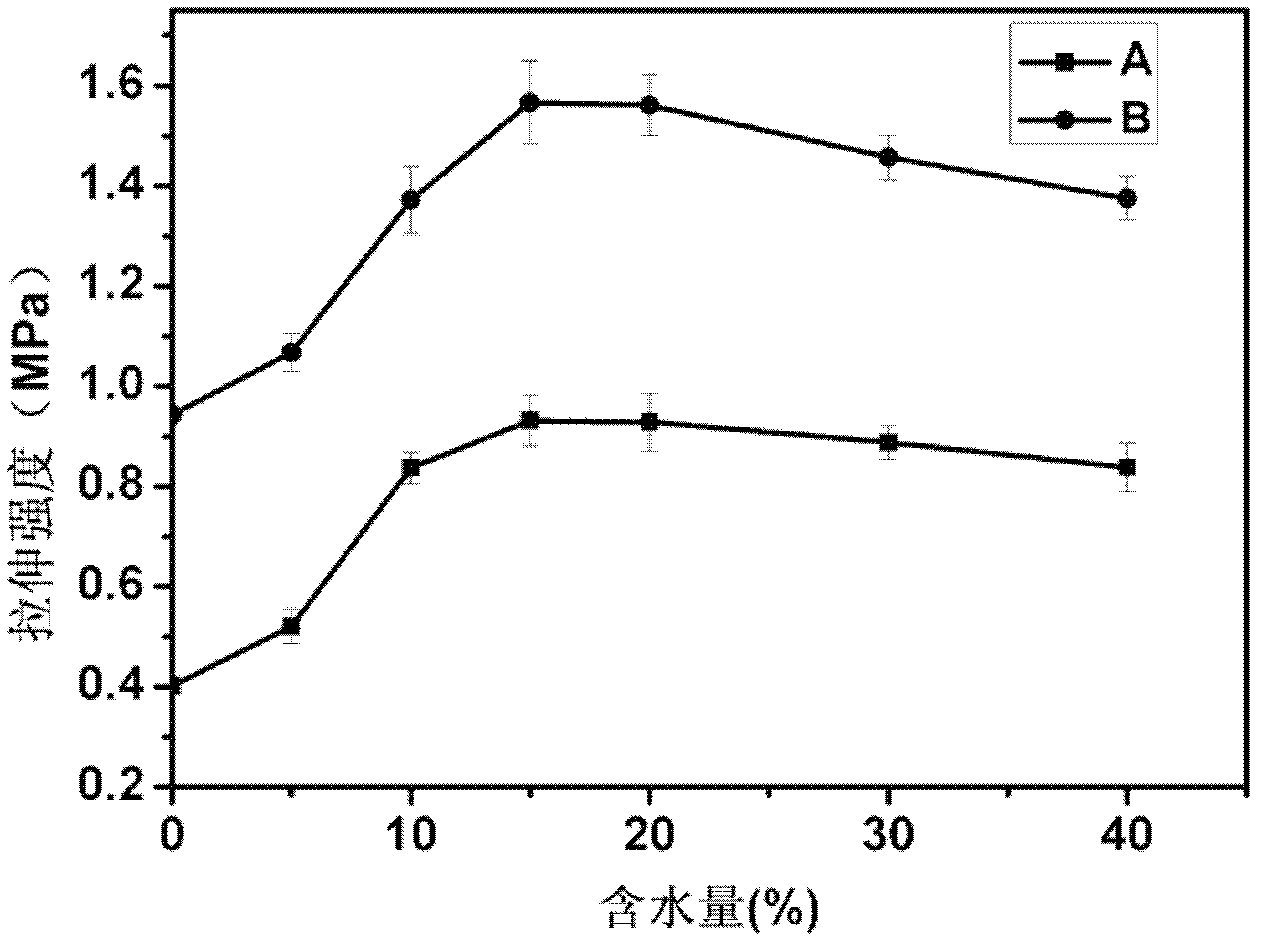
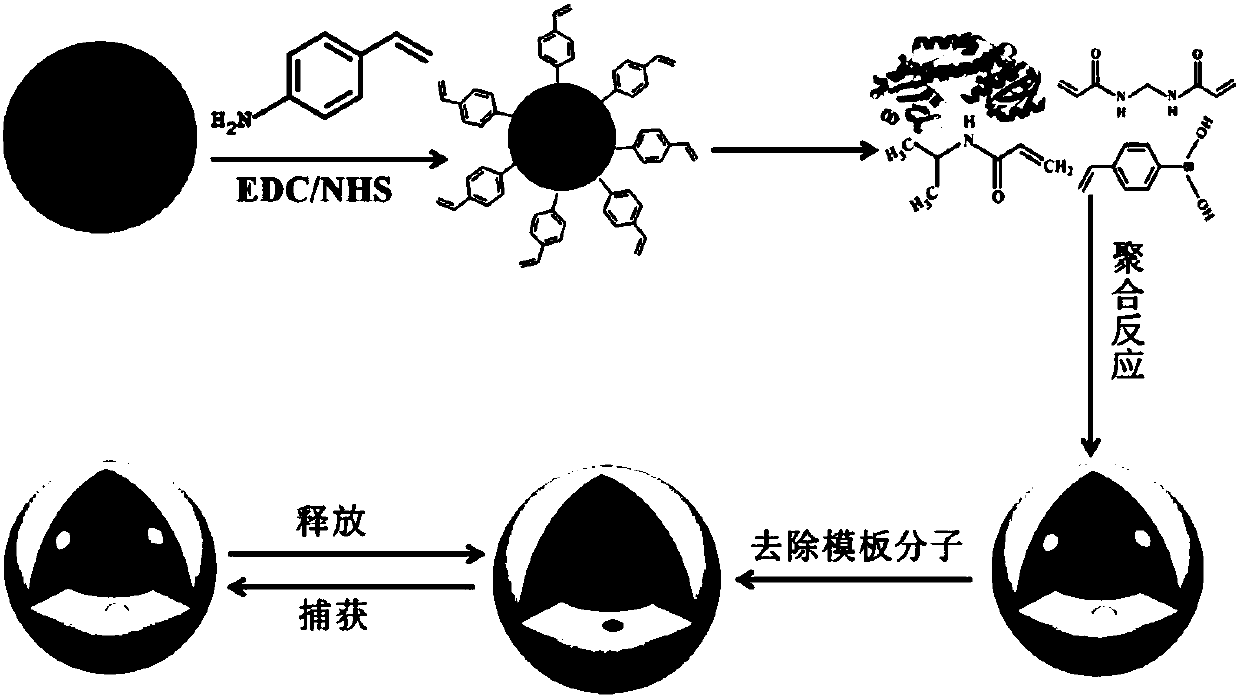
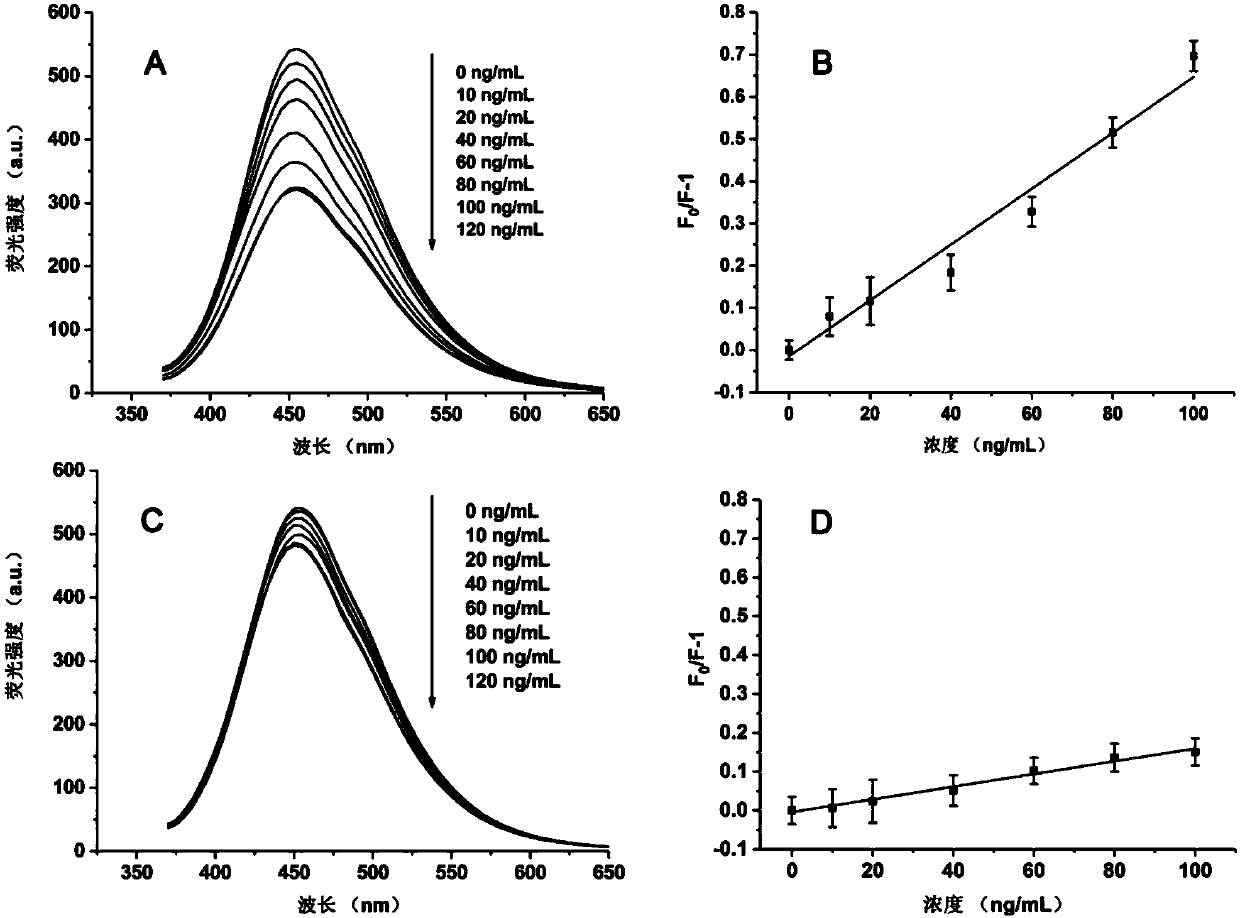
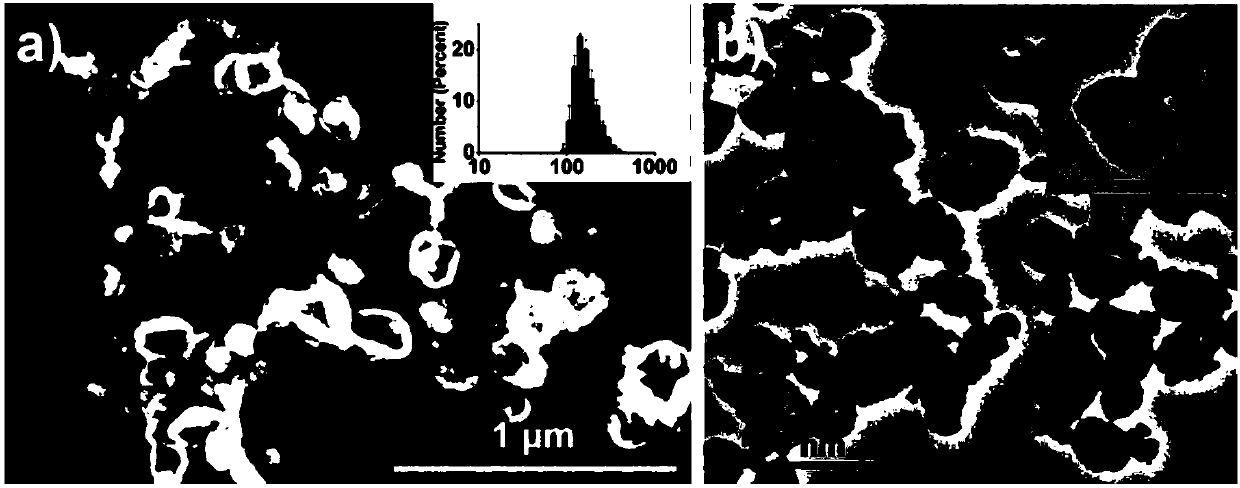
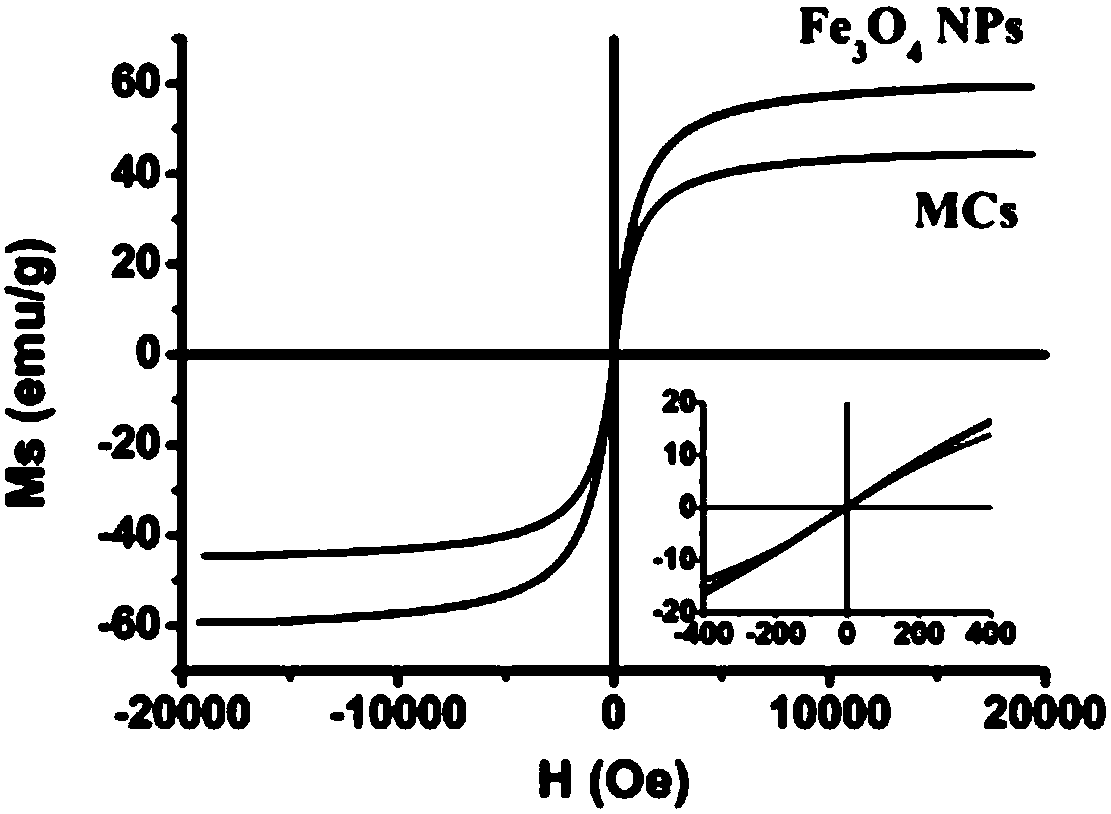
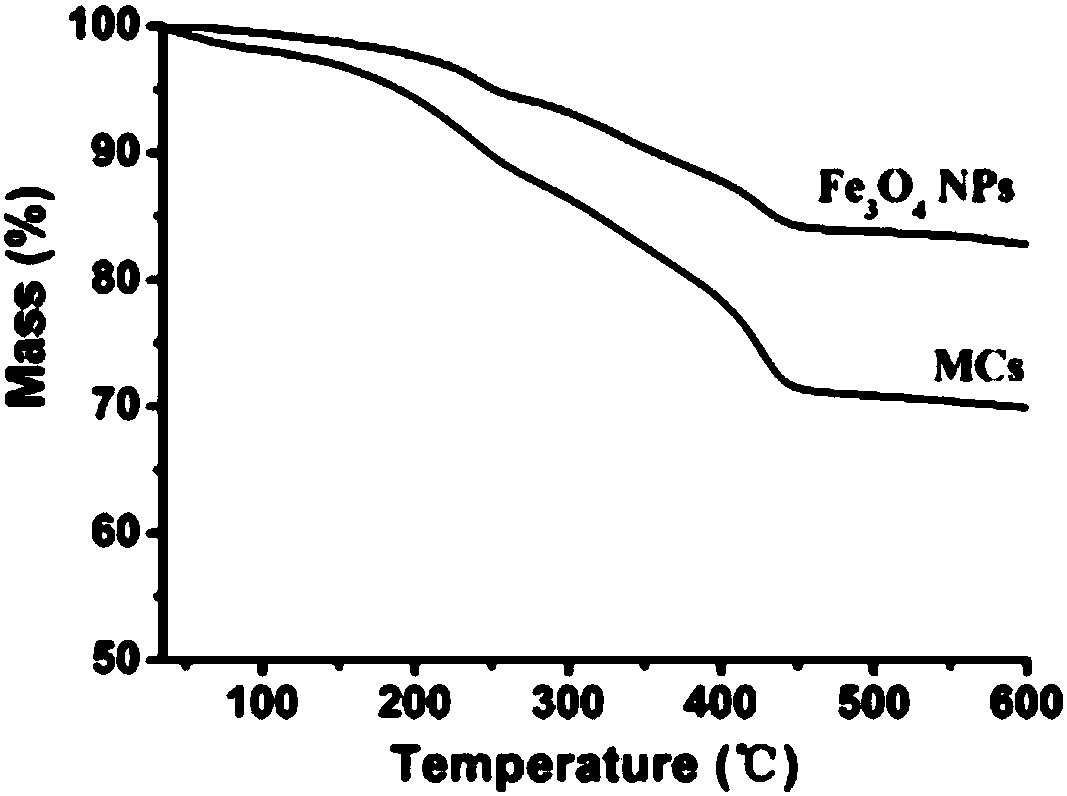
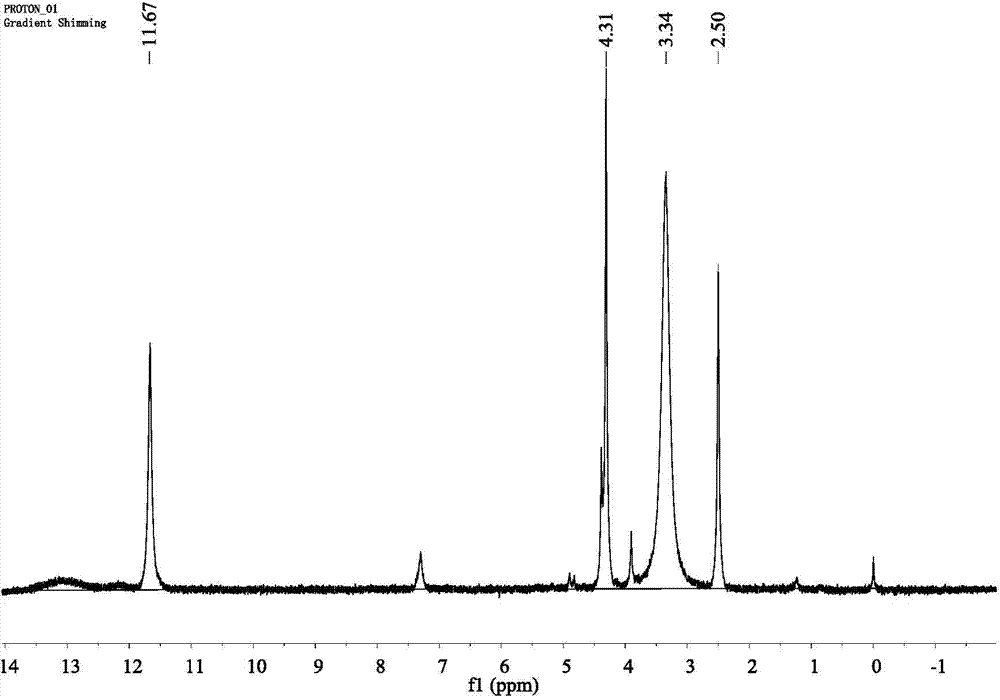
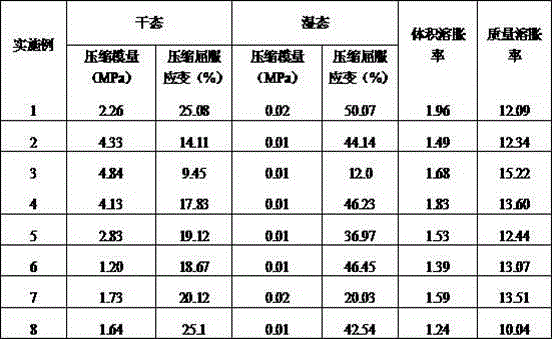
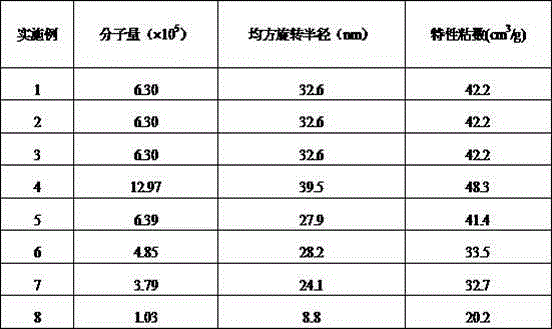
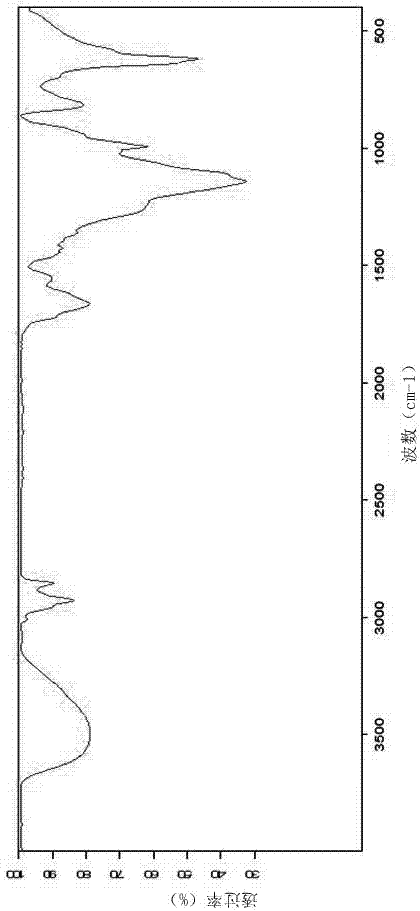
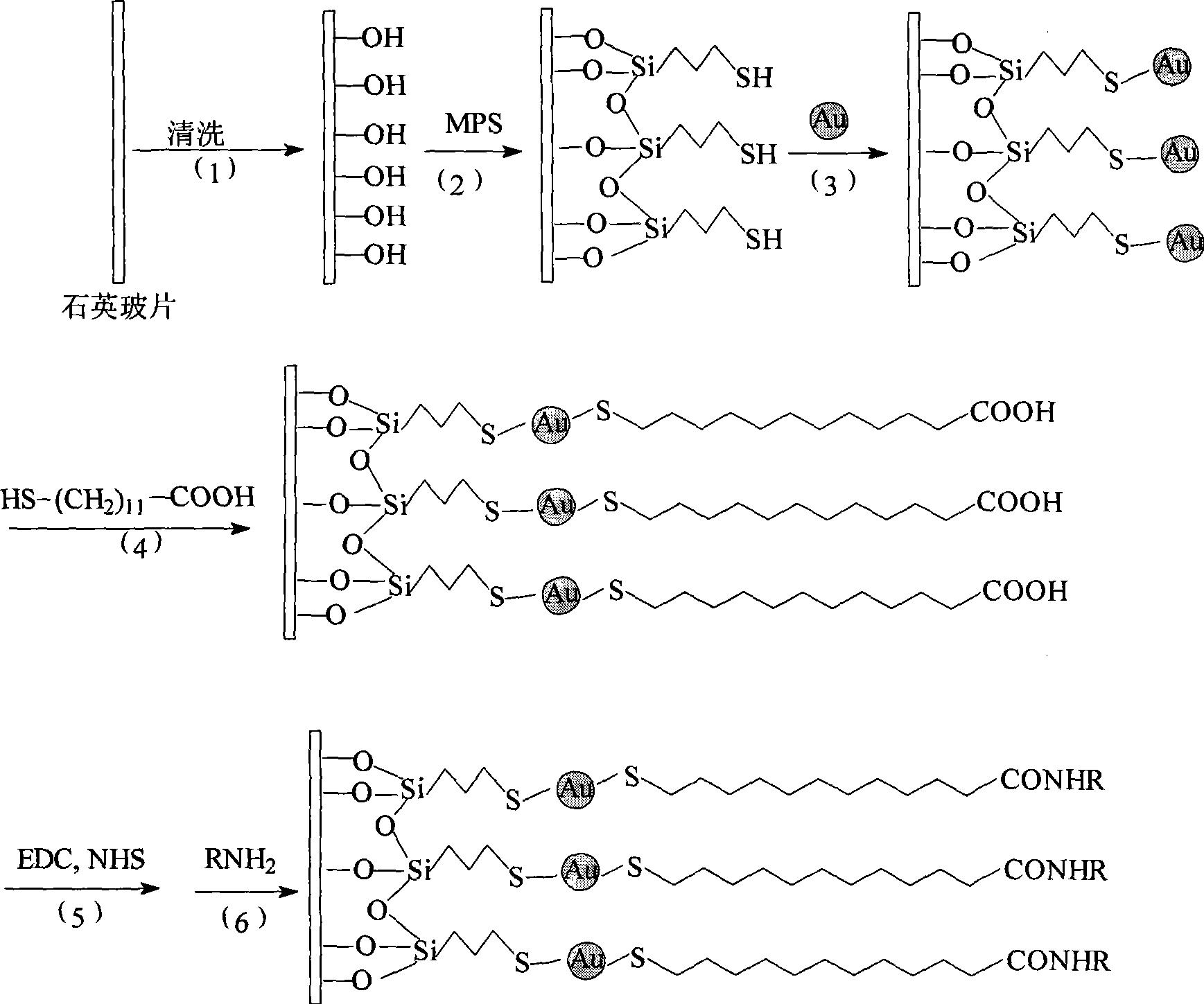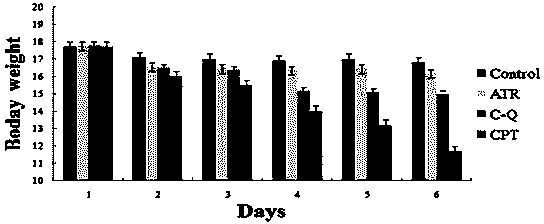Patents
Literature
289 results about "Carbodiimide hydrochloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation and application of magnetic nano-composite material gamma-Fe2O3/PDA (Polydopamine)-GA (Gallic Acid)
InactiveCN103721688ASolve the problems of low adsorption efficiency, difficult separation, easy to produce secondary pollution, etc.Reduce sensitivityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPyrrolidinonesEthyl group
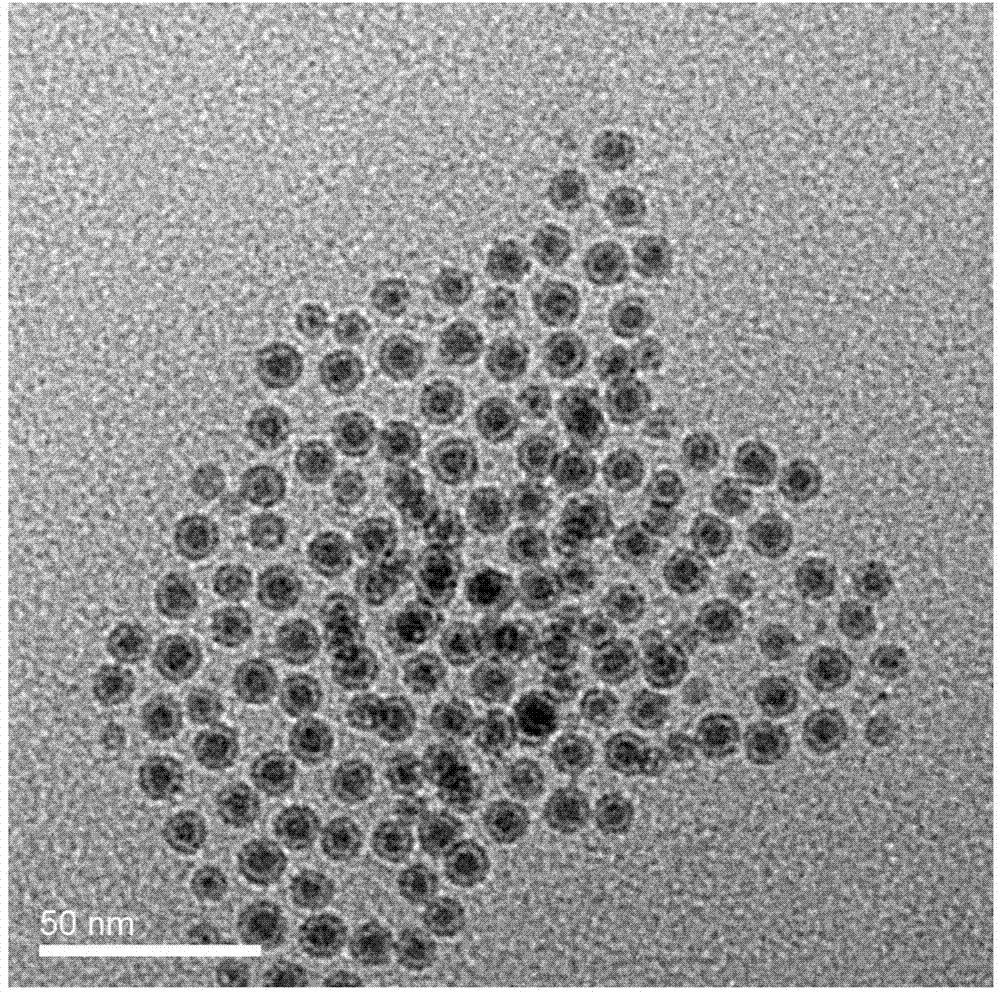
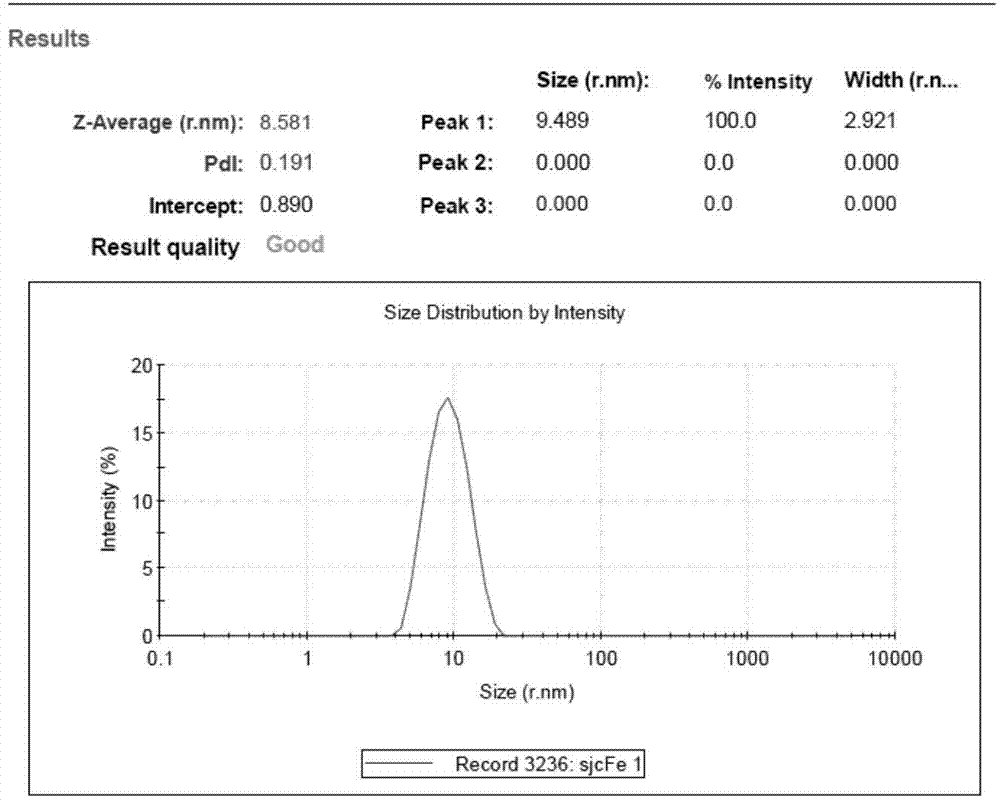
The invention discloses preparation and application of magnetic nano-composite material gamma-Fe2O3 / PDA (Polydopamine)-GA (Gallic Acid). The preparation comprises the following steps of carrying out a hydrothermal reaction and calcinations to obtain a gamma-Fe2O3 nano particle carrier by taking FeCl3.6H2O with low price as an iron source, ethylene glycol (EG) as a reducing agent, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a dispersing agent and a protective agent, and natrium aceticum (NaAc) as an alkali source; then wrapping a layer of polydopamine (PDA) in a buffer solution of tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane-hydrochloric acid (Tris-HCl) with pH of 8.5; and finally introducing gallic acid (GA) to an ethanol system by using 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride and n-hydroxysuccinimide as cross-linking agents, wherein a specific synthetic schematic diagram is seen in attached drawing 1. Then the adsorption effects of the synthesized magnetic nano-particle on metal ions Cu<2+> and Pb<2+> are discussed, the detection effects of a glassy carbon electrode modified by the magnetic nano-particle on the metal ions Cu<2+> and Pb<2+> are researched. Results show that gamma-Fe2O3 / PDA-GA has excellent detection and adsorption effects on heavy metal ions in a water environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres
InactiveCN102964610AImprove mechanical propertiesGood anti-swelling performanceMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereN-Hydroxysuccinimide
The invention discloses a preparation method of polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres, which comprises the following steps of: under the protection of nitrogen, grafting dopamine to alginic acid by use of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride; polymerizing the synthesized dopamine modified alginic acid under the slight alkaline condition to obtain a polydopamine modified alginic acid solution; dropwise adding the polydopamine modified alginic acid solution into a CaCl2 solution by a syringe; and aging to obtain polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, and the prepared modified alginic acid microspheres have higher swelling resistance and good mechanical properties.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
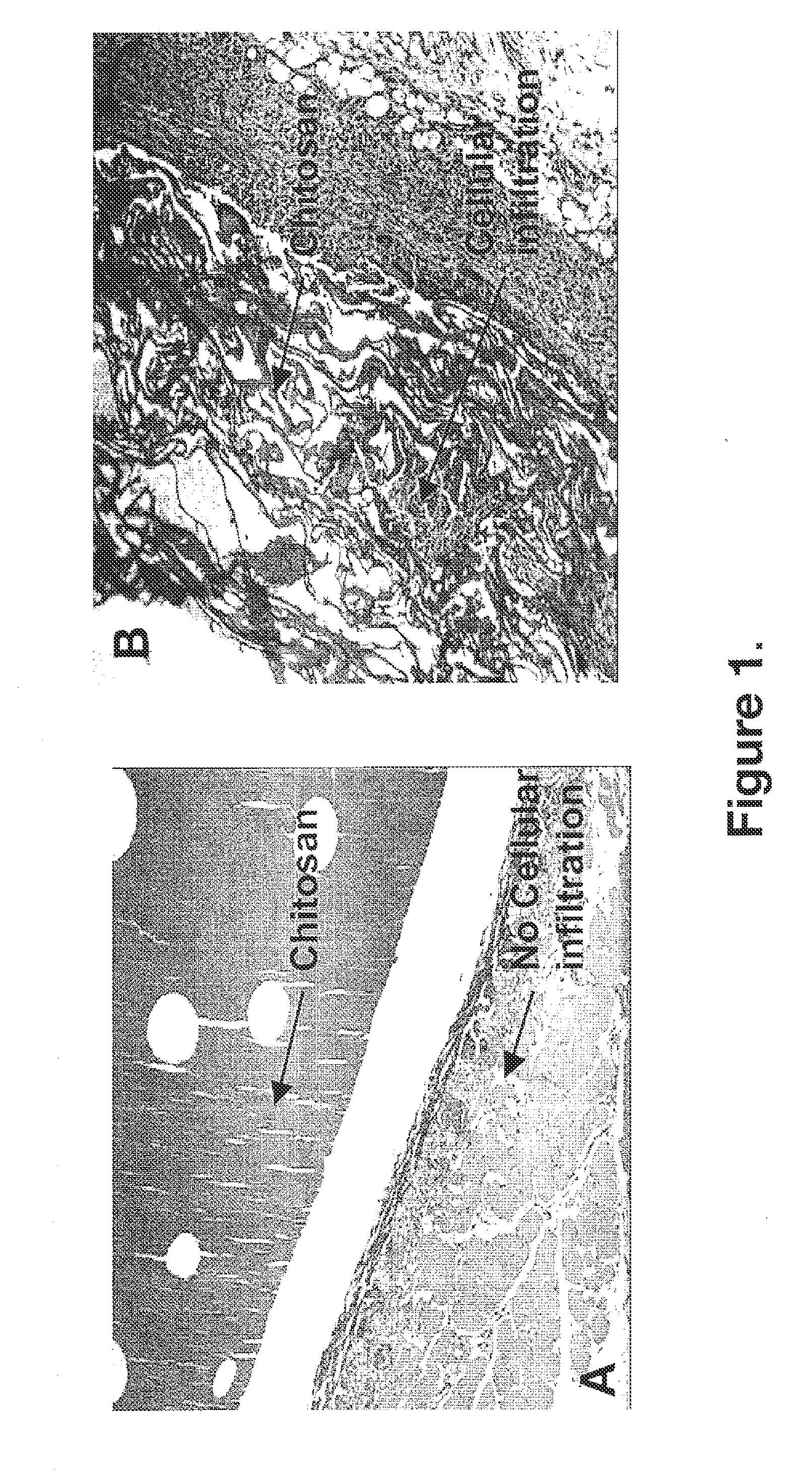
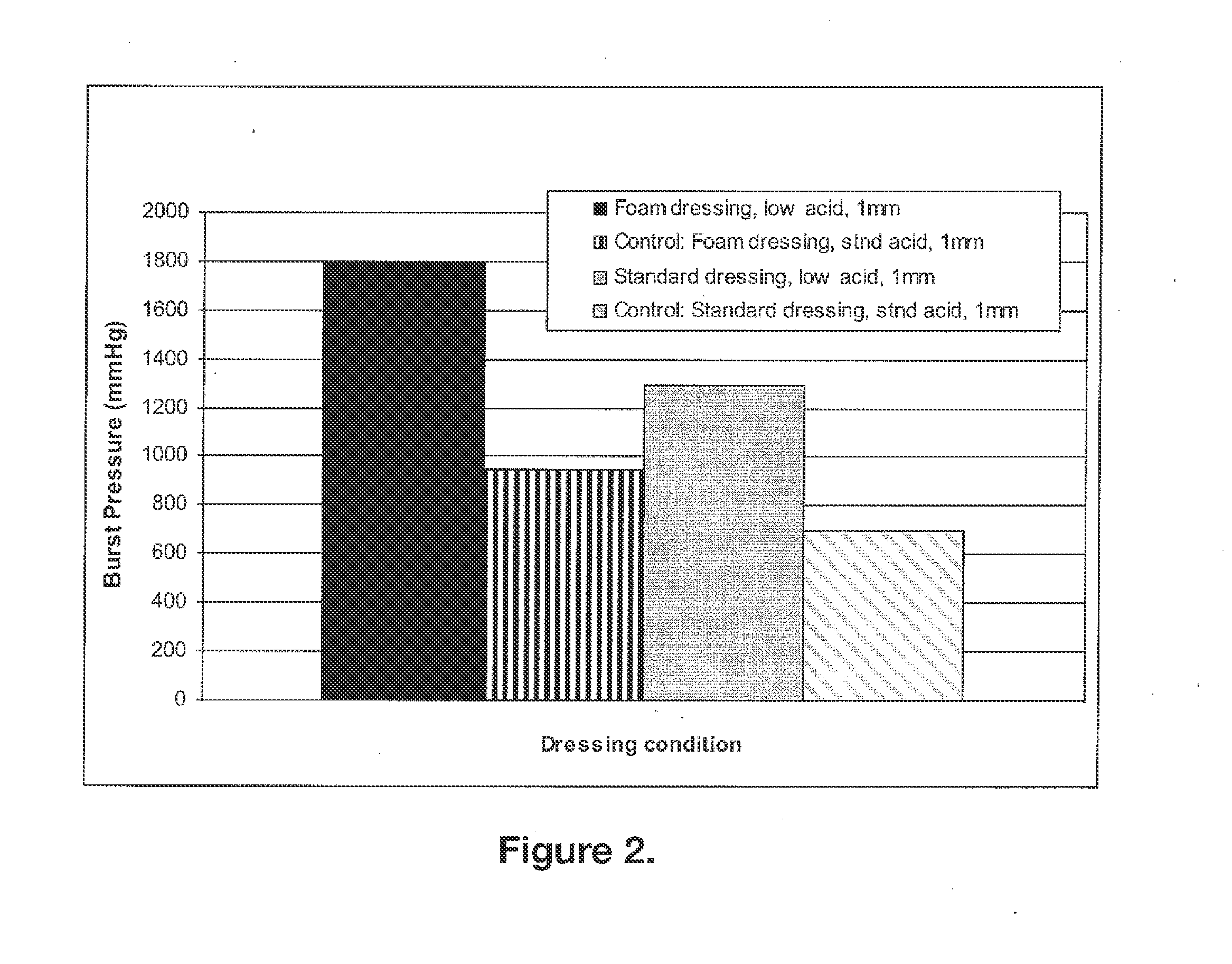
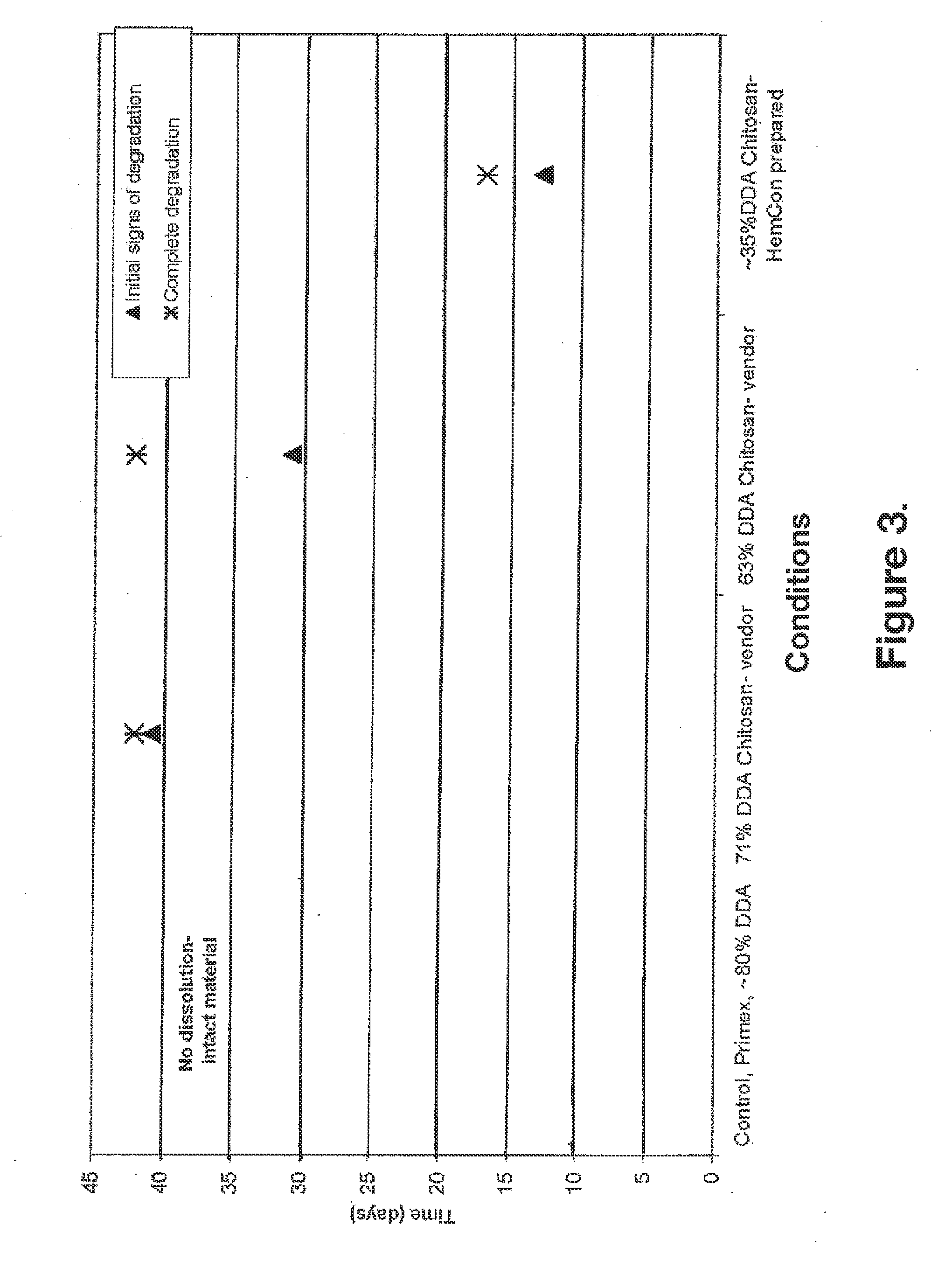
Biocompatible and bioabsorbable derivatized chitosan compositions
ActiveUS20140275291A1Reduces unnecessary riskQuick controlCompounds screening/testingBiocideCrosslinked chitosanChemical composition
The invention relates to biocompatible, bioabsorbable derivatized non-crosslinked chitosan compositions optionally crosslinked to gelatin / collagen by 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) for biomedical use and methods of making and testing such compositions, including a modified acute systemic toxicity test. The compositions comprise derivatized chitosan reacetylated to a degree of N-deacetylation (DDA) of between about 15% and 40%. The compositions are typically bioabsorbed in about 90 days or less and can be made to bioabsorb at differing rates of speed. The compositions are initially soluble in aqueous solution below pH 6.5. The compositions have an acid content that can be adjusted between about 0% (w / w) and about 8% (w / w) to customize the composition for uses that require and / or tolerate differing levels of cytotoxicity, adhesion, composition cohesion, and cell infiltration into the composition.
Owner:TRICOL BIOMEDICAL INC
In-situ crosslinked alginate hydrogels and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102408496AGood biocompatibilityGood water solubilityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryNitrogen gasOxygen
The invention relates to in-situ crosslinked alginate hydrogels with an active ingredient of disulfide bond disulfide bond alginate derivative. The preparation method thereof is as follows: the organic liquids of carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide eater are added into the alginate aqueous liquid of the alginate to activate the carboxyl of the alginate aqueous liquid; then the organic liquid of 4-aminothiolphenol is added under the conditions of keeping in dark place under 10 DEG C and nitrogen protection, so that the amino of the 4-aminothiolphenol and the carboxyl of the alginate aqueous liquid form an amido bond. The proportions of each matter adjusted and the pH value of muriatic acid is adjusted to 6.0, ethanol is deposited, frozen and dried to obtain sulfhydrylation alginates of different sulfydryl contents. The alginate aqueous liquid of the alginate oxidizes the sulfydryl thorugh the oxygen in the liquid under a room temperature to crosslink and form a disulfide bond, thus obtaining the crosslinked alginate hydrogels. The hydrogels prepared through the method has pH sensitivity and reduction responsiveness, and has potential application values in drug delivery field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Heavy metal ion adsorbent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106076279AFast adsorption rateImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsEnd-groupSilanes
The invention relates to a heavy metal ion adsorbent. The heavy metal ion adsorbent is characterized in that a silicon dioxide carrier is used as a raw material, and is modified by a grafting reagent and a functional reagent, so as to form the heavy metal ion adsorbent; the grafting reagent is silane of which the end group is provided with amino, and the functional reagent is alginate and alginic acid. A preparation method comprises the following steps of dispersing the silicon dioxide carrier into water, and adding the grafting reagent, so as to obtain a solid and liquid mixture I; separating solid and liquid, washing, and drying, so as to obtain the amino-modified silicon dioxide; dissolving the functional reagent into water, sequentially adding 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, and the amino-modified silicon dioxide, and reacting, so as to obtain a solid and liquid mixture II; separating solid and liquid, washing, and drying, so as to obtain the heavy metal ion adsorbent. The heavy metal ion adsorbent has the characteristics that the adsorbing speed is quick, the adsorbing capacity is high, the regeneration process is simple, and the property is still stable even after recycling for multiple times; the steps of the preparation method are simple, the cost is low, the condition is mild, and the environment-friendly effect is realized.
Owner:汪竹青
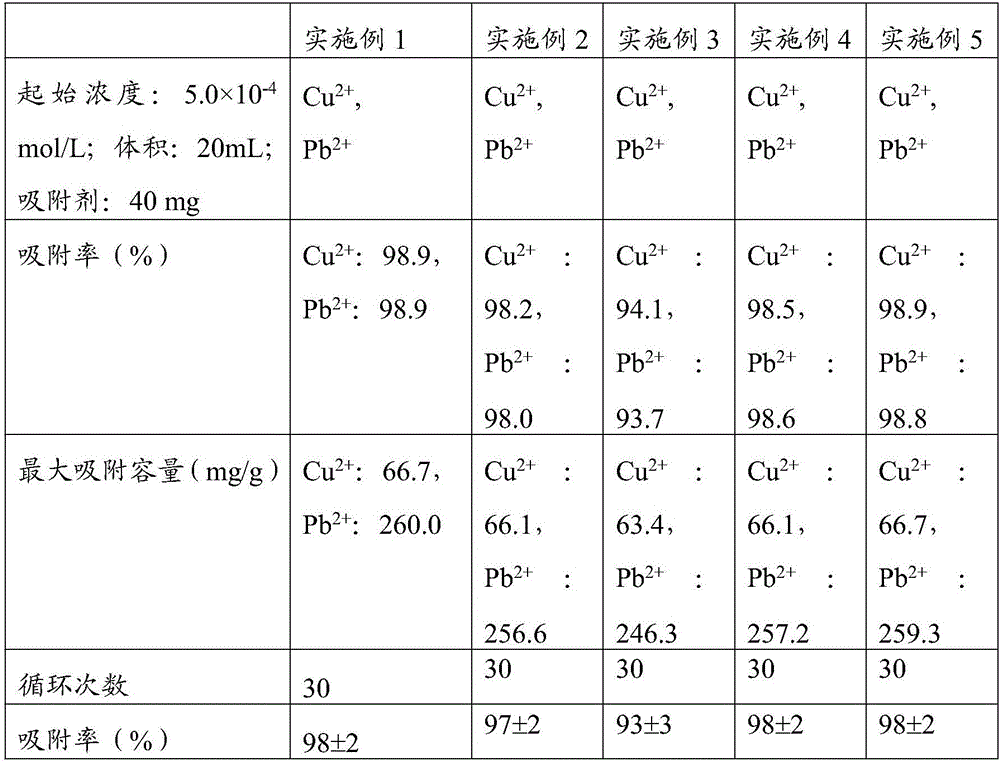
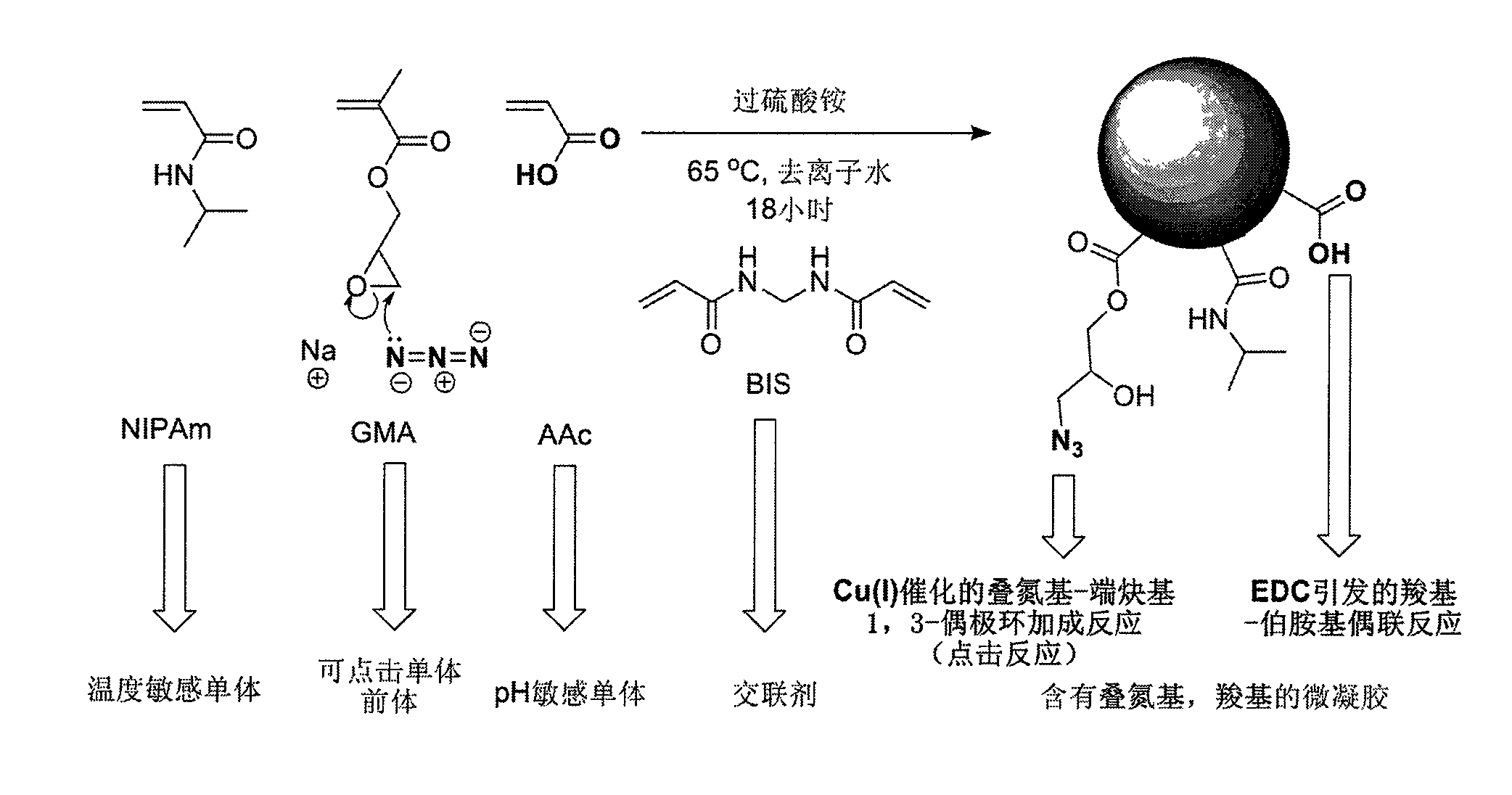
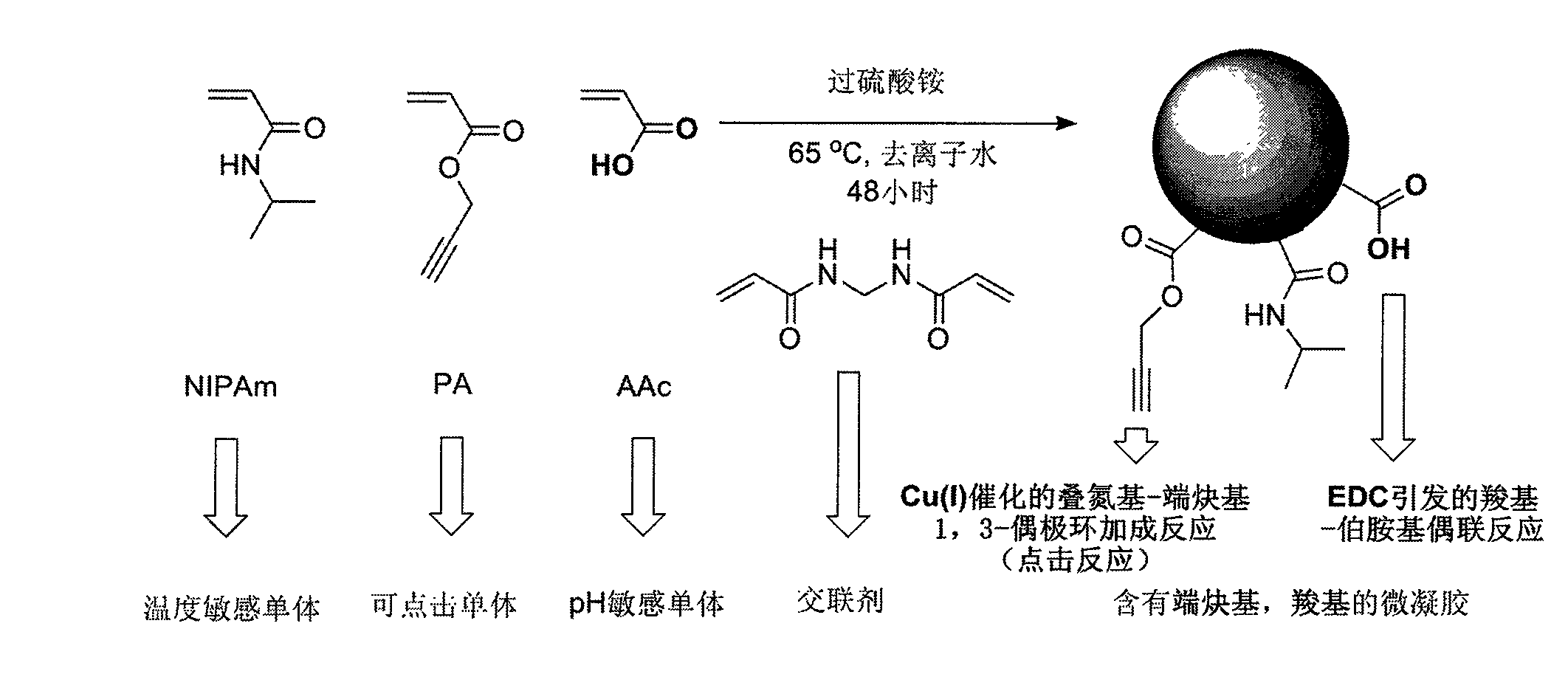
Point-and-click temperature/pH-sensibility microgel
The invention provides a chemical approach which can adopt point-and-click chemistry to realize functional grouping on the bodies or the surfaces of high molecular hydrogel particles. The high molecular hydrogel particles are generally formed by the cross linking of a hydrophilic monomer and a functional group monomer. The invention mainly puts forward a point-and-click functional group which can be introduced by adopting a copolymerization mode and can carry out a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of triazo-end alkynyl catalyzed by Cu (I). Simultaneously, a point-and-click reaction catalyzed by the Cu (I) and a coupling reaction of carboxyl-primary amine radicals initiated by 1-(3-dimethylin propyl)-3-ethyl carbon diimine hydrochloride are carried out in a water phase, are not disturbed mutually and are mutually orthogonal. The characteristic can be beneficial to the multi-function grouping of the microgel simultaneously. The temperature / pH-sensibility microgel containing the point-and-click functional group has potential application value in the aspects of targeting medicine release, molecular treatment, chemical / biologic sensors, water treatment and the like.
Owner:孟智平
Low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102220128AGood low toxicityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityFluorescence
The invention relates to a low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of a special molecular recognition and diagnosis reagent. The method comprises the following steps that functional-group amino is connected on beta-cyclodextrin by a chemical modification method to obtain amino-group-beta-cyclodextrin;under the action of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl propylamine) carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, amino-group-beta-cyclodextrin is coupled with folic acid to obtain folic acid-beta-cyclodextrin; and by taking silver, zinc and other low-toxicity elements as raw materials, an oil-solubility near-infrared quantum dot is prepared, and folic acid-Beta-cyclodextrin is used to carry out water-solubility modification to the oil-solubility near-infrared quantum dot so as to obtain the low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin. The quantum dot has good water-solubility and low-toxicity; and as emission spectrum is in a near-infrared area, and the folic acid is coupled, the quantum dot can be used for special fluorescence detection of tumors.
Owner:江苏迈健生物科技发展股份有限公司
Process for preparing chitosan microsphere immobilized lipolytic enzyme
InactiveCN101113433AImprove bindingHigh recovery rateHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierCandida spPhosphate
A preparation technique of chitosan microspheres immobilization lipase comprises the steps that: (1) lipase from candida SP is dissolved in phosphate buffer solution by taking chitosan microspheres as an immobilization carrier and adopting glutaraldehyde cross-linking, lipase A is obtained. (2) candida SP lipase solution of 0.70-0.80mg / mL prepared by phosphate buffer solution b with a pH value of 6.5-7.5 is added with immobilization lipase A (final concentration is 0.005-0.0055g / ml) and after being stirred, ethyl (3-dimethylamino propyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride solution is added, the mixture is then stirred to be fully immobilized, chitosan microspheres immobilization lipase B is obtained after the treatment of the mixture. The chitosan microspheres immobilization lipase prepared by the preparation technology of the invention improves apoenzyme combination rate and activity recovery, has powerful immobilization lipase activity and specific activity and the immobilization lipase can be recycled for six times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for covalent grafting heparin on surface of polymer film
InactiveCN1563157AImprove surface anticoagulant propertiesSimple method for covalent grafting of heparinCross-linkFiber
The method is featured as washing and extracting polymer film by alcohol, placing it in ammonium persulfate aqueous solution for forming peroxide perssad with activation initiating polymerization of vinyl monomer containing carboxy on surface by ferrisulphas ammonium, converting carboxyl to be end azyl by using 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl propyl) EDC as cross-linking agent to react with a,W-aminopropyl-polyglycol and fixing heparin on polymer film surface by covalent bond through condensation of carboxyl and azyl in heparin structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Application of carboxymethyl chitosan self-crosslinking polymer in silicon negative electrode of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN105702963AImprove mechanical propertiesReduce crystallinityCell electrodesSecondary cellsCyclic processSilicon particle
The invention discloses an application of a carboxymethyl chitosan self-crosslinking polymer in a silicon negative electrode of a lithium ion battery. The carboxymethyl chitosan self-crosslinking polymer is obtained by adding carboxymethyl chitosan to cross-liking agent 1-(3-(dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride in a self-crosslinking manner; the polymer has a three-dimensional structure, and is taken as a binder to be applied to preparation of the silicon negative electrode of the lithium ion battery; the self-crosslinking polymer shows high mechanical performance and adhesive property; chemical bonds with self-repairing capability are formed between the self-crosslinking polymer and the silicon particles; the silicon negative electrode with large volume change in the charging-discharging process can be effectively accommodated; the powder-fall-off phenomenon with structural damage caused by severe volume changes of the silicon particles in the circulating process of the silicon negative electrode is solved; and a new approach for improving the cycle performance of the silicon negative electrode of the lithium ion battery is provided.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of hepatoma carcinoma cell targeted molybdenum disulfide drug-loaded nano tablets
InactiveCN104800845ARealize integrationStrong active targetingOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsDoxorubicin HydrochloridePhotothermal therapy
The invention provides a preparation method of a hepatoma carcinoma cell targeted molybdenum disulfide drug-loaded nano tablets. The preparation method comprises following steps: step 1, molybdenum disulfide nano tablets are obtained via hydro-thermal synthesis; step 2, the molybdenum disulfide nano tablets are added into a gelatin solution, and gelatinized molybdenum disulfide nano tablets are obtained via sufficient reaction; step 3, lactobionic acid, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, and N-hydroxy succinimide are weighed and added into the gelatinized molybdenum disulfide nano tablets so as to obtain lactobionic acid modified molybdenum disulfide nano tablets; and step 4, a doxorubicin hydrochloride aqueous solution is prepared, and the lactobionic acid modified molybdenum disulfide nano tablets obtained via step 3 are added into the doxorubicin hydrochloride aqueous solution, an obtained mixture is stirred for 8 to 24h under vacuum conditions, and is subjected to centrifugalization and washing so as to obtain the hepatoma carcinoma cell targeted molybdenum disulfide drug-loaded nano tablets via collecting. The hepatoma carcinoma cell targeted molybdenum disulfide drug-loaded nano tablets can be used for photothermal therapy and CT imaging, and can be used for realizing combination of diagnosis and treatment of hepatoma carcinoma.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
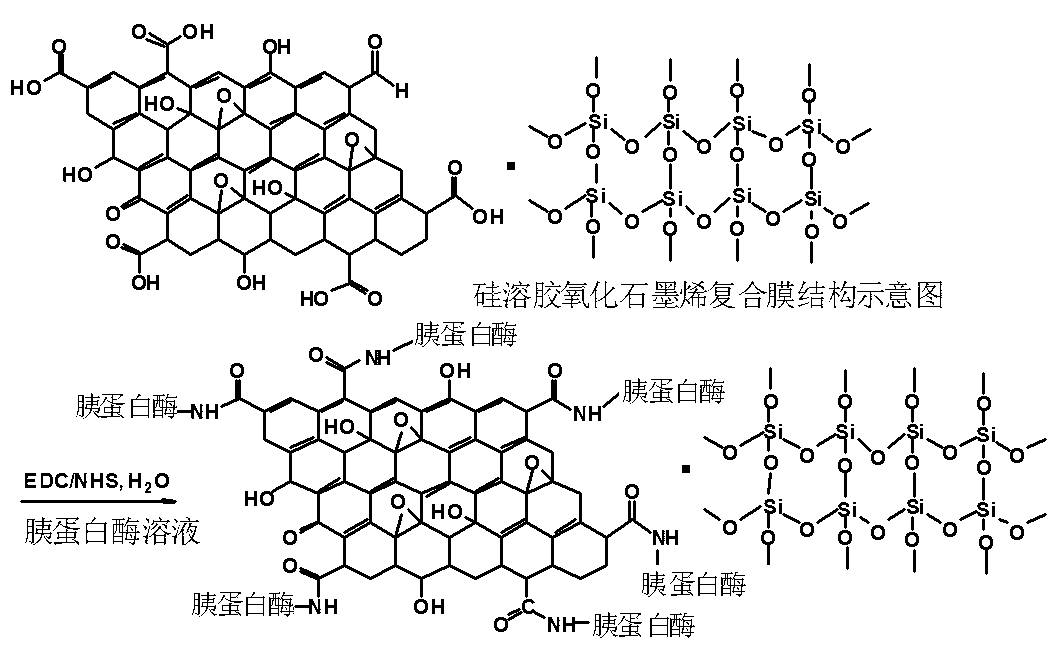
Proteolysis micro-fluidic chip based on silica gel oxidized graphene composite membrane and fabrication method of proteolysis micro-fluidic chip
InactiveCN103013824ALow priceSimple processEnzyme production/based bioreactorsCarboxyl radicalSilica gel
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-fluidic chips, and particularly relates to a proteolysis micro-fluidic chip based on a silica gel oxidized graphene composite membrane and a fabrication method of the proteolysis micro-fluidic chip. The fabrication method comprises the steps that chemical oxidization and ultrasonic dispersion are conducted on graphite powder, and an oxidized graphene aqueous solution is obtained; the oxidized graphene aqueous solution is mixed with a silica solution prepared by hydrolyzing n-silicane ethyl ester, and injected into an organic glass micro-fluidic chip channel with the surface subjected to silica gelation treatment; a modification solution is removed after a certain time; a micro-fluidic chip modified with the silica gel oxidized graphene composite membrane is obtained after drying; then, a mixed solution of 1-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxyl succinimide is injected into the channel to allow carboxyl of oxidized graphene on the surface of the channel to be activated; a protease solution such as trypsin is injected to allow protease to be fixed by a covalent bond; and the proteolysis micro-fluidic chip is obtained. A micro-fluidic chip proteolysis reactor has the advantages of short enzymolysis time, low sample consumption, cheap price and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Process for preparing high-performance sensing film of fluorescent sensor by covalently immobilizing indicator dye
InactiveCN101446555AAvoid smallGood reversibilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceCarboxylic acidCarbon chain
The invention discloses a process for preparing a high-performance sensing film of a fluorescent sensor by covalently immobilizing an indicator dye. The process comprises the following steps: cleaning a quartz glass plate sequentially with 3% HF acid, 10% H2O2 and distilled water; introducing thiohydroxy on the surface of the cleaned glass plate by (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPS); self-assembling the glass plate with the thiohydroxy in gold nanoparticle colloidal solution for 12-24h (preferred 15h) and fixing the gold nanoparticles on the glass plate; immersing the glass plate on which the gold nanoparticles are fixed in ethanol solution of (1.0-5.0)*10<-3>mol L<-1> (preferred 2.0*10<-3>mol L<-1>) mercapto carboxylic acid for 10-18h (preferred 12h), introducing long carbon chains and carboxyl on the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles, wherein, the carbon chain of the adopted mercapto carboxylic acid comprises preferably 10-16 carbon atoms; activating the carboxyl on the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS); and immersing the glass plate on which the carboxyl is activated in acetone solution (2.0*10<-4>-5.0*10<-3>mol L<-1> of the indicator dye RNH2 with primary amido, preferred 1.0*10<-3>mol L<-1>) for 4.0-9.0h (preferred 6h), then the indicator dye is covalently immobilized on the outmost layer of the glass plate to form the ultrathin sensing film, then preparing the fluorescent sensor with the covalently immobilized indicator dye. The sensing film of the sensor has the advantages of no dye loss, quick response (response time is less than 2s), easy regeneration and good reversibility when in use.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Natural pullulan polysaccharide hydrogel wound dressing and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a natural pullulan polysaccharide hydrogel wound dressing, which is prepared by undergoing a cross-linking reaction on a carboxy methylation pullulan polysaccharide and a hydrazine or diamine, wherein the crosslinking degree of carboxyl of the carboxy methylation pullulan polysaccharide and the hydrazine or the amino of the diamine is 30-90 percent. A preparation method of the wound dressing comprises the following steps of: performing carboxy methylation on the natural pullulan polysaccharide, preparing the carboxy methylation pullulan polysaccharide into a solution of which the concentration is 0.1-1.0g / ml by using deionized water, adding the hydrazine or diamine into the aqueous solution of the carboxy methylation pullulan polysaccharide with stirring at normal temperature and under normal pressure, adding an aqueous solution of 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-carbodiimide hydrochloride of which the concentration is 0.5-1.0g / ml after uniformly stirring, and uniformly stirring; and standing the obtained solution at normal temperature, crosslinking for at least 10 minutes, soaking into deionized water for at least 6 days after crosslinking, removing impurities, and drying in vacuum to obtain the natural pullulan polysaccharide hydrogel wound dressing.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fluorescent nanometer molecular imprinting biomimetic sensor, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN107607498ASolve the problem of difficult mass transferOvercomes the effect of weakening hydrogen bondsFluorescence/phosphorescenceCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention relates to a fluorescent nanometer molecular imprinting biomimetic sensor, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method comprises: weighing carbon quantum dot powder, ultrasonically dispersing in a borate buffer solution, sequentially adding 1-ethyl-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, carrying out a stirring reactionat a room temperature under a dark condition, adding 4-vinylaniline, continuously carrying out the stirring reaction, carrying out dialysis on the obtained product in water, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain surface double bond functionalized carbon quantum dots; adding a template molecule and two different functional monomers to a pore forming agent, ultrasonically dissolving, and carryingout stirring pre-polymerization at a room temperature to obtain a pre-assembly solution A; ultrasonically dispersing the surface double bond functionalized carbon quantum dots in a pore forming agentto obtain a solution B; uniformly mixing the solution A and the solution B, adding a cross-linking agent and an initiator, introducing nitrogen, stirring, carrying out centrifugation, collecting theprecipitate, and washing with distilled water; and finally carrying out elution on the template protein by using HAc-SDS, and carrying out freeze drying on the obtained product so as to obtain the fluorescent nanometer molecular imprinting biomimetic sensor.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation of collagen base biological medical material
InactiveCN101264337AGood biocompatibilityGood blood compatibilitySurgeryAbsorbent padsFreeze-dryingFibril
The invention discloses a preparation method for collagen-based biomedical materials, which is characterized in that: fresh animal skin and / or tendon and / or sheet-beam are adopt to make collagen fiber dispersion liquid (gel) or freeze-dry the collagen fiber materials via the enzymatic method, then are immersedly treated for 20 to 60 minutes through ethanol alcohol solution with concentration of 35 to 65 percent with 8 to 12g / L 2- sulfonic acid under the temperature of 15 to 40 DEG C, and then are immersedly treated for 4 to 24 hours through solution with 1.0 to 5.5g / L N-hydroxy amber imide and 0.8 to 4.0g / L carbodiimide hydrochloride under the temperature of 15 to 40 DEG C; the collagen raw materials are cleaned and immersed for two times through ethanol with concentration of 80 to 95 percent, each time for 10 to 30 minutes, then are immersed and cleaned for one time through Na2HPO4 solution with concentration of 1.5 to 2.0 percent and NaCl solution with concentration of 5.5 to 6.5 percent respectively, the time is 30 to 60 minutes; then are immersed and cleaned for 2 times through distilled water immersion, each time for 10 to 30 minutes, the materials after being cleaned are freeze-dried, and the collagen-based biomedical materials are obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing superoxide dismutase (SOD)-loaded gamma-poly glutamic acid hydrogel
InactiveCN103977447AImprove activity retention performanceEvenly dispersedCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCarboxyl radicalSide chain
The invention discloses a method for preparing superoxide dismutase (SOD)-loaded gamma-poly glutamic acid hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride / N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC / NHS) activation system, and forming an SOD-gamma-polyglutamic acid (PGA) immobilized product by using lysine residues and poly glutamic acid side chain carboxyl of SOD; crosslinking the SOD-gamma-PGA obtained by the reaction by using a diamine crosslinking agent cysteamine hydrochloride, so as to form an SOD-gamma-PGA gel system. The gel system can be applied to wound dressing or mask, and can play the antioxidant damage action, and the skin wound is quickly repaired.
Owner:TIANJIN AROLYN BIOTECH
Biological material for brain injury renovation and its preparing process
The invention relates to a biological material used to recover hurt brain. Wherein, it uses transparent hyaluronic acid as raw material, guided by carbodiimide hydrochlorate (EDC), to use adipic acid adipoyl (ADH) to cross, to obtain the hyaluronic acid gel, as the carrier of graft antibody; and uses antibody solidification technique to graft the antibodies of axon growth restrain factor MAG, OMgp and Nogo-A to the hyaluronic acid gel, to be the antibody transfer system carrying special antibody and sensitive to pH value. The invention can be used to seal the never axon regeneration restrain factor of myelin and accelerate the regeneration of hurt brain organism.
Owner:首都医科大学北京神经科学研究所
Carboxylation beta-cyclodextrin modified low-toxicity functional quantum dot and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102206487AGood low toxicityGood water solubilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityPropylamine
The invention relates to a carboxylation beta-cyclodextrin modified low-toxicity functional quantum dot and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of specific molecular recognition diagnostic reagent. In the invention, the preparation method of the carboxylation beta-cyclodextrin modified low-toxicity functional quantum dot comprises the steps that: a functional group carboxyl is connected on beta-cyclodextrin through a chemical modification method to obtain carboxy-beta-cyclodextrin; under the action of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl propylamine) carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, activated folic acid is firstly coupled with amino-terminated poly (ethylene glycol) and then coupled with the carboxy-beta-cyclodextrin to obtain folic acid-beta-cyclodextrin; silver, zinc and other low-toxicity elements are utilized as raw materials to prepare an oil soluble infrared quantum dot, and the folic acid-beta-cyclodextrin is utilized to perform water-soluble modification on the oil soluble infrared quantum dot to obtain the carboxylation beta-cyclodextrin modified low-toxicity functional quantum dot. The quantum dot prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has good water solubility and low toxicity, and the emission spectrum is in a near infrared area, and the quantum dot can be used for specific fluorescence detection on tumors because of being coupled with the folic acid.
Owner:江苏迈健生物科技发展股份有限公司
Magnetic material for efficiently detecting circulating tumor cell and preparation method of magnetic material
ActiveCN107858144ANarrow particle size distributionHigh saturation magnetizationOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismTumor/cancer cellsBiocompatibility TestingSuperparamagnetism
The invention provides a magnetic material for efficiently detecting a circulating tumor cell and a preparation method of the magnetic material. The preparation method comprises the steps of: (1) allowing hyaluronic acid, 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, cysteamine hydrochloride and dithiothreitol to react to prepare HA-SH, (2) grafting rhodamine onto HA-SH to prepare RhB-HA-SH, (3) allowing an Fe3O4 nanoparticle, RhB-HA-SH and H2O2 to react to prepare superparamagnetic fluorescent HA-SH, and (4) allowing superparamagnetic fluorescent HA-SH, 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, PEG-FA and anti-EpCAM (epithelial cell adhesion molecule) to perform antibody reaction to prepare the magneticmaterial. The magnetic material is high in saturation magnetization, and good in magnetic response and biocompatibility, can achieve specific binding with the circulating tumor cell and has certain universality.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance sensor for detecting melamine based on magnetic nanoparticles, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103920168ARealize detectionThe preparation method is simple and safeNMR/MRI constrast preparationsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolubilityMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance sensor for detecting melamine based on magnetic nanoparticles. The nuclear magnetic resonance sensor is a Fe / Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle containing an acceptor unit which is capable of specific recognition of melamine and having water-solubility, superparamagnetism, uniform particle size distribution and a particle size of about 10 to 20 nm. A preparation method for the sensor comprises the following steps: preparation of a Fe / Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle through high temperature pyrolysis; preparation of Dopa-PEG and Dopa-acceptor unit by using N-hydroxy succinimide and 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride; and preparation of a target nanoparticle for preparation of the nuclear magnetic resonance sensor used for detecting melamine in virtue of coordination of oxygen and connection of the nanoparticle. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of easiness, safety, economy and easy availability of raw materials and good process controllability. According to the invention, a novel prospect--a nanometer magnetic resonance sensor is provided for application of a nanometer magnetic resonance contrast agent material, and the research area of nano-materials is broadened.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
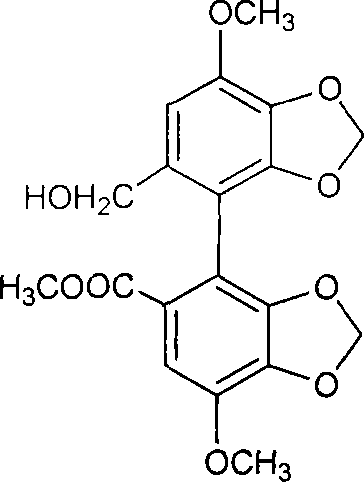
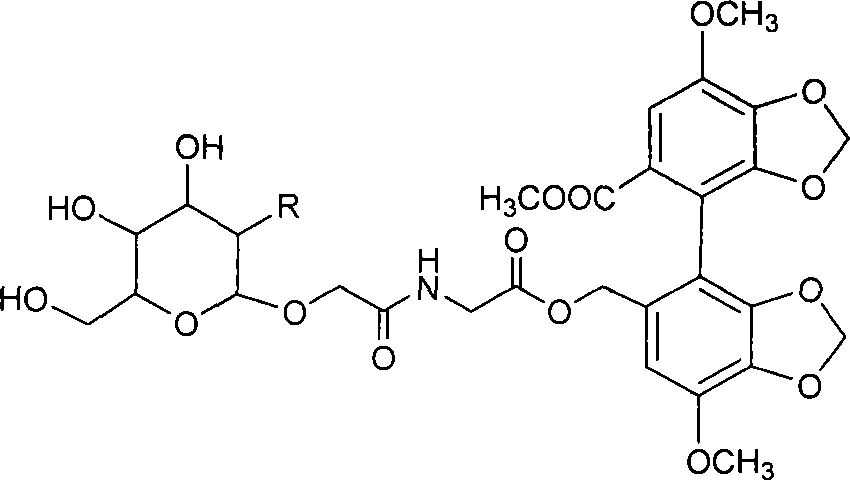
Camptothecin and artesunate conjugate, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104163823AHas antitumor activityReduce harmOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryOrganic solventMedicinal chemistry
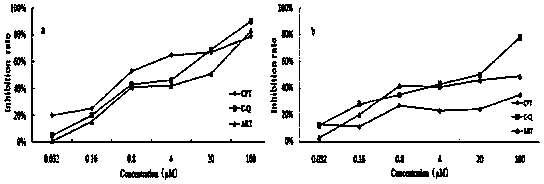
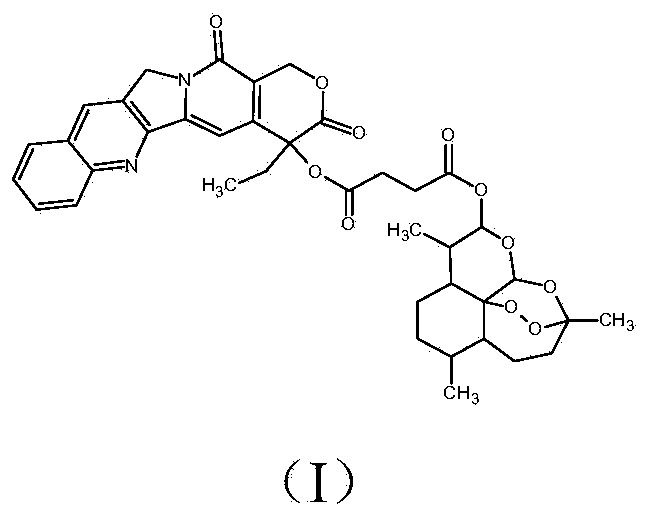
The present invention discloses a camptothecin and artesunate conjugate represented by a formula (I). The preparation method comprises the steps of dissolving camptothecin represented by a formula (II) and artesunate represented by a formula (III) in an organic solvent, carrying out a stirring reaction at a temperature of 15-50 DEG C under the effects of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride and 4-dimethylaminopyridine, performing TLC tracking monitoring until the reaction is over, and post-treating the reaction solution to obtain the camptothecin and artesunate conjugate represented by the formula (I). The camptothecin and artesunate conjugate of the present invention can be used for preparing various anti-tumor drugs. The formulas (I), (II) and (III) are shown as follows.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Cadmium ion adsorbent and preparation method and application thereof
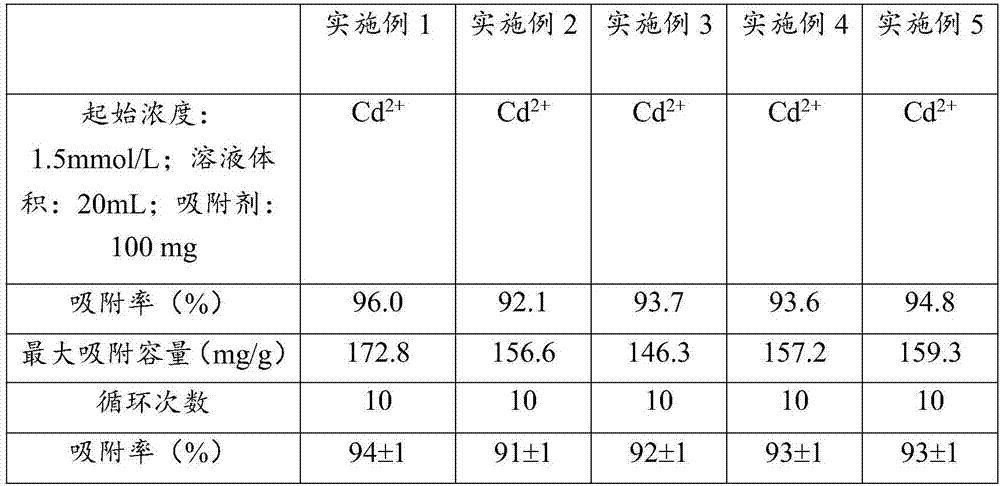
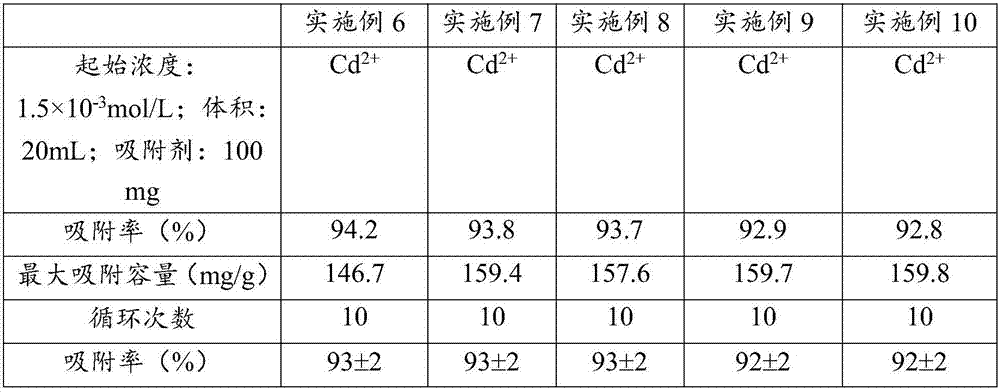
ActiveCN107262073AFast adsorption rateImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsEthylenediamineAlkaline earth metal
The invention discloses a cadmium ion adsorbent made from alginate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid salt; carboxyl groups in the alginate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid salt are activated via 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, ethylenediamine is added as a linker so as to cause condensation aeration of amino groups at two ends with the alginate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid salt, the alginate and the ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid salt are linked and are then gelled in an alkaline-earth metal ionic liquid, and drying is performed to obtain the cadmium ion adsorbent. The cadmium ion adsorbent has the advantages that selectivity for cadmium ions is high, adsorbing capacity is high, recycling is easy, the regenerating process is simple, and the adsorbing property of the adsorbent is kept stable after multiple recycling; the adsorbent is applicable to the treatment of cadmium-ion-containing wastewater and the treatment of various water samples acquired by treating cadmium-containing solid samples, and has good application value.
Owner:ANQING NORMAL UNIV
Juicy food packaging biodegradable chitosan film preparation method
The invention discloses a juicy food packaging biodegradable chitosan film preparation method. The method includes dissolving chitosan powder into acetic acid solution, then adding alkylated nano cellulose, mixing completely, filtering and purifying, and obtaining alkylated nano cellulose / chitosan solution through ultrasound treatment; dissolving gallic acid or gallic acid ester substances into ethanol, adding 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide reagent for full reaction, adding the mixture into the alkylated nano cellulose / chitosan solution, stirring at low temperature, placing at room temperature, performing ultrasonic dispersion and vacuum deaeration treatment, drying, and obtaining the film; soaking with alkali solution, flushing and treating through water till neutral, drying at room temperature, and obtaining the product. The method has the advantages that the chitosan is modified through the nano cellulose and gallic acid, and the tensile strength, oxidation resistance and antibacterial properties of the chitosan film are improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
Carboxylated fluorescent microsphere, preparing method thereof and applications of the carboxylated fluorescent microsphere
ActiveCN104119540AMeet application requirementsAvoid post-functionalization reactionsFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsAntigenGlycidyl methacrylate
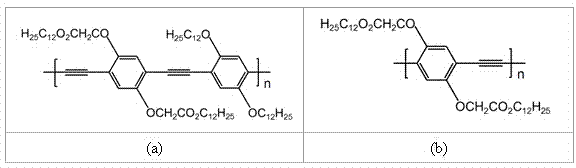
The invention relates to a carboxylated fluorescent microsphere, a preparing method thereof and applications of the carboxylated fluorescent microsphere. The carboxylated fluorescent microsphere based on a conjugated polymer is prepared by steps of: preparing a poly(arylene ethynylene) polymer with a side chain containing carboxyl by utilization of a hydrolysis reaction method; activating the carboxyl with N-(3-dimethyllaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-Hydroxysuccinimide; and bonding a fluorescent polymer onto an APGMA microsphere in a covalent bond manner by adopting a monodisperse amino-modified porous poly(glycidyl methacrylate) APGMA microsphere having a size of 5 [mu]m as a substrate sphere. The carboxylated fluorescent microsphere has biological reaction sites, and good biological coupling performance, and can detect the biomolecule BSA. If a needed antibody is coupled to the fluorescent microsphere through the carboxyl on the side chain of the polymer, a fluorescent microsphere with an antibody labeling is prepared and can be used for detection of the corresponding antigen.
Owner:纳谱分析技术(苏州)有限公司
Waterborne polyurethane dispersion body and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108484862AImprove heat resistanceLow costNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyesterPolyurethane dispersion
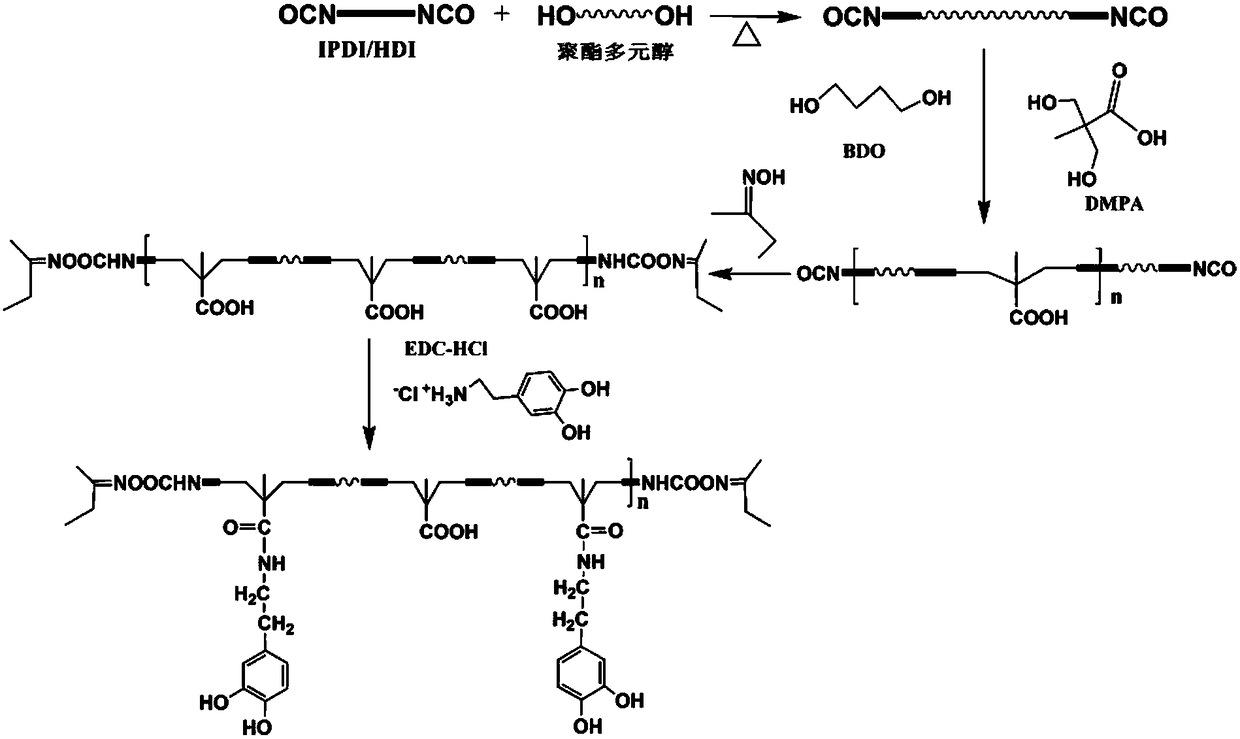
The invention discloses a waterborne polyurethane dispersion body and a preparation method thereof, wherein the waterborne polyurethane dispersion body is prepared from the following ingredients and raw materials in proportion: 100 parts of polyester polyol, 20 to 45 parts of diisocyanate, 2 to 6 parts of dimethylolpropionic acid, 0.5 to 3 parts of 1,4-butanediol, 2 to 4 parts of trimethylolpropane, 2 to 10 parts of methyl ethyl ketoxime, 1 to 2 parts of carbodiimide hydrochloride, 2 to 4 parts of 3-hydroxytyramine hydrochloride, 1.2 to 1.8 parts of triethylamine and 110 to 160 parts of deionized water. An adhesion unit containing catechol groups and polyurethane containing sealed isocyanate functional groups are combined; an adhesion material with high heat resistance, low cost and wide substrate applicability is obtained through preparation.
Owner:肇庆市华莱特复合新型材料有限公司
Dicycloglycosides compound, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101104629AGood water solubilityIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilityAltrose
Disclosed is a preparation method of a bicyclol glycoside compound, which is characterized in that first bicyclol and glycine protected by Fmoc are condensed under the catalysis of 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and 4-dimethylamino pyridine, and then protecting group of Fmoc is removed under the effect of acetonitrile diethylamine to obtain intermediate bicyclol-glycine ester which is the condensation of the bicyclol and the glycine. At last, Alpha or Beta glycosyl carboxyl methyl glycoside of glucose, galactose, mannose, allose, altrose, gulose, idose, talose, acetyl-glucosamine or acetyl galactosamine has condensation reaction with the intermediate bicyclol-glycine ester in solvent N-methyl pyrrolidone and under the effect of condensing agent and alkali. The water solubility of the bicyclol can be increased with the invention, and the bioavailability of the bicyclol is improved, which can provide enough raw material and effective compound route for the study of the anti-hepatitis drug. The invention has the advantages that the preparation method is simple and convenient; the condition is easy to control.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation of hyaluronic acid coupling molybdenum disulfide/carbon nano tube composite medicine-carrying optothermal agent
InactiveCN104324376ATargetedIncrease diversityOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsModified carbonCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hyaluronic acid coupling molybdenum disulfide / carbon nano tube composite medicine-carrying optothermal agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing thioctic acid modified amination polyethylene glycol; weighing hyaluronic acid, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide to be dissolved into dimethyl sulfoxide; weighing the thioctic acid modified amination polyethylene glycol to be dissolved into dimethyl sulfoxide; adding a solution of the thioctic acid modified amination polyethylene glycol to a mixed solution, and depositing to obtain hyaluronic acid modified thioctic acid / amination polyethylene glycol; mixing a molybdenum disulfide modified carbon nano tube and the hyaluronic acid modified thioctic acid / amination polyethylene glycol, adding the mixture to an amycin water solution to obtain the hyaluronic acid coupling molybdenum disulfide / carbon nano tube composite medicine-carrying optothermal agent. The hyaluronic acid coupling molybdenum disulfide / carbon nano tube composite medicine-carrying optothermal agent can be used for the early diagnosis, treatment and research of tumor the field of biomedicine.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method of preparing highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket
InactiveCN104548200APromote swellingImprove mechanical propertiesAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryPolymer sciencePleurotus tuber-regium
The invention discloses a method of preparing a highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket and belongs to the technical field of natural polymer materials. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing highly branched polysaccharide of pleurotus tuber-regium into NaOH and isopropanol, carrying out reaction with chloroacetic acid at the temperature of 60 DEG C, carrying out reaction, cooling, neutralization, dialysis and freeze drying to obtain carboxymethyl highly branched polysaccharide, dissolving the obtained carboxymethyl polysaccharide into a phosphoric acid buffer salt solution with a pH value to be 7.4, carrying out activation on 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide for 15 minutes to 4 hours, and carrying out crosslinking reaction on an activated product and a fibroin solution for 6-48h at the temperature of 4-37 DEG C to obtain the highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket. The method is simple in operation and rich in raw material source; in addition, the prepared bracket material has the drug controlled release property and biocompatibility and is good in mechanical property; the highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket can be used for preparing an artificial tissue bracket.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
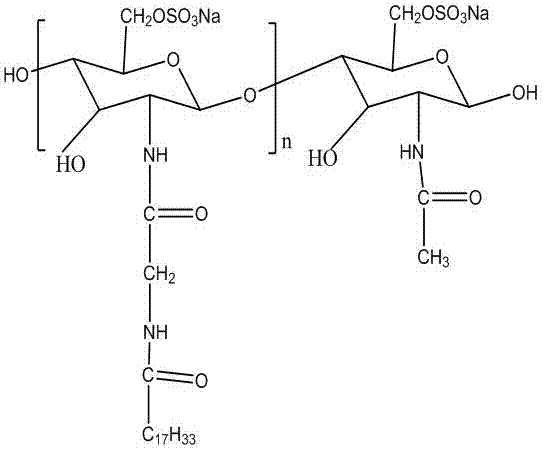
Sodium N-(N'-oleoylglycyl)-chitosan sulfonate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106967183AGood biocompatibilityAdjustable surface activityTransportation and packagingMixingIce waterBiocompatibility
Sodium N-(N'-oleoylglycyl)-chitosan sulfonate and a preparation method thereof relate to the technical field of chemical and medicine; N-hydroxysuccinimide and dicyclohexylcarbodiimide are mixed with DMF (dimethyl formamide) solution of oleic acid to obtain filtrate; glycine and potassium carbonate are dissolved in water, the filtrate is dropwise added under ice water bath, and reacting is allowed at room temperature to obtain n-hydroxysuccinimide; N-oleoylglycyl solution is adjusted to neutrality and is mixed with chitosan, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide for reacting to obtain N-(N'-oleoylglycyl)-chitosan, swelling with DMF for sulfonation reaction, supernate is collected and dialyzed to obtain filtrate, and the filtrate is lyophilized to obtain sodium N-(N'-oleoylglycyl)-chitosan sulfonate. The finished sodium N-(N'-oleoylglycyl)-chitosan sulfonate is a green surfactant having good biocompatibility, high performance, zero toxify and adjustable surface activity.
Owner:YANGZHOU POLYTECHNIC INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com