Duck tembusu virus (DTMUV) infectious clone attenuated vaccine strain and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of duck tembusu virus and infectious cloning, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problem of lack of vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
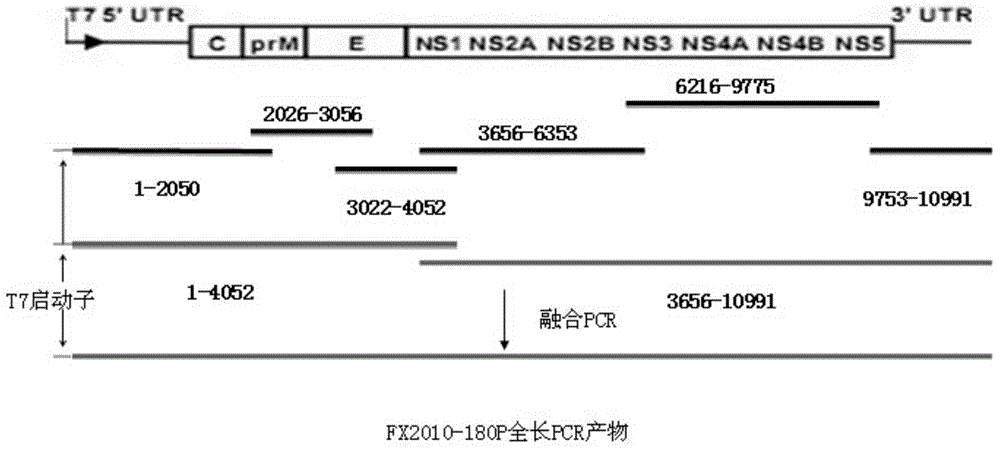
[0041] Example 1 Construction of full-length cDNA clone of duck Tembusu virus attenuated strain FX2010-180P genome
[0042] 1. Materials
[0043] 1.1 Viruses and Cells
[0044]Duck Tembusu virus FX2010-180P strain and DF-1 cells were preserved by Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
[0045] 2. Method
[0046] 2.1 Extraction of viral RNA
[0047] Use Takara’s RNAisoPlus reagent to extract viral RNA, and operate according to the instructions on the product manual. The specific method is as follows: draw 300 μl of virus culture solution, add 700 μl RNAisoplus Reagent, put it in a 1.5ml RNase-free centrifuge tube, pipette and mix, and then stand at room temperature for 5 minute. Add 200 μl chloroform to the mixture, vibrate vigorously for 15 seconds, and let stand at room temperature for 3 minutes. Centrifuge at 12000r / min at 4°C for 10min. Transfer the supernatant to another clean RNase-free centrifuge tube. Add an equal volume...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2 Rescue and Identification of Duck Tembusu Virus Attenuated Strain FX2010-180P
[0105] 1. In vitro transcription
[0106] Using the full-length PCR product of the above virus as a template, use In vitro transcription kit for in vitro transcription to prepare infectious RNA.
[0107] React at 37°C for 5 hours, and the reaction is performed on a PCR machine.
[0108] Purify the transcription product by lithium chloride precipitation method, add 30 μl Nuclease-freeWater and 30 μl LiCl to the transcription termination product, and mix gently. Carefully remove the supernatant, add 1ml of 70% ethanol (prepared with DEPC water), centrifuge at 14,000g at 4°C for 15min, discard the supernatant to completely evaporate the ethanol, add 20μl Nuclease-freeWater to dissolve the RNA precipitate, and store at -70°C.
[0109] 2. Transfection
[0110] Use the LTX transfection kit to transfect the above RNA into DF-1 cells, spread the cells the day before, so that the cell ...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Example 3 Using duck Tembusu virus as a carrier to express foreign protein
[0133] 1. Materials
[0134] 1.1 Viruses and Cells
[0135] Duck Tembusu virus disease FX2010-180P strain is preserved by our laboratory; DF-1 cells are preserved by our laboratory.
[0136] 2. Method
[0137] 2.1 Selection of insertion sites and primer design for foreign genes
[0138] 2.1.1 Construction scheme of recombinant virus genome
[0139] Such as Figure 10 As shown, the sequence of the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and the green fluorescent protein gene (EGFP) were inserted once between the NS5 gene and the 3' non-coding sequence of the FX2010-180P strain genome.
[0140] 2.1.2 Primer design
[0141] In order to insert the IRES+EGFP sequence into the Duck Tembusu virus genome, a specific sequence of Duck Tembusu virus FX2010-180P was introduced at the 5' end of the IRES sequence and the 3' end of the EGFP sequence by PCR method. The NS5 gene is the 3' end of the duck Tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com