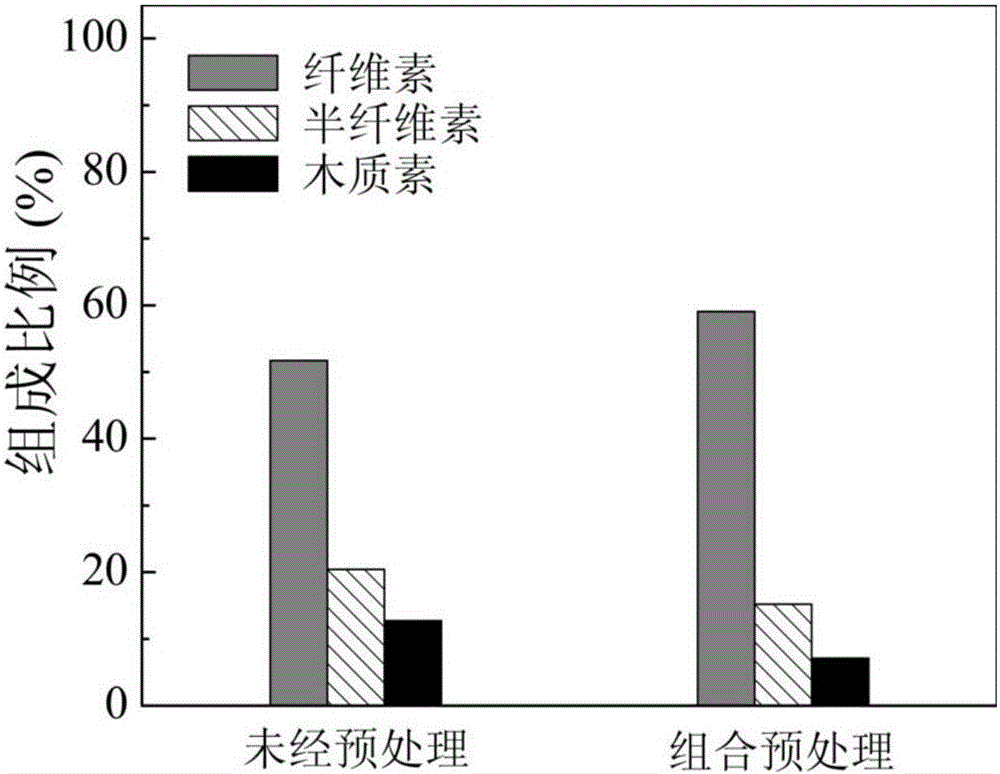
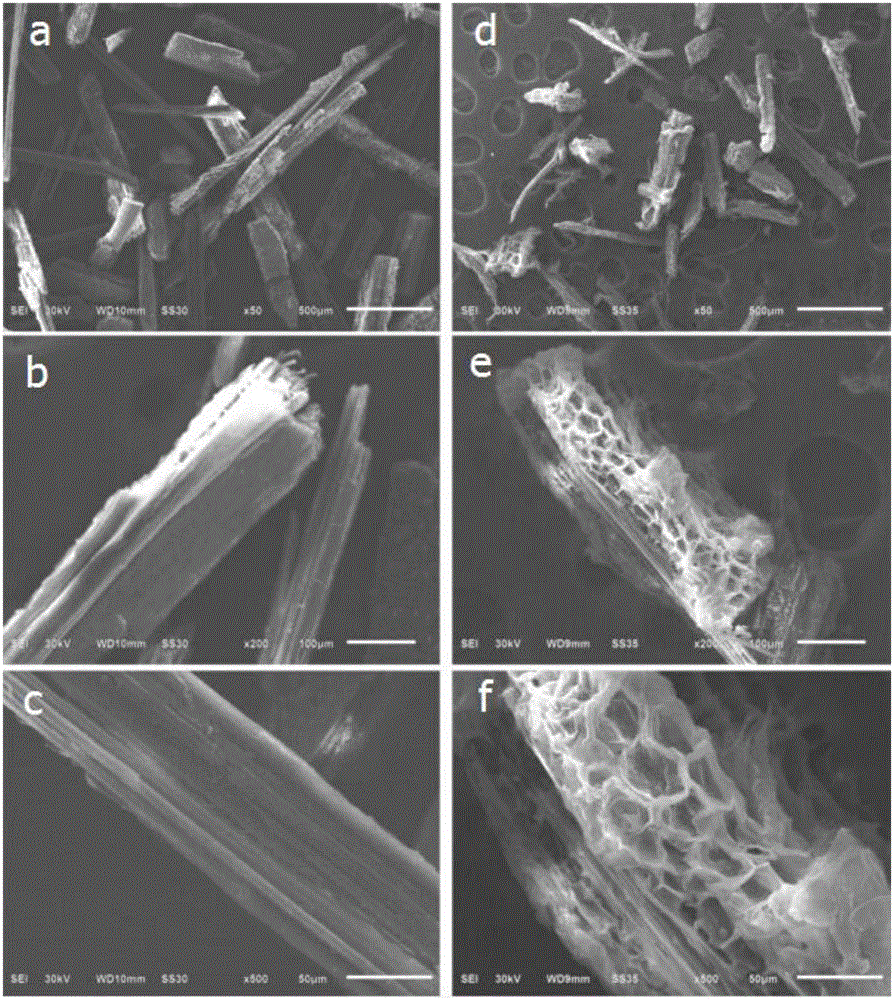
Combined pretreatment process for improving lignocellulose saccharification effect
A lignocellulosic and pretreatment technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, etc., to achieve the effects of increased economic benefits, low equipment investment, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 40 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 55°C until constant weight.
[0023] (2) Further place lignocellulose in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH / urea solution with a concentration of 2% / 3% according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:20 (g / ml), and place it in a constant temperature environment at 4°C After 4h, wet residue A was obtained by filtration and separation.
[0024] (3) The wet slag A obtained through filtration and separation was further rinsed repeatedly with distilled water until the pH of the rinsing solution was neutral, and dried at 50-60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry slag B.
[0025] (4) Further place the dry residue B in a container of appropriate size, add ultrapure water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:40 (g / ml), place it under a 120W ultrasonic instrument for 30 minutes, and filter to obtain wet residue C.
[0026] (5) The wet slag C obtained through filtration and sep...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 40 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 55°C until constant weight.
[0030] (2) Further place lignocellulose in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH / urea solution with a concentration of 2% / 3% according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20 (g / ml), and place it in a constant temperature environment of -10°C After 4 hours, the wet residue A was obtained by filtration and separation.
[0031] (3) The wet slag A obtained through filtration and separation was further rinsed repeatedly with distilled water until the pH of the rinsing solution was neutral, and dried at 50-60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry slag B.
[0032] (4) Further place the dry residue B in a container of appropriate size, add ultrapure water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:40 (g / ml), place it under a 120W ultrasonic instrument for 30 minutes, and filter to obtain wet residue C.
[0033] (5) The wet slag C obtained through filt...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 40 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 55°C until constant weight.
[0037] (2) Further place lignocellulose in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH / urea solution with a concentration of 4% / 6% according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20 (g / ml), and place it in a constant temperature environment of -10°C After 4 hours, the wet residue A was obtained by filtration and separation.
[0038] (3) The wet slag A obtained through filtration and separation was further rinsed repeatedly with distilled water until the pH of the rinsing solution was neutral, and dried at 50-60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry slag B.
[0039] (4) Further place the dry residue B in a container of appropriate size, add ultrapure water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:40 (g / ml), place it under a 120W ultrasonic instrument for 30 minutes, and filter to obtain wet residue C.
[0040] (5) The wet slag C obtained through filt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com