Method for producing beta-mannase by bacillus germs
A technology of halobacterium bacillus and mannanase, which is applied in the field of bacterial production of β-mannanase, achieving the effects of short cycle, high enzyme activity and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
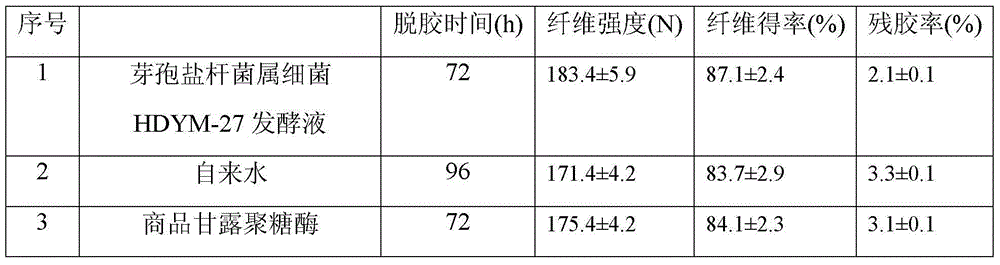
[0018] Specific embodiment one: the method for producing β-mannanase by bacteria of the genus Halobacterium bacillus in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0019] 1. Inoculate the bacteria HDYM-27 of the genus Sporohalobacter sp. in the konjac flour medium, so that the initial cell concentration in the medium is (1.0~2.0)×10 7 a / mL;
[0020] 2. Cultivate for 36-60 hours at a temperature of 32-38° C. to obtain a fermented liquid, and extract the fermented liquid to obtain β-mannanase.
[0021] After the fermentation, the β-mannanase activity in the fermentation broth is 2000-3000U / mL. The method has the advantages of short fermentation period, low cost and simple operation; the composition of the fermentation liquid is simple, the β-mannanase is easy to purify, and the fermentation liquid has no pollution to the environment. The fermented liquid is used for flax degumming with short time, complete removal of gum, low residual gum rate, high yiel...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one in that: the konjac flour culture medium described in step one is made of 2g konjac flour, 0.5g ammonium nitrate, 0.5g sodium chloride and 100mL tap water. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 2 in that: the pH value of the konjac flour culture medium is 6.4-7.4. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com