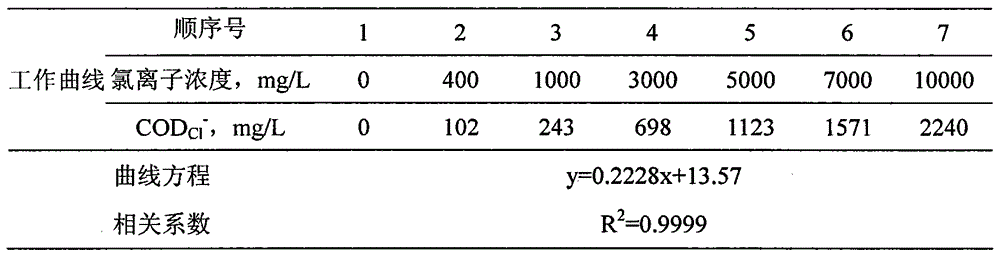
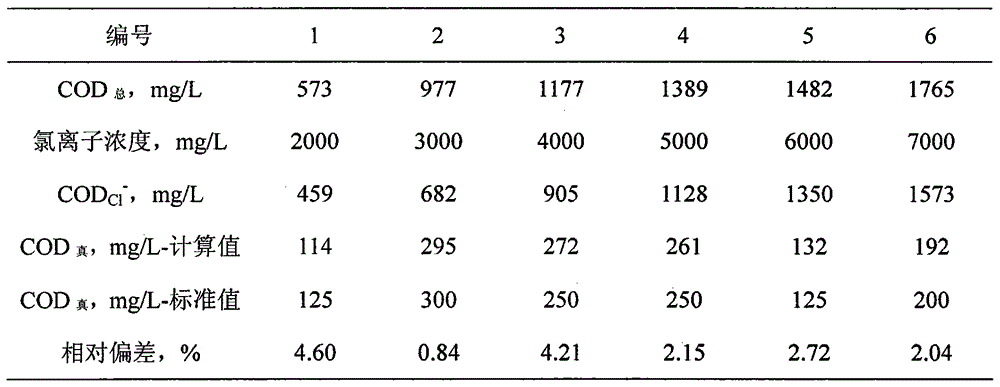
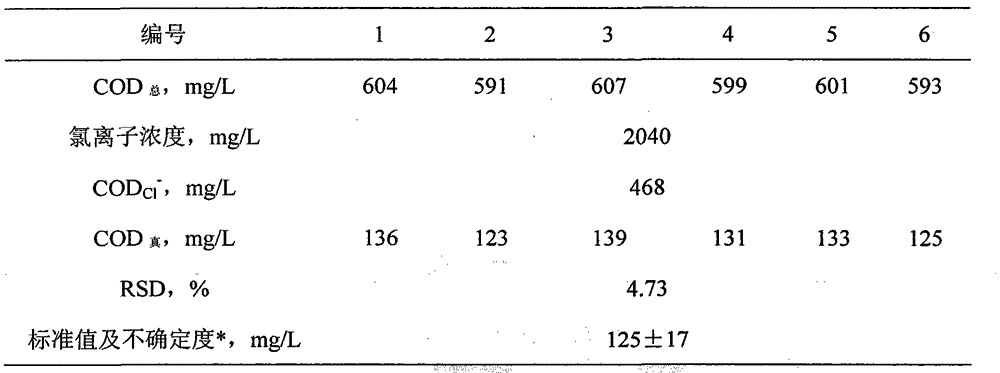
Method for measuring chemical oxygen demand of high-chlorine wastewater
A chemical oxygen demand, high chlorine wastewater technology, applied in material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by chemical reaction of materials, etc., can solve the problem of environmental pollution, highly toxic, difficult to accurately Determining the K size, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Main instruments and reagents
[0031] Reflux device: an all-glass reflux device with a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with a No. 24 standard ground mouth. The length of reflux condensation is 300-500mm; heating device; acid burette.
[0032] Reagent: copper sulfate (CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O), concentrated sulfuric acid (ρ=1.84g / mL), potassium dichromate, ammonium ferrous sulfate, o-phenanthroline, potassium hydrogen phthalate, sodium chloride, silver nitrate. Water is distilled water.
[0033] 2. Reagent solution
[0034] 2.1 Concentrated sulfuric acid saturated copper sulfate catalyst
[0035] Add 1.5-2.5g of copper sulfate pentahydrate to 500mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and use it after standing for 24 hours. Shake well before use.
[0036] 2.2 Potassium dichromate standard solution
[0037] First dry an appropriate amount of potassium dichromate powder at 105°C for 2 hours. Then weigh 24.516g-39.226g of dried potassium dichromate, dissolve it in water, and dilute to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com