Novel method utilizing edible fungus residues to produce dairy cattle protein feed through fermentation
A protein feed and edible fungus technology, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve the problems of wasting the environment, discarding fungus residue, pollution, etc., and achieves the effects of wide application range, crude fat reduction, and good economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The present invention will be further elaborated below through specific examples. It should be noted that the following descriptions are only for explaining the present invention, and do not limit its content.
[0023] 1. Fermentation strains:
[0024] Aspergillus candidus is a strain numbered CICC40217 in China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Center; it is rich in cellulase, glucoamylase and protease.
[0025] Candida utilis (Candida utilis) is the strain numbered CICC1314 of the China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center; the bacterium is high-quality protein, high in vitamin B, and can utilize five-carbon sugars and six-carbon sugars.
[0026] Lactobacillus plantarum (lactobacillus plantarum) is a strain numbered CICC20764 by the China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Management Center; it has antiseptic, promotes the absorption of nutrients, and maintains the balance of intestinal flora.
[0027] 2. Medium:
[002...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Multifunctional bacterial fermentation compound protease feed related index detection
[0041] The edible fungus slag prepared in Example 1 of the present invention was re-fermented for crude protein, crude fat, crude fiber, and other indicators and the cow feeding test was compared with unfermented feed. The results are shown in Table 1-4.
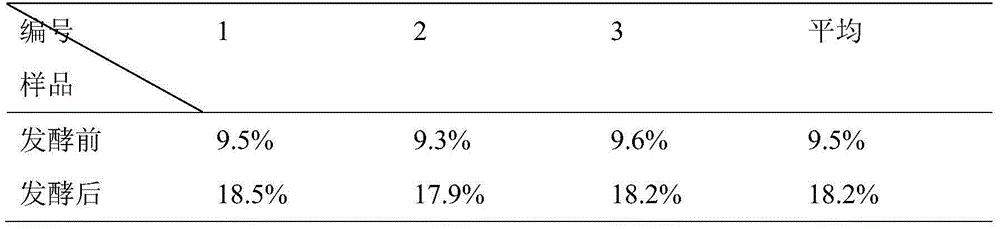
[0042] Determination of protein content in bacterial residue before and after table 1 fermentation
[0043]
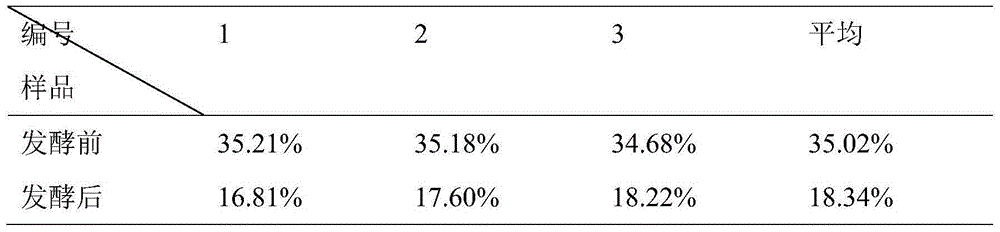
[0044] Table 2 Crude fiber content of fungus residue before and after fermentation
[0045]
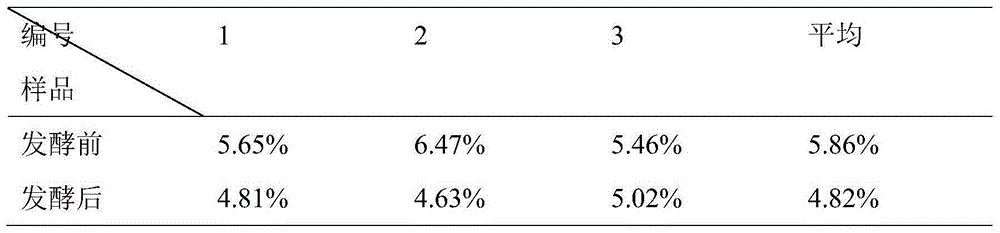
[0046] Table 3 Crude fat content of bacteria residue before and after fermentation
[0047]
[0048] From Tables 1, 2, and 3, it can be seen that the protein content before and after fermentation has been significantly increased, the unutilized cellulose has been significantly reduced, and the crude fat has also decreased, which is of great significance for the improvement of feed quality.
[0049] Table 4 ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The processing steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the edible mushroom is Pleurotus eryngii.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com