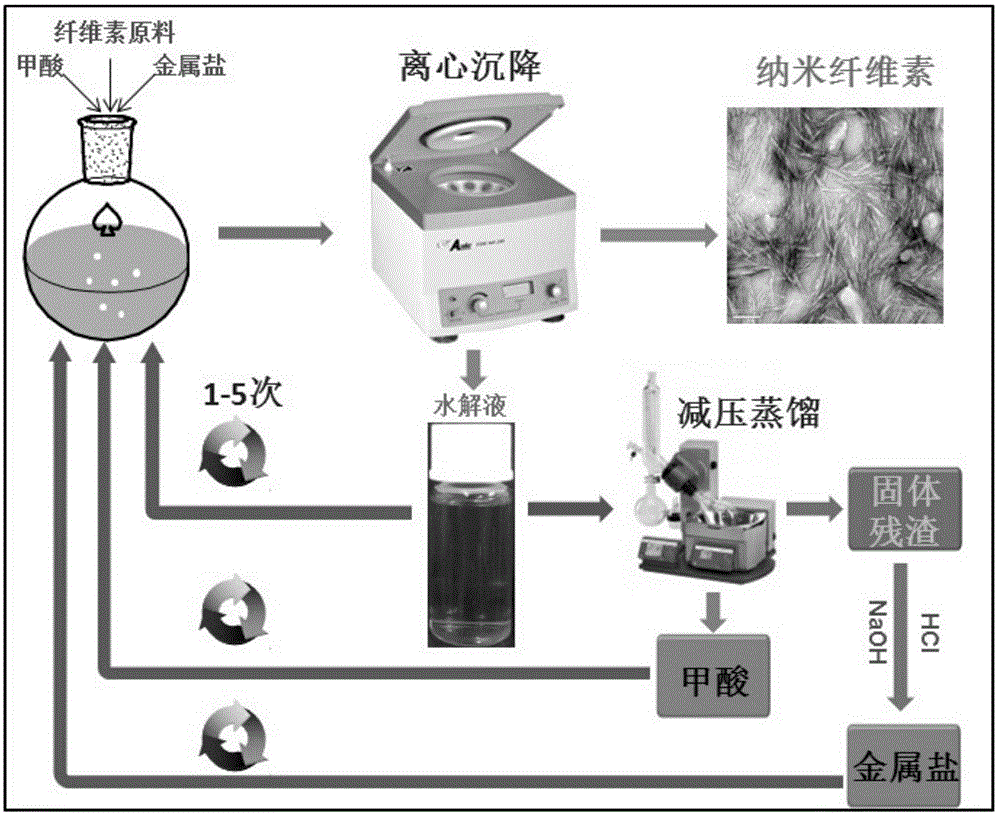
Method for preparing nano cellulose by formic acid hydrolysis by using metal salt catalyst
A technology of nano-cellulose and metal salts, which is applied in the field of natural polymer material preparation, can solve the problems of high concentration of formic acid, difficulty in recovering inorganic acid, and long reaction time of formic acid, etc., and achieves easy control of the reaction, high crystallinity, and easy The effect of recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] In step 1) of the method for preparing nanocellulose crystals according to the present invention, based on 100 parts by weight of the cellulose raw material, the metal salt addition is 0.5-30 parts by weight. When the metal salt addition is less than 0.5 parts by weight, the hydrolysis The promoting effect of the reaction is not obvious; and when the added amount of the metal salt is greater than 30 parts by weight, it may cause the metal salt to remain on the nanocellulose crystals, which will adversely affect the properties of the product.
[0038] The weight ratio of the added cellulose raw material to the added formic acid solution is 1:10-100, when the weight ratio is less than 1:10, that is, the amount of formic acid solution added is insufficient, and the reaction is not complete; and when the weight ratio is greater than 1:100, That is, an excessive amount of formic acid solution is not economical enough.
[0039] One of the advantages of the method for preparin...
Embodiment 1
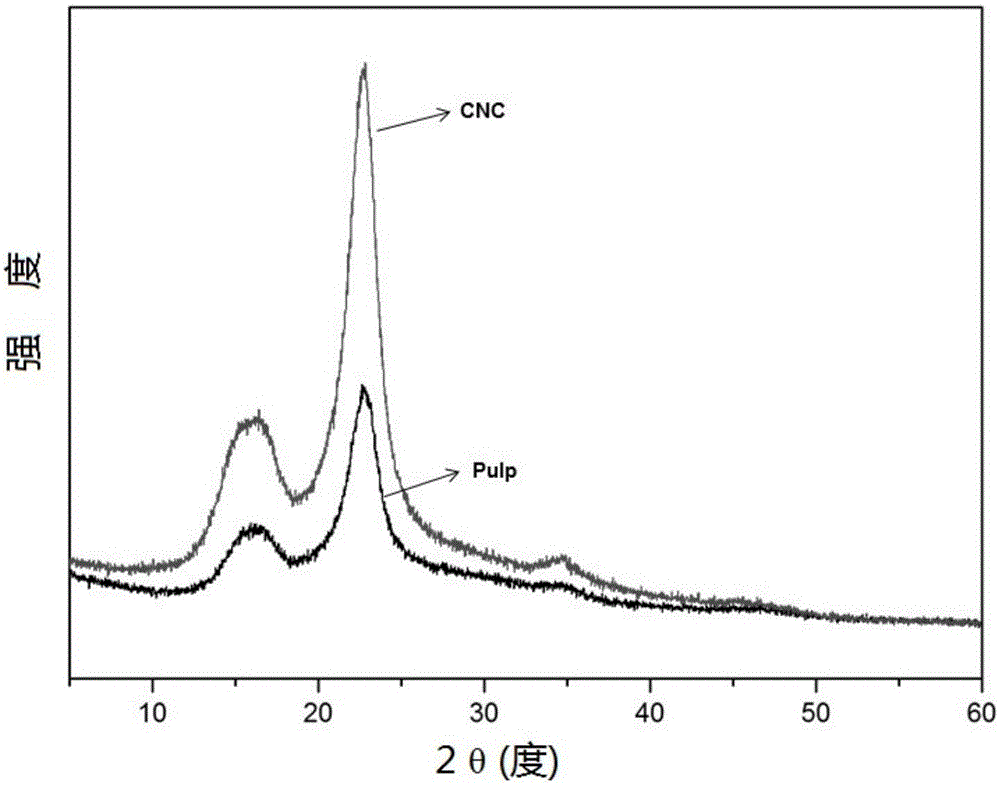
[0042] Weigh 3g of dry bleached eucalyptus pulp and 0.3g of anhydrous ferric chloride into a 250mL round bottom flask, add 100mL of 88% (w / w) formic acid solution, and stir magnetically at 95°C for 6h. After the reaction, the flask was quickly placed in a cold water bath to cool to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was transferred into a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 min. The hydrolyzate can be directly returned to prepare the next batch of nanocellulose. The precipitated jelly is centrifuged and washed with distilled water until neutral, and the centrifuged product is freeze-dried to obtain nanocellulose crystals. The yield of nanocellulose obtained in the present embodiment is 75% (relative to the original dry bleached eucalyptus pulp), and the crystallinity is increased to 75% of nanocellulose (CNC) from 65% of the original pulp (Pulp) , the XRD patterns before and after hydrolysis are shown in the appendix figure 2 .
Embodiment 2
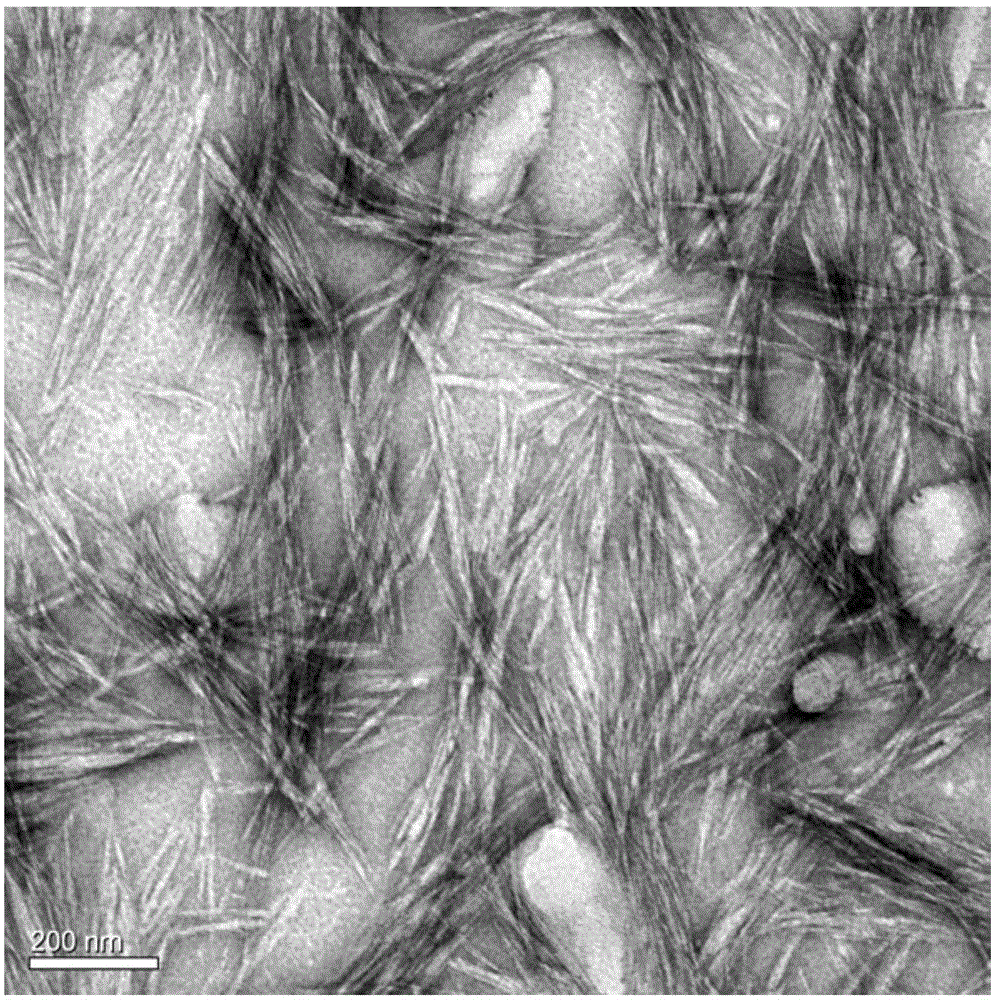
[0044] Weigh 2 g of dry bleached eucalyptus pulp and 0.1 g of anhydrous magnesium nitrate into a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 100 mL of 85% (w / w) formic acid solution, and stir magnetically at 80° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, the flask was quickly placed in a cold water bath to cool to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was moved into a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min. The hydrolyzate can be directly reused to prepare the next batch of nanocellulose. The precipitated jelly is centrifuged and washed with distilled water until neutral, and the centrifuged product is freeze-dried to obtain nanocellulose crystals. The yield of nanocellulose obtained in this example is 78% (relative to the original dry bleached eucalyptus wood pulp), the width is 10-20nm, and the length is 100-300nm. image 3 Transmission electron microscope pictures in .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com