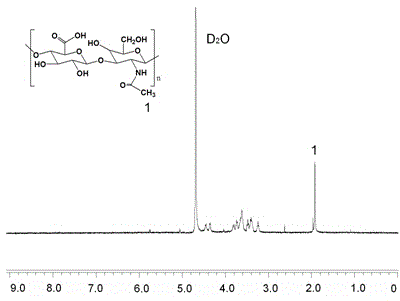
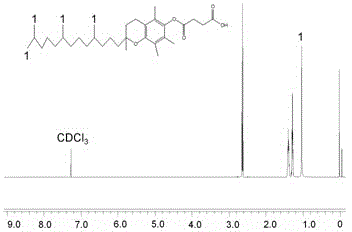
Hyaluronic acid vitamin E derivative and preparation and application
A technology of hyaluronic acid and sodium hyaluronate, applied in the direction of liposome delivery, can solve the problems of biocompatibility, biotoxicity, drug-carrying system limitation, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Synthesis of hyaluronic acid and vitamin E derivatives
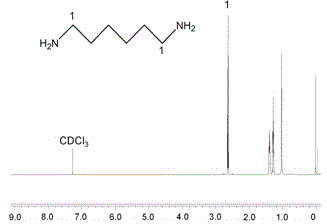
[0037] Weigh 0.5g vitamin E succinate (VES), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), 0.1g N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (NHS) into a 50ml single-necked flask, add 25ml dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min. Another 0.2 g of hexamethylenediamine was weighed, dissolved in 10 ml of DMSO, slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution, stirred at room temperature for more than 8 hours, and the reaction solution A was obtained.
[0038] Weigh 0.38g sodium hyaluronate (HA-Na) with a molecular weight of about 6700 (n+m=17), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC ), 0.1g perimide (NHS) into a 100ml single-necked flask, add 60ml of water and ethanol mixed solution, stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min, slowly add reaction solution A dropwise, and stir at room temperature for 4h. The reaction solution was dialyze...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (1) Weigh 0.5g vitamin E succinate (VES), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), 0.1g N-hydroxysulfosuccinate Put imide (NHS) into a 50ml single-necked flask, add 25ml dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min. Another 0.2g of cystamine was weighed, dissolved in 10ml of DMSO, slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution, and stirred at room temperature for more than 8 hours to obtain the reaction solution A.
[0065]Weigh 0.38g sodium hyaluronate (HA-Na) with a molecular weight of about 6700 (n+m=17), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC ), 0.1g perimide (NHS) into a 100ml single-necked flask, add 60ml of water and ethanol mixed solution, stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min, slowly add reaction solution A dropwise, and stir at room temperature for 8h. The reaction solution was dialyzed in deionized water for 3-4 days to remove the catalyst and unreacted monom...
Embodiment 3
[0073] (1) Weigh 0.5g vitamin E succinate (VES), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), 0.1g N-hydroxysulfosuccinate Put the imide (NHS) into a 50ml single-necked flask, add 25ml dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min. Another 0.2 g of 3-aminopropanol was weighed, dissolved in 10 ml of DMSO, slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution, stirred at room temperature for more than 8 hours, and the reaction solution A was obtained.
[0074] Weigh 0.38g sodium hyaluronate (HA-Na) with a molecular weight of about 6700 (n+m=17), 0.45g 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC ), 0.1g 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) into a 100ml single-necked flask, add 60ml of water and ethanol mixed solution, stir and dissolve at room temperature for 60min, slowly add reaction solution A dropwise, and stir at room temperature for 8h. The reaction solution was dialyzed in deionized water for 3-4 days to remove...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| critical micelle concentration (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com