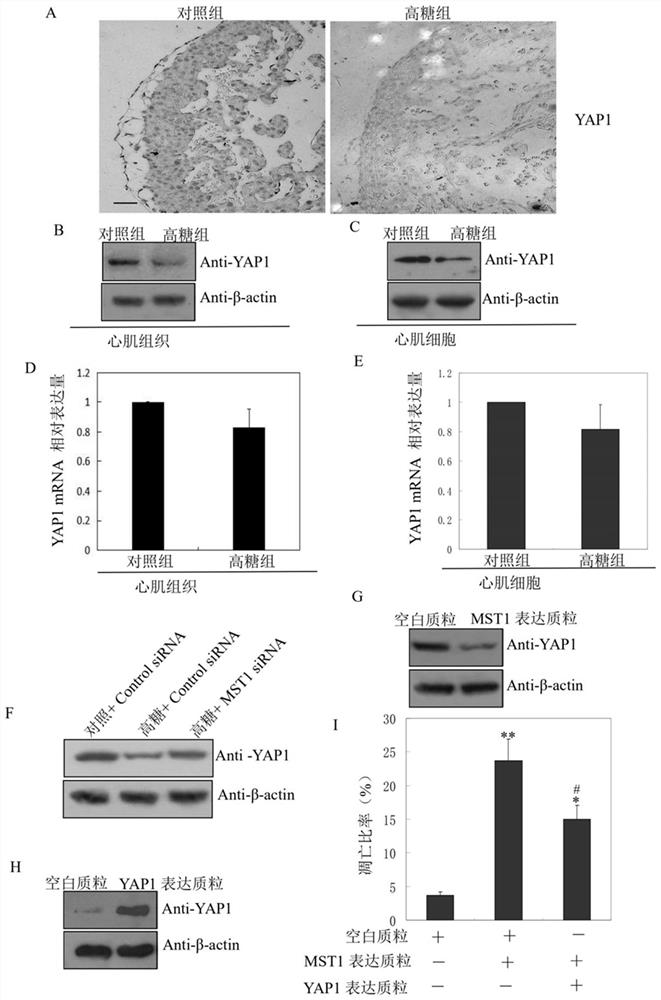
Application of MST1 gene in detecting and/or regulating excessive apoptosis of myocardial cells
PendingCN112280847ADetection of apoptosisAccurate judgmentOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMedicineApoptosis
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and provides a preparation for detecting myocardial cell excessive apoptosis and a method for detecting myocardial cell excessive apoptosis. The invention also provides an application of the MST1 gene expression plasmid in preparation of a preparation for improving the myocardial cell apoptosis rate in a high-glucose environment, an application of the siRNA interference plasmid of the MST1 gene in preparation of a preparation for reducing the myocardial cell apoptosis rate in the high-glucose environment, and a method for regulating andcontrolling the myocardial cell apoptosis rate. By utilizing the relationship between the MST1 gene and myocardial cell excessive apoptosis, especially myocardial cell excessive apoptosis in a high-glucose environment, the preparation for detecting myocardial cell excessive apoptosis provided by the invention can be used for efficiently and accurately detecting the apoptosis condition of myocardial cells in the high-glucose environment; and therefore, whether excessive apoptosis occurs to cardiac muscle cells cultured in vitro or development of heart tissue during fetal development in a motherbody or not is accurately judged.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
Application of alkaloid compound in preparation of product for preventing and/or treating heart injury
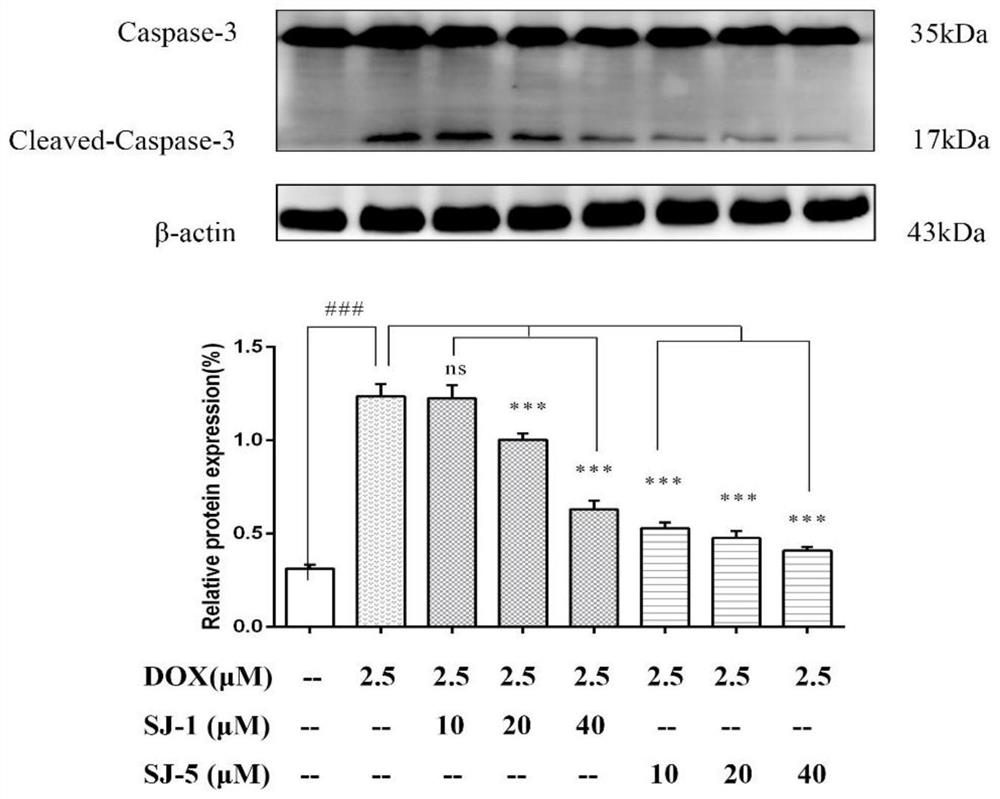
ActiveCN113209065AAvoid toxicityInhibit apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseCaspase
The invention discloses an application of an alkaloid compound in preparation of a product for preventing and / or treating heart injury, activity research is performed on the alkaloid compound, and it is verified that the alkaloid compound can inhibit apoptosis induced by myocardial toxicity. According to the present invention, by down-regulating the expression level of p-JNK and / or Cleaved-Caspase-3, the myocardial apoptosis induced by the anthracycline drug DOX is inhibited so as to alleviate the myocardial cytotoxicity effect, achieve the myocardial cytotoxicity prevention and / or treatment effect, and can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / or treating myocardial injury related diseases.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
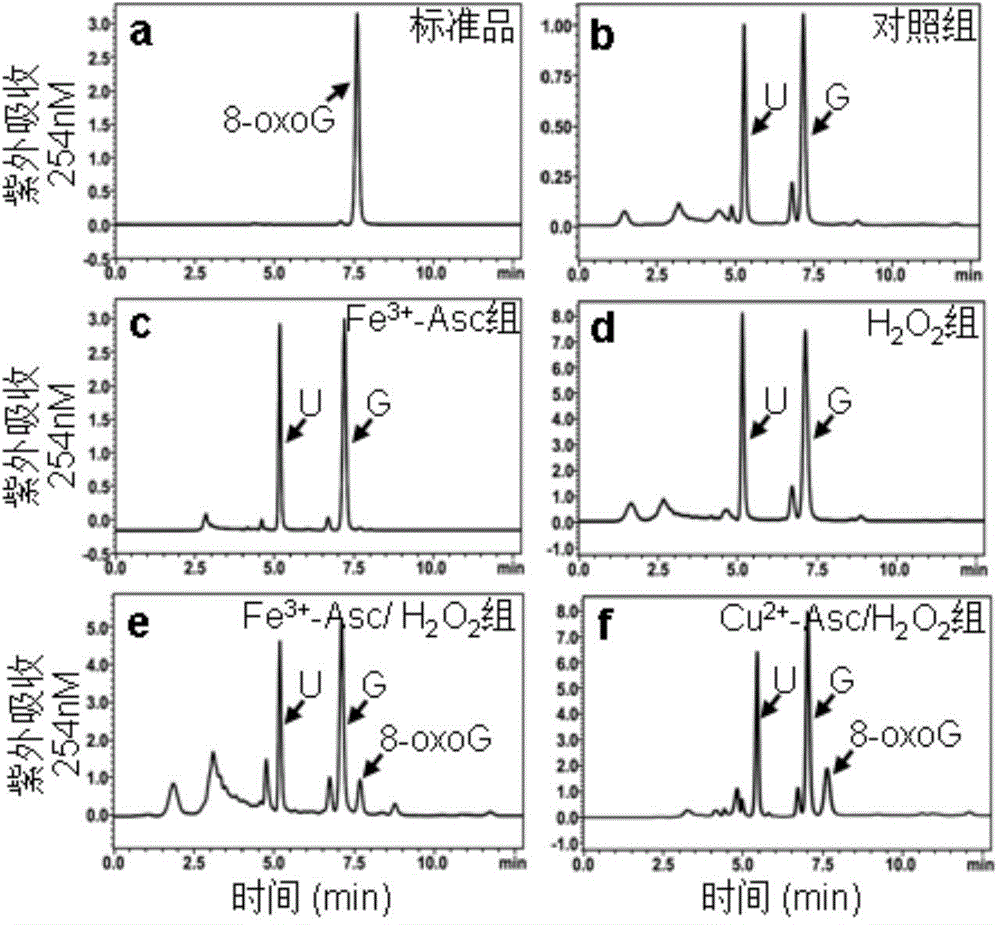
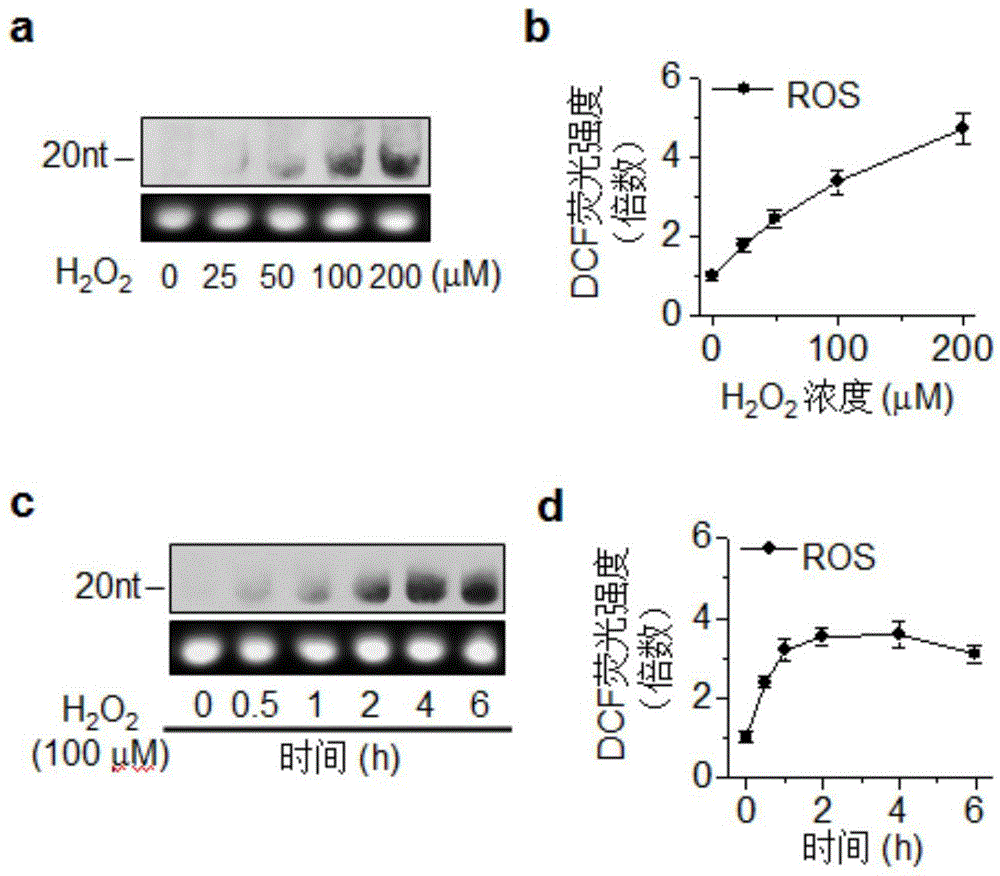
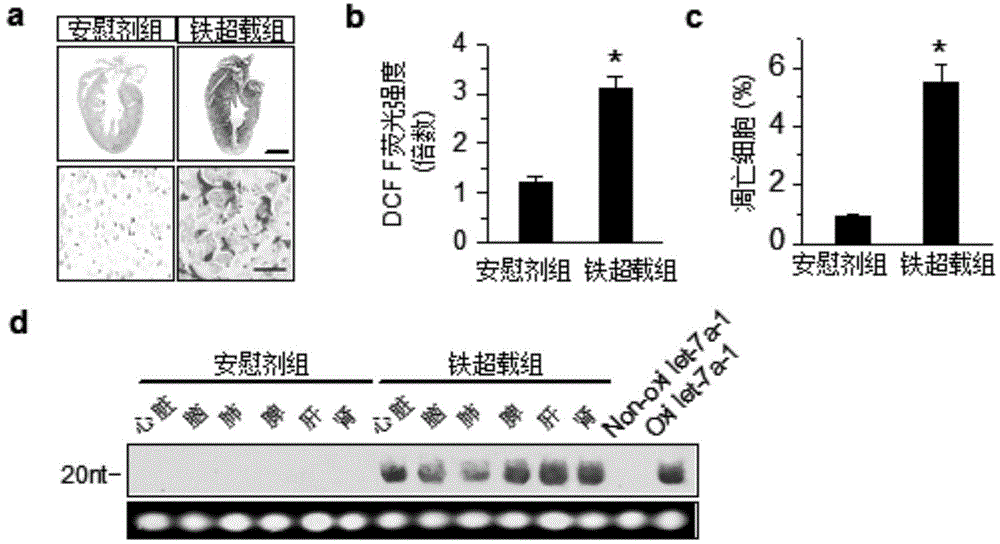
Method for attacking miRNAs through free radicals to cause oxidative damage to RNAs
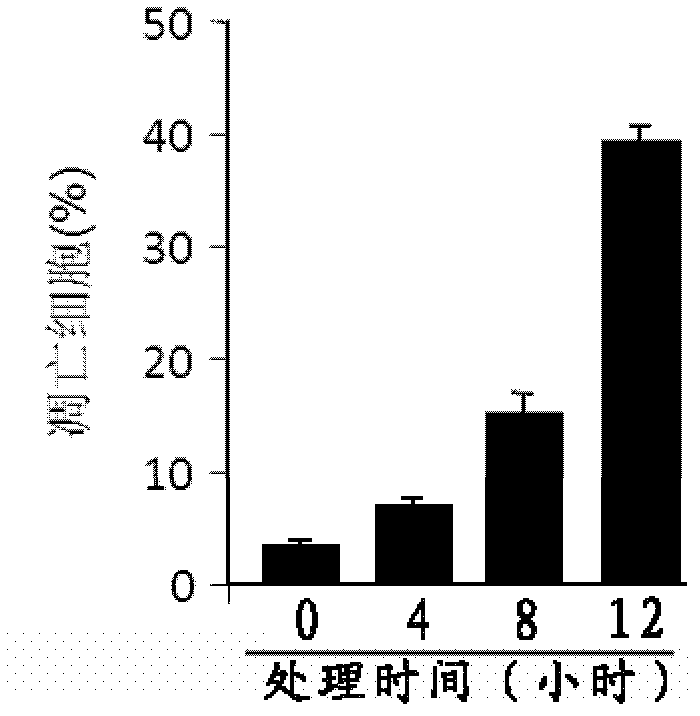
InactiveCN104940230AUnderstanding Molecular MechanismsSimple processHeavy metal active ingredientsPeroxy compound active ingredientsReperfusion injuryFenton reagent
The invention relates to a method for attacking miRNAs through free radicals to cause oxidative damage to the RNAs. According to the method, 8-oxoguanine is generated through oxidation of guanine 8-bit carbon in an oxidative stress state so that the miRNAs undergo oxidative damage. A damage mode is selected from one or more of the following modes: (1) the oxidative damage is caused to the miRNAs through a Fenton reagent oxidation system; (2) the oxidative damage is caused to the miRNAs in the process of using H2O2 to process and induce apoptosis; (3) the oxidative damage is caused to the miRNAs in a Fe overloading induced myocardial injury animal model; and (4) the oxidative damage is caused to the miRNAs in a myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury animal model. According to the method, the miRNA subtype variety of the miRNAs undergoing the oxidative damage in the process of using H2O2 to induce the myocardial apoptosis is determined, and functional differences are expressed through the generation and degradation of the oxidative damage miRNAs in myocardial cells, location characteristics, the synergistic effect with other biomacromolecule and oxidative damage miRNA regulatory genes. The method is simple in process and obvious in damage effect, the applied range is wide, and the method has application environment friendliness.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Application of trigonelline in preparation of medicine or food for treating or preventing hypoxic injury
ActiveCN108014109BTreat or prevent hypoxic injuryHypoxic damage protectionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderFenugreeksNerve cells
The invention discloses new application of gynesine, namely application of the gynesine in preparing a medicine or food for treating or preventing hypoxic damage, and the medicine or the food preparedfrom the gynesine and used for treating or preventing hypoxic damage. The research finds that the gynesine has a function of treating or preventing hypoxic damage, and can be used for preparing the medicine or the food for treating or preventing hypoxic damage; a cell experiment and an animal experiment prove that the gynesine can be beneficial to protecting hypoxic nerve cell damage, reducing myocardial apoptosis caused by hypoxia, prolonging the survival time of rats in a normal pressure anoxia tolerance test, and increasing the survival rate of the rats in an acute low pressure hypoxia test.
Owner:杭州方回春堂健康科技有限公司
MiRNA-140 inhibitor and applications thereof
ActiveCN103243091BFunction increaseImprove heart functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention provides a miRNA-140 inhibitor and applications thereof, wherein a sequence of the inhibitor has at least 90% of homology with a nucleotide sequence showing in the following SEQ ID NO:1: 5'-CUACCAUAGGGUAAAACCACUG-3', wherein each basic group is modified by 2'-O-methyl; and the miRNA-140 inhibitor is used for preparing a medicament or a kit for diagnosing, preventing, treating and / or prognostically evaluating heart diseases. The miRNA-140 inhibitor is changed in treatment of myocardial ischemia injury and myocardial apoptosis and has a myocardial preservation effect.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
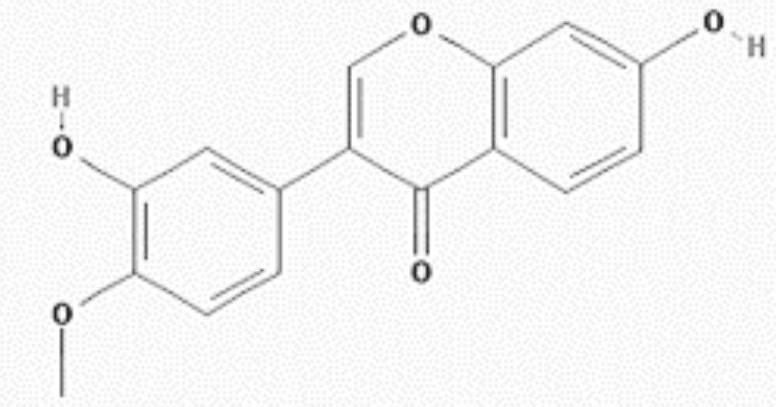
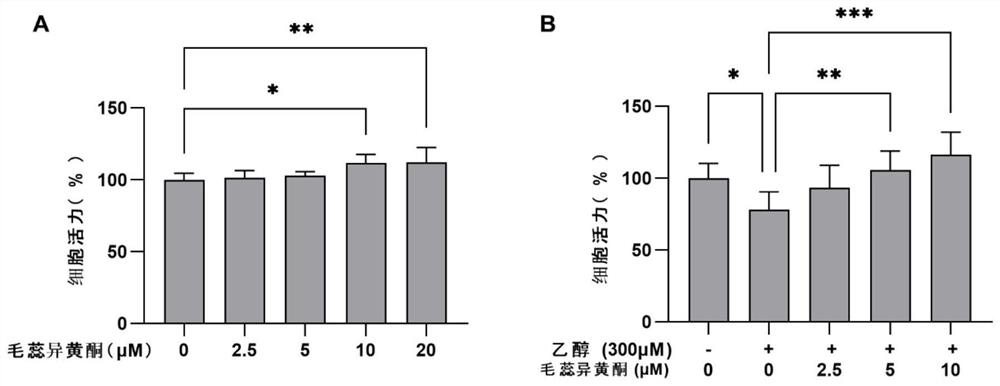
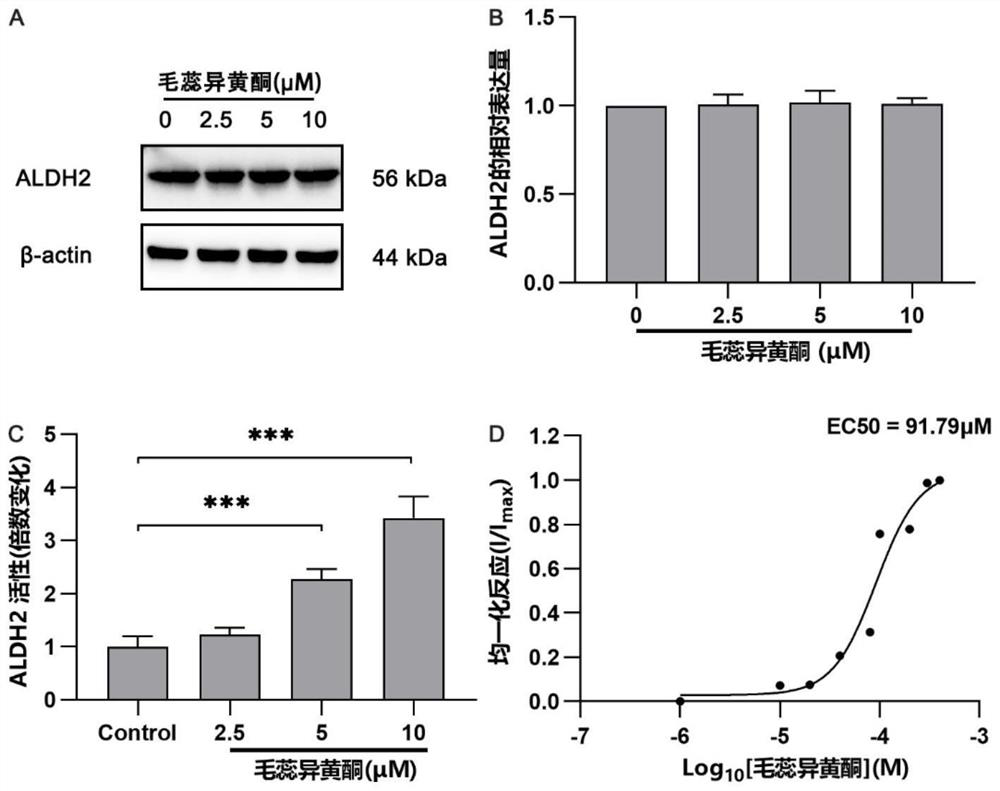
Application of calycosin in preparation of ALDH2 agonist medicines
ActiveCN113786398AInhibit apoptosisIncrease vitalityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderPharmacologyInternal medicine
The invention discloses an application of calycosin in preparation of ALDH2 agonist medicines, and belongs to the field of medicines. The invention particularly discloses application of calycosin in preparation of ALDH2 agonist medicines, application of calycosin in preparation of alcoholic cardiomyopathy prevention and treatment medicines and application of calycosin in preparation of alcohol-induced myocardial cell apoptosis inhibition medicines. According to the calycosin disclosed by the invention, by improving the activity of cardiac muscle cell ALDH2, increasing activated aldehydes and inhibiting alcohol-induced cardiac muscle cell apoptosis, a scientific basis is further provided for application of the calycosin in preparation of ALDH2 agonists and medicines for preventing and treating alcoholic cardiomyopathy, the calycosin is low in toxicity to normal cells, and the calycosin is derived from traditional Chinese medicines such as astragalus membranaceus and liquorice, has certain safety, is relatively low in preparation cost and has a clinical application prospect.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Application of novel flavonoid compound Hyd
ActiveCN111840304AReduce lactate dehydrogenaseReduce the content of NOOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderApoptosisNerve repair
The invention discloses an application of a novel flavonoid compound Hyd. A hippophae rhamnoides seed meal extract is eluted through an MCI gel column; semi-preparative separation is sequentially performed through a C18 chromatographic column, a diol chromatographic column and a C18 chromatographic column to obtain the novel flavonoid compound Hyd; the compound Hyd is subjected to activity research, it is verified that the compound Hyd can reduce the content of lactic dehydrogenase and NO in myocardial cells, apoptosis of the myocardial cells is delayed by reducing the protein expression levelof Bcl-2 and Bax in the cells, and the compound Hyd can be used for preparing medicine for preventing or treating myocardial injury related diseases. The invention also provides application of the new compound Hyd in preparation of products with neuroprotection and / or nerve repair effects, and verifies that the compound Hyd can improve neurosynaptic atrophy and reduce tau protein excessive phosphorylation, and can be used for preparing medicines for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Myocardial ischemia re-perfusion injury marker circRNA and application thereof
ActiveCN113265458ADeprotectionReduce infarct sizeOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCardiac muscleIschemic reperfusion injury
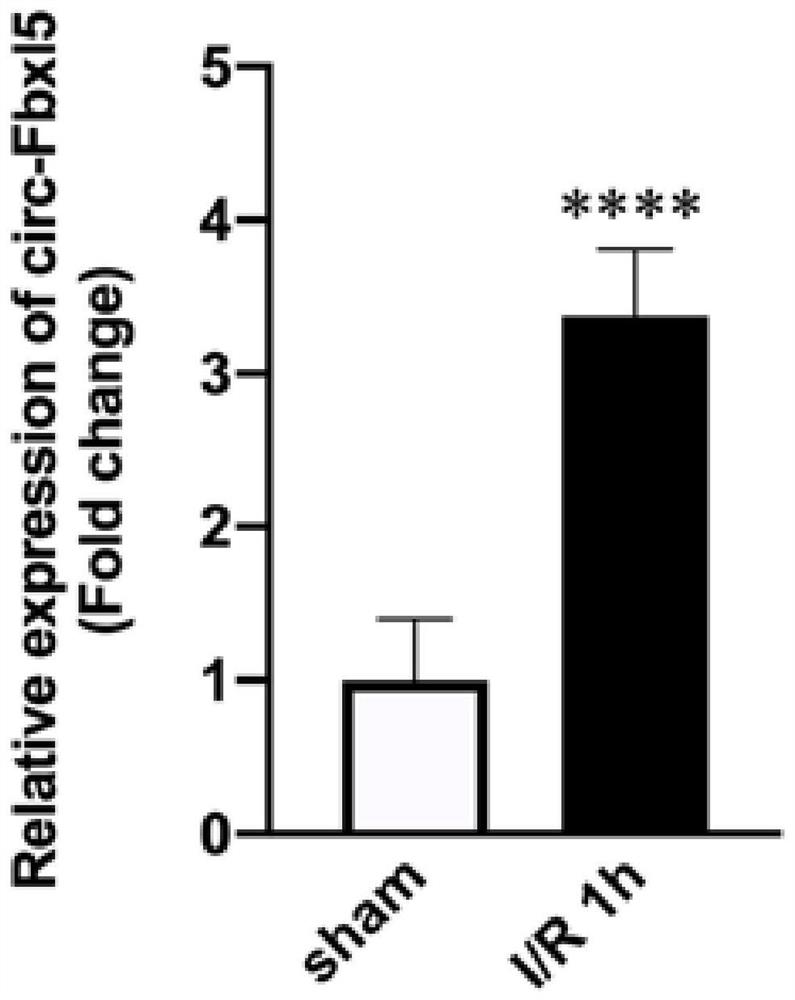
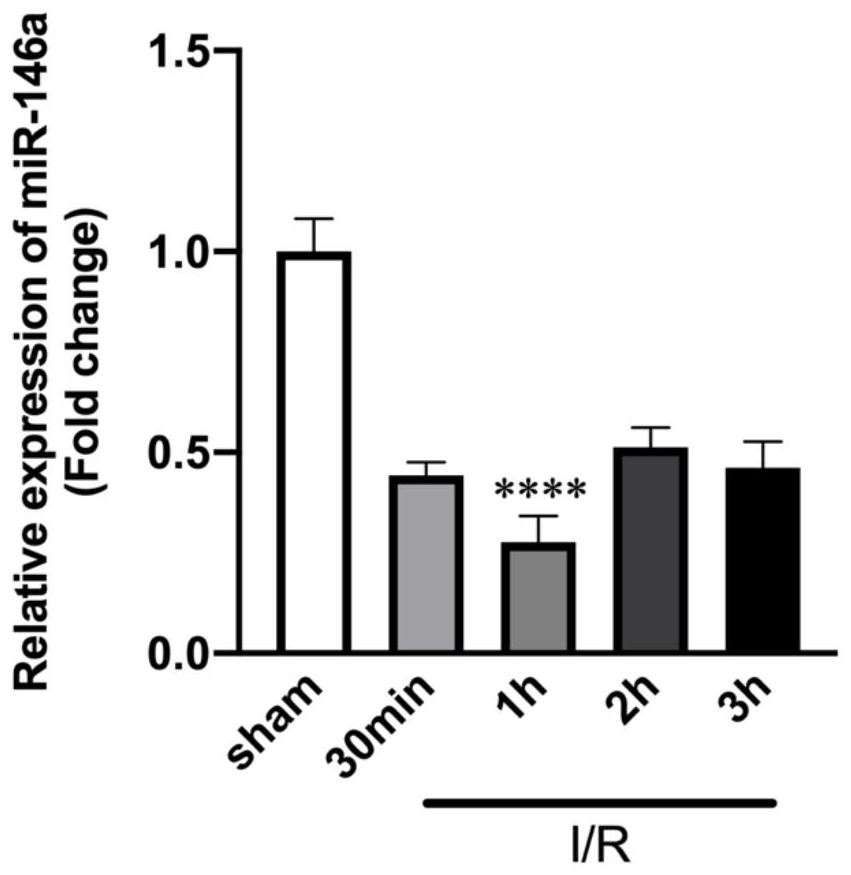
The invention discloses a myocardial ischemia re-perfusion injury marker circRNA and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention proves that circ-Fbxl5 can form a sponge adsorption relationship with miRNA-146a in myocardial cells so as to relieve the protective effect of the miRNA-146a on myocardial ischemia re-perfusion injury, and a shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) capable of knocking down circ-Fbxl5 expression is designed. Through detection, the prepared shRNA can knock down circ-Fbxl5 expression quantity, the infarct area of a myocardial ischemia re-perfusion mouse can be remarkably reduced, the myocardial apoptosis level is reduced, and it is proved that the prepared shRNA can be applied to the medicine for preventing and treating myocardial ischemia re-perfusion injury.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Use of medicinal composition in preparing medicine for treating cardiocytes fading
ActiveCN1714818AReduce apoptosisLower blood pressureCardiovascular disorderPlant ingredientsRadioimmunoassayFosinopril
The present invention belongs to the field of medicine technology, and is especially one kind of medicine composition in preparing medicine for treating myocardial apoptosis. The experiments of administrating the medicine composition to spontaneous hypertension rats, measuring the left venticle thickening index, and radioimmunoassay measuring the local Ang II concentration in cardiac muscle and blood plasma and the aldosterone concentration in blood plasma show that the said medicine composition can lower SHR myocardial apoptosis and reduce left venticle thickness when used alone or together with fosinopril.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
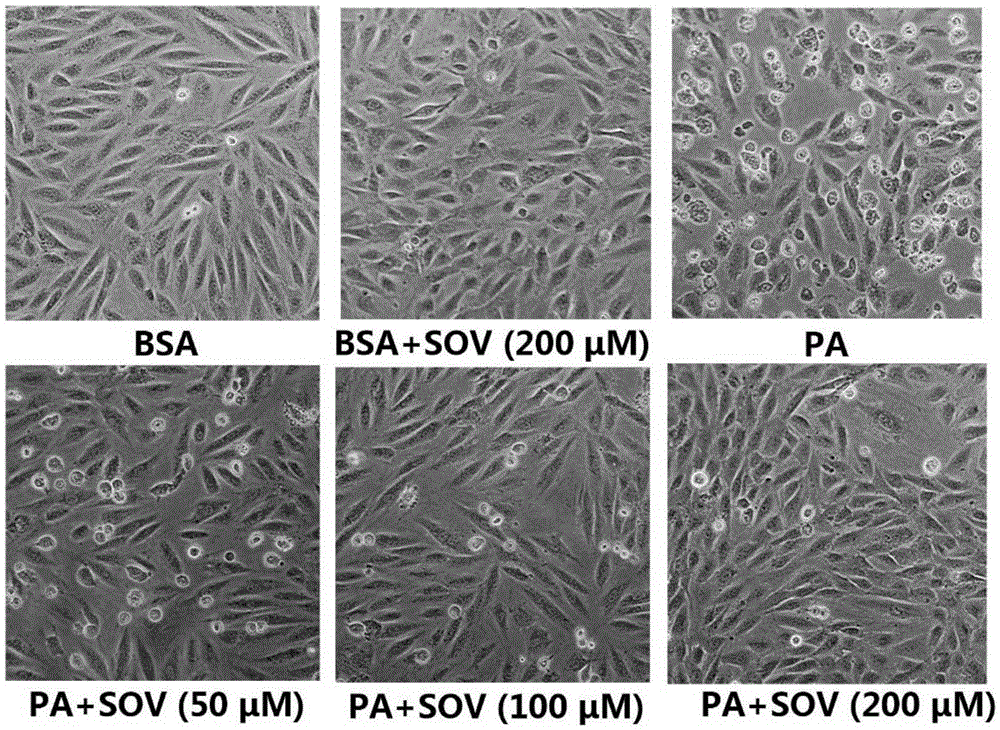
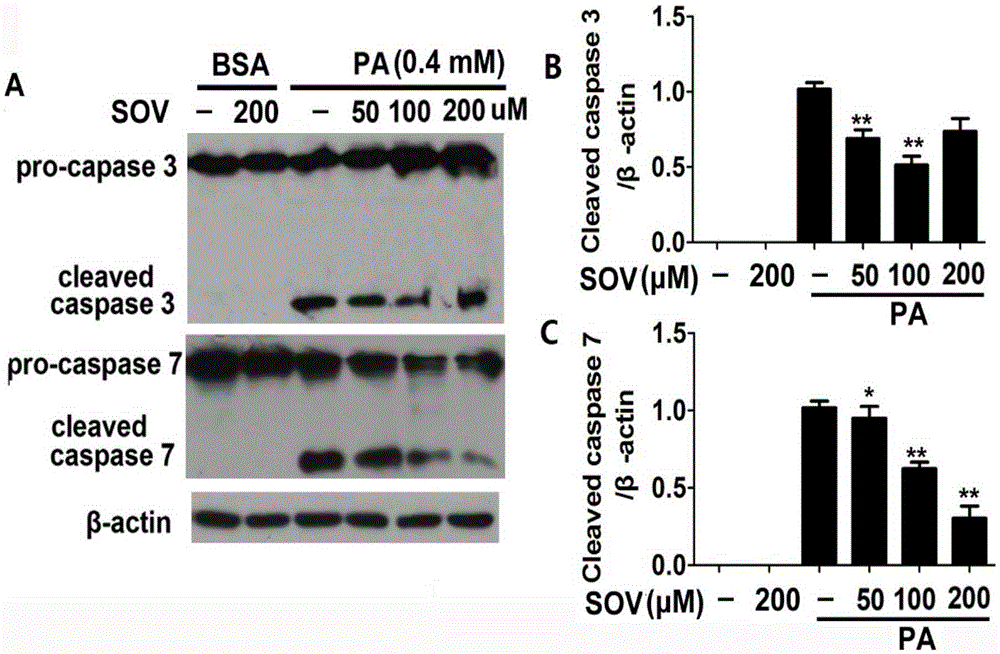
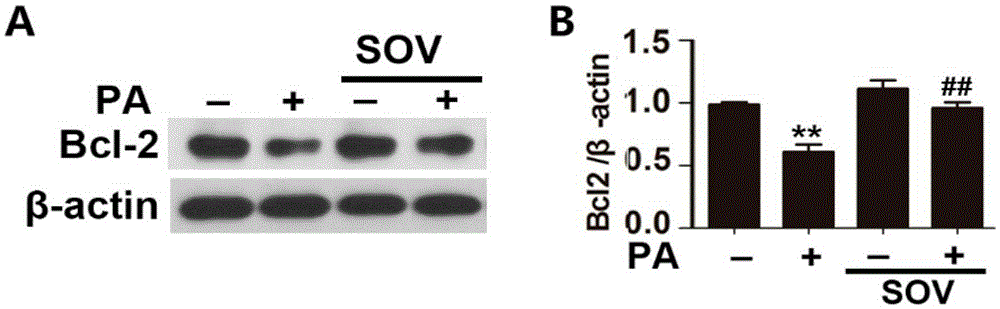
Application of sodium orthovanadate in preparation of medicine for resisting myocardial apoptosis
InactiveCN105250328AInhibit apoptosisBroad scientific researchHeavy metal active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseasePyknosis
The invention discloses application of sodium orthovanadate in preparation of medicine for resisting myocardial apoptosis caused by excessive lipid accumulation. Experiments prove that the sodium orthovanadate can effectively inhibit the myocardial apoptosis induced by long-chain saturated fatty acid palmitic acid, and it is specifically shown that the sodium orthovanadate inhibits the apoptosis induced by the palmitic acid from executing cutting of a caspase precursor, promotes protein expression of anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 and obviously reduces the apotosis rate and pyknosis of nucleus chromatin. On the basis, it is expected that application is supplied to SOV in aspect of preparing the medicine for treating the myocardial apoptosis induced by excessive lipid accumulation along with diseases such as obesity and diabetes in clinical research, and it is indicated that the wide scientific research and clinical development prospects are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Application of irisin in myocardial ischemia reperfusion
ActiveUS9682121B2Inhibit oxidative stressDecrease the enlargement of the myocardial infarction areaHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsCreatine kinaseMyocardial reperfusion
The invention discloses application of irisin in the preparation of drugs for preventing myocardial ischemia reperfusion injuries. Experimental results show that irisin can decrease the myocardial infarction area caused by ischemia reperfusion, reduce the increase of the contents of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponin (cTnI), creatine kinase (CK), and other myocardial enzyme markers caused by ischemia reperfusion, meanwhile reducing the inflammatory response, myocardial apoptosis, and oxidative stress response caused by myocardial ischemia reperfusion, promote peroxysome proliferator-activated receptor γ nuclear translocation, and inhibit nuclear transcription factor NF-κB nuclear translocation and accordingly decrease myocardial structure injuries and load increase caused by ischemia reperfusion. Therefore, irisin can be used for preventing and decreasing myocardial reperfusion injuries and has important clinical significance on the treatment of myocardial ischemia.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Medicine composition for treating heart failure and application thereof
InactiveCN104434920AReduce adverse reactionsProtect mitochondriaOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderTrimetazidineCardiac muscle
The invention discloses a medicine composition for treating heart failure and application thereof. The medicine composition is prepared from an active ingredient and medicinal auxiliaries, wherein the active ingredient comprises (1) tortuosine and (2) trimetazidine or medicinal salt thereof. The medicine composition can be used for synergistically resisting myocardial apoptosis and protecting cardiac muscle mitochondria so as to achieve the aim of preventing and treating heart failure.
Owner:QINGDAO MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com