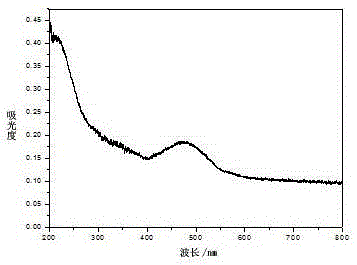
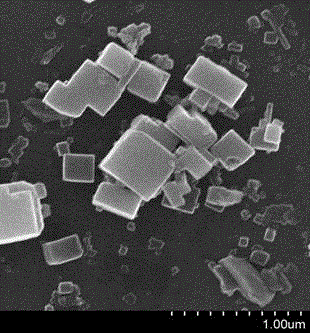
Prussian blue and Prussian blue analogue nanosheet film materials and in-situ preparation method thereof
A technology similar to Prussian blue and Prussian blue, applied in the field of inorganic nanofilm materials and their preparation, Prussian blue and Prussian blue-like nanosheet film materials and their in-situ preparation, which can solve the problem of single nanoparticle morphology and little research on size control. , the easy agglomeration of nanoparticles, etc., to achieve the effect of simple equipment, convenient process and easy operation, and good dispersibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Dissolve 20 mg of polyallylamine hydrochloride (PAH) and polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSS) in 20 mL of deionized water, respectively, to prepare a 1 mg / mL aqueous solution;
[0035] (2) Place the clean substrate in step The resulting PAH solution was taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen; then the substrate was placed in the PSS solution obtained in step 1, taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen. The completion of one modification of PAH and PSS is called one modification cycle, and 3 to 4 modification cycles are performed to obtain a substrate modified by two polymers;
[0036] (3) Weigh 0.027gFeCl 3 ·6H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=2), and the configuration concentration is 0.005mol / LFeCl 3 Aqueous solution; Weigh 0.042gK 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ]·3H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=4), and the configuration concentrat...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Dissolve 20 mg of polyallylamine hydrochloride (PAH) and polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSS) in 20 mL of deionized water, respectively, to prepare a 1 mg / mL aqueous solution;
[0040] (2) Place the clean substrate in step The resulting PAH solution was taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen; then the substrate was placed in the PSS solution obtained in step 1, taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen. The completion of one modification of PAH and PSS is called one modification cycle, and 3 to 4 modification cycles are performed to obtain a substrate modified by two polymers;
[0041] (3) Weigh 0.054g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=2), and the configuration concentration is 0.01mol / LFeCl 3 Aqueous solution; Weigh 0.084gK 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ]·3H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=4), and the configuration concentrati...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Dissolve 20 mg of polyallylamine hydrochloride (PAH) and polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSS) in 20 mL of deionized water, respectively, to prepare a 1 mg / mL aqueous solution;
[0045] (2) Place the clean substrate in step The resulting PAH solution was taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen; then the substrate was placed in the PSS solution obtained in step 1, taken out after 20 minutes, rinsed three times with distilled water, and blown dry with nitrogen. The completion of one modification of PAH and PSS is called one modification cycle, and 3 to 4 modification cycles are performed to obtain a substrate modified by two polymers;
[0046] (3) Weigh 0.216g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=2), and the configuration concentration is 0.04mol / LFeCl 3 Aqueous solution; Weigh 0.338gK 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ]·3H 2 O is dissolved in 20mL HCl aqueous solution (pH=4), and the configuration concentrat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com