Method for treating swine wastewater
A treatment method and waste water technology, which is applied in animal husbandry waste water treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the unsustainable recycling of magnesium ammonium phosphate and affect the recycling of magnesium ammonium phosphate , no ammonia nitrogen removal performance and other problems, to achieve the effect of low treatment cost, low project investment cost, and solve pollution problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
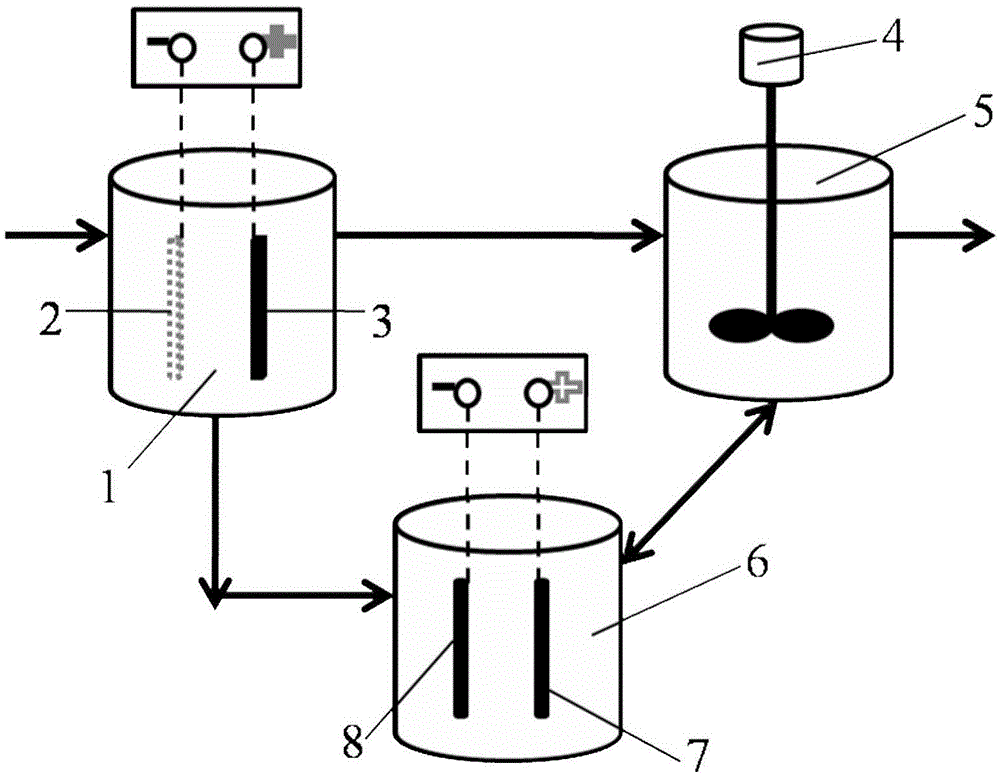
[0029] according to figure 1 The schematic flow chart of the processing method of the shown pig wastewater, at first:
[0030] a. Take 1m 3Pig raising wastewater with an ammonia nitrogen concentration of 890mg / L and a phosphorus concentration of 135mg / L is added to the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool 1, the anode magnesium metal plate 3 of the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool has a magnesium content of 92%, and the cathode 2 is a stainless steel mesh, and then the direct current is turned on Power supply, adjust the current density at 120mA / cm, and release magnesium ions through the electrolysis of the anode magnesium alloy plate. During this period, start the stirrer and control the stirring speed at 220rpm to make the waste water mix evenly. When the pH of the waste water rises to 9, turn off the power. Stop the electrolysis, let stand for 60min to carry out solid-liquid separation, the supernatant enters the ammonia sinking tank 5, and recovers the magnesium amm...
Embodiment 2
[0036] a. Take 1m 3 Pig raising wastewater with an ammonia nitrogen concentration of 890mg / L and a phosphorus concentration of 135mg / L is added to the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool. The magnesium content of the anode magnesium metal plate of the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool is 95%, and the cathode is graphite. Then turn on the DC power supply and adjust the current When the density is 180mA / cm, magnesium ions are released through the electrolysis of the anode magnesium alloy plate. During this period, the stirrer is started and the stirring speed is controlled at 180rpm to make the waste water mix evenly. When the pH of the waste water rises to the range of 9.5, turn off the power and stop the electrolysis. Stand still for 90 minutes for solid-liquid separation, the supernatant enters the ammonia sink tank, and recovers the magnesium ammonium phosphate solid precipitated at the bottom of the tank for future use.
[0037] B, the ammonium magnesium phosphate sol...
Embodiment 3
[0042] a. Take 1m 3 Pig raising wastewater with an ammonia nitrogen concentration of 890mg / L and a phosphorus concentration of 135mg / L is added to the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool 1, the anode magnesium metal plate magnesium 3 content of the electrolytic phosphorus recovery pool is 93%, the cathode is a platinum electrode 2, and then the direct current is turned on Power supply, adjust the current density at 160mA / cm, and release magnesium ions through the electrolysis of the anode magnesium alloy plate. During this period, start the stirrer and control the stirring speed at 200rpm to make the waste water mix evenly. When the pH of the waste water rises to 9.5, turn off the power and stop Electrolysis, standing for 80min for solid-liquid separation, the supernatant enters the ammonia sinking tank 5, and recovers the magnesium ammonium phosphate solid precipitated at the bottom of the tank for future use.
[0043] B, the ammonium magnesium phosphate solid that reclaims...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com